Two-Stream Neural Network Fusion Model for Highway Fog Detection
-
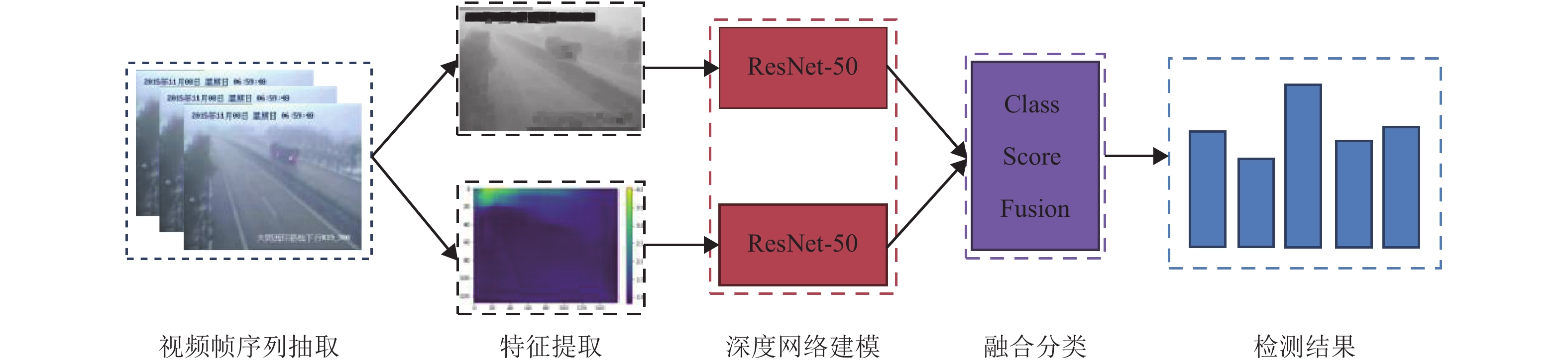
摘要: 高速公路天气状况实时监察对于高速行车安全具备重要意义,然而气象检测只能对大范围区域的气象情况进行预报,不能满足高速行车各个路段气象情况实时检测的需求. 为此,提出一种基于双路神经网络融合模型的高速公路雾天检测算法. 该算法基于双路深度神经网络融合模型,提取雾天图像的可视深度图以及暗通道图像两种视觉特征,并利用深度神经网络进行建模,获得初步分类结果;然后,再利用均值融合层进行分数融合. 为了全面评测该算法的性能,构建了一个覆盖多个省份高速公路的视频监控雾天数据集(express way fog detection dataset,EWFD),该数据集能够全面涵盖国内高速公路的天气情况,并在该数据集上做了全面的分析对比实验. 实验结果显示,本文所提出的双路神经网络融合模型的雾天监测算法取得了93.7%的准确率,与国际前沿的检测分类算法101层残差网络(ResNet-101)相比,本文提出的算法准确率提高了10%以上.Abstract: The real-time detection of weather conditions on highways has a significant impact on high-speed traffic safety. However, the weather forecast reports weather conditions over a wide range of areas only, which cannot meet the demand of real-time detection of weather conditions in various sections of high-speed traffic. Therefore, we present here a two-stream neural network fusion model for fog detection, which detect current weather condition for the surveillance area automatically. This model is based on a dual branches of deep neural networks, which integrates visual depth maps and dark-channel images for fog detection. These two modalities of features are discriminative in representing the pattern of fog and extracted from the surveillance video frame. The intermediate scores produced by the neural networks are fed into a mean fusion layer for the final prediction. To comprehensively evaluate the performance of our algorithm, we built an Express Way Fog Detection dataset (EWFD), which covers highway scenes across multiple provinces of China. A variety of highway weather conditions are contained in the EWFD. We conducted a comprehensive analysis and comparison experiment on the EWFD dataset. The results of the experiment also demonstrate that the two-stream neural network fusion model proposed here achieved an accuracy of 93.7%, which is a more than 10% improvement compared to the state-of-the-art classification method ResNet-101.
-
Key words:
- image processing /
- fog detection /
- depth map /
- dark channel prior /
- deep learning
-
表 1 双路神经网络融合对比实验
Table 1. Experiments on two-stream neural network fusion
特征 数据集 测试数 正确数 正确率/% RGB EWFD 4 000 3 292 82.3 暗通道 EWFD 4 000 3 664 91.6 深度图 EWFD 4 000 3 488 87.2 暗通道+深度图 EWFD 4 000 3 748 93.7 表 2 现有方法对比实验
Table 2. Comparing with existing method
方法 数据集 测试数 正确数 正确率/% AlexNet EWFD 4 000 3 502 76.3 VGGNet-16 EWFD 4 000 3 184 79.6 ResNet50 EWFD 4 000 3 288 82.3 ResNet101 EWFD 4 000 3 308 82.7 双路神经网络融合检测 EWFD 4 000 3 748 93.7 -
孙刚,陈陶,李建林. 高速路雾天行车诱导系统道路能见度检测装置[J]. 科技通报,2015(12): 164-166 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.2015.12.060SUN Gang, CHEN Tao, LI Jianlin. Highway foggy road guidance system road visibility testing device[J]. Technology Bulletin, 2015(12): 164-166 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.2015.12.060 包左军, 汤窃巧, 李长城, 等. 公路交通安全与气象影响[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2008: 57-63 张巧汉, 何勇, 刘洪肩, 等. 商速公路雾区交通安全保暗技术[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2009: 38 BRONTE S, BERGASA L M, ALCANTARILLA P F. Fog detection system based on computer vision techniques[C]//Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2009: 1-6 PAVLIC M, BELZNER H, RIGOLL G, et al. Image based fog detection in vehicles[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2012: 1132-1137 TAN R T. Visibility in bad weather from a single image[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2008. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2008: 1-8 HAUTIERE N, LABAYRADE R, AUBERT D. Real-time disparity contrast combination for onboard estimation of the visibility distance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation System, 2006, 7(2): 201-212 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2006.874682 BUSCH C, DEBES E. Wavelet transform for analyzing fog visibility[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 1998, 13(6): 66-71 doi: 10.1109/5254.736004 SCHECHNER Y Y, NARASIMHAN S G, NAYAR S K. Polarization based vision through haze[J]. Appl. Opt., 2003, 42(3): 511-525 doi: 10.1364/AO.42.000511 NARASIMHAN S G, NAYAR S K. Contrast restoration of weather degraded images[J]. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2003, 25(6): 713-724 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1201821 NAYAR S K, NARASIMHAN S G. Vision in bad weather[J]. Proc. 7th IEEE ICCV, 1999, 2(6): 820-827 NARASIMHAN S G, NAYAR S K. Removing weather effects from monochrome images[J]. Proc. IEEE Conf. CVPR, 2001, 2(6): 186-193 ROBERT G H, MATTHEWS M P, PISANO P A. Automated extraction of weather variables from camera imagery[C]//Proceedings of the Mid-Continent Transportation Research Symposium. Ames: [s.n.], 2005: 1031-1043 ROBERT G H, MICHAEL P M. Using camera imagery to measure visibility & fog[R]. Ames: For FHWA Presentation, 2001 ROBERT G H, MICHAEL P M. Clarus research: visibility estimation from camera imagery[R]. Ames: For FHWA CLARUS Meeting, 2006 BAUMER D, VERSICK S, VOGEL B. Determination of the visibility using a digital panorama camera[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42: 2593-2602 doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.06.024 ZEILER M D, FERGUS R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. [S.l.]: Springer, 2014: 818-833 REN S, CAO X, WEI Y, et al. Face alignment at 3000 FPS via regressing local binary features[C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2014: 1685-1692 REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal network[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Boston: MIT Press, 2015: 91-99 SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Boston: MIT Press, 2014: 568-576 KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neuralnetworks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. [S.l.]: ACM, 2012: 1097-1105 ZEILER M D, FERGUS R.Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. [S.l.]: Springer International Publishing, 2014: 818-833 SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2015: 1-9 HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2016: 770-778 HUANG G, LIU Z, MAATEN L V D, et al. Densely connected convolutional network[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. [S.l.]: IEEE Computer Society, 2017: 2261-2269 CAI B, XU X, JIA K, et al. DehazeNet:an end-to-end system for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187-5198 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2598681 REN W, LIU S, ZHANG H, et al. Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks[M]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2016. [S.l.]: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 154-169 HE K, SUN J, TANG X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341-2353 LAINA I, RUPPRECHT C, BELAGIANNIS V, et al. Deeper depth prediction with fully convolutional residual networks[C]//Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2016: 239-248 JIA, Y, SHELHAMER E, DONAHUE J, et al. Caffe: convolutional architecture for fast feature embeddi-ng[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM international conference on Multimedia. Orlando: ACM, 2014: 675-678 -




 下载:
下载: