Stress Characteristics and Failure Mechanisms of Plain Concrete Piles of Composite Foundation under Embankment
-
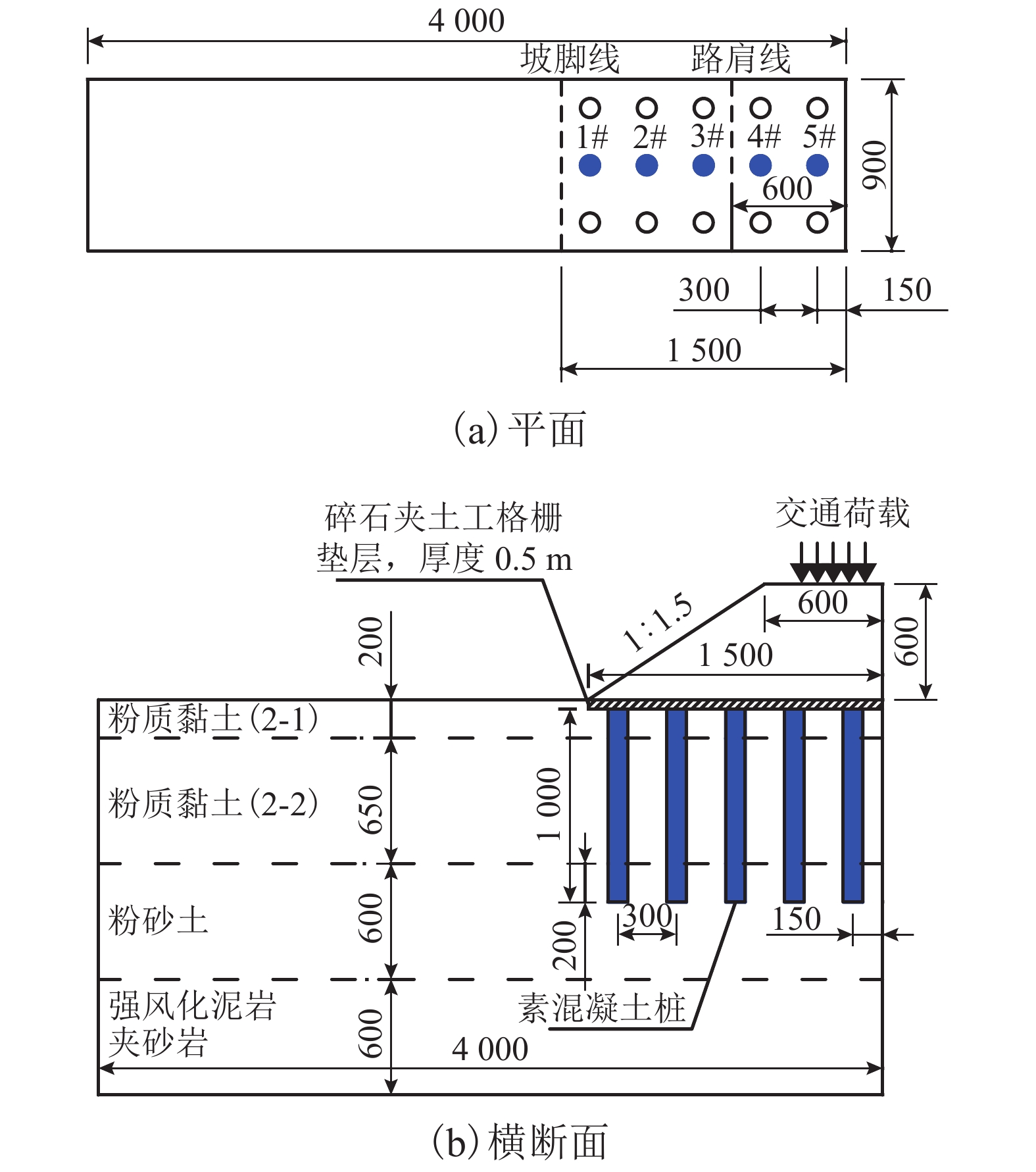
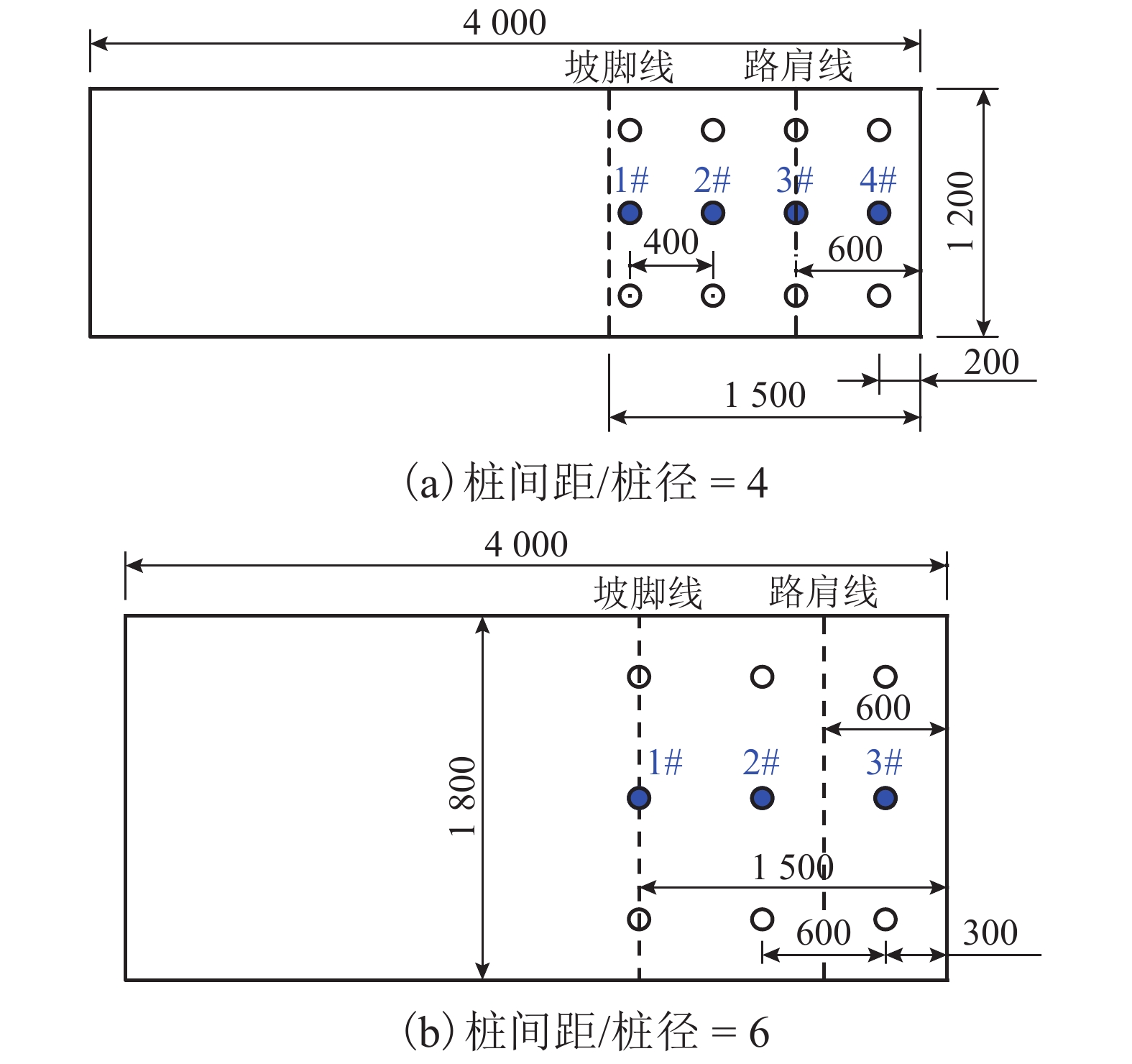
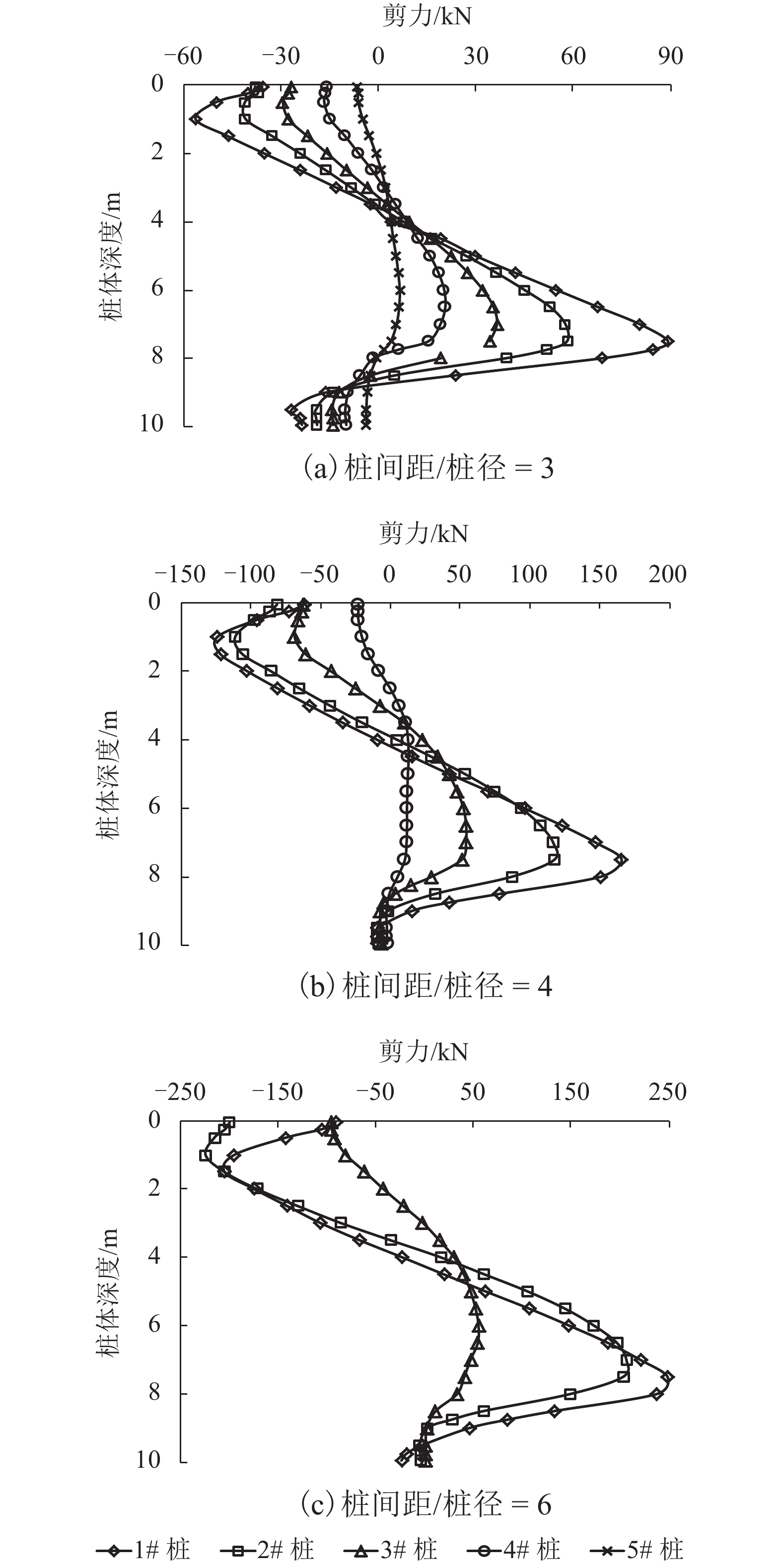
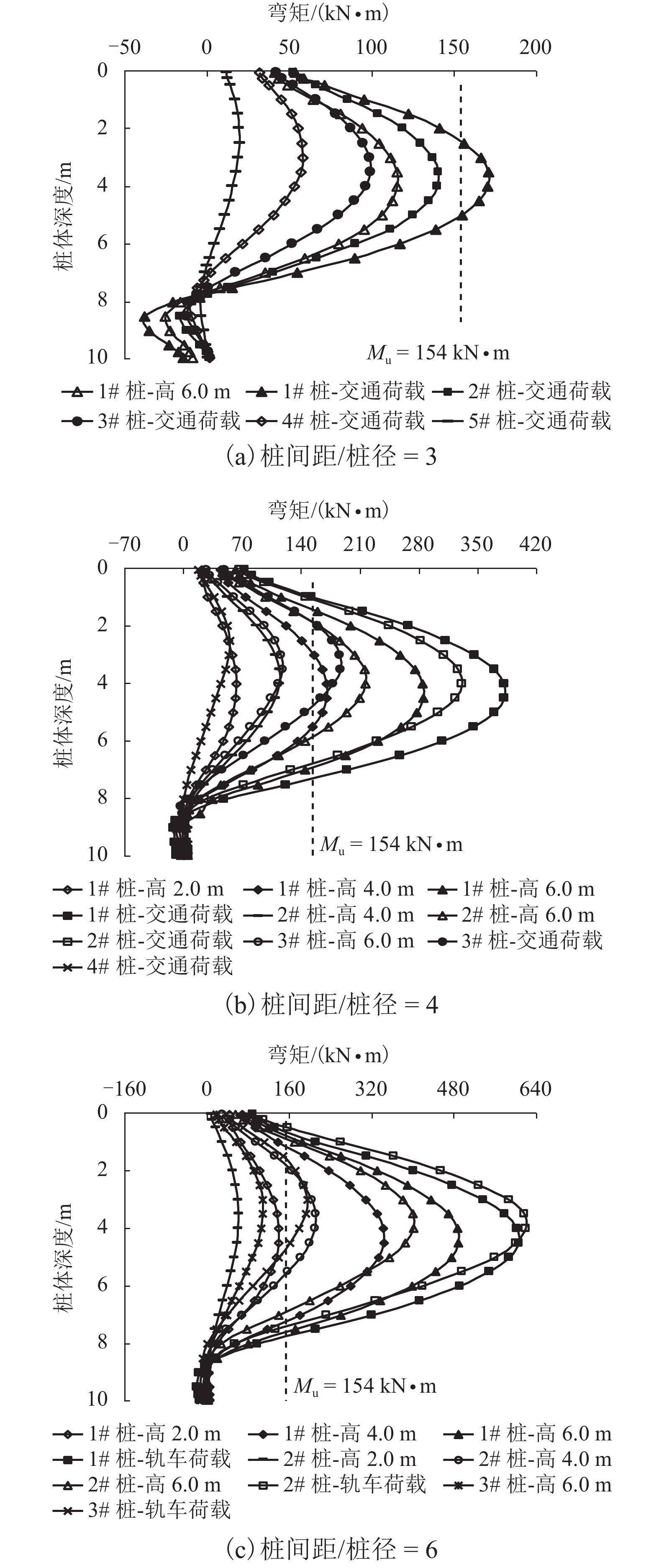
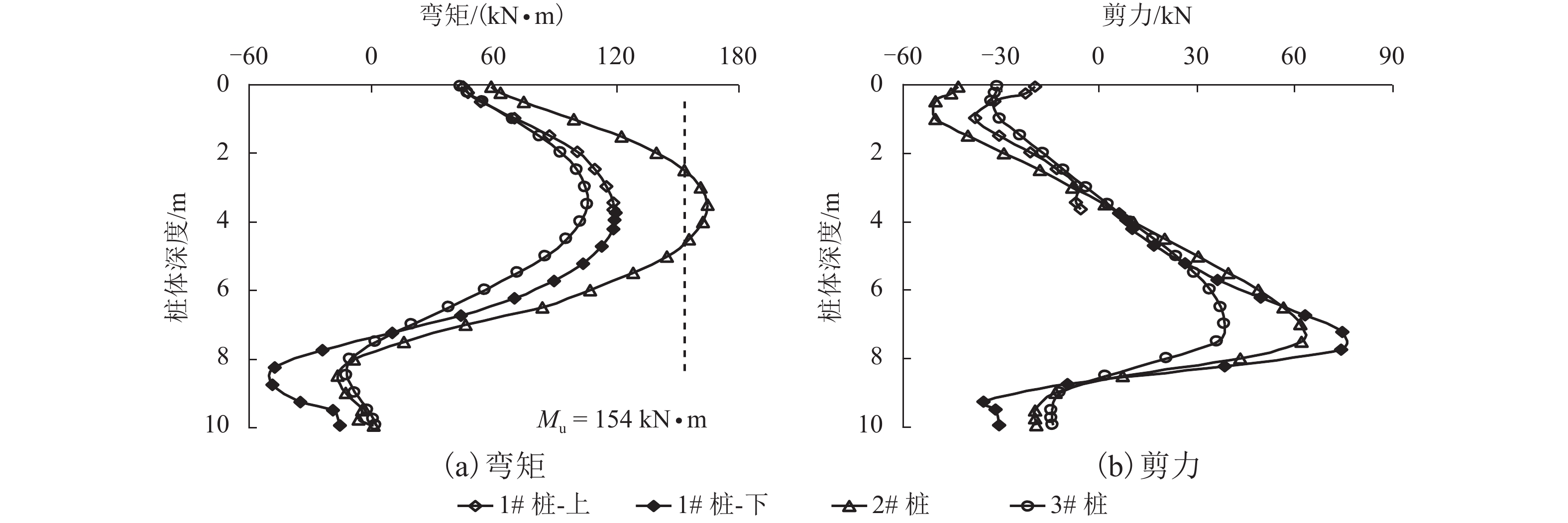
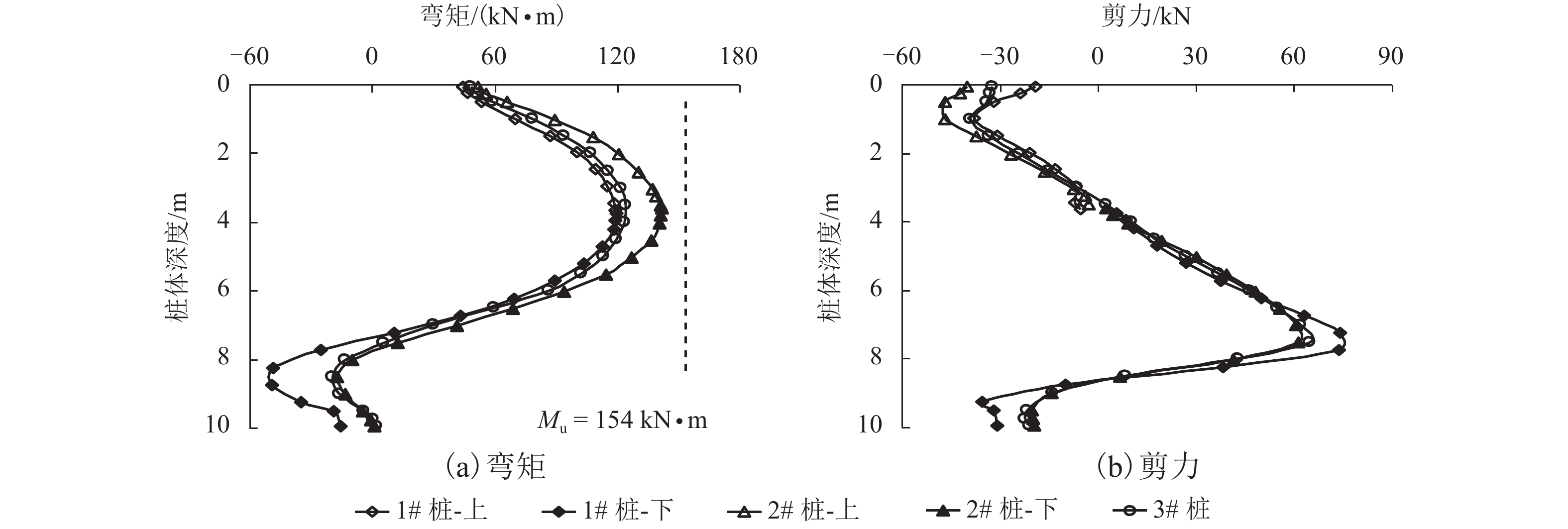
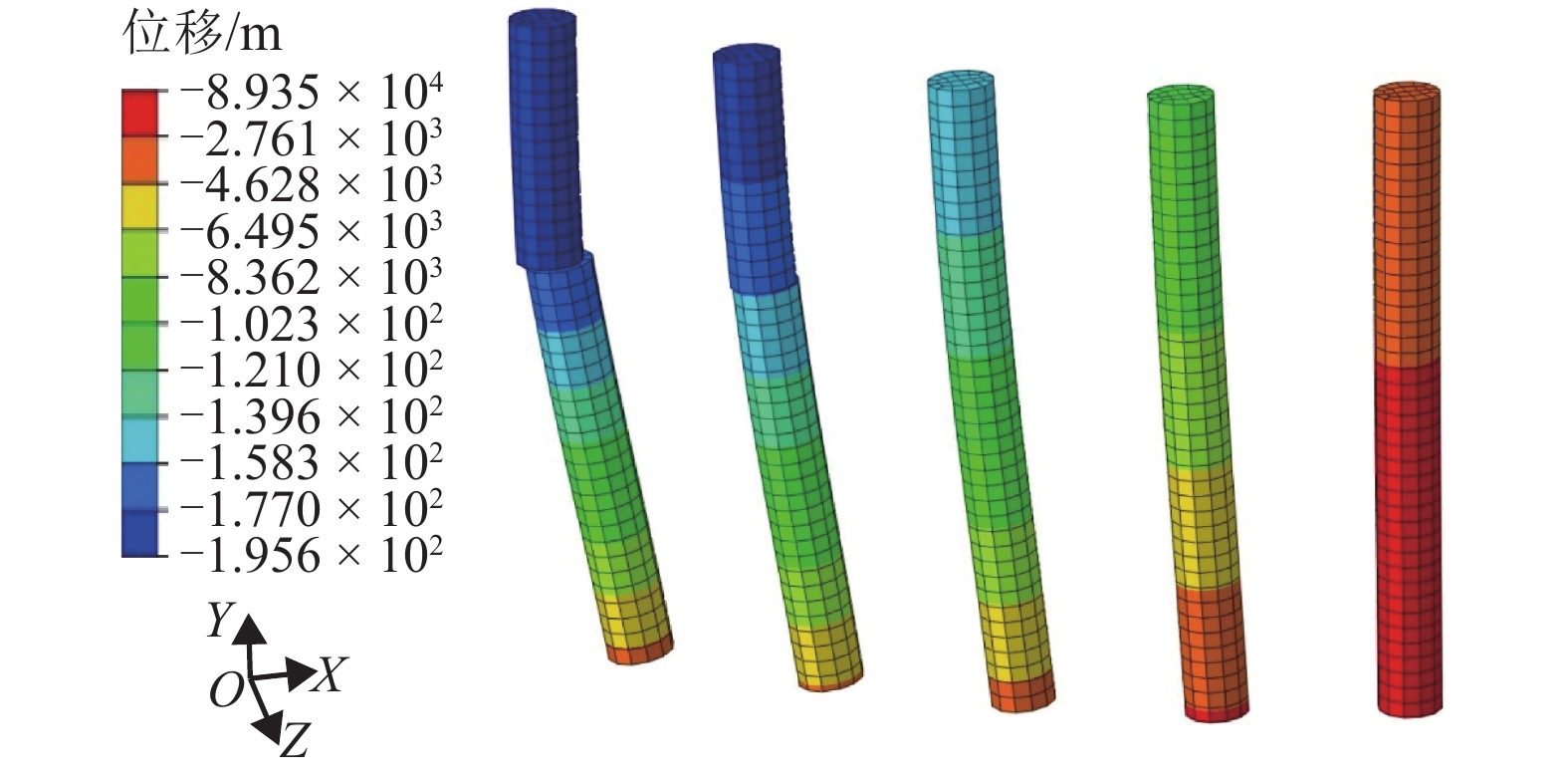
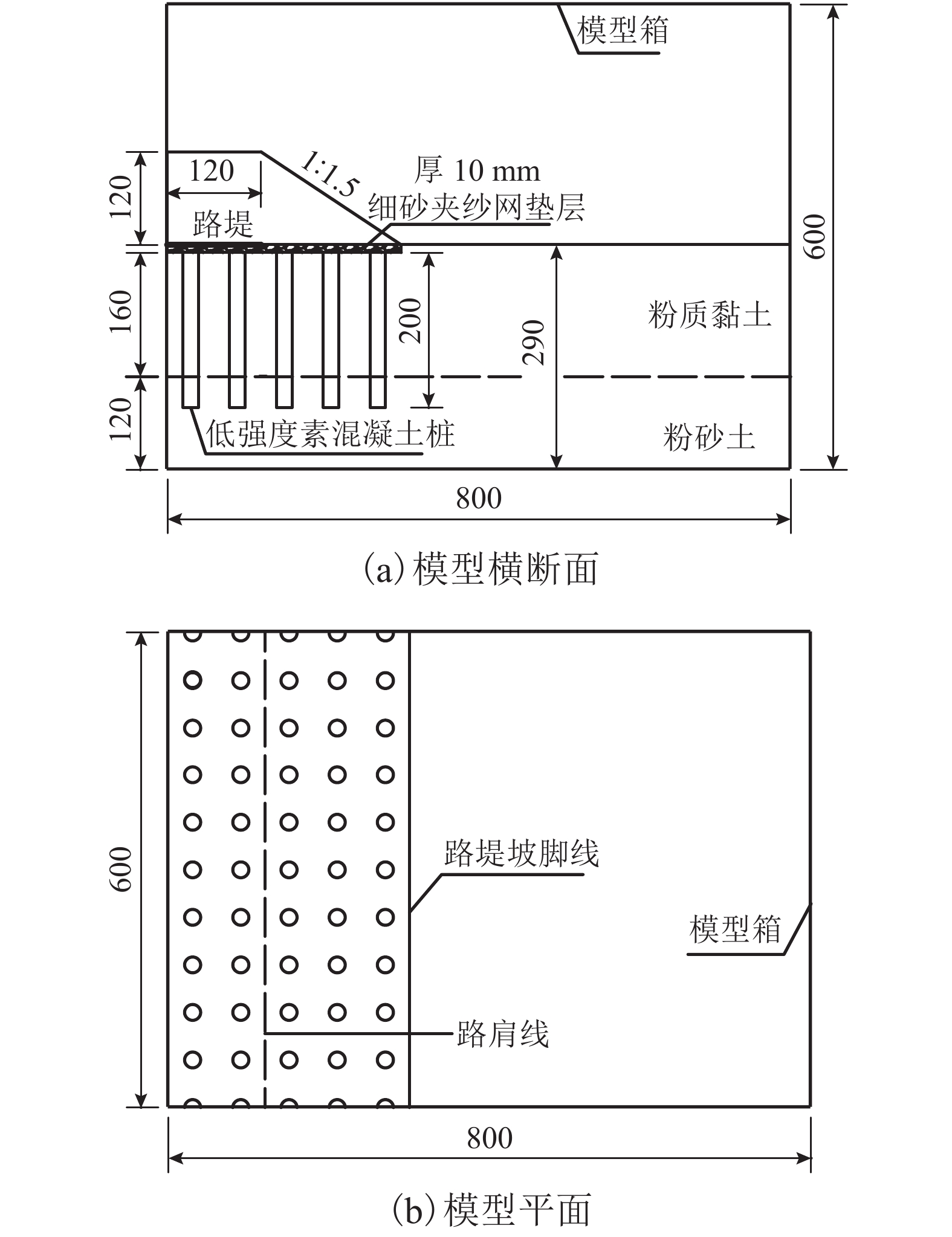
摘要: 为了合理分析软土地区路堤下素混凝土桩复合地基的稳定性,基于离心模型试验和仿真分析,研究了不同桩间距条件下路堤下素混凝土桩复合地基桩体的受力特征,引入桩体破坏逐一退出机制,分析了桩体破坏模式. 结果表明:在路堤自重和列车荷载作用下,路堤下复合地基素混凝土桩受力特征和破坏模式具有显著的桩间距效应,当桩间距分别增大至4倍和6倍桩径时,最靠近坡脚的第1列与第1、2列素混凝土桩分别产生了断桩破坏;在桩间距不变的条件下,随着上部荷载的增大,素混凝土桩最大弯矩和剪力均逐渐增大;施加列车荷载后,桩体最大弯矩和剪力往路基坡脚方向呈逐渐增大的规律,桩间距由3倍增大至6倍桩径时,靠近坡脚的桩体最大弯矩由172.9 kN•m增大至601.0 kN•m,大于桩体标定极限弯矩值,剪力由89.4 kN增大至249.1 kN,小于桩体标定极限剪力值,表明离心模型试验中素混凝土桩产生弯曲破坏而不是剪切、受压和受拉破坏,最靠近坡脚的桩最先发生弯曲破坏,随后往路基中心方向呈逐一弯曲破坏模式.Abstract: In order to reasonably analyze the stability of embankment supported on composite foundation with plain concrete piles in soft clay area, centrifugal model tests and simulation analyses were conducted to study the stress characteristics of the piles with different spacings under embankment, and a one-by-one exiting method of piles due to rupture breaking was introduced to investigate the failure modes of the piles. The results show that the stress characteristics and failure modes of the piles under embankment self-weight and train load have significant pile spacing effect. While the ratios of the pile spacing to the pile diameter are 4 and 6 respectively, rupture occurs to the first column and the first and second columns of the plain concrete piles close to the embankment toe. With a constant pile spacing, the maximum bending moment and shearing force of the piles increase with an increase in the upper load. When train loads are applied on the embankment surface, piles bear a larger maximum bending moment and shearing force with a closer distance to the embankment toe. When the pile spacing increases from 3 to 6 times the pile diameter, the maximum bending moment of piles increase from 172.9 to 601.0 kN•m, much larger than the ultimate bending moment value calibrated by test; meanwhile, the maximumshearing force of piles increase from 89.4 to 249.1 kN, much less than the ultimate shearing force value. This indicates that the plain concrete piles of composite foundation under embankment in the centrifugal model are governed by bending failure other than shear failure, tension failure or compression failure. Therefore, the piles closest to the embankment toe fail first; then, failure developing towards the embankment center, piles fail one by one in bending failure mode.
-
Key words:
- composite foundation /
- plain concrete piles /
- stress characteristics /
- failure mechanism
-
表 1 模型地基土主要力学参数
Table 1. Main mechanical parameters of soils used in the model
名称 含水率/% 密度/(kg•m–3) 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 粉质黏土 31.98 1 940 30.4 25.1 粉砂土 30.31 1 930 5.7 28.0 表 2 离心机试验方案加载历程
Table 2. Loading regime of all centrifuge tests
模拟工况 加速度/(×g) 加载时间/min 持续时间/min 路堤高 2.0 m 16.67 2.04 103.68 路堤高 4.0 m 33.33 1.95 25.92 路堤高 6.0 m 50.00 1.90 11.52 服役 1 a(施加车-轨荷载) 50.00 7.94 210.00 表 3 数值模型主要计算参数
Table 3. Main calculation parameters of numerical models
部件名称 密度/(g•cm–3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 摩擦角/(°) 粘聚力/kPa 路堤填土 1.95 51.0 0.28 38.0 35.0 加筋垫层 2.10 108.8 0.26 45.0 40.0 桩 2.40 15.0 0.20 粉质黏土(2-1) 1.94 13.8 0.34 25.1 30.4 粉质黏土(2-2) 1.94 13.8 0.34 25.1 30.4 砂性土 1.93 30.6 0.30 28.0 5.7 强风化泥岩 2.20 680.0 0.24 40.0 160.0 表 4 各数值模型桩身最大轴力
Table 4. Maximum axial forces of main piles of models
模型序号 桩间距/桩径 最大轴力/kN 桩号 C-1 3 349.2 1# 756.8 3# 959.9 5# 443.1 1# C-2 4 811.4 2# 1 205.0 4# 425.1 1# C-3 6 1 160.0 2# 1 436.0 3# -
中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑地基处理技术规范: JGJ79—2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2013 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路路基设计规范: JTGD30—2015[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2015 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 港口工程地基规范: JTS147-1—2010[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2010 国家铁路. 铁路路基设计规范: TB10001—2016[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2017 郑刚,李帅,刁钰. 刚性桩复合地基支承路堤稳定破坏机理的离心模型试验[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,34(11): 1977-1989.ZHENG Gang, LI Shuai, DIAO Yu. Centrifugal model tests on failure mechanisms of embankments on soft ground reinforced by rigid piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 34(11): 1977-1989. 郑刚,刘力,韩杰. 刚性桩加固软弱地基上路堤的稳定性问题(Ⅰ)——存在问题及单桩条件下的分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2010,32(11): 1648-1657.ZHENG Gang, LIU Li, HAN Jie. Stability of embankment on soft subgrade reinforced by rigid piles (Ⅰ) — Background and single pile analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2010, 32(11): 1648-1657. 郑刚,刘力,韩杰. 刚性桩加固软弱地基上路堤的稳定性问题(Ⅱ)——群桩条件下的分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2010,32(12): 1811-1820.ZHENG Gang, LIU Li, HAN Jie. Stability of embankment on soft subgrade reinforced by rigid inclusions (Ⅱ) — group piles analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2010, 32(12): 1811-1820. HAN J, CHAI J C, DOV L, et al. Evaluation of deep-seated slope stability of embankments over deep mixed foundations[C]//GeoSupport 2004: Drilled Shafts, Micropiling, Deep Mixing, Remedial Methods, and Specialty Foundation Systems. [S.l.]: ASCE, 2004: 945-954 HUANG J, HAN J, PORBAHA A. Two and three-dimensional modeling of DM columns under embankments[C]//Proceedings of GeoCongress 2006. [S.l.]: ASCE, 2006: 1-5 KITAZUME M, MARUYAMA K. Collapse failure of group column type deep mixing improved ground under embankment[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Deep Mixing 2005. [S.l.]: ASCE, 2005: 245-254 NAVIN M P, FILZ G M. Numerical stability of analyses of embankments supported on deep mixed columns[C]//Proceedings of Sessions of Geo-Shanghai 2006. [S.l.]: ASCE, 2006: 1-8 黄兵,耿建宇,蒋鑫,等. 系梁式桩网结构加固斜坡软弱地基路堤的数值模拟[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2014,14(6): 35-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2014.06.005HUANG Bing, GENG Jianyu, JIANG Xin, et al. Numerical simulation of embankment on sloped weak ground reinforced by pile-net structure with collar beam[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2014, 14(6): 35-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2014.06.005 顾行文,黄炜旺,谭祥韶,等. 基底倾斜的管桩复合地基路堤破坏模式研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(增刊1): 204-208. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2017S1040GU Xingwen, HUANG Weiwang, TAN Xiangshao, et al. Failure mechanisms of embankment on inclined soft foundation reinforced by pipe piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(S1): 204-208. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2017S1040 朱小军,赵学亮,龚维明,等. 刚性桩复合地基垫层破坏机理研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2014,27(5): 105-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2014.05.003ZHU Xiaojun, ZHAO Xueliang, GONG Weiming, et al. Study on failure mechanism of cushion in rigid pile composite foundation[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2014, 27(5): 105-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2014.05.003 俞建霖,王传伟,谢逸敏,等. 考虑桩体损伤的柔性基础下刚性桩复合地基中桩体受力及破坏特征分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2017,48(9): 2432-2440.YU Jianlin, WANG Chuanwei, XIE Yimin, et al. Analysis of stress and failure mechanism on composite foundation improved by rigid piles under flexible foundation considering damage of piles[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2017, 48(9): 2432-2440. 邵国霞,苏谦,尹紫红,等. 不同垫层下管桩复合地基现场对比试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(2): 279-285.SHAO Guoxia, SU Qiao, YING Zihong, et al. Field comparative experiments of pipe composite foundation with different cushion lagers[J]. Journal of southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(2): 279-285. BROMS B B. Deep soil stabilization: design and construction of lime and lime/cement columns[D]. Stockholm: Royal Institute of Technology, 2003 -




 下载:
下载: