Energy Management Strategy for Trams with Novel Power System
-
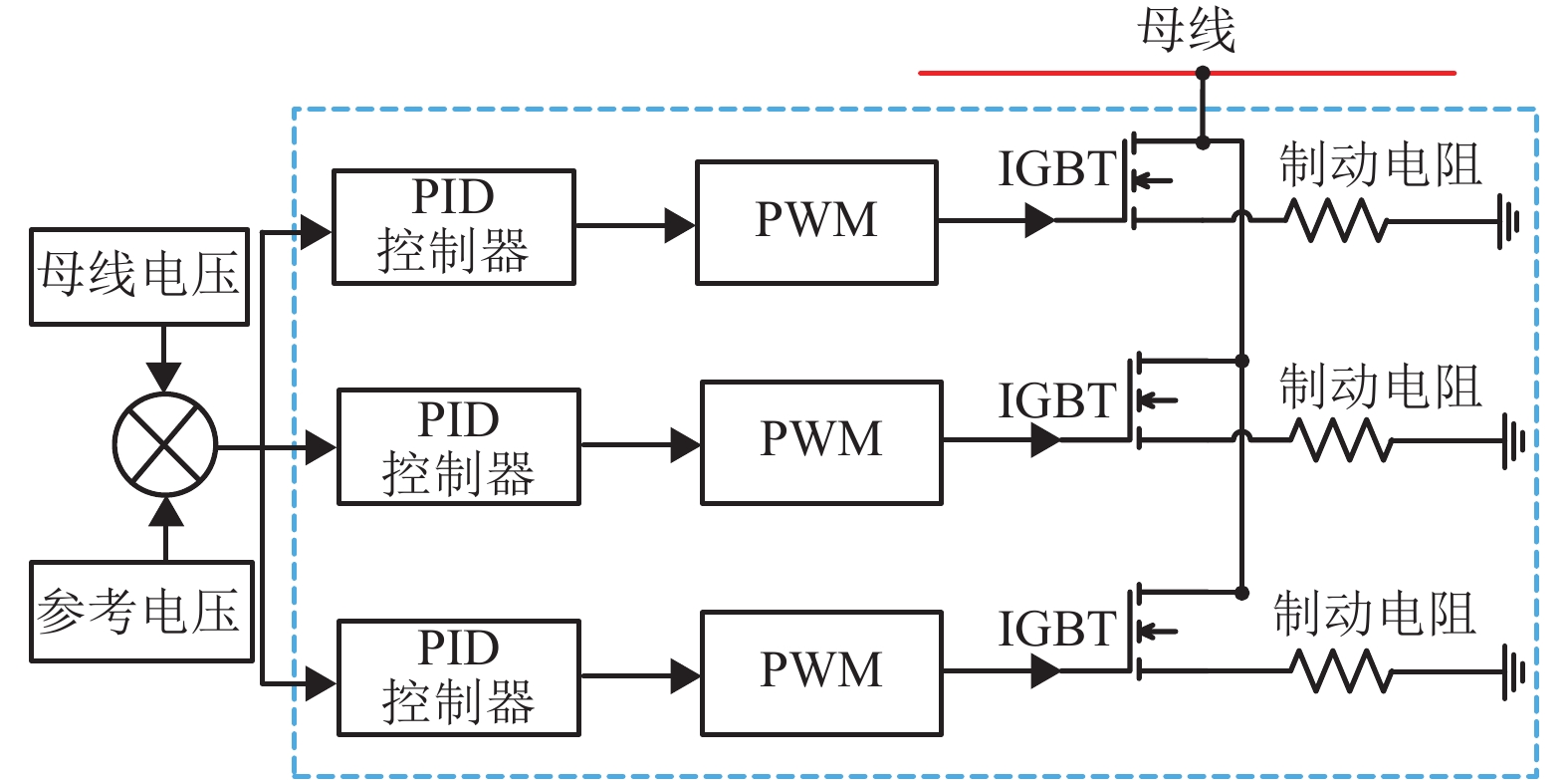
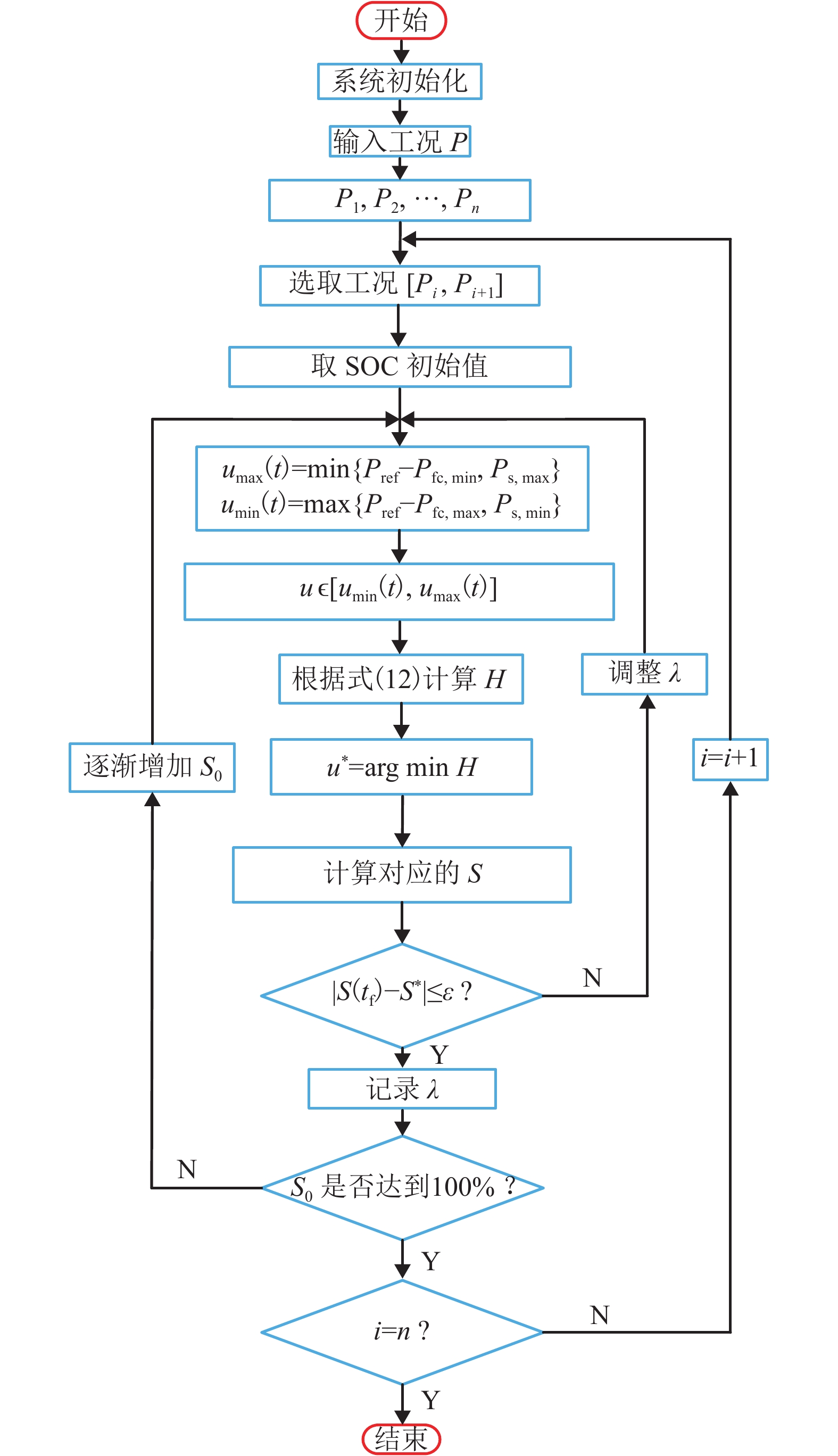
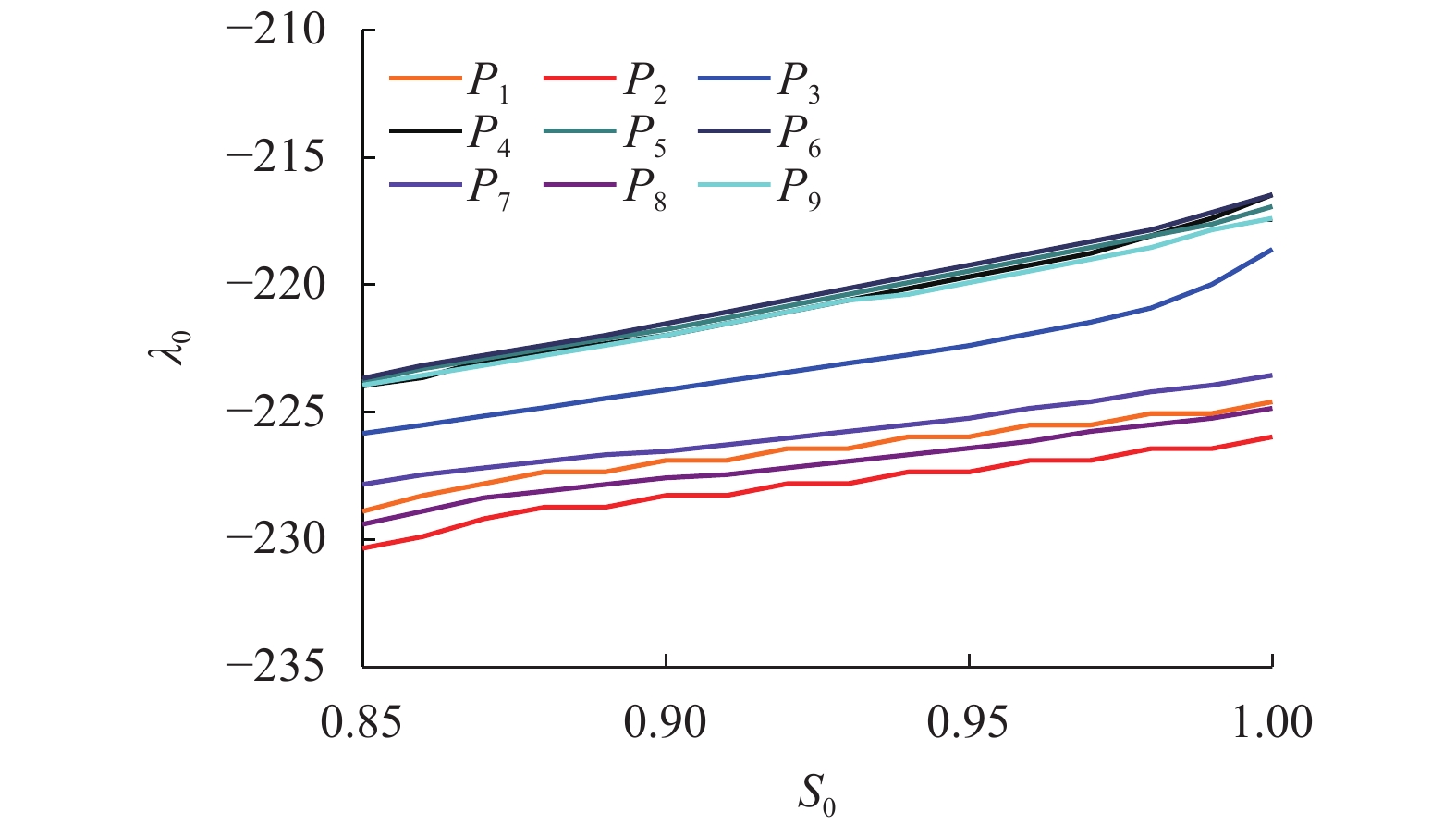
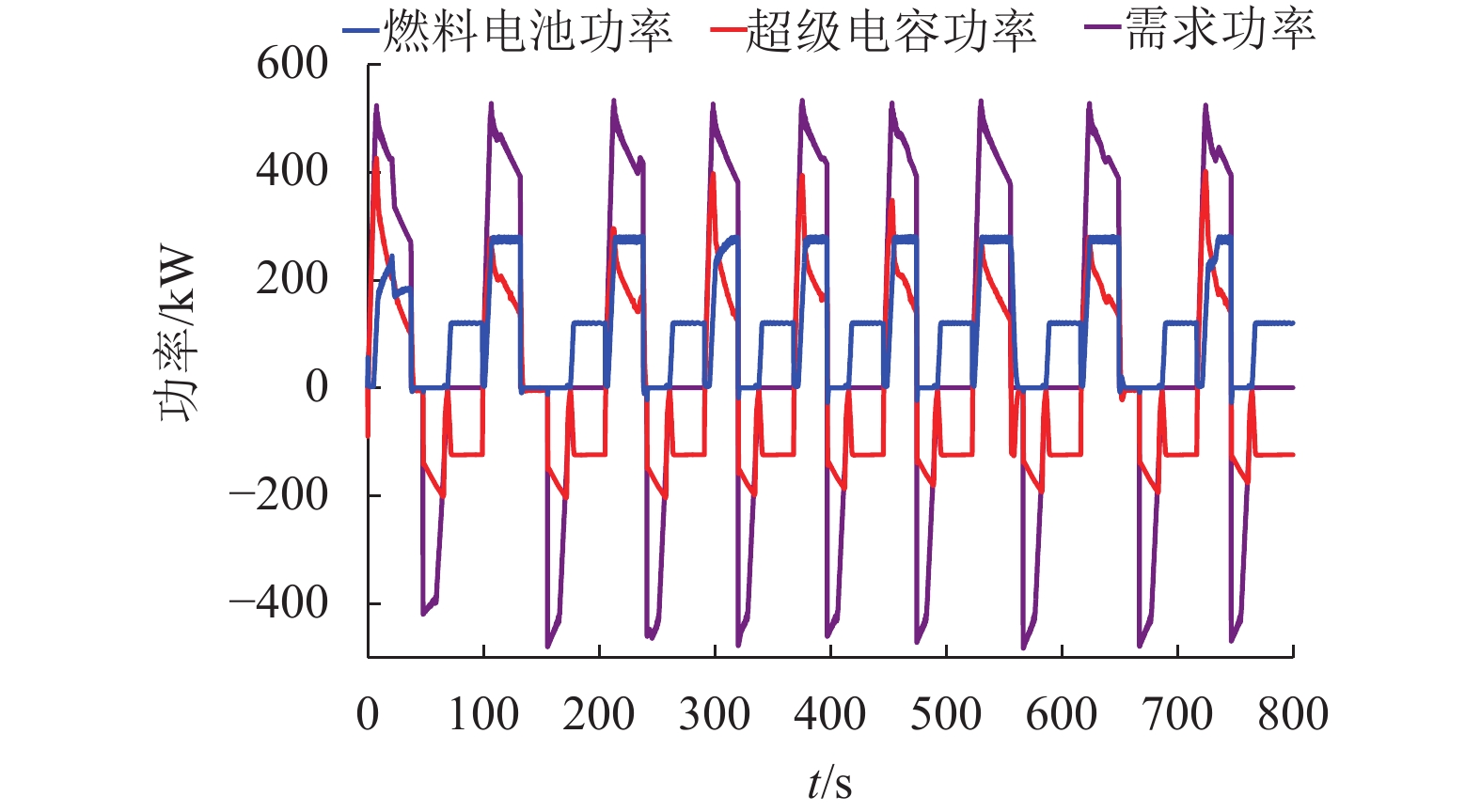
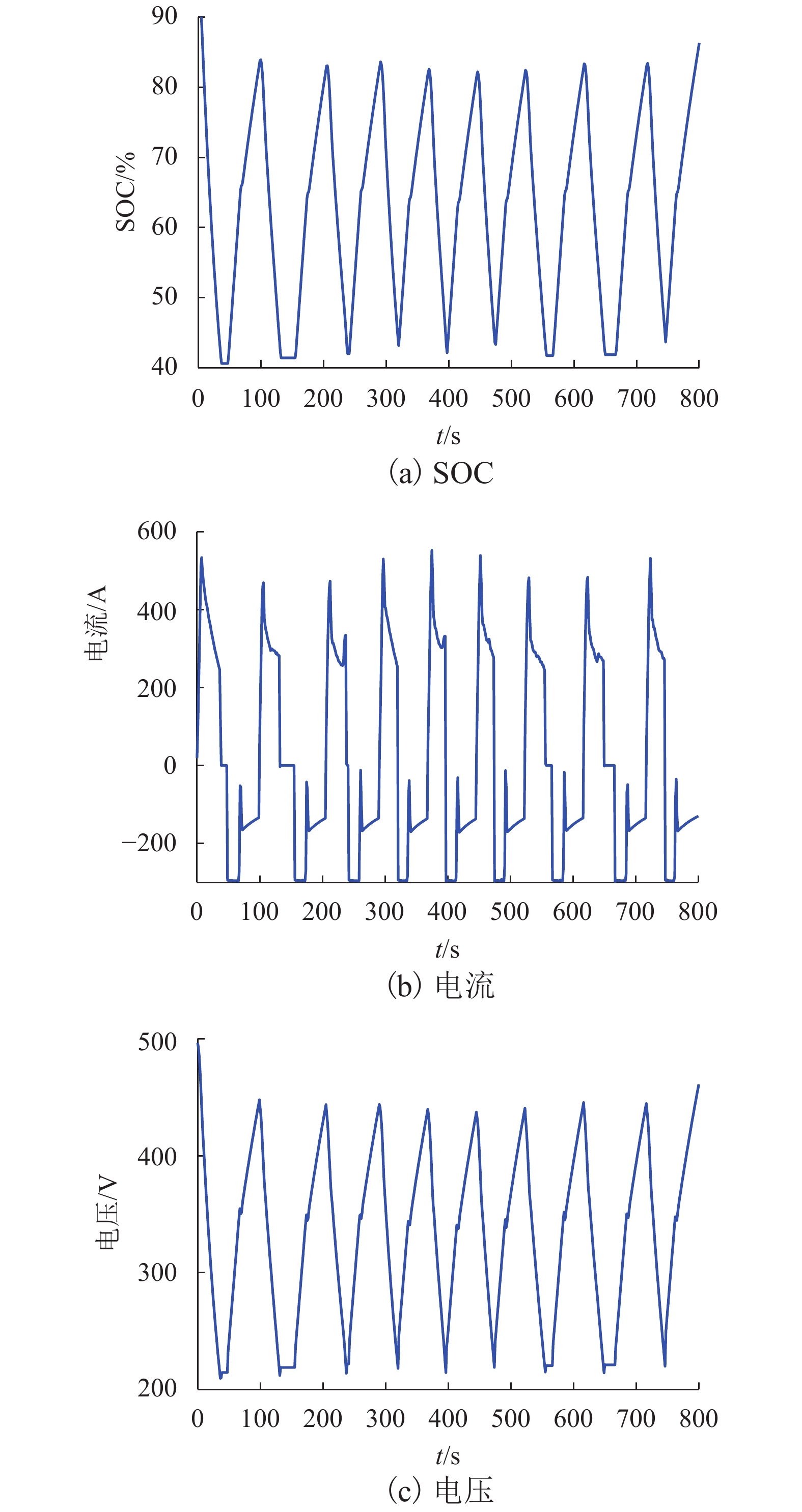
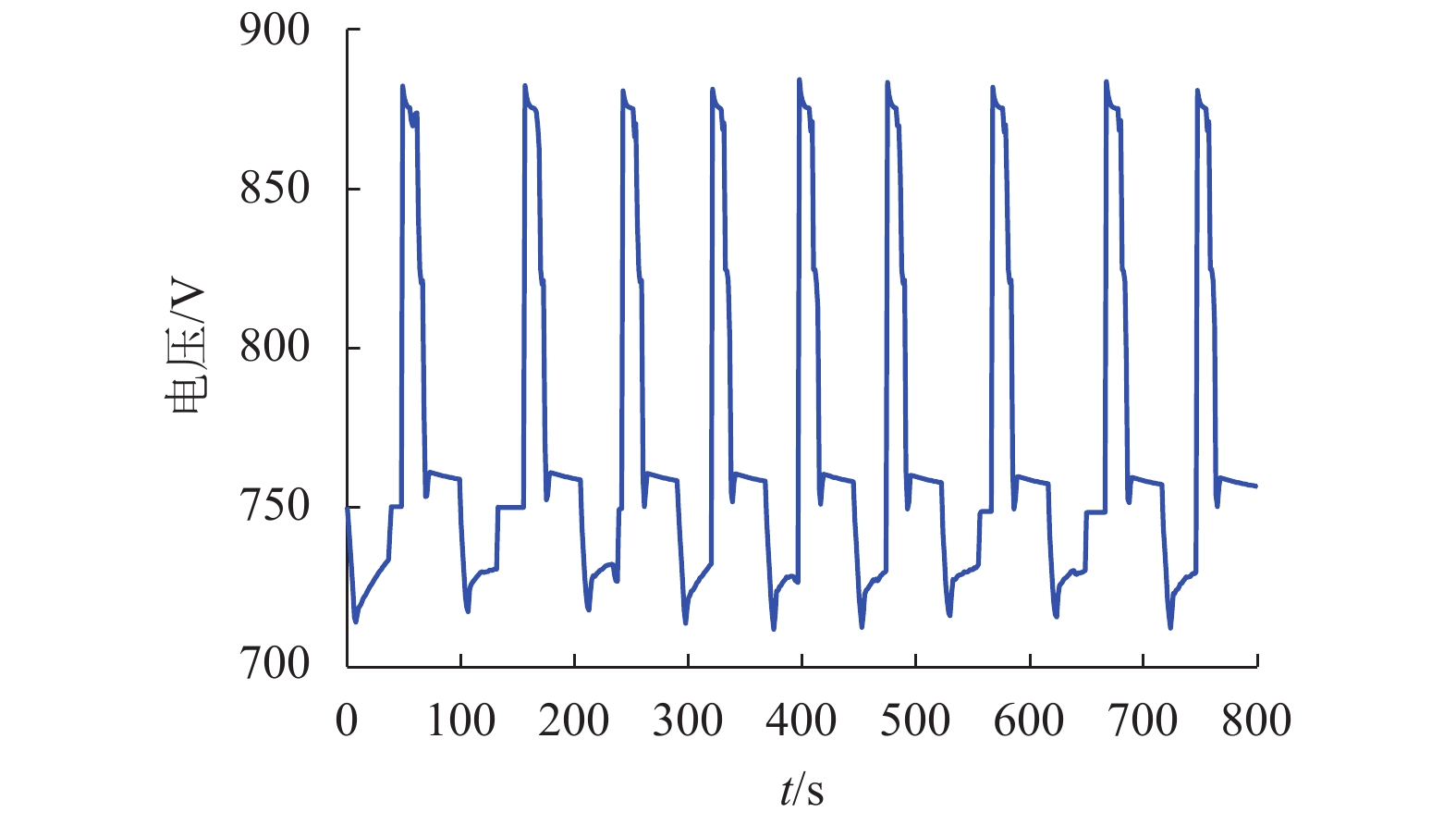
摘要: 为了提高混合动力有轨电车制动过程中制动能量的回收效率,提出一种考虑储能系统始末状态的能量管理策略. 在有轨电车从启动到制动的运行过程中,基于极小值原理对混合动力系统进行功率分配,以实现对超级电容荷电状态(state of charge,SOC)安全范围的有效控制,并保证在制动时刻超级电容具有足够的SOC余量来吸收制动功率;同时,将有轨电车启动、运行过程中的牵引控制策略与制动过程的能量回收策略相结合,采用绝缘栅门极晶体管(insulated gate bipolar translator,IGBT)斩波器与制动电阻相结合使用的方式,抑制母线电压的抬升; 最后基于实际的有轨电车运行工况,在MATLAB/Simulink平台下进行了仿真测试. 结果显示,在有轨电车制动时刻,超级电容SOC均能够按照预期下降到0.4左右,且在制动全过程中,有轨电车母线电压始终处于875 V以下,满足母线电压的控制要求.Abstract: In order to improve the efficiency of absorbing the braking energy for hybrid trams, an energy management strategy is proposed, which takes into account the initial and final states of charge (SOC) of an energy storage system. The strategy allocates the load power for the hybrid power system by using the minimum principle from the tram start to the braking, which achieves the effective control on the safety range of the supercapacitor SOC, and ensures sufficient remaining SOC to absorb the braking energy as the tram brakes. Furthermore, the strategy combines the tram traction control during start and traction operation with the energy recovery during the braking process, and uses an integrated device composed of the insulated gate bipolar transistor chopper and braking resistor to suppress the bus voltage rise. Finally, based on the actual tram operating conditions, a simulation test is conducted with the MATLAB/Simulink platform. The results show that at the moment of tram braking, the supercapacitor SOC can reach about 0.4 as expected, and during the entire braking process, the bus voltage can always lie below 875 V, which meets the requirements of bus voltage control.
-
Key words:
- tram /
- novel traction power system /
- hybrid system /
- energy management strategy
-
表 1 燃料电池电堆参数
Table 1. Parameters of fuel cells
参数 取值 输出电压范围/V 570~650 输出电流范围/A 20~320 额定功率/kW 150 额定工作温度/°C 50~60 质量/kg 710 表 2 超级电容参数
Table 2. Parameters of super capacitor module
超级电容参数 取值 电容量/F 165 电压/V 48 最低工作电压/V 28.8 最大持续电流/A 100 内阻/mΩ 6.3 放电深度/% 100 最大存储能量/(kW•h) 52.8 × 10−3 表 3 车辆参数
Table 3. Vehicle Parameters
电车参数 取值 AW0/t 61.9 AW2/t 79.0 AW3/t 83.0 编组 两动两拖 最高速度/(km•h−1) 70 最大常用制动减速度/(m•s−2) 1.2 新/旧车轮直径/mm 600/540 -
陈维荣,钱清泉,李奇. 燃料电池混合动力列车的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2009,44(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.01.001CHEN Weirong, QIAN Qingquan, LI Qi. Investigation status and development trend of hybrid power train based on fuel cell[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2009, 44(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.01.001 陈维荣,刘嘉蔚,李奇,等. 质子交换膜燃料电池故障诊断方法综述及展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2017,37(16): 4712-4721.CHEN Weirong, LIU Jiawei, LI Qi, et al. Review and prospect of fault diagnosis methods for proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Proceeding of the CES, 2017, 37(16): 4712-4721. HONG L, CHEN J, LIU Z, et al. A nonlinear control strategy for fuel delivery in PEM fuel cells considering nitrogen permeation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(2): 1565-1576. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.07.240 李奇,孟翔,陈维荣,等. 燃料电池混合动力系统参数匹配与多目标优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(5): 1079-1086.LI Qi, MENG Xiang, CHEN Weirong, et al. Parameter matching and multi-objective optimization of fuel cell hybrid system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(5): 1079-1086. 黄文强,李奇,陈维荣,等. 基于制动速度优化策略的新型供电方式有轨电车再生制动能量回收方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(18): 5406-5414,5588.HUANG Wenqiang, LI Qi, CHEN Weirong, et al. A regenerative braking energy recovery method based on braking speed optimization strategy for novel power supply model tram[J]. Proceeding of the CESS, 2019, 39(18): 5406-5414,5588. XIE Changjun, XU Xinyi, BUJLO P, et al. Fuel cell and lithium iron phosphate battery hybrid powertrain with an ultracapacitor bank using direct parallel structure[J]. Power Sources, 2015, 279: 487-494. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.029 LI Q, CHEN Weirong, LIU Zhixiang, et al. Development of energy management system based on a power sharing strategy for a fuel cell-battery-supercapacitor hybrid tramway[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 279: 267-280. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.12.042 侯明,衣宝廉. 燃料电池技术发展现状与展望[J]. 电化学,2012,18(1): 1-13.HOU Ming, YI Baolian. Progress and perspective of fuel cell technology[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry, 2012, 18(1): 1-13. 陈维荣,卜庆元,刘志祥,等. 燃料电池混合动力有轨电车动力系统设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(3): 430-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.03.003CHEN Weirong, BU Qingyuan, LIU Zhixiang, et al. Power system design for a fuel cell hybrid power tram[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(3): 430-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.03.003 GONZÁLEZ-GIL A, PALACIN R, BATTY P, et al. A systems approach to reduce urban rail energy consumption[J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2014, 80: 509-524. HAN Ying, LI Qi, WANG Tianhong, et al. Multi-source coordination energy management strategy based on SOC consensus for a PEMFC-battery- supercapacitor hybrid tramway[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(1): 296-305. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2747135 李云峰,卿云,李长青,等. 北京地铁8号线二期工程地铁车辆电空配合制动验证[J]. 机车电传动,2017(4): 77-79.LI Yunfeng, QING Yun, LI Changqing, et al. Verification test of electric-pneumatic braking for metro vehicle of beijing metro line 8 Ⅱ project[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2017(4): 77-79. 段继超,伍智敏,邓谊柏. 储能式现代有轨电车制动系统[J]. 电力机车与城轨车辆,2015(4): 10-12.DUAN Jichao, WU Zhiming, DENG Yibo. Brake system of energy modern tram[J]. Electric Locomotive Mass Transit Vehicles, 2015(4): 10-12. 陈维荣,张国瑞,孟翔,等. 燃料电池混合动力有轨电车动力性分析与设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.001CHEN Weirong, ZHANG Guorui, MENG Xiang, et al. Dynamic performance analysis and design of fuel cell hybrid locomotive[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.001 石英乔,何彬,曹桂军,等. 燃料电池混合动力瞬时优化能量管理方法研究[J]. 汽车工程,2008,30(1): 30-35. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-680X.2008.01.007SHI Yingqiao, HE Bin, CAO Guijun, ea tl. A study on the energy management strategy for fuel cell electric vehicle based on instantaneous optimization[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2008, 30(1): 30-35. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-680X.2008.01.007 许世景,吴志新. 基于PMP的HEV全局最优能量管理策 研究[J]. 中国机械工程,2014,25(1): 138-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2014.01.026XU Shijing, WU Zhixin. Investigation of global optimization energy management strategy of HEV based on PMP[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 25(1): 138-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2014.01.026 HAN J, PARK Y, KUM D. Optimal adaptation of equivalent factor of equivalent consumption minimization strategy for fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles under active state inequality constraints[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 267(4): 491-502. SCIARRETTA A, SERRAO L, DEWANGAN P C, et al. A control benchmark on the energy management of a plug-in hybridelectric vehicle[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2014, 29(6): 287-298. 林歆悠,孙冬野. 基于ECMS混联式混合动力客车工况识别控制方法[J]. 湖南大学学报(自科版),2012,39(10): 43-49.LIN Xinyou, SUN Dongye. Driving recognition based on ECMS and its application to control strategy for a series-parallel hybridelectric bus[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2012, 39(10): 43-49. 张培昌,余达太. 质子交换膜燃料电池温度的 MPC 控制[J]. 系统仿真学报,2009,21(5): 1305-1313.ZHANG Peichang, YU Datai. Model predictive control of PEMFC temperature model[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2009, 21(5): 1305-1313. 徐梁飞,华剑锋,包磊,等. 燃料电池混合动力客车等效氢 耗优化方法[J]. 中国公路学报,2009,22(1): 104-108. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2009.01.017XU Liangfei, HUA jianfeng, BAO Lei, et al. Optimized strategy on equivalent hydrogen consumption for fuel cell hybrid electric bus[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2009, 22(1): 104-108. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2009.01.017 周祥,宋璐,付主木,等. ISG-FHEV等效燃油消耗最小控制方法[J]. 计算机测量与控制,2016,24(4): 83-86.ZHOU Xiang, SONG Lu, FU Zhumu, et al. Equivalent consumption minimization strategy for full hybrid electric vehicle assisted by integrated starter generation[J]. Computer Measurement and Control, 2016, 24(4): 83-86. 曾望云,刘小飞,隗寒冰. 基于PMP的plug-in柴电混合动力汽车油耗与排放最优控制策略[J]. 汽车工程学报,2017,7(4): 244-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1469.2017.04.02ZENG Wangyun, LIU Xiaofei, WEI Hanbing. Optimal control strategy to minimize fuel consumption and missions for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles based on Pontryagin’s minimum principle[J]. Chinese Journal Automotive Engineering, 2017, 7(4): 244-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1469.2017.04.02 LI Qi, HUANG Wenqiang, CHEN Weirong, et al. Regenerative braking energy recovery strategy based on Pontryagin’s minimum principle for fell cell/supercapacitor hybrid locomotive[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(11): 5454-5461. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.10.115 -




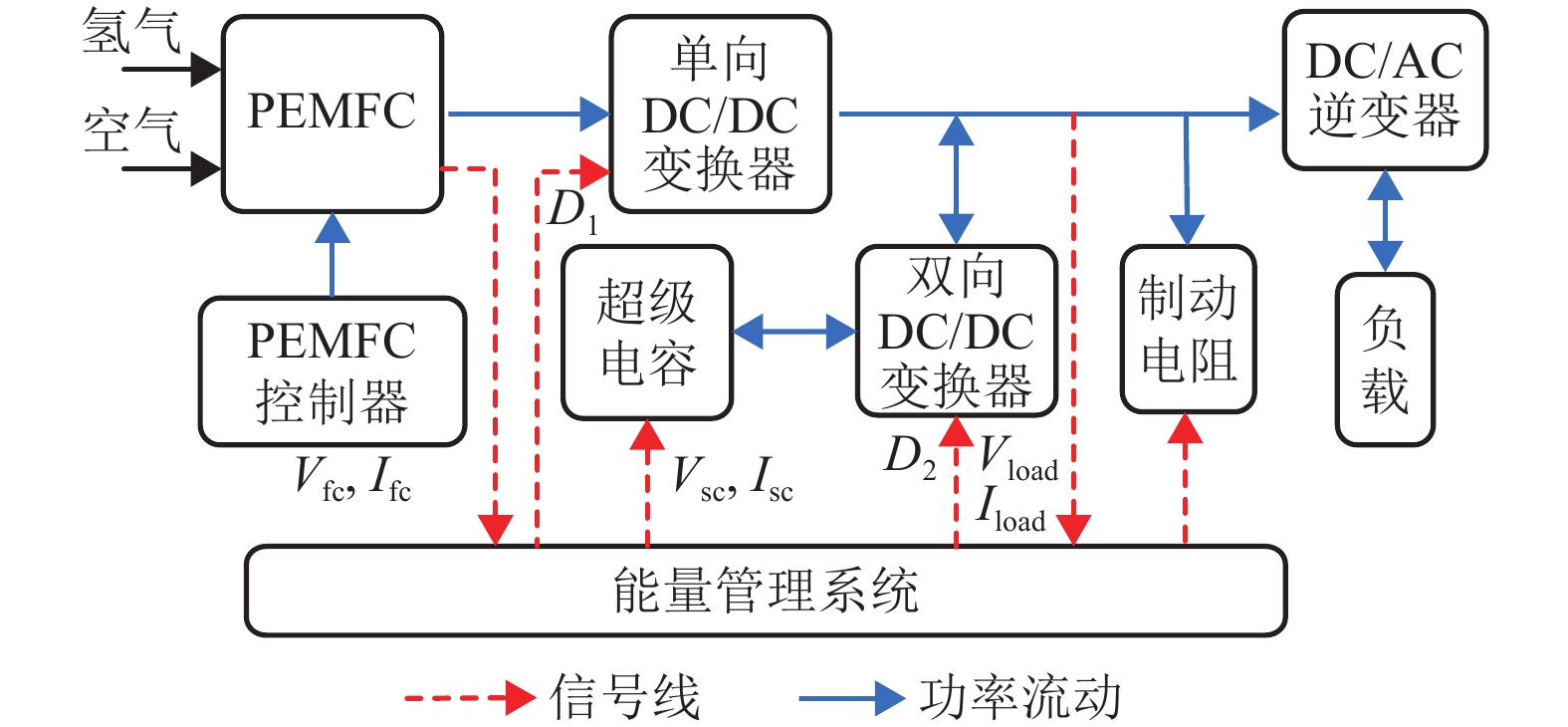
 下载:
下载: