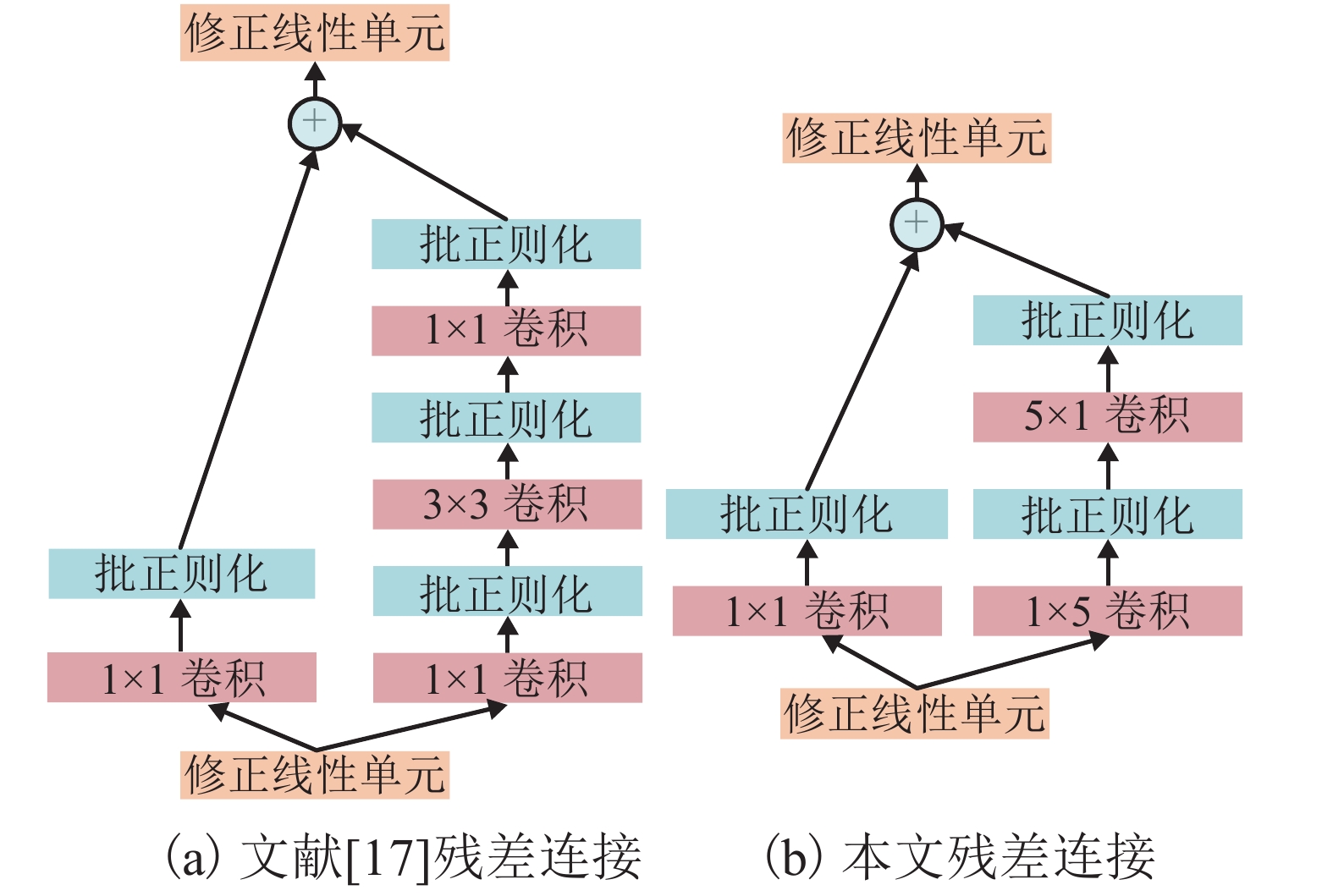
Combined Neural Networks Based on Deep Learning for Signal Detection in Aeronautical Communications
-
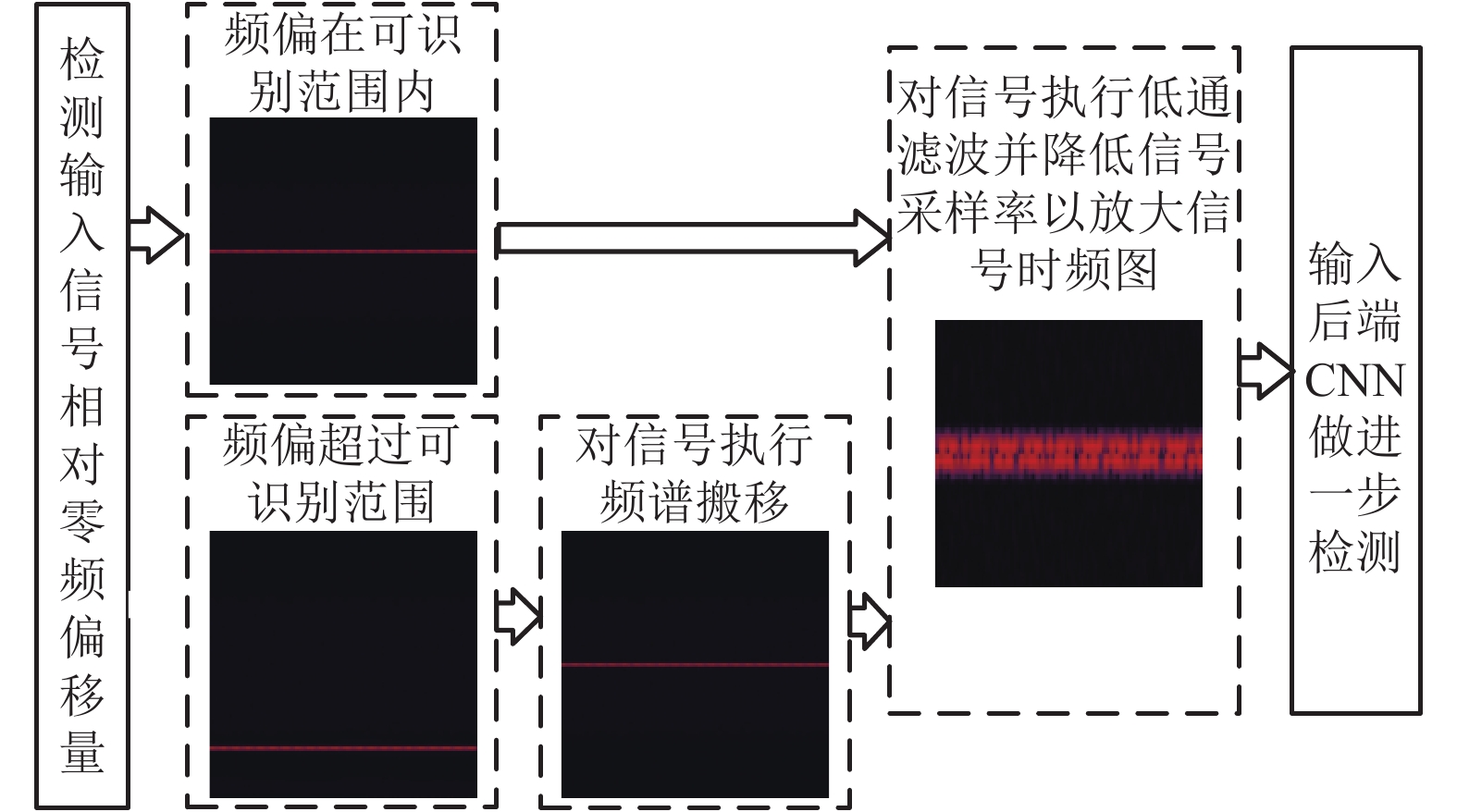
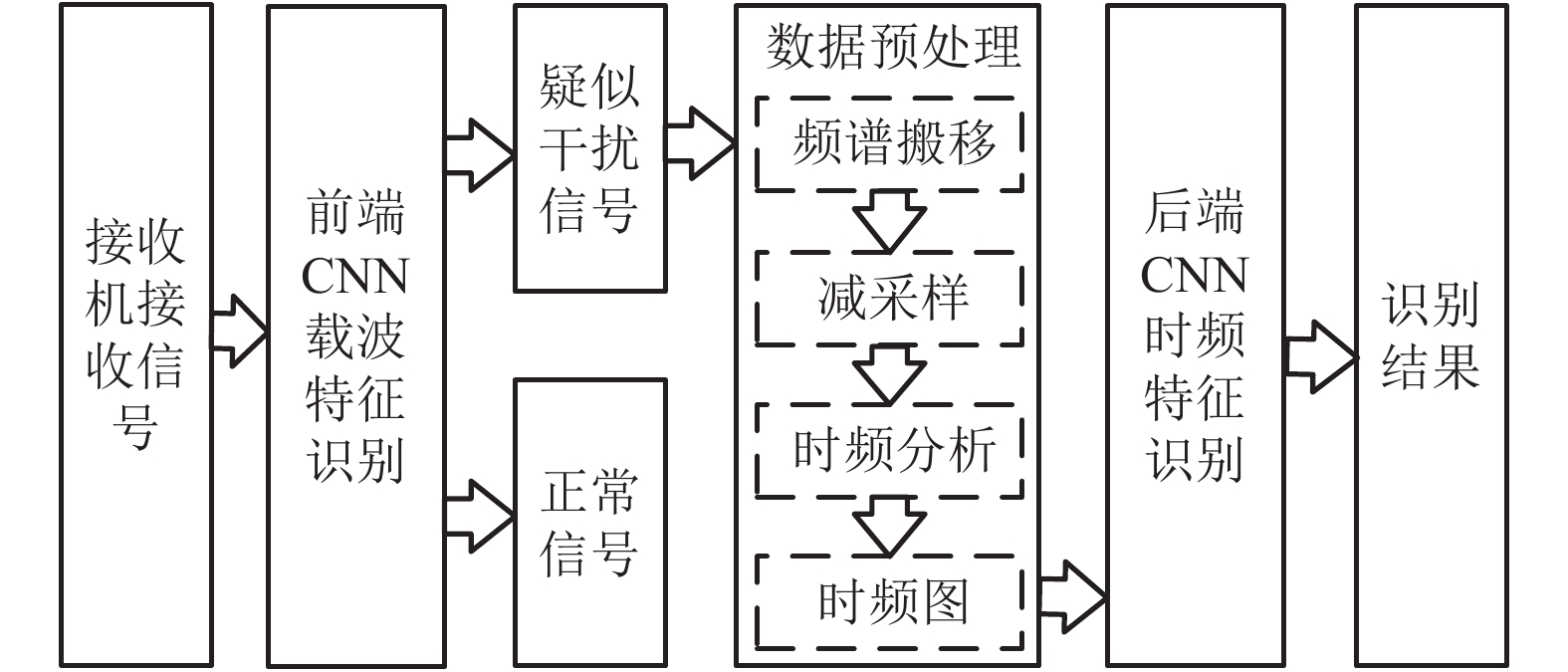
摘要: 针对信号调制识别对复杂通信环境缺乏适应性与精度不足的问题,提出一种基于深度学习的多特征复合神经网络框架. 该框架首先使用前端卷积神经网络检测信号载波特征,再对前端初筛选信号执行预处理将其转换为信号时频图,最后设计了后端轻量化卷积神经网络,检测信号时频特征. 基于TensorFlow平台的复合神经网络对机场真实信号检测精度达到99.23%,实验表明该方法可有效应用于实时机场信号检测.Abstract: In order to increase the generality and accuracy of radio modulation recognition in complex radio propagation environment, a multiple feature combined convolutional network system based on deep learning is proposed. Carrier features were detected with front convolutional network in the first stage. Then, the signal filtered by the front CNN was converted into spectrograms with the proposed pre-process method. Finally, the lightweight backend convolutional network was designed to extract the time-frequency features of spectrograms. The networks, which run on TensorFlow, achieved 99.23% accuracy with real airport communication signals. The experiment indicates that the proposed networks could be applied in real-time airport radio detection.
-
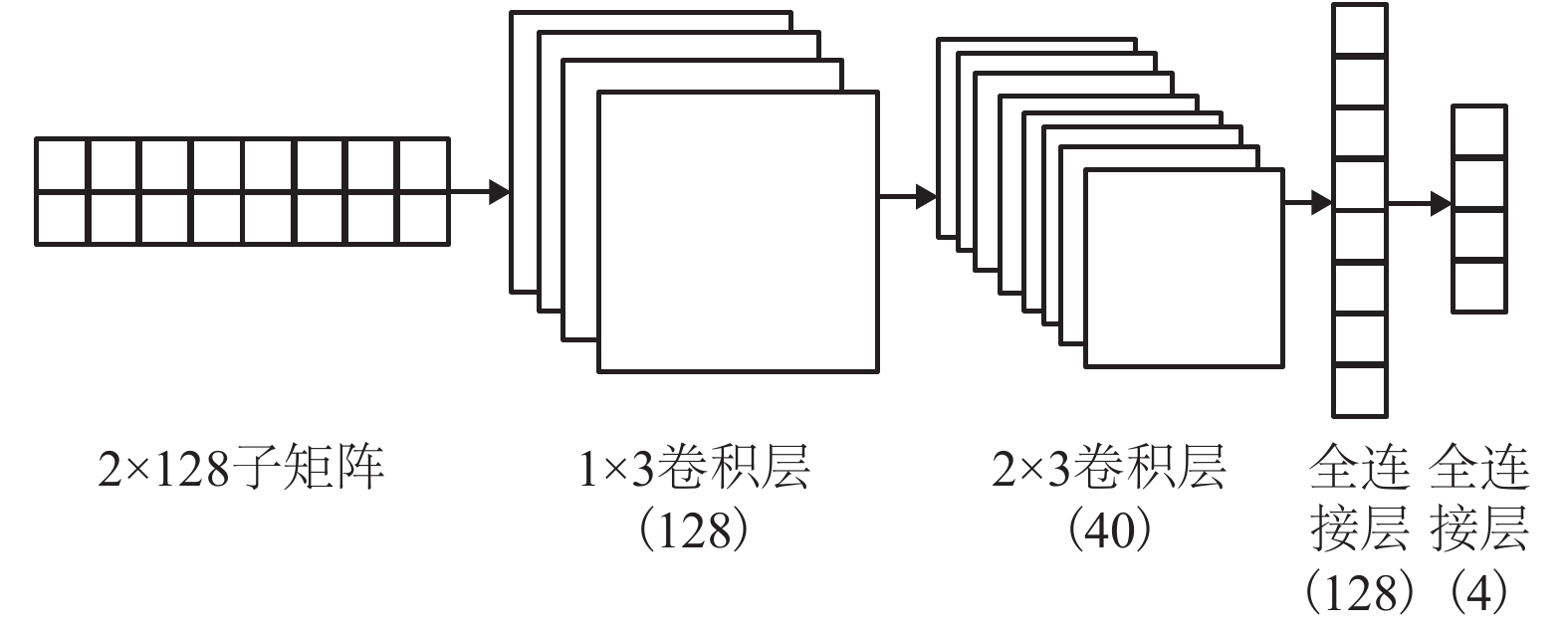
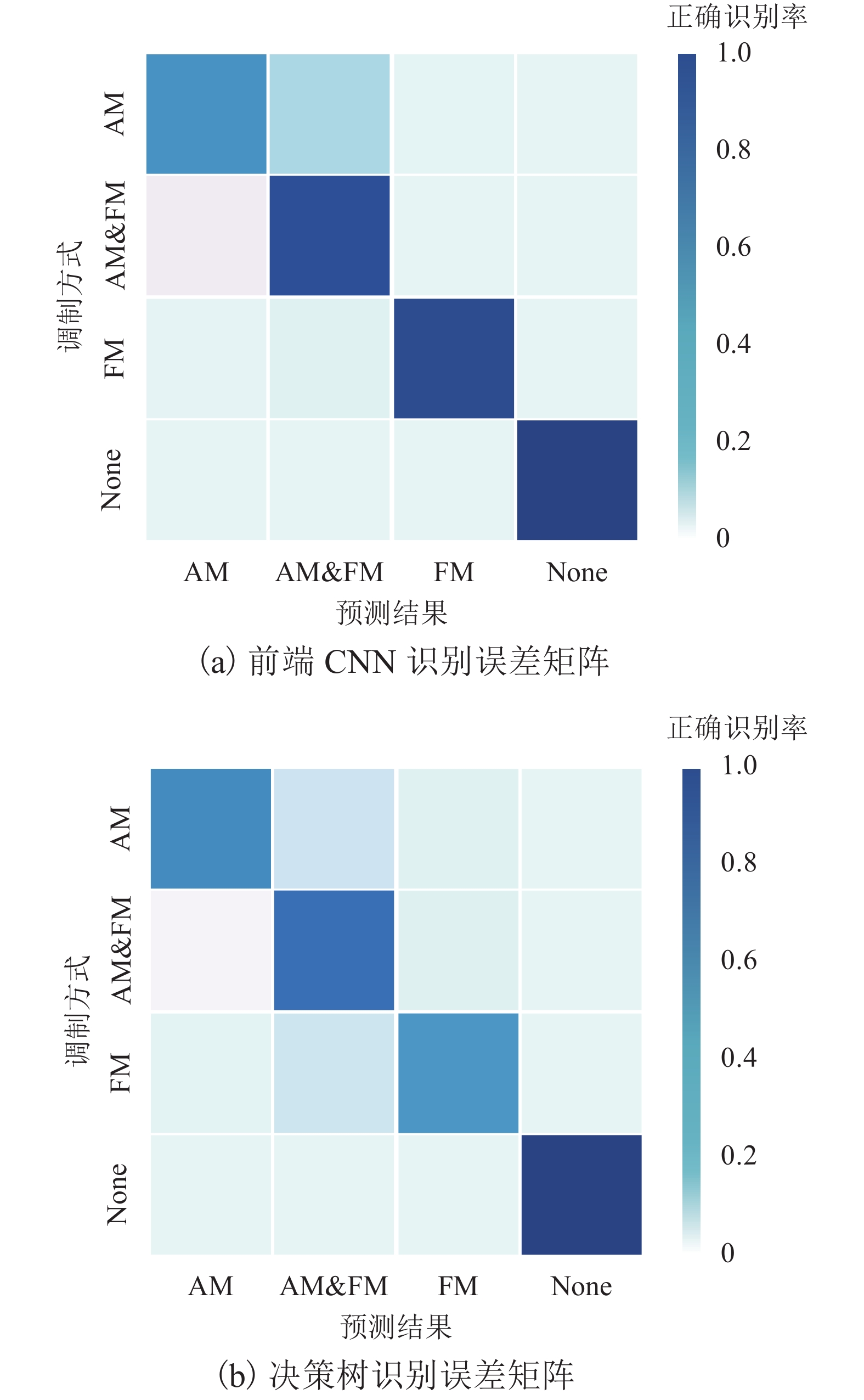
表 1 决策树与前端CNN对比结果
Table 1. Comparison between decision-tree and front CNN
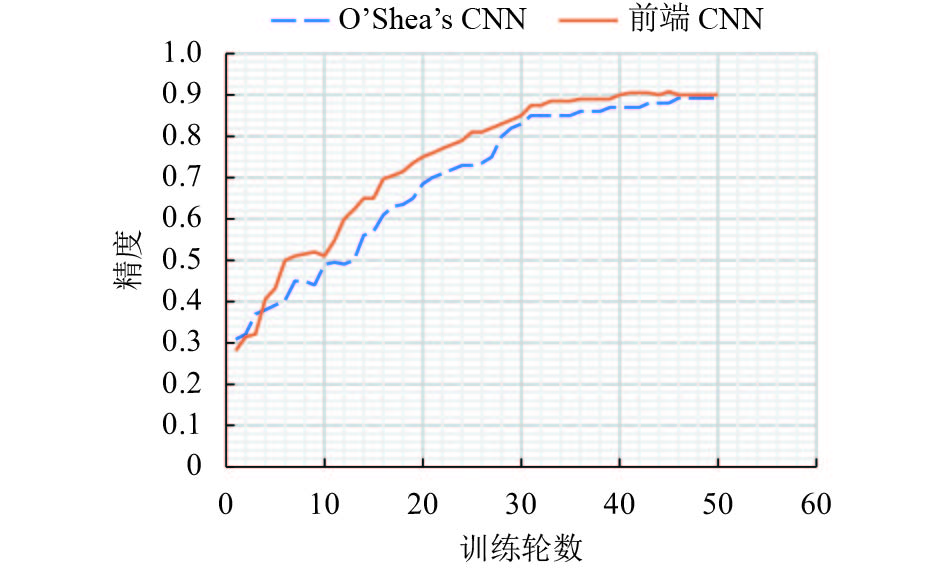
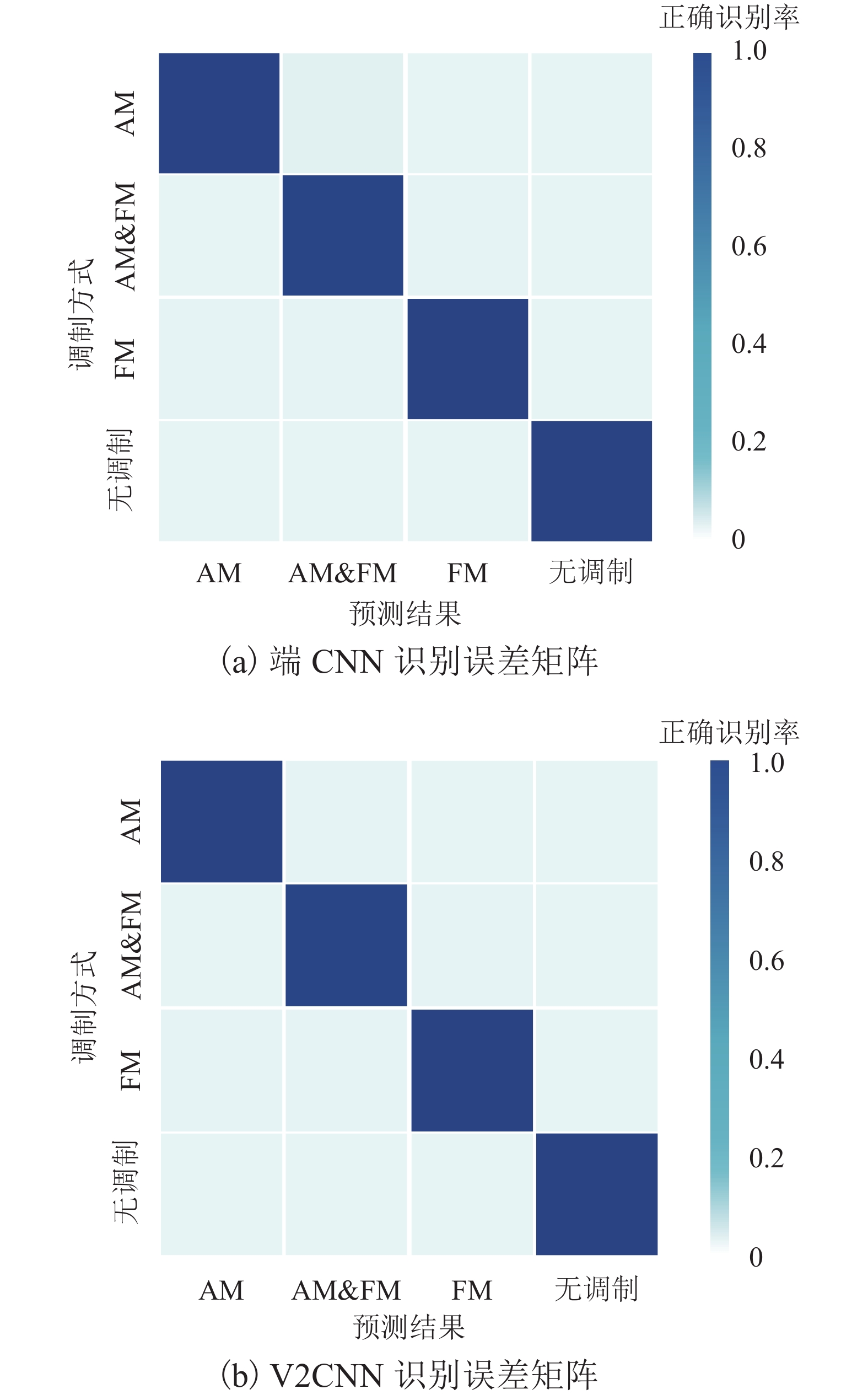
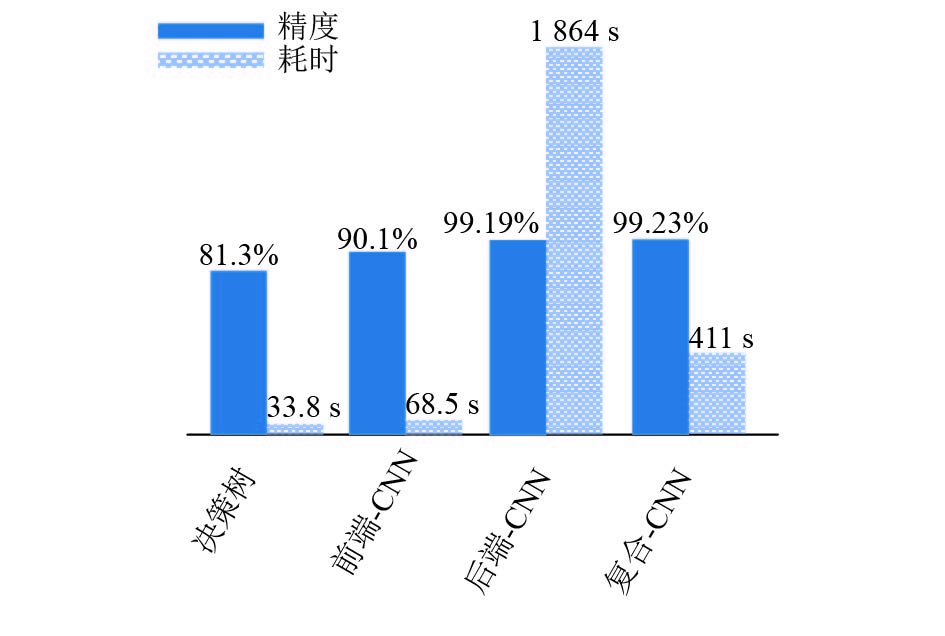
方法 识别准确率/% 耗时/s 前端 CNN 90.1 68.5 决策树 81.3 33.8 方法 识别准确率/% 耗时/s CNN参数量 前端 CNN 90.1 68.5 707 756 文献[8] CNN 89.3 112.7 2 828 628 表 3 后端CNN与V2 CNN对比结果
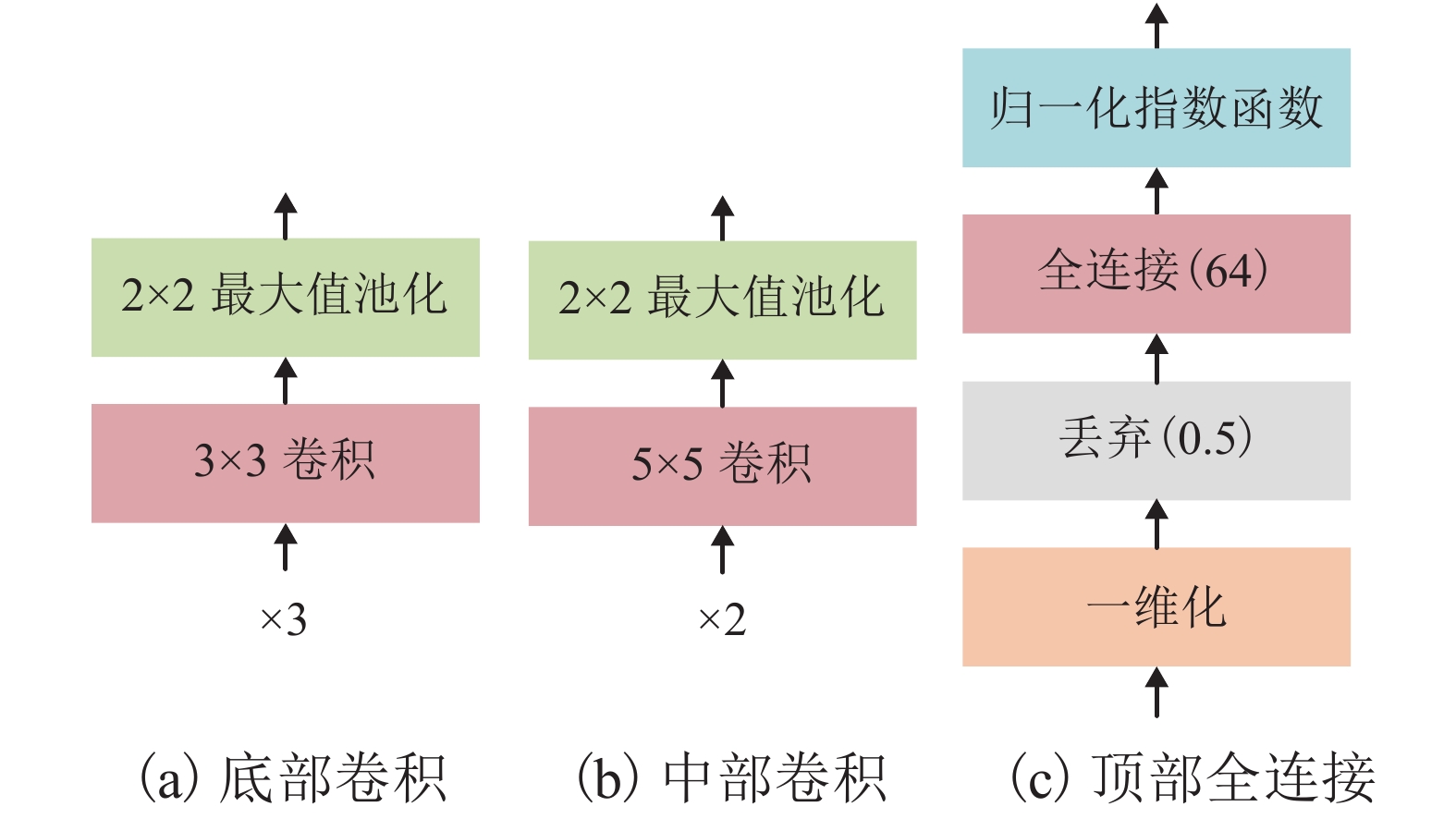
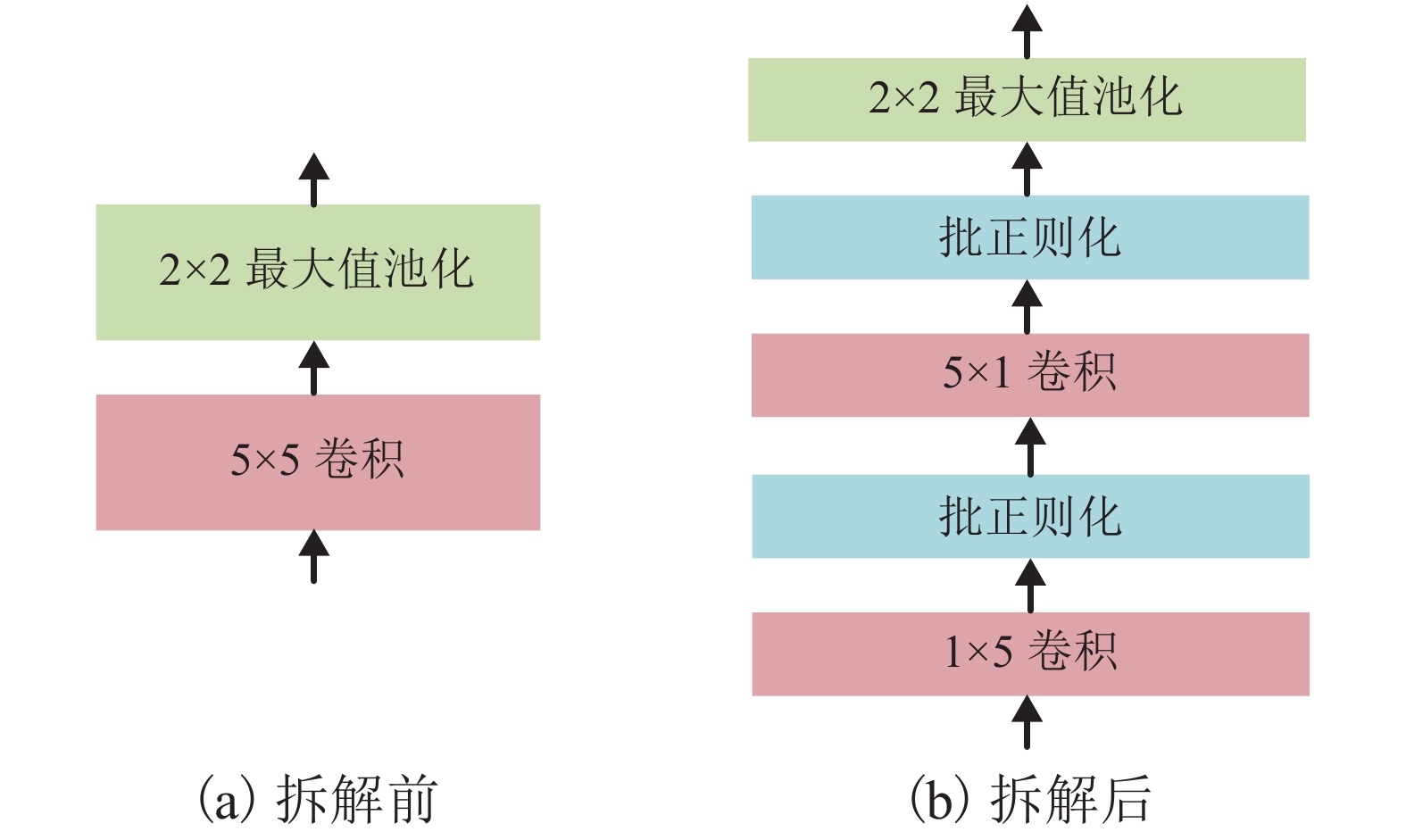
Table 3. Comparison of backend CNN and V2 CNN
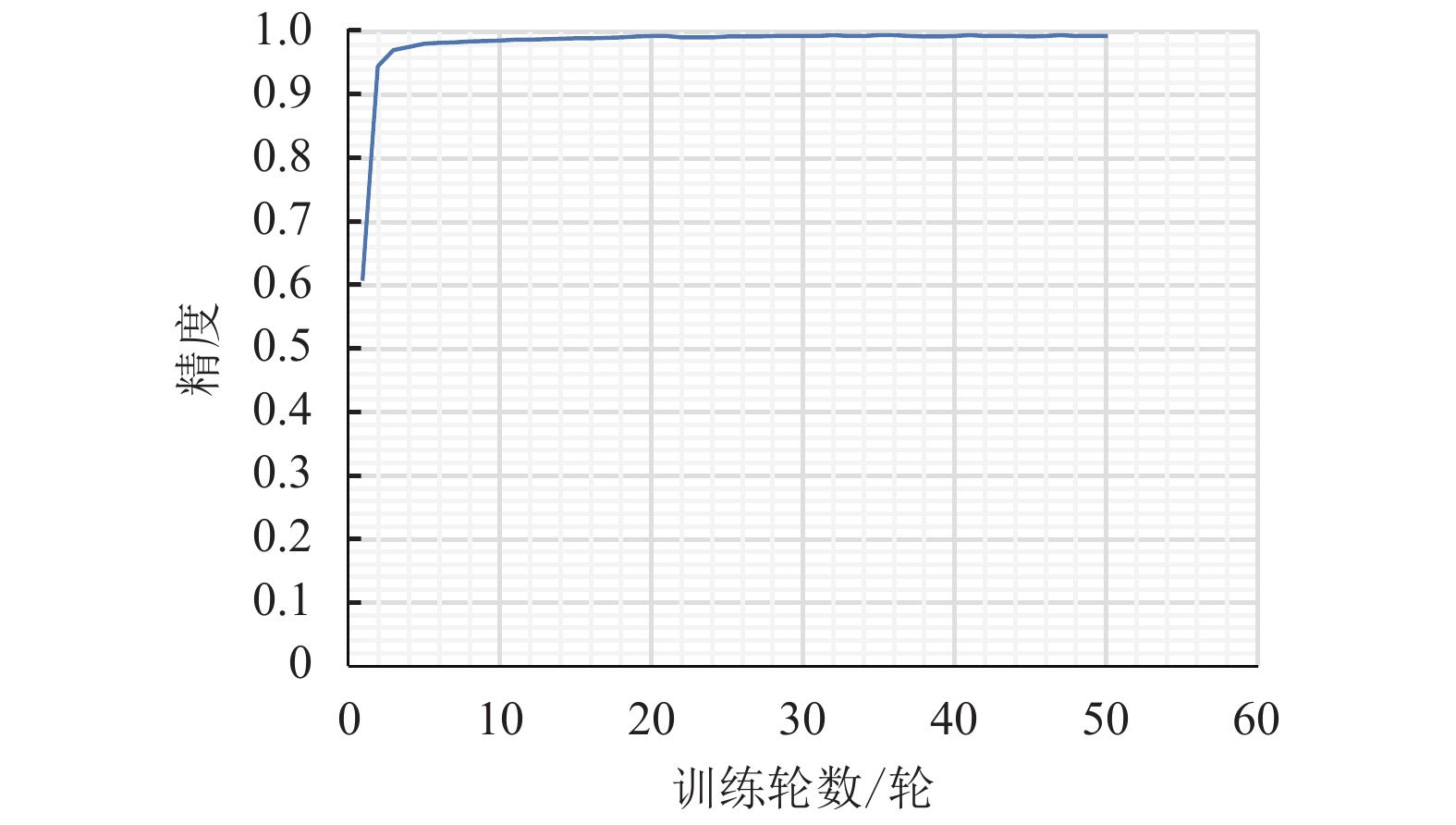
方法 识别准确率/% 耗时/s CNN参数量 后端 CNN 99.19 1 864.6 685 380 V2 CNN 99.96 2 343.3 58 837 142 表 4 基于复合CNN的实验
Table 4. Combined CNN experiment
方法 识别准确率/% 耗时/s 复合 CNN 99.23 411 -
温欣. 基于决策树的调制模式及GNU Radio模块实现[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010 LI Shiping, CHEN Fangchao, WANG Long. Modulation recognition algorithm of digital signal based on support vector machine[J]. Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), 2012, 229(5): 3326-3330. AHN W H, NAH S P, SEO B S. Automatic classification of digitally modulated signals based on k-nearest neighbor[J]. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, 2015, 329(1): 63-69. WONG M L D, TING S K, NANDI A K. Naïve Bayes classification of adaptive broadband wireless modulation types with higher order cumulants[C]//International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems. Gold Coast: [s.n.], 2009, 5(2): 1-5 XU J L, SU Wei, ZHOU Mengchu. Distributed automatic modulation classification with multiple Sensors[J]. IEEE Sensor Journal, 2010, 10(11): 1779-1785. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2010.2049487 HELMY M O, ZAKI F W. Identification of linear dimensional digital modulation schemes via clustering algorithms[C]//International Conference on Computer Engineering & Systems. Cairo: [s.n.], 2009, 5(1): 358-390 HARING L, CHEN Y, CZYLWIK A. Automatic modulation classification methods for wireless OFDM system in TDD mode[J]. IEEE Transaction on Communications, 2010, 58(9): 2480-2485. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2010.080310.090228 O’SHEA T J, CORGAN J, CLANCY T C. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks[C]//International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks. Aberdeen: [s.n.], 2016, 6(1): 213-226 O’SHEA T J, WEST N. Radio machine learning dataset generation with gnu radio[C]//Proceedings of the GNU Radio Conference. Boulder: [s.n.], 2016, 1(1): 69-74 WEST N E, O’SHEA T J. Deep architectures for modulation recognition[C]//IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks. Baltimore: [s.n.], 2017: 1-6 LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convoluiotnal networks for large-scale image recognititon[DB/OL]. [2018-02-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556 HUBEL D H, WIESEL T N. Receptive fields,binocular inter-action and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex[J]. The Journal of Physiology, 1962, 160(1): 106-154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837 FUKUSHIMA, K NEOCOGNITRON. A self organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition un-affected by shift in position[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1980, 36(4): 193-202. doi: 10.1007/BF00344251 IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille: [s.n.], 2015, 33(1): 448-456 SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016, 26(1): 2818-2826 HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016, 26(1): 770-778 LIN M, CHEN Q, YAN S. Network in network[DB/OL]. [2018-02-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.4400 KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe: [s.n.], 2012, 60(2): 1097-1105 SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]// Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco: [s.n.], 2017: 936-940 -




 下载:
下载: