Construct and Application of LM-CDBN Deformation Prediction Model for Supertall Buildings
-
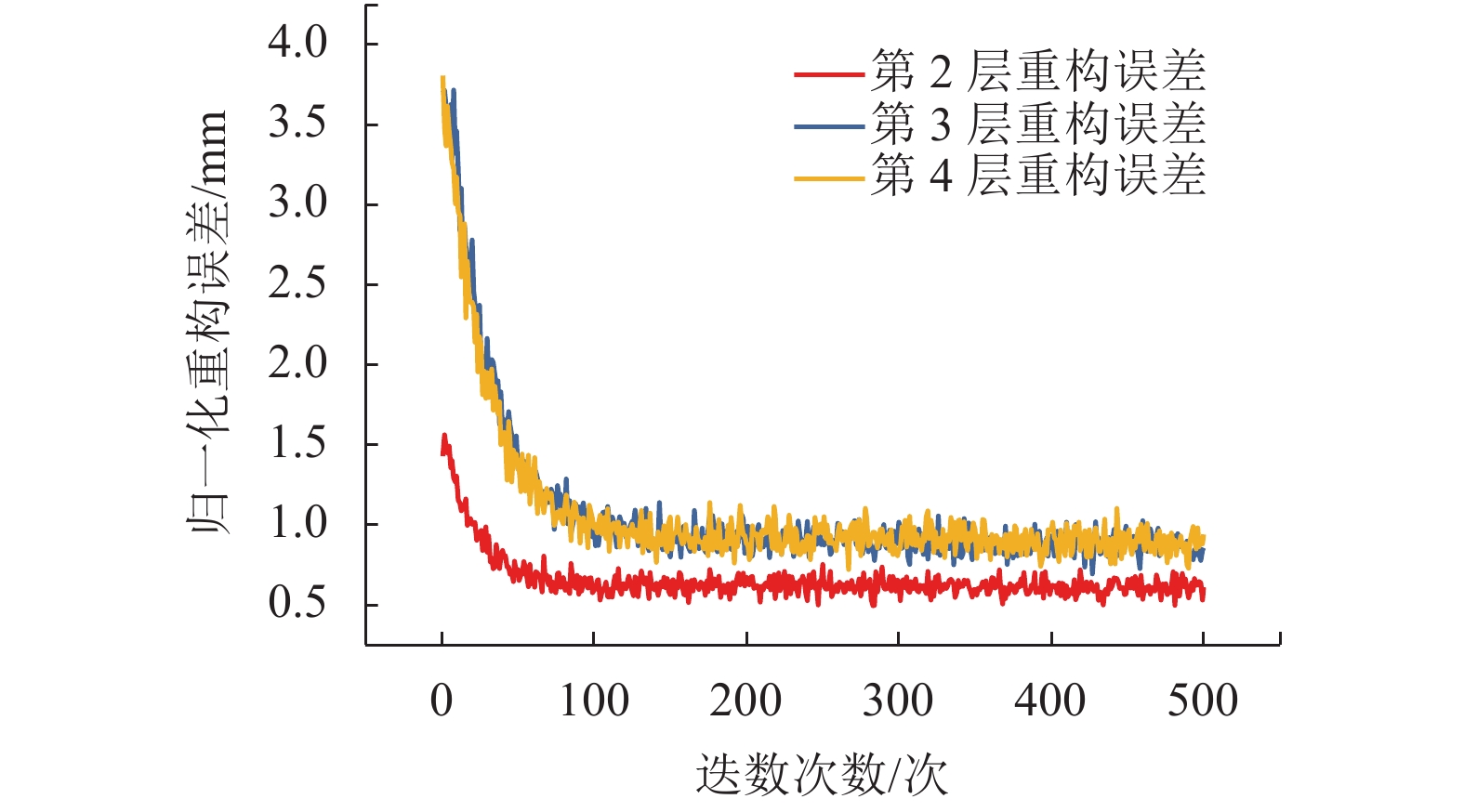
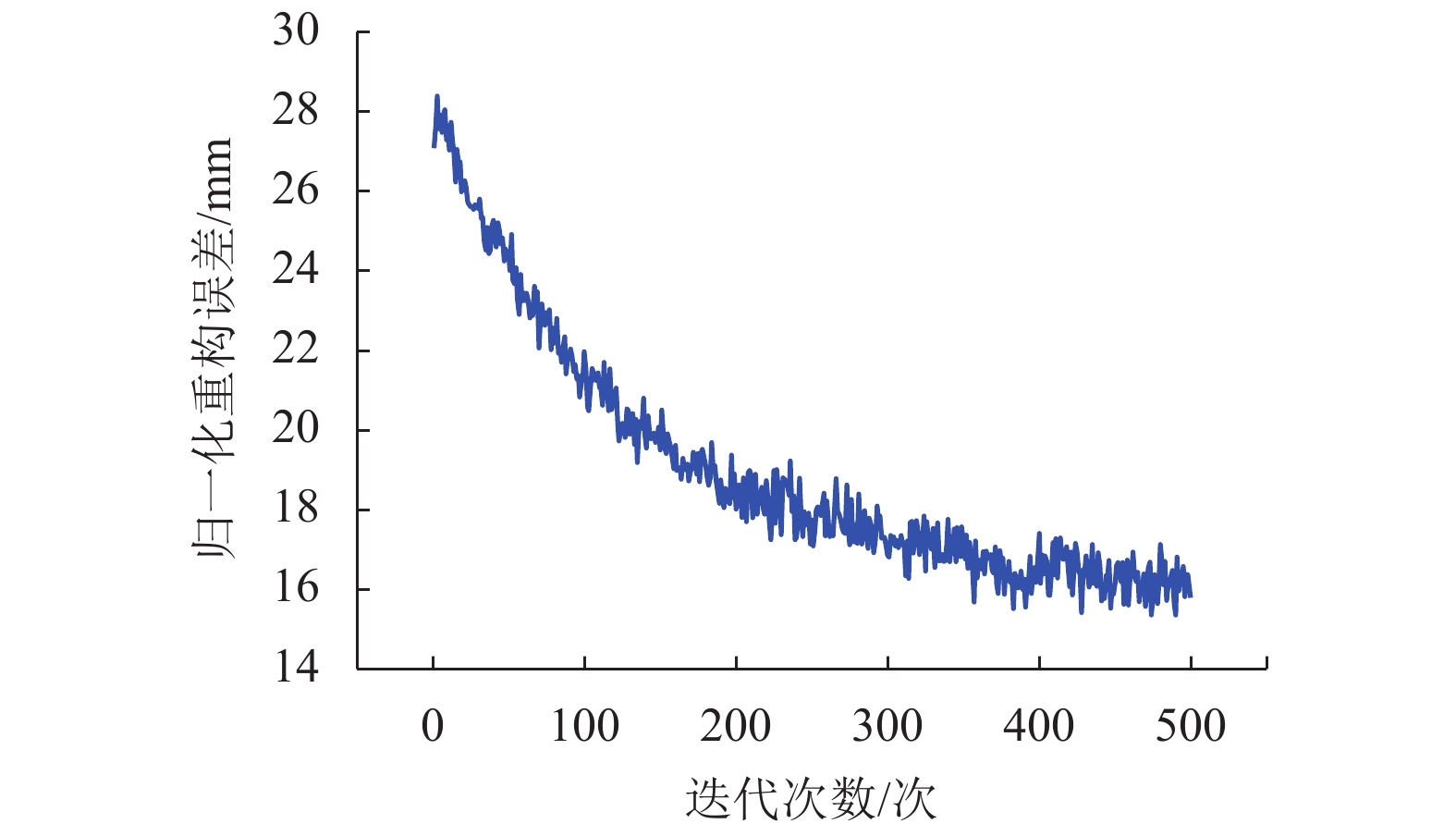
摘要: 为提高超高层建筑变形预测精度,对附有条件的深度信念网络(conditional deep belief network,CDBN)模型中权值及阈值调整方法进行了改进,使用LM (Levenberg-Marquardt)算法作为新的模型定权机制,构建了LM-CDBN网络模型;将构建的LM-CDBN超高层变形预测模型应用于一座298 m超高层建筑中;然后用训练误差、预测值拟合度、预测结果稳定性组成的综合评价体系对模型进行了评价;最后,将LM-CDBN模型分别与深度信念模型(deep belief network,DBN)、极限学习机(extreme learning machine,ELM)、基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的支持回归向量机(unscented Kalman filter-support vector regression,UKF-SVR)进行了预测结果对比. 结果表明:在超高层建筑的变形预测中,相比DBN、ELM和UKF-SVR,LM-CDBN预测精度分别提升了32%、55%及24%,模型的信息提取稳定性及处理时变系统非线性问题的泛化能力得到了提高.Abstract: In order to improve the prediction accuracy of supertall building deformation, the method of adjusting the weight and threshold in the conditional deep belief network (CDBN) model was improved. The LM (Levenberg-Marquardt) algorithm was used as a weighting method to construct the LM-CDBN network model. This method was applied to the deformation prediction of a 298 m supertall building. Then, the model was fully evaluated in terms of training error, goodness of fit, and prediction stability. Finally, the prediction results of LM-CDBN model, deep belief network (DBN) model, extreme learning machine (ELM) and unscented Kalman filter-support vector regression (UKF-SVR) were compared. The result shows that the prediction performance of LM-CDBN was 32%, 55% and 24% higher than three other models respectively. LM-CDBN model improves in the information extraction stability and generalization ability of solving nonlinear problems in time-varying systems.
-
Key words:
- deep belief networks /
- deformation /
- prediction /
- data processing /
- parameter estimation
-
表 1 A1办公楼监测数据表
Table 1. Monitoring data of A1 office building
序号 时间 位移变形值/mm 温度/℃ 风速/(m•s−1) 光照强度/Lx 1 2016-08-23 00:00 28.281 24.1 5.9 2.351 2 2016-08-23 06:00 27.556 23.3 5.4 20.307 3 2016-08-23 12:00 28.428 24.2 5.5 434.243 4 2016-08-23 18:00 29.779 24.9 5.4 267.839 5 2016-08-24 00:00 30.250 24.8 4.9 4.299 6 2016-08-24 06:00 27.895 24.1 5.2 37.456 $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ 139 2016-09-26 12:00 49.753 31.9 6.7 780.412 140 2016-09-26 18:00 49.341 27.6 7.5 413.485 表 2 预测结果对比表
Table 2. Prediction comparison
观测时间 $\hat y/{\rm{mm}}$ CDBN LM-CDBN ELM UKF- SVR 预测值/mm XRE/% 预测值/mm XRE/% 预测值/mm XRE/% 预测值/mm XRE/% 2016-08-24 12:00 47.510 45.369 4.51 46.214 2.73 41.535 12.58 52.683 10.89 2016-08-24 18:00 46.653 45.173 3.17 45.537 2.39 40.083 14.08 44.297 5.05 2016-08-25 00:00 46.025 44.345 3.65 45.027 2.17 43.629 5.21 46.913 1.93 2016-08-25 06:00 46.769 44.220 5.45 45.626 2.44 45.756 2.17 48.587 3.89 2016-08-25 12:00 46.385 44.342 4.40 45.315 2.31 49.168 6.00 45.179 2.60 2016-08-25 18:00 48.308 46.040 4.69 46.829 3.06 47.051 2.60 50.576 4.69 2016-08-26 00:00 49.739 48.576 2.34 47.891 3.72 44.774 9.98 52.940 6.44 2016-08-26 06:00 52.424 47.736 8.94 49.742 5.12 46.998 10.35 51.630 1.51 2016-08-26 12:00 49.753 47.547 4.43 47.906 3.71 48.372 2.78 48.568 2.38 2016-08-26 18:00 49.341 47.360 4.01 47.603 3.52 47.187 4.37 50.018 1.37 XARE/% 4.56 3.12 7.01 4.08 表 3 预测结果评价表
Table 3. Evaluation for different prediction results
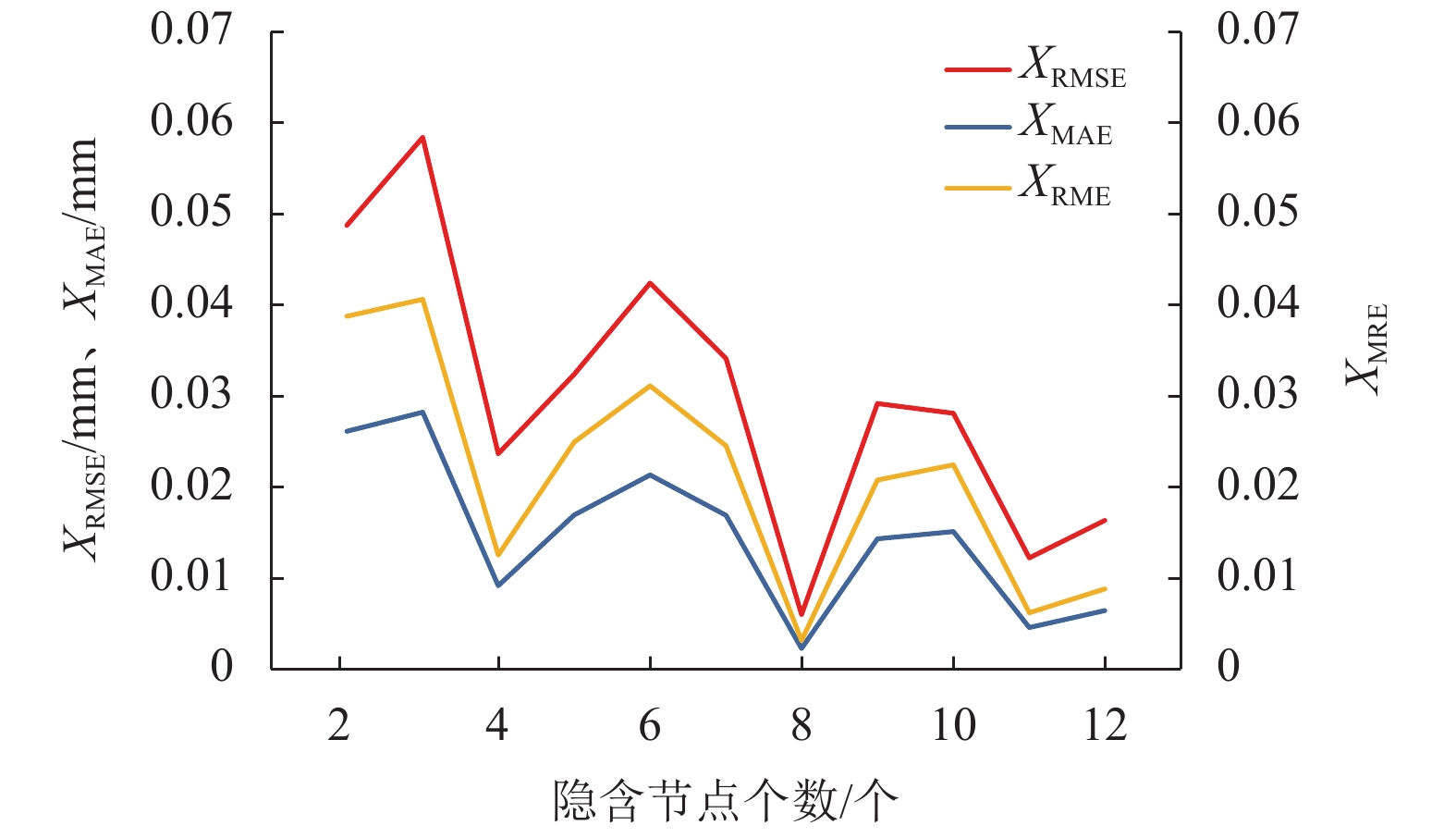
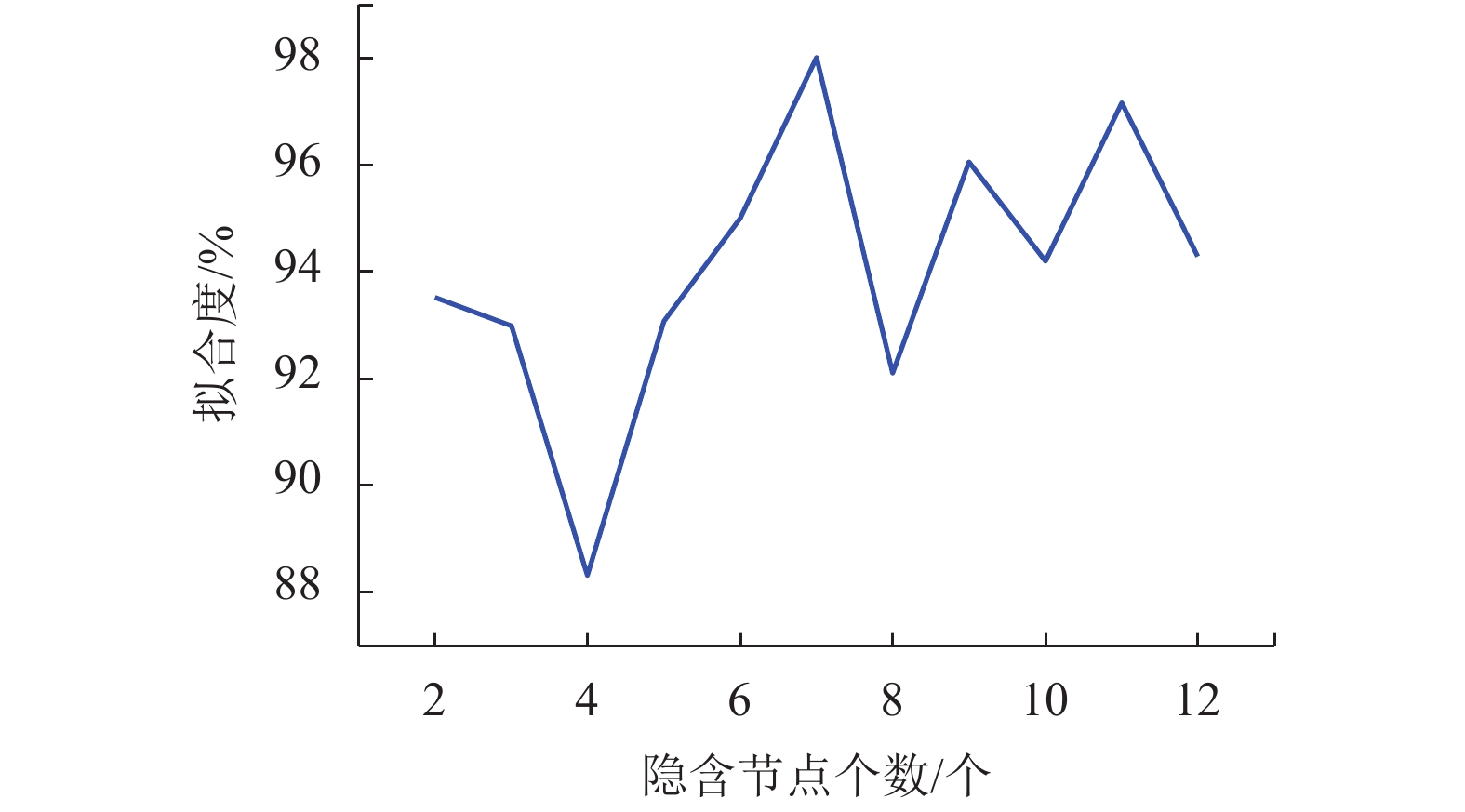
评价标准 CDBN LM-CDBN ELM UKF-SVR XMSE/mm 4.397 0 2.559 0 15.559 0 5.570 0 XMRE/mm 0.023 9 0.004 7 0.059 1 0.031 4 XMAE/mm 0.014 0 0.003 5 0.033 3 0.017 5 XRMSE/mm 0.017 1 0.009 5 0.041 3 0.021 3 R% 97 98 92 96 -
邓勇,张冠宇,李宗春,等. 遗传小波神经网络在变形预报中的应用[J]. 测绘科学,2012,37(5): 183-186.DENG Yong, ZHANG Guanyu, LI Zongchun, et al. Application of genetic wavelet neural network in deformation forecast[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2012, 37(5): 183-186. 段明旭,邱冬炜,李婉,等. 改进灰色人工神经网络模型的超高层建筑变形预测[J]. 测绘科学,2017,42(4): 141-146.DUAN Mingxu, QIU Dongwei, LI Wan, et al. The GM-BPNN prediction research in the deformation forecasting of the super high-rise building[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, 42(4): 141-146. WANG Xiaoyu, YANG Kan, SHEN Changsong. Study on MPGA-BP of gravity dam deformation prediction[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2017, 2017(6): 1-13. HINTON G E, SALAKHUTDINOV R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504-507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 CHEN H, MURRAYA F. Continuous restricted Boltzmann machine with an implementable training algorithm[J]. IEE Proceedings—Vision,Image and Signal Processing, 2003, 150(3): 153-158. doi: 10.1049/ip-vis:20030362 周晓莉,张丰,杜震洪,等. 基于CRBM算法的时间序列预测模型研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版),2016,43(4): 442-451. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2016.04.011ZHOU Xiaoli, ZHANG Feng, DU Zhenhong, et al.A study on time series prediction model based on CRBM algorithm[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 2016, 43(4): 442-451. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2016.04.011 HINTON G E, OSINDERO S, TEH Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets[J]. Neural computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527-1554. doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 CHEN Siqi, AMMAR H B, TUYLS K, et al. Conditional restricted Boltzmann machines for negotiations in highly competitive and complex domains[C]//International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Beijing: AAAI, 2013: 69-75. SPILIOPOULOU A. Investigation of deep CRBM networks in modeling sequential data[D]. Edinburgh: University of Edinburgh, 2008. MNIH V L H, HINTON G E. Conditional restricted Boltzmann machines for structured output prediction[C]//Twenty-Seventh Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Barcelona: AUAI Press, 2011: 514-522. 周晓莉. 基于深度学习的浙江近岸船舶数据赤潮生物量趋势性预测研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016. MADSEN K, NIELSEN H B, TINGLEFF O. Methods for nonlinear least squares problems[J]. Society for Industrial & Applied Mathematics, 2004, 2012(1): 1409-1415. QUESADA-OLMO N, JIMENEZ-MATINEZ M J, FARJAS-ABADIAM. Real-time high-rise building monitoring system using global navigation satellite system technology[J]. Measurement, 2018, 123(1): 115-124. LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G E. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 GAO Jun. Newton-Gauss curvature matrix based cdbnfor online edible fungus drying prediction model[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2017, 81(1): 273-279. HRASKO R, PACHECO A G C, KROHLING RA. Time series prediction using restricted Boltzmann machines and backpropagation[C]//Information Technology and Quantitative Management. Suzhou: Elsevier, 2015: 990-999. BA J, HINTON G E, MNITH V, et al. Using fast weights to attend to the recent past[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona: Elsevier, 2016: 4331-4339. SRIVASTAVA N, SALAKHUTDINOV R, HINTON G E. Modeling documents with a deep Boltzmann machine[C]//Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Bellevue: AUAI press, 2013: 616-624. -




 下载:
下载: