Present Situation and Prospect of Evacuated Tube Transportation System
-
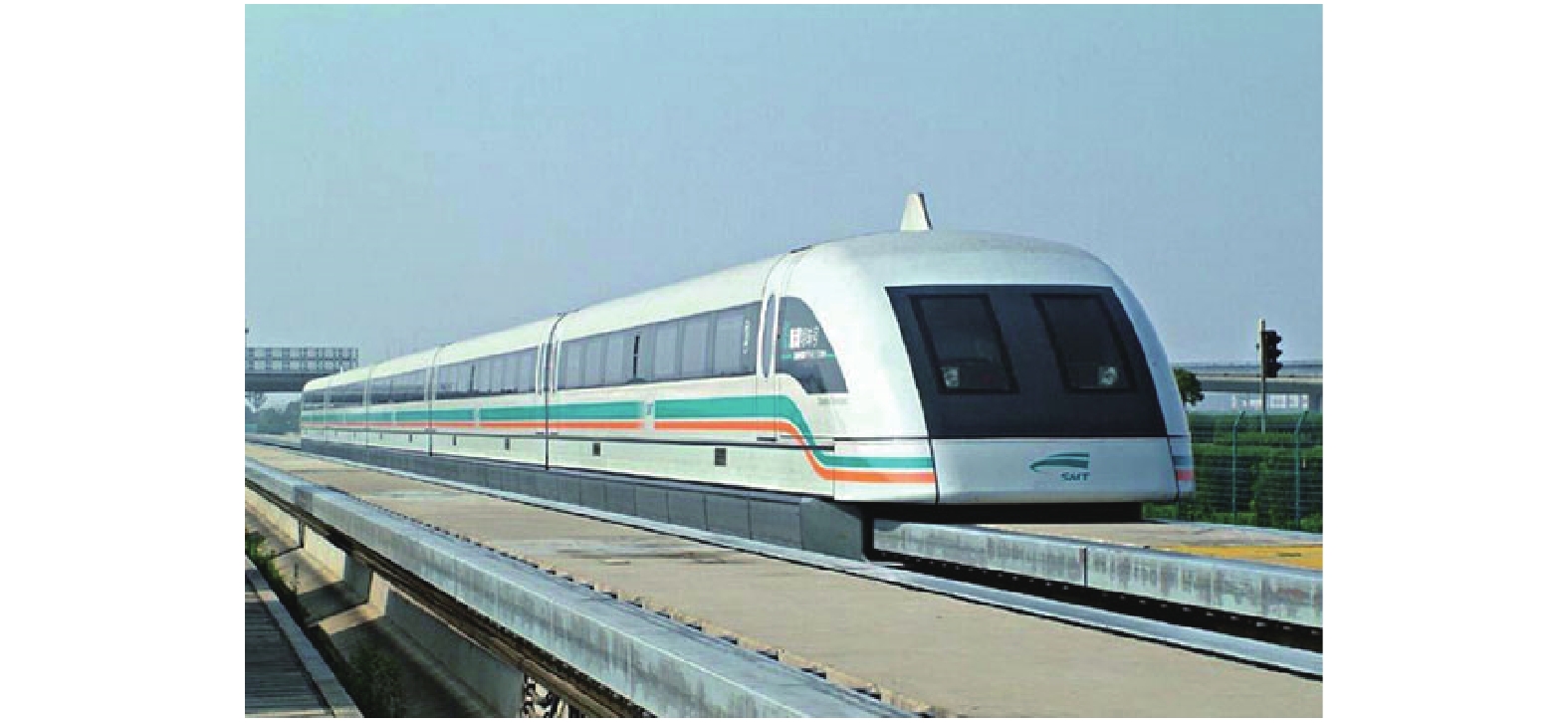
摘要: 作为一种新型交通系统,真空管道运输系统将悬浮列车技术和低气压管道技术相结合,理论上能够最大限度地减小列车高速运行时的摩擦阻力和气动阻力.为了促进真空管道运输系统的发展,从基本原理角度,系统论述了真空管道运输系统的可行性及车辆、管道、驱动装置等子系统关键构成,指出了其快速、便捷、安全、环保和高效等优势;介绍了国内外真空管道运输系统的研究现状,包括美国ET3、美国Hyperloop、瑞士超高速地铁Swissmetro,以及西南交通大学真空管道高温超导磁悬浮车试验平台,比较分析了各单位在车辆、管道、驱动装置及造价等方面的技术特点和优势;展望了当前发展真空管道运输系统亟需解决的关键问题,并指出车轨作用、高速直线牵引、气动和散热、管道密封以及管道内通信、救援这几个方面是今后需要重点研究的领域.Abstract: As a new type of transit system, the evacuated tube transportation system, combining magnetic levitation train technology and low-air-pressure tube technology, theoretically decreases friction and aerodynamic drag of high-speed trains as much as possible. In order to promote the evacuated tube transportation development, from the point of view of fundamental principles, the feasibility and the key components of vehicle, tube and propulsion were systematically discussed. Meanwhile, its advantages such as fast, convenience, safety, environmental protection and high efficiency were pointed out. The research status of the evacuated tube transportation system was introduced, including the ET3 (America), the Hyperloop (America), the Swiss Super High-speed Metro Swissmetro, and the evacuated tube high temperature superconducting maglev vehicle test platform of Southwest Jiaotong University. Their technical characteristics and advantages in vehicle, tube, propulsion device and cost were compared and analyzed. The key development and research issues which need to be urgently solved were prospected, such as train/track interaction, high-speed linear propulsion, aerodynamics and heat dissipation, tube sealing, in-pipe communication and rescue.
-
表 1 几种悬浮技术的对比
Table 1. Comparison of several suspension technologies
项目 悬浮技术 常导磁悬浮 低温超导磁悬浮 高温超导磁悬浮 气动悬浮 路轨要求 高 较高 低 极高 控制系统 复杂 较复杂 简单 难以控制 悬浮状态 须耗能 低速需轮轨 静止悬浮 依靠气膜悬浮 悬浮高度/mm 8 100 10~30 0.5~1.3 成本 高 高 低 低 表 2 各种运输系统能耗及成本对比
Table 2. Comparison of consumption and cost among several transport systems
指标 运输系统 水路 公路 铁路 民航 单位能耗/(×103 kg•t−1•km−1) 9 64 10 434 单位成本/(×103 元•t−1•km−1) 19 219 22 2 800 表 3 ET3、Swissmetro和Hyperloop系统参数对照
Table 3. Parameters comparison among ET3,Swissmetro and Hyperloop system
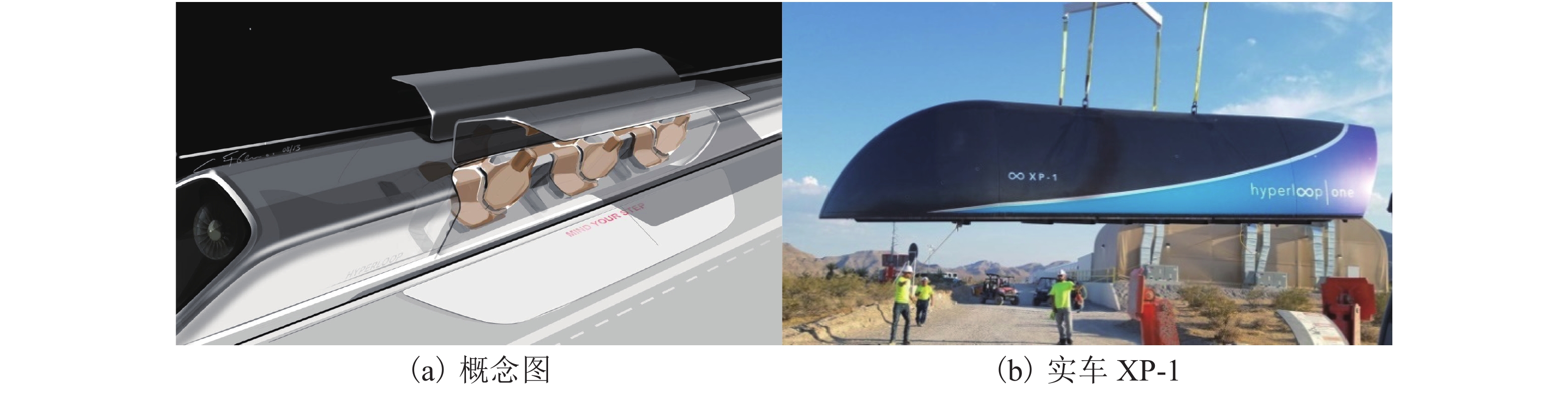
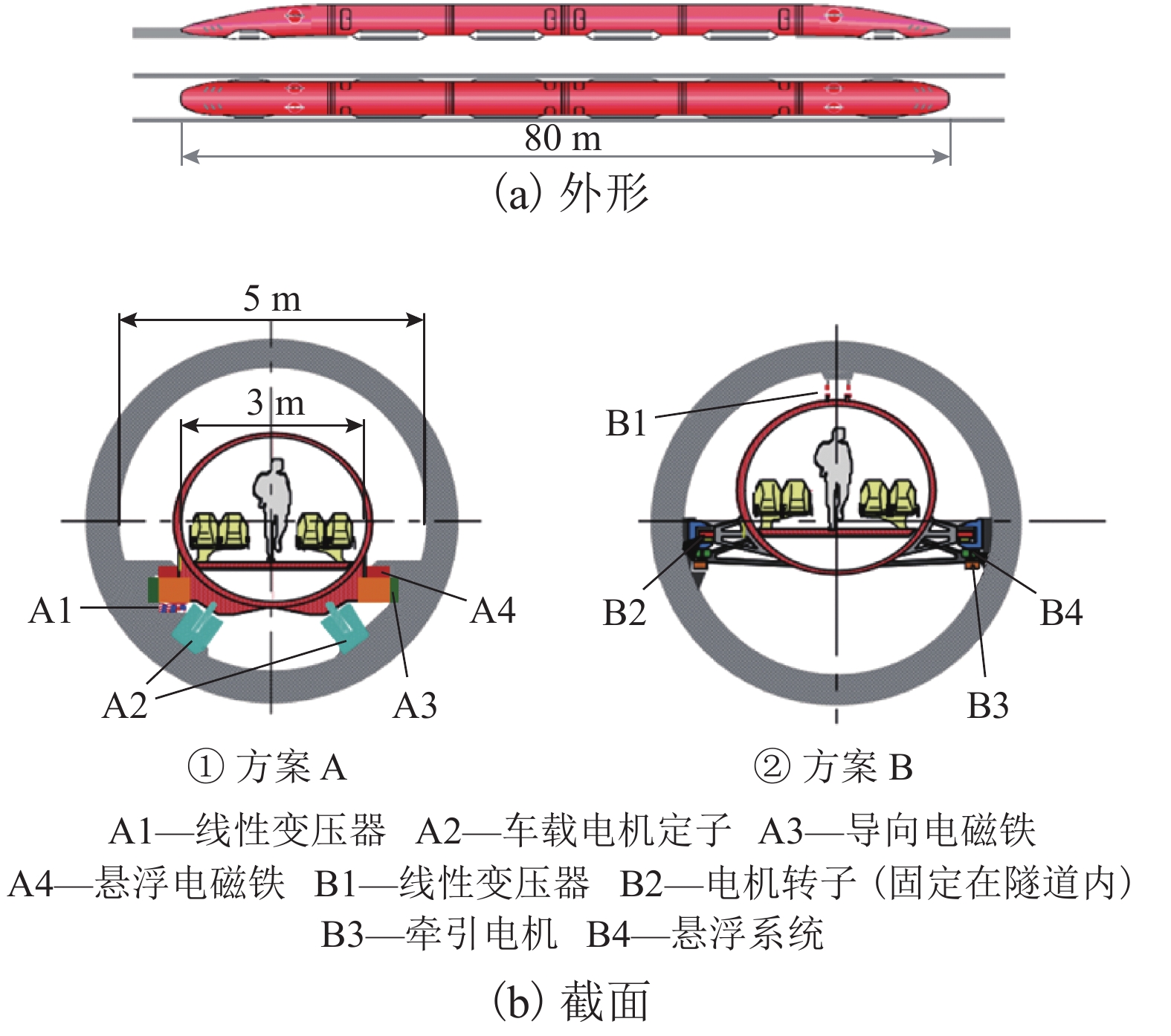
系统 车辆 管道 其它 规划 悬浮类型 形状 尺寸/m 车重/t 承载人数/位 结构 位置 材料 气压/kPa 驱动装置 供电装置 经费 试验线路及线路长度/km 最高时速/(km•h−1) ET3 磁悬浮 胶囊小车 直径1.30,长4.80 183×10−3 6 双向 10.13 直线电机 供电网和蓄电池 140万美元/km,2.8万美元/辆 纽约—好莱坞,
4 6006 500 Swissmetro 电磁悬浮 列车 直径3.50,长200.00 100 800 双向并行 地下隧道 钢筋混凝土管片 10.13 直线电机 供电网和蓄电池 50亿瑞士法郎 日内瓦—洛桑,63 500 Hyperloop 气动悬浮 Hyperloop 宽1.35,高1.10 15 28 双向并行 高架桥 金属 0.10 电动空气压缩机 太阳能和蓄电池 60亿美元 加州5号公路沿线,8 1 220 表 4 Super-Maglev具体参数
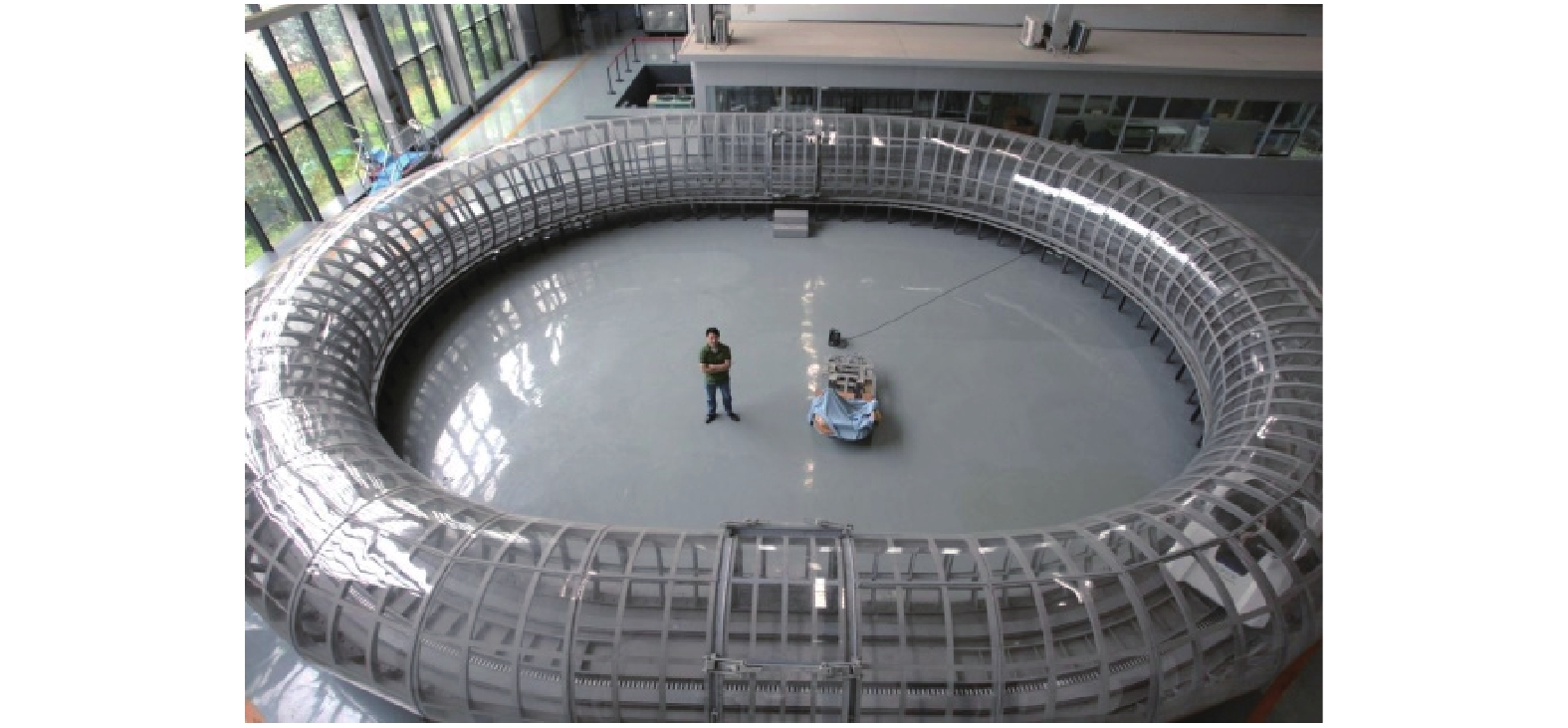
Table 4. Super-Maglev parameters
管道直径/m 长度/m 气压
/kPa实验速度/(km•h−1) 牵引制动 2.0 45.0,环形;弯道半径6.0,直线段长度3.6 101.0~
10.10~50 直线感应电机配合机械混合制动 -
GODDARD H R. Apparatus for vacuum tube transportation: U S, 2488287[P]. 1945-10-06. GODDARD H R. Vacuum tube transportation system: U S, 2511979[P]. 1950-06-20. KEMPER H. The invention of a hovertrack with wheelless vehicles which hover along iron rails using magnetic fields: Germany, DE1934K130005D[P]. 1934-08-11. 郝瀛. 中国铁路建设概论[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1998: 294-295. MOSSI M, ROSSEL P. Swissmetro: a revolution in the high-speed passenger transport systems[C]//1st Swiss Transport Research Conference. Ascona: IEEE, 2001: 1-16. SOLTER M R. Trans-planetary subway systems: a burgeoning capability[R/OL]. Rand Organization, 1978 [2018-4-13]. https://www.rand.org/content/dam/rand/pubs/papers/2009/P6092.pdf. OSTER D, FLA R C. Evacuated tube transportation: U S, 5950543[P]. 1999-09-14. MUSK E. Hyperloop alpha[EB/OL]. 2013[2018-4-13]. http://www.spacex.com/sites/spacex/files/hyperloop_alpha.pdf. 沈志云. 关于我国发展真空管道高速交通的思考[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2005,40(2): 133-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2005.02.001SHEN Zhiyun. On developing high-speed evacuated tube transportation in China[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2005, 40(2): 133-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2005.02.001 SCHETZ A J. 高速列车空气动力学[J]. 力学进展, 2003, 33(3): 404-423. 沈志云. 高速磁浮列车对轨道的动力作用及其与轮轨高速铁路的比较[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2001,1(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2001.01.001SHEN Zhiyun. Dynamic interaction of high speed maglev train on girders and its comparison with the case in ordinary high speed railways[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2001, 1(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2001.01.001 吴祥明. 磁浮列车[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2003: 96-97. MOTOHARU O, SHUNSAKU K, HISAO O. Japan’s superconducting maglev train[J]. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 2002, 5(1): 9-15. 王家素, 王素玉. 超导技术应用[M]. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社, 1995: 145-152. WANG Jiasu, WANG Suyu, ZENG Youwen, et al. The first man-loading high temperature superconducting maglev test vehicle in the world[J]. Physica C, 2002, 378/379/380/381: 809-814. SCHULTZ L, HAAS O, VERGES P, et al. Superconductively levitated transport system-the supratrans project[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2005, 15(2): 2301-2305. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2005.849636 SOTELO G G, OLIVEIRA R A H, COSTA F S, et al. A full scale superconducting magnetic levitation (maglev) vehicle operational line[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2015, 25(3): 1-5. KOVALEV K L, KONEEV S M A, POLTAVEC V N, et al. Magnetically levitated high-speed carriages on the basis of bulk HTS elements[C]//Proceeding of the 19th International Symposium on Magnetic Suspension Technology. Dresden: [s. n.], 2005: 51. D ’OVIDIO G, CRISI F, LANZARA G. A " V” shaped superconducting levitation module for lift and guidance of a magnetic transportation system[J]. Physica C, 2008, 468(14): 1036-1040. doi: 10.1016/j.physc.2008.05.154 杨学实. 气悬浮列车研究的新进展[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2003,3(3): 66-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2003.03.014YANG Xueshi. New developments in research of air suspension trains[J]. Communication and Transportation Systems Engineering and Information, 2003, 3(3): 66-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2003.03.014 王家素,王素玉. 高温超导磁悬浮列车研究综述[J]. 电气工程学报,2015,10(11): 2-12.WANG Jiasu, WANG Suyu. High temperature superconducting maglev train[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2015, 10(11): 2-12. 张耀平,梅绍祖,曾学贵. ETT——引领21世纪的高速运输[J]. 世界科技研究与发展,2002,24(2): 60-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2002.02.009ZHANG Yaoping, MEI Shaozu, ZENG Xuegui. ETT—lead the high-speed transportation of the 21st century[J]. World Sci-Tech R & D, 2002, 24(2): 60-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2002.02.009 严作人. 运输经济学[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2009: 33-38. 董焰. 我国综合交通运输的效率、效益及管理体制问题[C]//中国工程院第32场工程科技论坛——中国综合交通运输发展战略. [出版地不详]: 中国工程院, 2004: 15-32. OSTER D, KUMADA M, ZHANG Y. Evacuated tube transport technologies (ET3) tm;a maximum value global transportation network for passengers and cargo[J]. Journal of Modern Transportation, 2011, 19(1): 42-50. doi: 10.1007/BF03325739 张瑞华等. 一种新的高速磁悬浮列车——瑞士真空管道高速磁悬浮列车方案[J]. 变流技术与电力牵引,2004(1): 44-46.ZHANG Ruihua, et al. A new high-speed maglev train-the swiss vacuum tube high-speed maglev train project[J]. High Power Converter Technology, 2004(1): 44-46. CASSAT A, ESPANET C. Swissmetro: combined propulsion with levitation and guidance[C]//Proceedings of Maglev. Shanghai: [s. n.], 2004: 747-758. 刘本林, 赵勇. 速车系统概论[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2009: 16-26. ZHOU Dajin, CUI Chenyu, ZHAO Lifeng, et al. Running stability of prototype vehicle in side-suspended HTS maglev circular test track system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2017, 27(1): 3600107. DENG Zigang, ZHANG Weihua, ZHENG Jun, et al. A high temperature superconducting maglev ring test line developed in Chengdu,China[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26(6): 3602408. DENG Zigang, ZHANG Weihua, ZHENG Jun, et al. A high-temperature superconducting maglev-evacuated tube transport (HTS Maglev-ETT) test system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2017, 27(6): 3602008. 王博. 真空管道高温超导磁悬浮车气动特性研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. 刘加利,张继业,张卫华. 真空管道高速列车气动特性分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2013,49(22): 137-143.LIU Jiali, ZHANG Jiye, ZHANG Weihua. Analysis of aerodynamic characteristics of high-speed trains in the evacuated tube[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(22): 137-143. 贾文广. 真空管道交通系统热动力学特性研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2013. LIU Lu, WANG Jiasu, WANG Suyu, et al. Levitation force transition of high-Tc superconducting bulks within a maglev vehicle system under different dynamic operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2011, 21(3): 1547-1550. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2010.2091099 -





 下载:
下载: