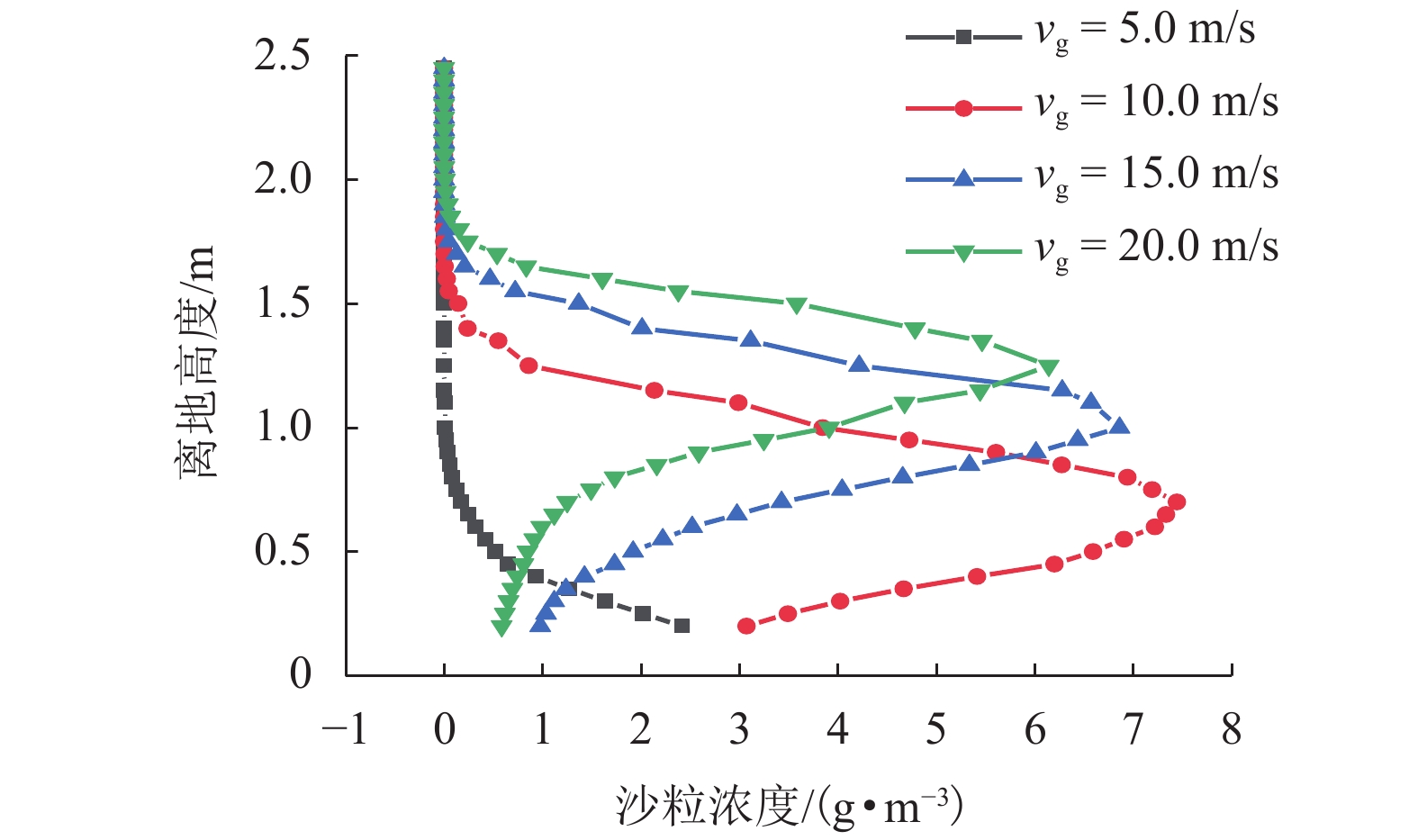
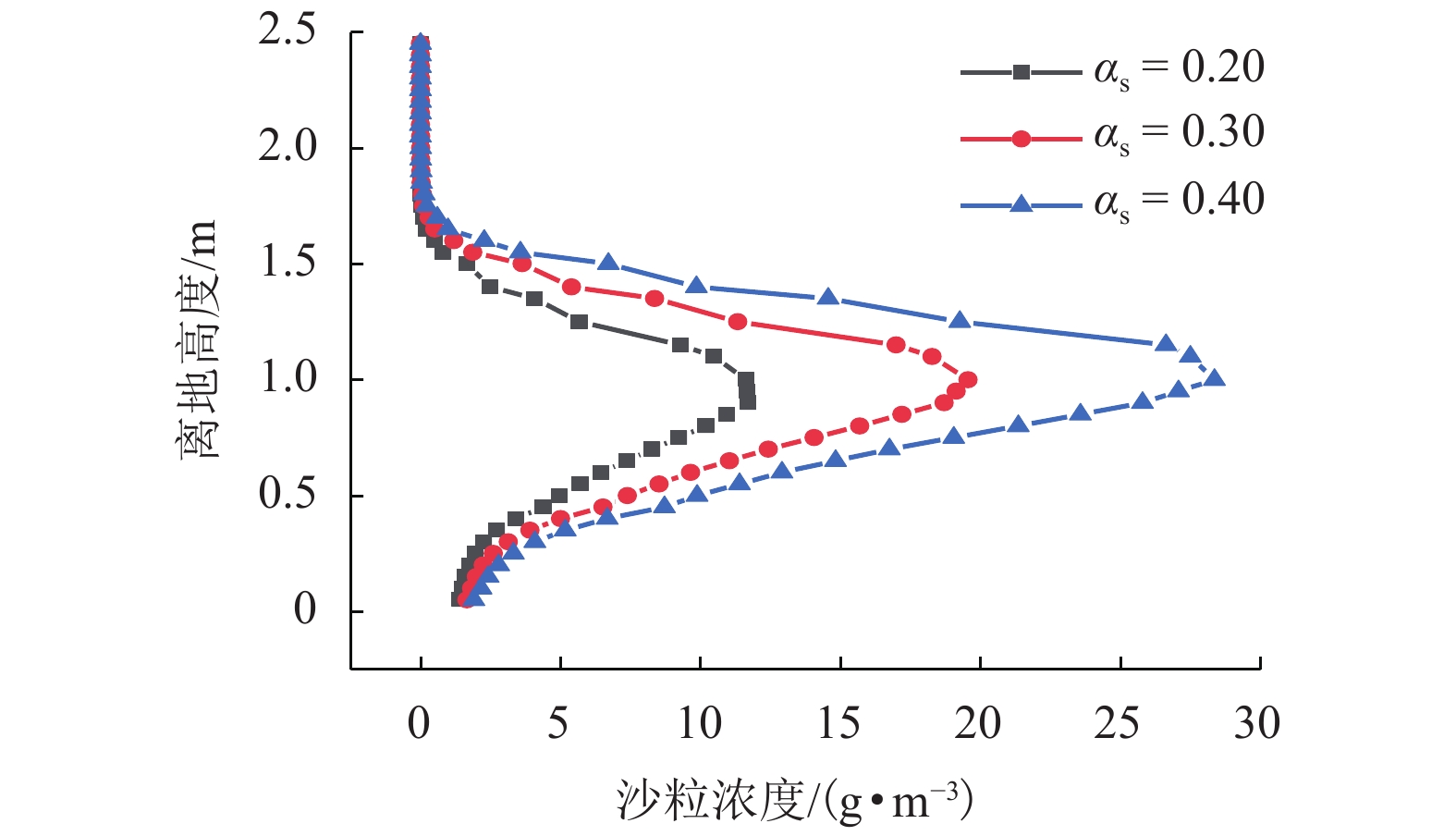
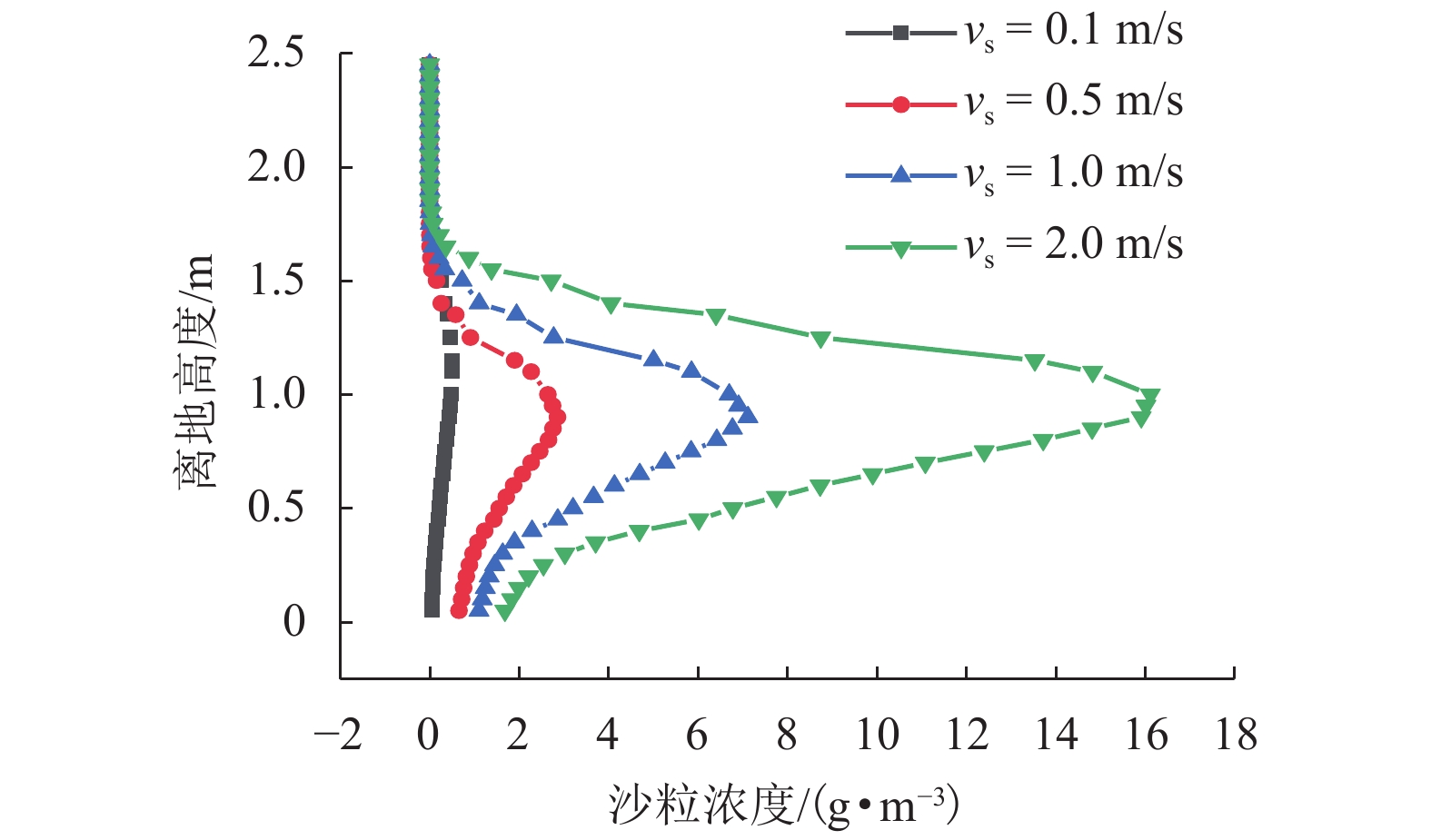
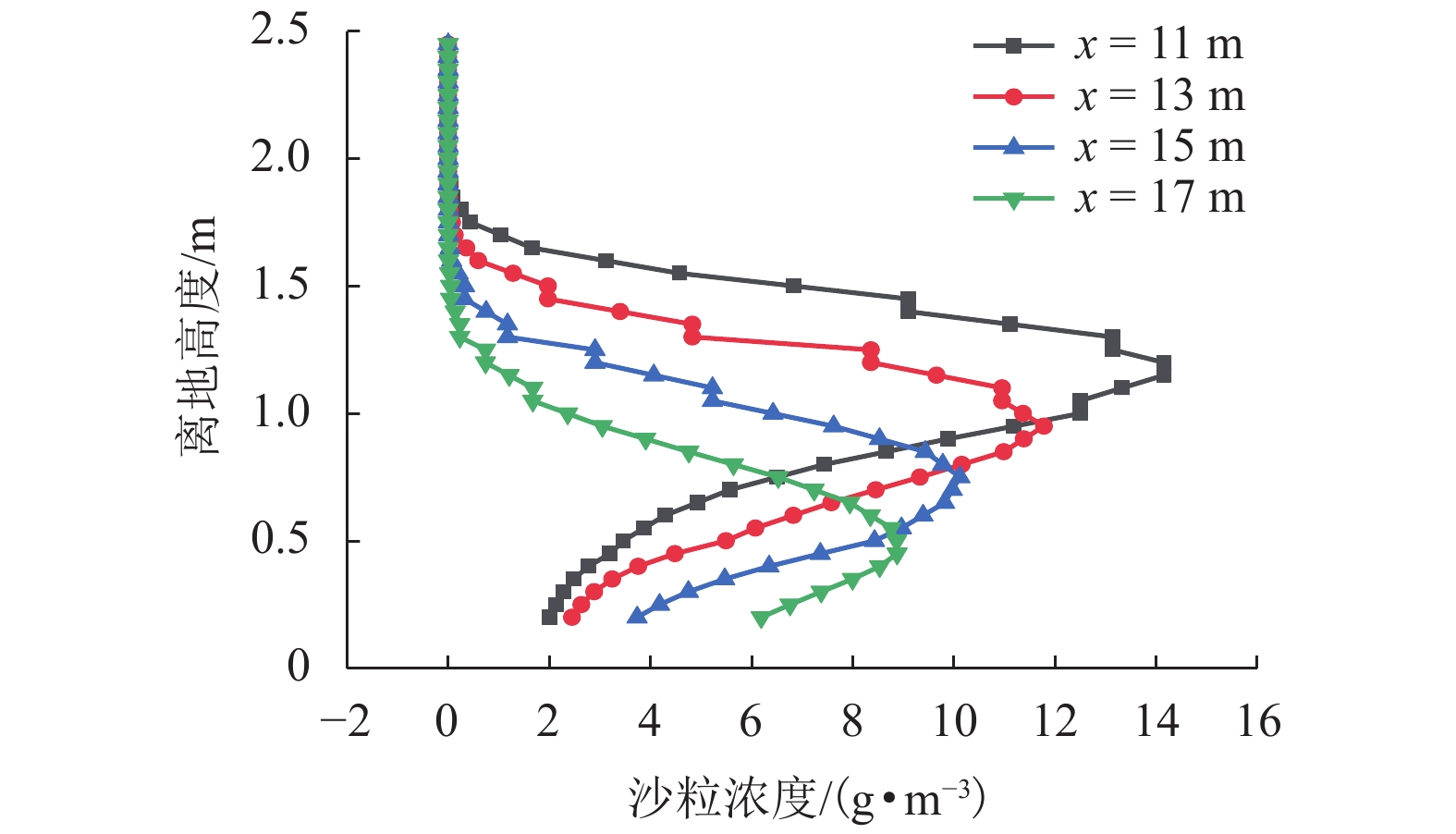
|
黄诗晴. 辽西北地区土地荒漠化的成因及治理对策分析[J]. 农业科技与信息,2016(35): 39-40.
|
|
张永民,赵士洞. 全球荒漠化现状及防治对策[J]. 西部大开发,2016(5): 17-19.
|
|
BAGNOLD R A. The physics of blown sand and desert dunes[M]. London: Methuen, 1941: 27-45.
|
|
OWEN P R. Saltation of uniform grains in air[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1964, 20(2): 225-242. doi: 10.1017/S0022112064001173
|
|
ANDERSON R S, HAFF P K. Wind modification and bed response during saltation of sand in air[J]. Acta Mechanica, 1991, 1(Sup1): 21-51.
|
|
ARUNDEL P A, HOBSON C A, LALOR M J, et al. Measurement of individual alumina particle velocities and the relative slip of different-sized particles in a vertical gas-solid suspension flow using a laser anemometer system[J]. Journal of Physics D, 1974, 6(6): 2288-2300. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4867.820
|
|
SHAO Y, LI A. Numerical modelling of saltation in the atmospheric surface layer[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1999, 91(2): 199-225. doi: 10.1023/A:1001816013475
|
|
PYE K. Wind as a geological process[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1987, 43(1): 90-91.
|
|
DING J, GIDASPOW D. A bubbling fluidization model using kinetic theory of granular flow[J]. AIChE Journal, 1990, 36(4): 523-538. doi: 10.1002/aic.690360404
|
|
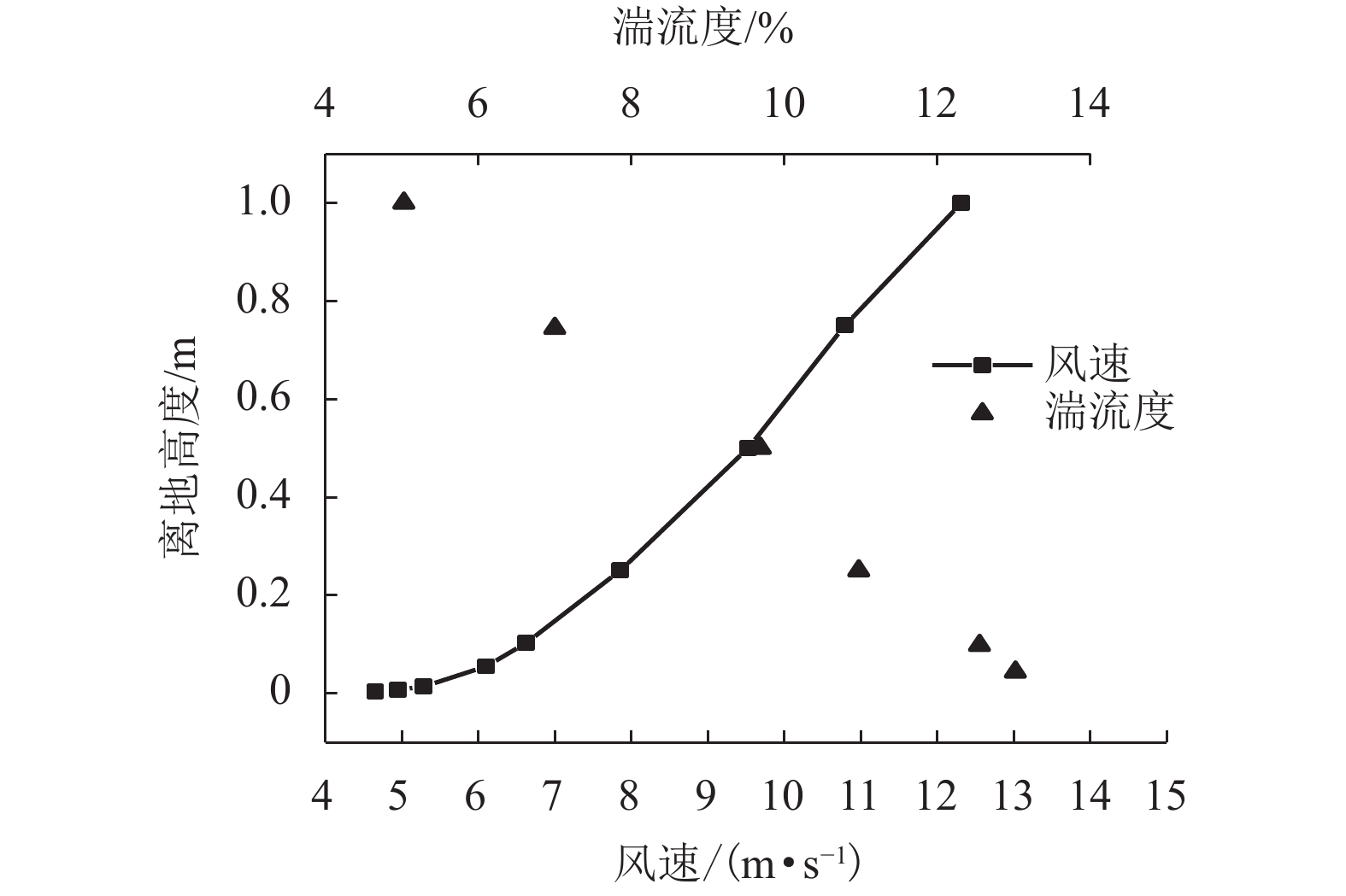
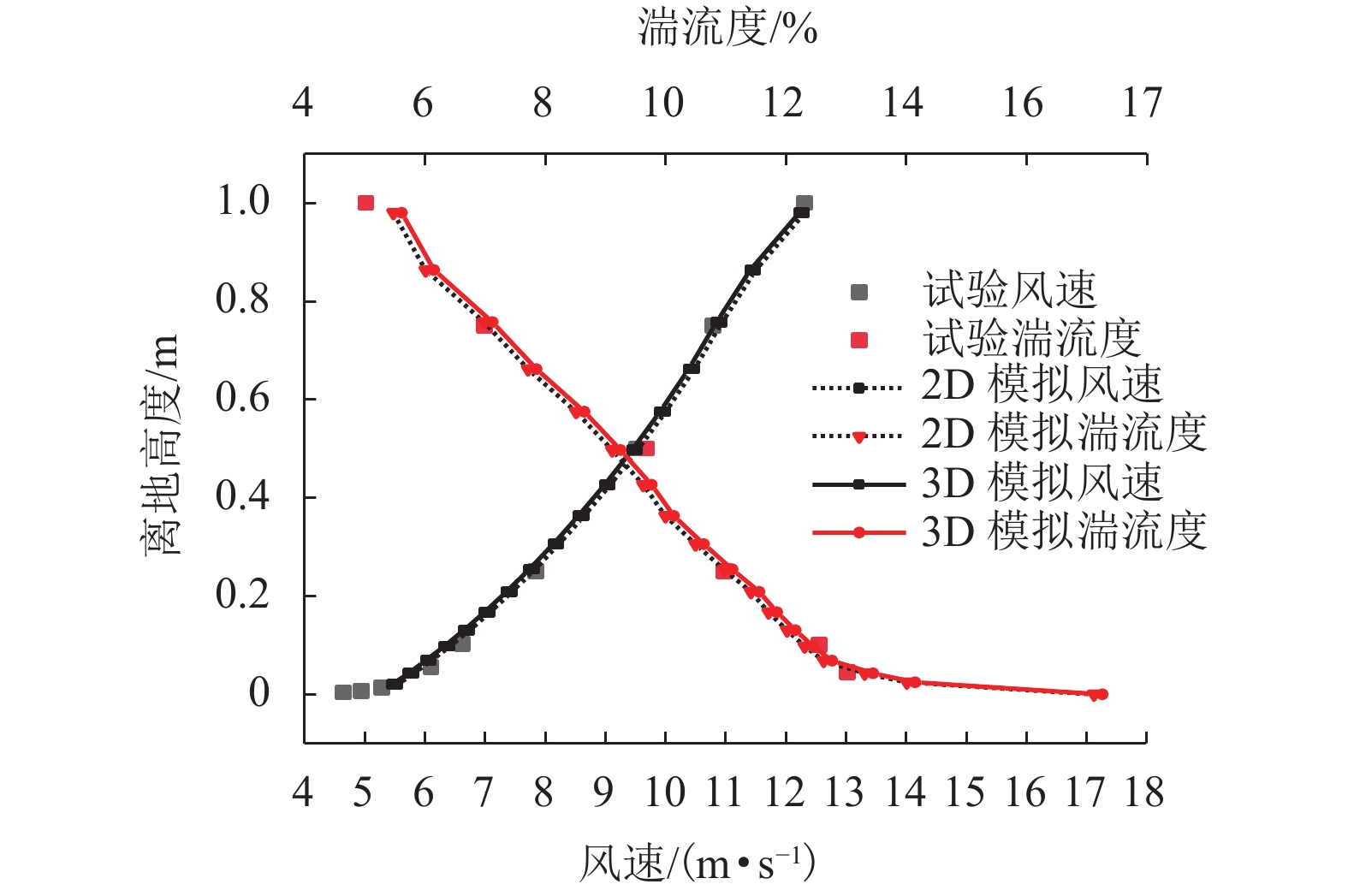
王萍,郑晓静. 野外近地表风沙流脉动特征分析[J]. 中国沙漠,2013,33(6): 1622-1628. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2013.00241
|
|
张伟民,王涛,汪万福,等. 复杂风况条件下戈壁输沙量变化规律的研究[J]. 中国沙漠,2011,31(3): 543-549.
|
|
李朝妹,袁树杰,张振彬. 风沙绕流建筑物流场的数值模拟研究[J]. 建筑热能通风空调,2012,31(2): 66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0344.2012.02.018
|
|
刘博. 风沙绕流群体建筑物的数值模拟研究[D]. 阿拉农: 塔里木大学, 2015.
|
|
李正农,王尚雨,宫博,等. 风沙对低矮建筑整体受力影响的风洞试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2017(1): 63-69.LI Zhengnong, WANG Shangyu, GONG Bo, et al. Wind tunnel test for impact of wind-sand flow on overall forces of low-rise building[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2017(1): 63-69.
|
|
岳高伟,毕伟,贾慧娜. 风沙运动的理论模拟和风洞实验对比研究[J]. 干旱区地理,2014,37(1): 81-88.YUE Gaowei, BI Wei, JIA Huina. Theoretical simulation and wind tunnel experiment in wind-blown sand movement[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2014, 37(1): 81-88.
|
|
李正农, 范晓飞, 蒲鸥, 等. 建筑物风沙流场与荷载的风洞试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(1): 152-158, 182LI Zhenglong, FAN Xiaofei, PU Ou. et al. Wind tunnel test on wind-sand flow field and wind-sand load on buildings[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020. 37(1): 152-158, 182
|
|
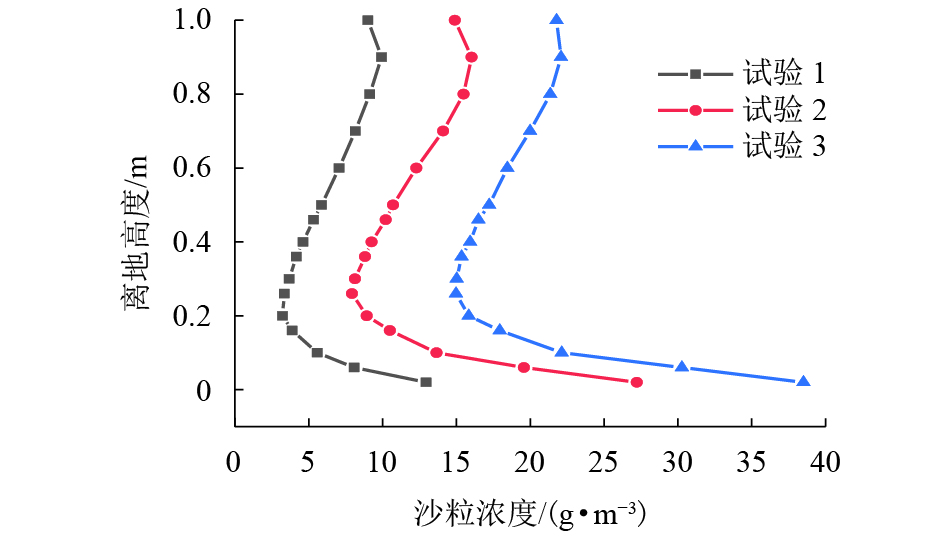
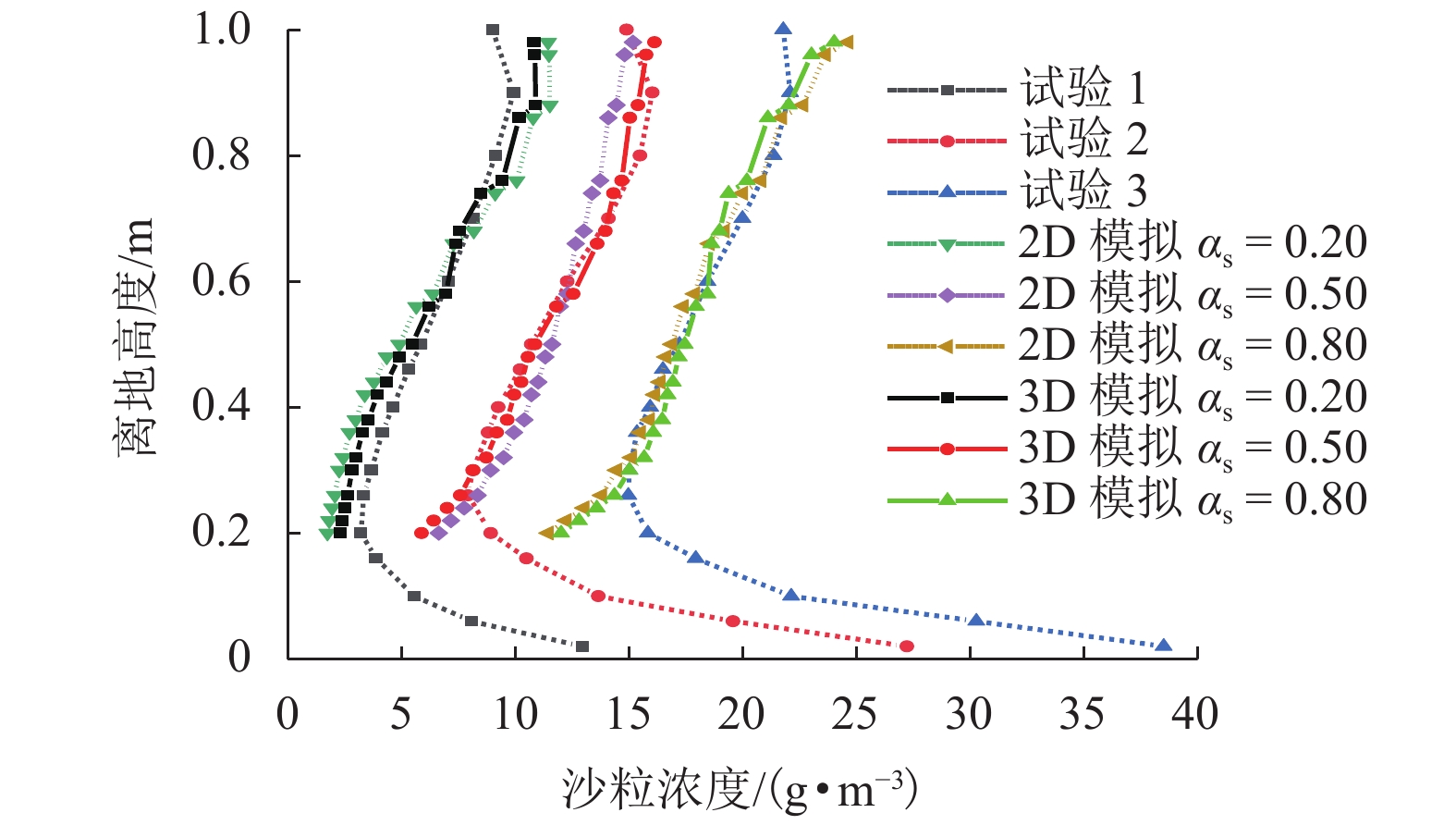
王康龙. 风沙流的双流体模型参数及输沙量分布特征研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2014.
|
|
MARSHALL J K. Drag measurements in roughness arrays of varying density and distribution[J]. Agricultural Meteorology, 1971, 8(71): 269-292.
|
|
GREELEY R, IVERSEN J. Book-review:wind as a geological process on earth,mars,venus and titan[J]. Earth Moon and Planets, 1986, 42: 311-313.
|




 下载:
下载: