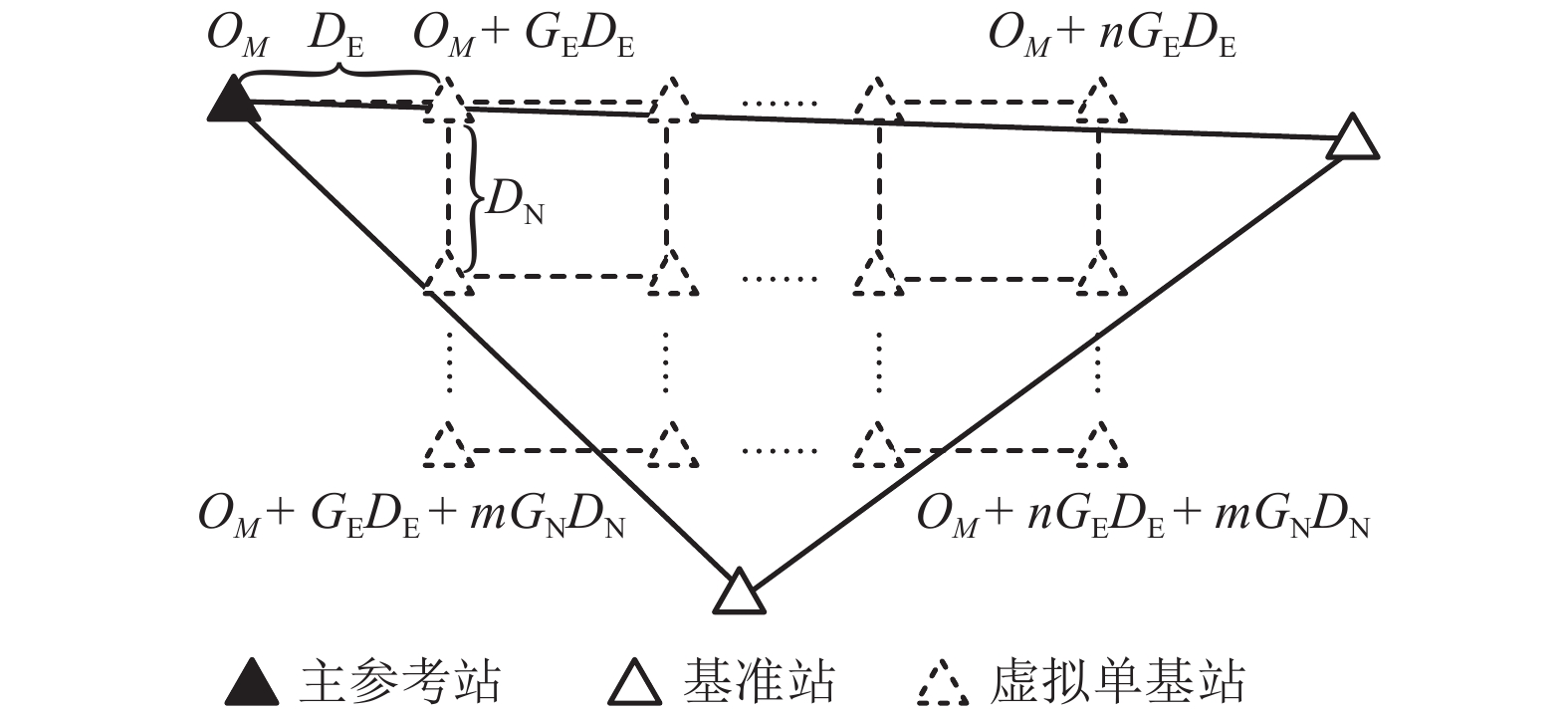
Technology for Virtual Reference Station Service with Gradient Information of Spatially Correlated Errors
-
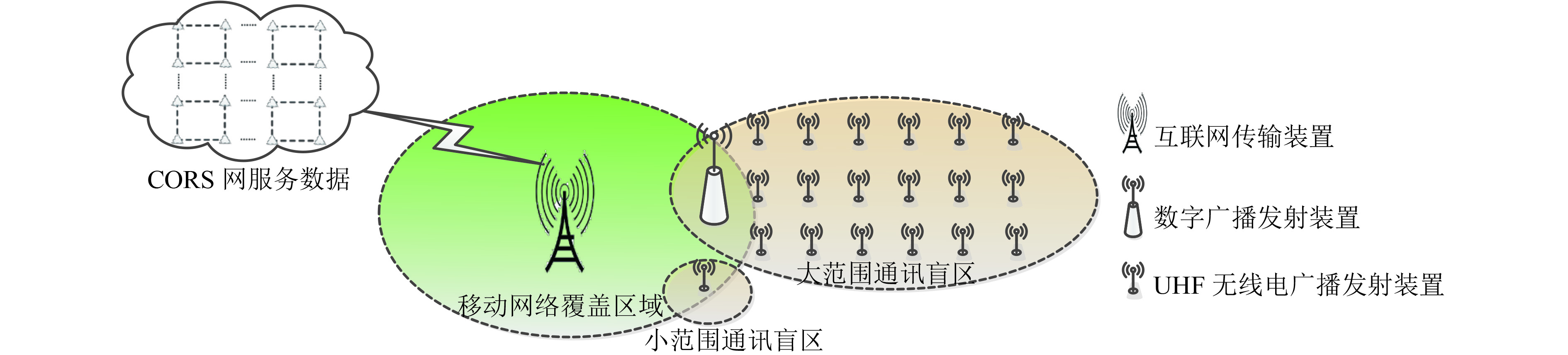
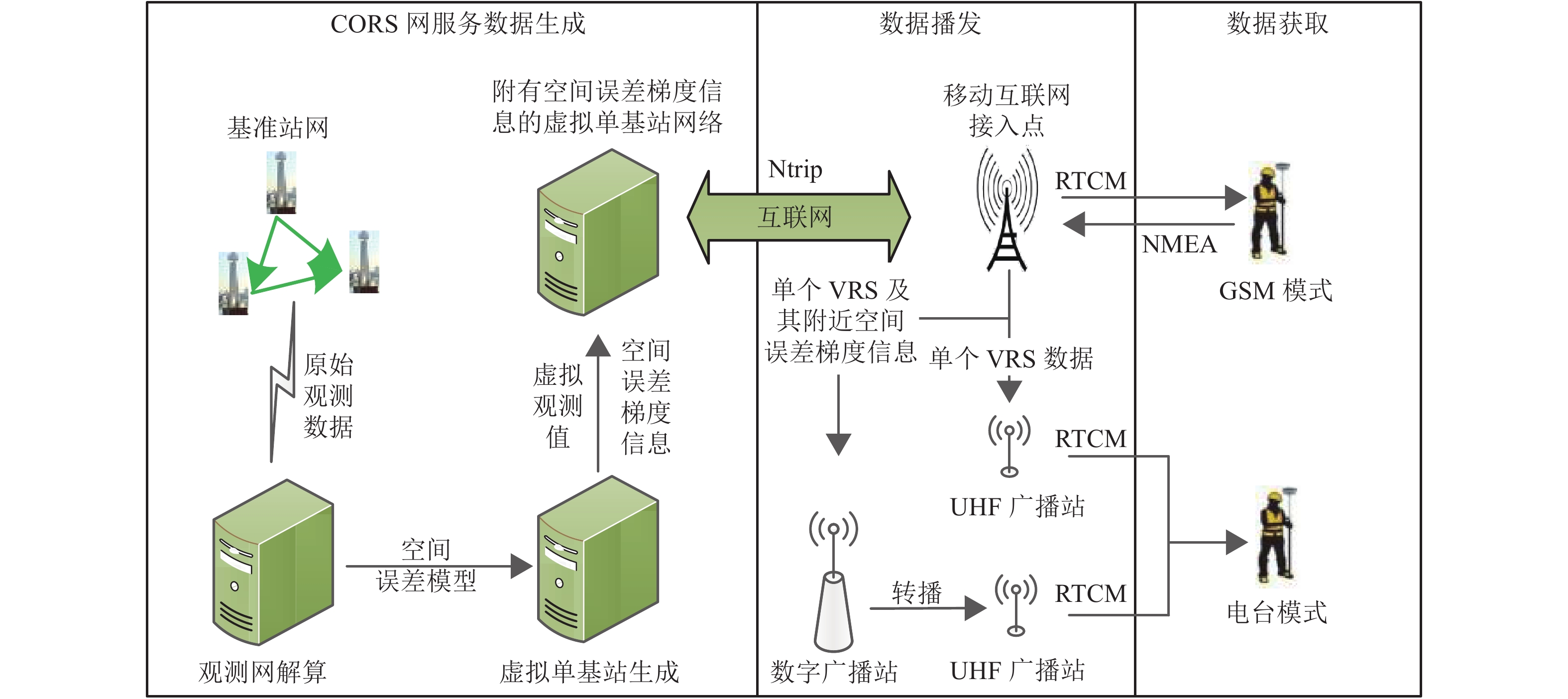
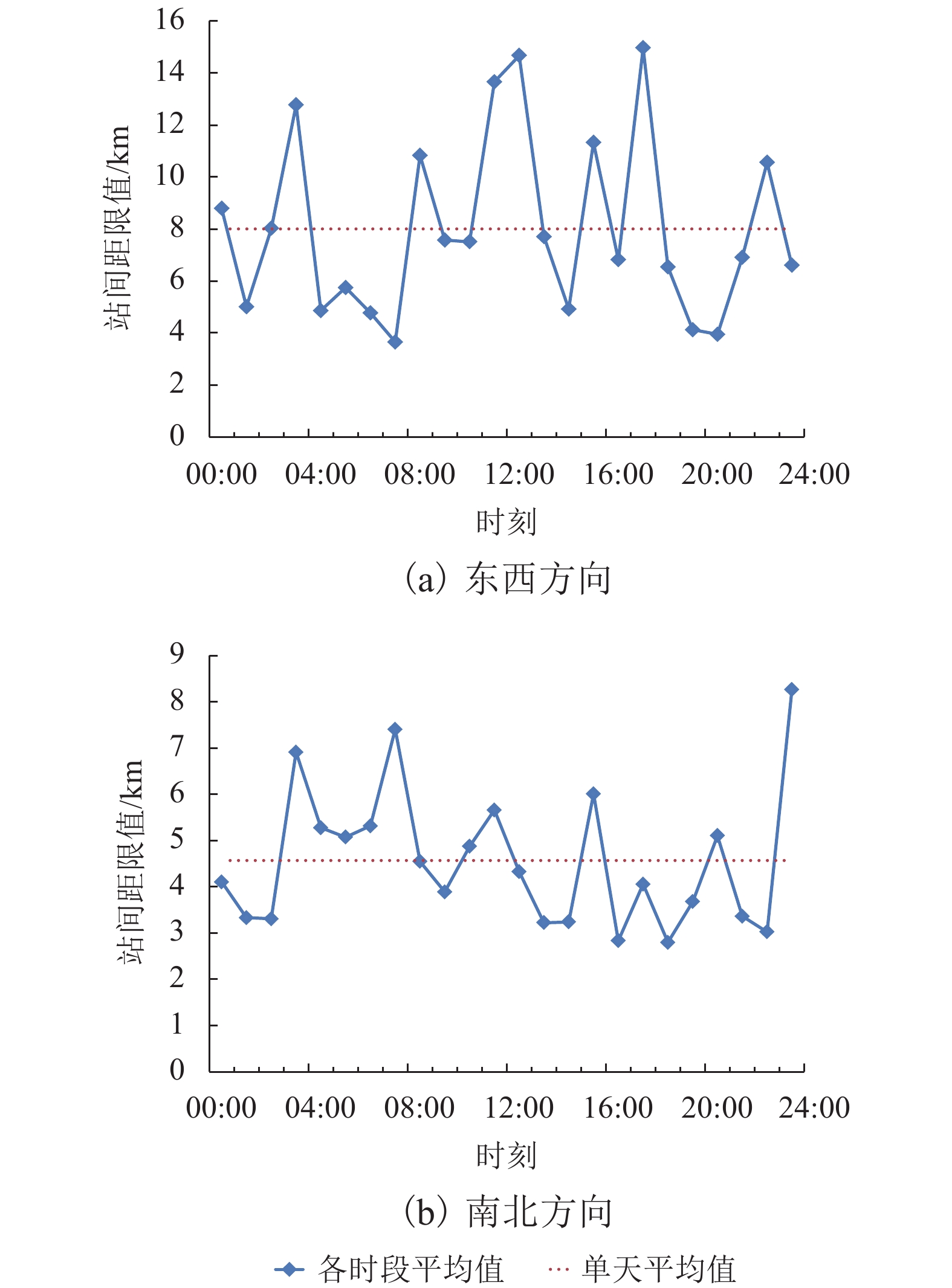
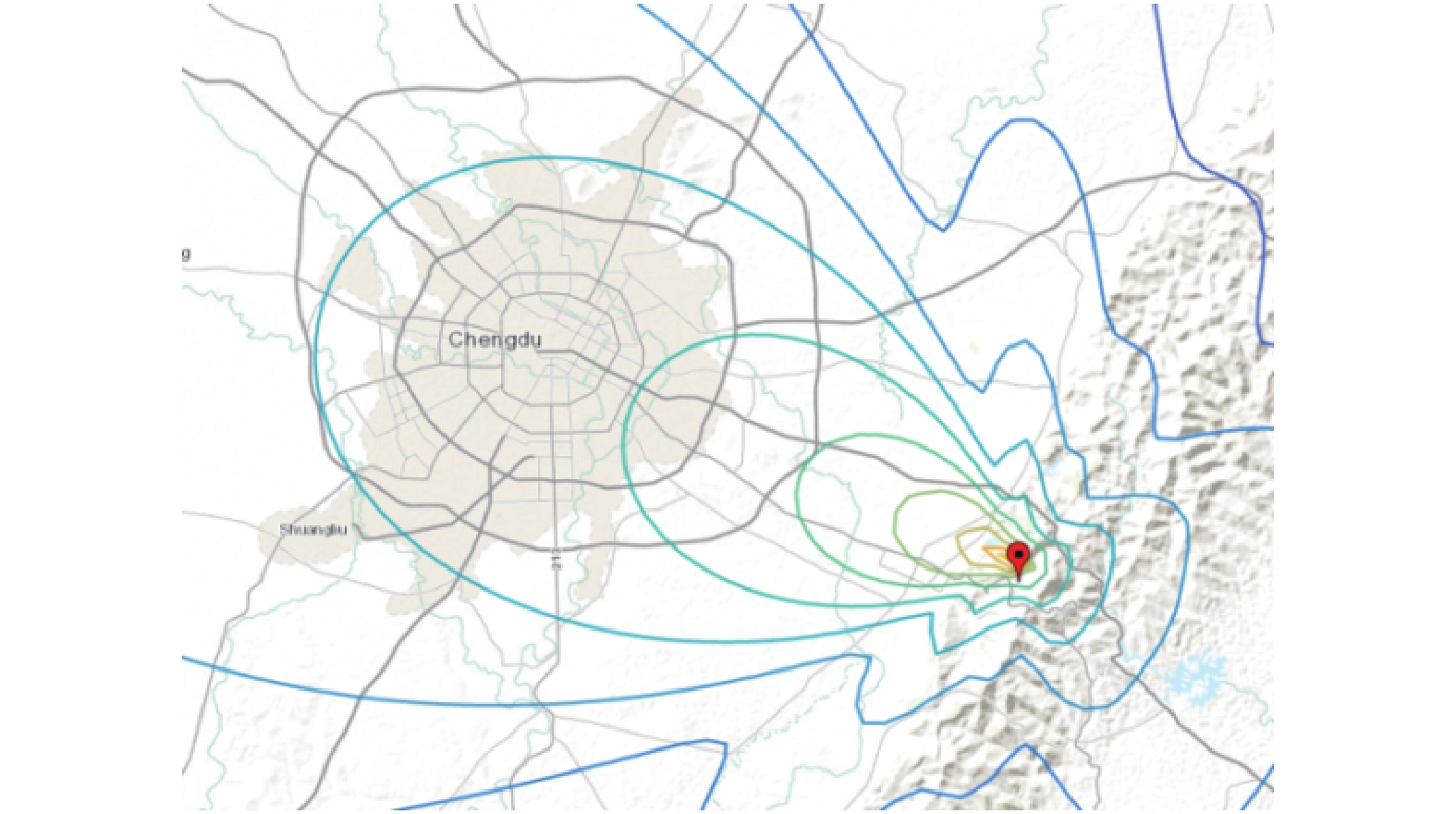
摘要: 为了克服传统虚拟基准站服务技术在长距离定位服务和全域范围服务中存在频繁换站,以及严重依赖互联网通讯的不足,利用现有RTK (real-time kinematic)设备兼容互联网模式和电台模式的基本条件,通过空间误差模型分析,将空间误差梯度信息附加在差分服务数据中,并结合互联网、共生调频数字广播和特高频无线电广播等技术手段,实现了面向全域范围的差分数据播发;同时,给出了传统虚拟基准站有效服务距离的计算模型. 实测结果显示:设定空间误差修正质量对流动站坐标各方向精度影响小于1 cm2的情况下,中纬度平原地区虚拟单基站网络站间距或者传统虚拟基准站服务的换站距离可以达到5 km;利用单个功率低于2 W的信号终端实现了27 km的远距离数据播发,突破了传统虚拟基准站服务需要数据交互且单个虚拟基准站有效服务距离只有几公里的限制,可满足包含数十公里通讯盲区的全域高精度定位应用需求.Abstract: Traditional virtual reference station (VRS) service usually needs to change VRS frequently and depends on internet communication heavily in long-distance positioning or positioning throughout the area. In order to overcome these deficiencies, a technology was proposed to realize the differential data broadcast throughout the area. Based on the analysis of spatial error model, a computing model of VRS effective service distance was obtained, and the gradient information of spatially correlated errors was appended to differential data. Considering that conventional real-time kinematic (RTK) equipment is compatible with internet and radio, Internet, symbiotic radio and ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio were also combined to broadcast the data. The experimental results show that the virtual single base-station (VSBS) spacing or the distance of VRS changing can reach 5 km in mid-latitude plain areas while the impact of spatially correlated errors is set as 1 cm2 in each coordinate component. A signal terminal with less than 2 W transmit power can broadcast the data to a distance of 27 km, which breaks the limits of data exchange needed in VRS service and several kilometers’ distance coverage of VSBS, and meets the application demands of high precision positioning in a distance of tens of kilometers with no internet access.
-
表 1 数字广播有效距离模型值与实测值
Table 1. Model values and experimental values of symbiotic radio’s effective distance
气象条件 发射功率/W 模型值/km 实测值/km 中雨 1.0 20 13 小雨 1.0 20 16 晴天 1.7 25 27 表 2 各测试点的初始化时间和定位精度统计
Table 2. Statistics of initialization time and positioning accuracies of inspection points
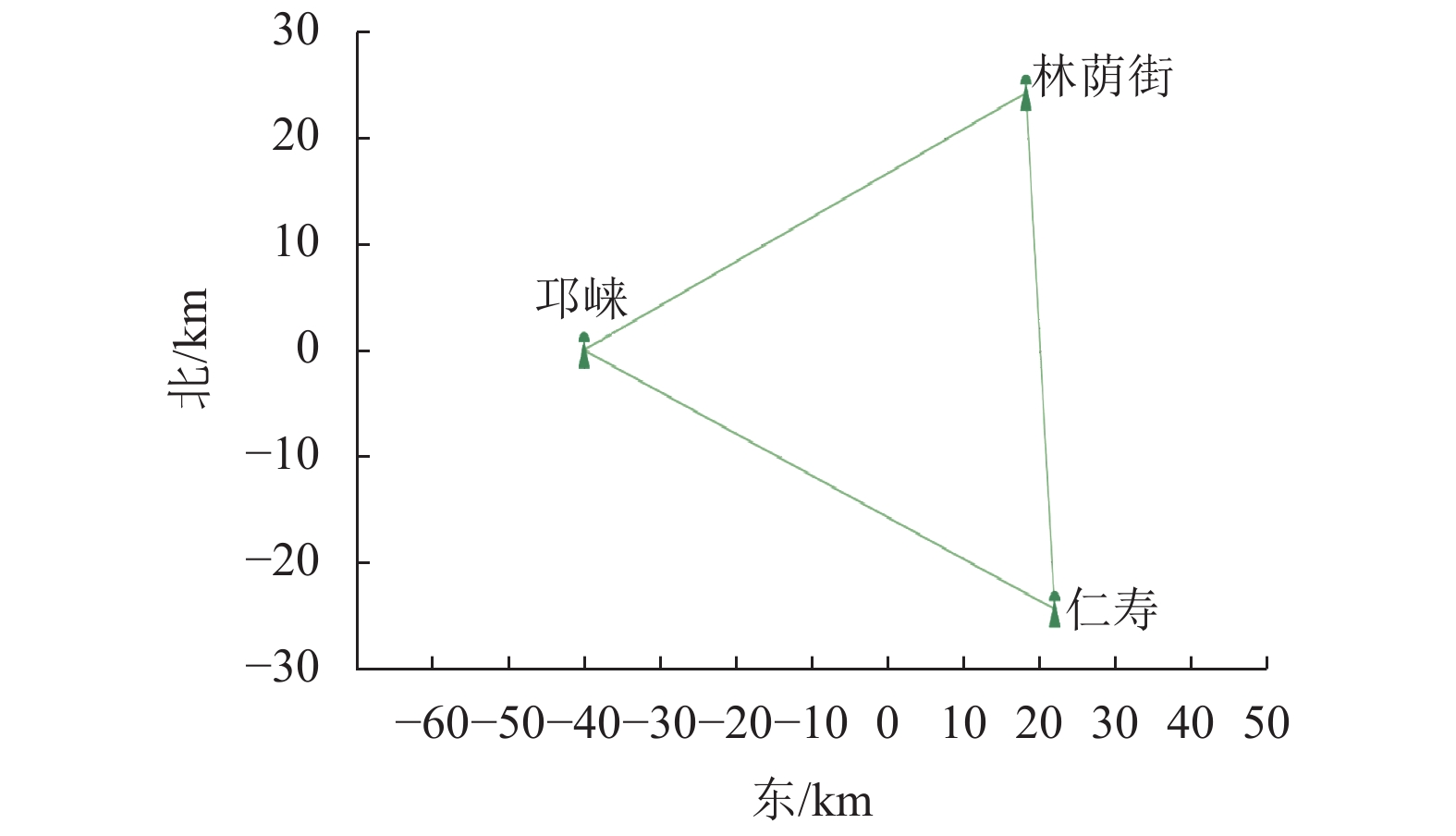
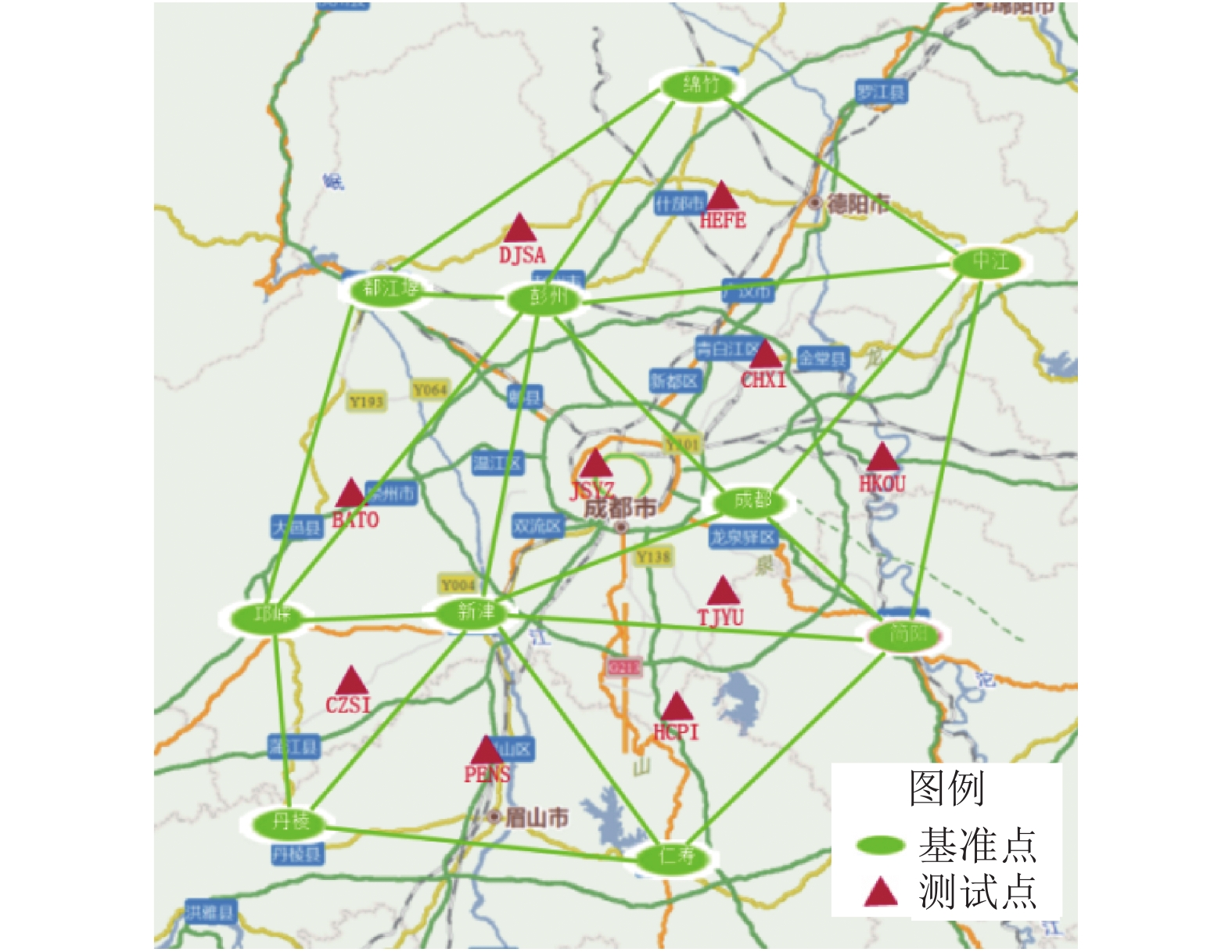
点名 初始化时间/s 内符合精度/cm 外符合精度/cm 平面 高程 平面 高程 BATO 6.6 0.94 1.28 3.5 4.49 CHXI 9.5 0.79 3.34 3.01 3.41 CZSI 7.2 0.44 1.13 2.13 1.93 DJSA 11.2 0.52 1.15 0.92 2.52 HCPI 9.2 2.11 3.17 3.82 6.75 HEFE 9.9 0.76 1.07 3.07 2.68 HKOU 9.5 1.21 2.32 3.68 6.66 JSYZ 9.5 0.75 1.28 1.88 1.28 PENS 11.5 0.64 1.23 2.24 4.61 TJYU 8.3 0.68 0.94 1.90 5.50 均值 9.3 0.98 1.70 2.62 3.99 -
国家测绘地理信息局. 测绘地理信息科技发展" 十三五”规划[EB/OL].(2016-10-18)[2018-3-1]. http//www.sbsm.gov.cn/zwgk/zcfgjjd/gfxwj/201610/t20161025_347926.shtml. WUBBENA G, BAGGE A, SCHMITZ M. RTK networks based on Geo++® GNSMART-concepts, implementation, results[C]//Proceedings of ION GPS 2001. Salt Lake City: ION, 2001: 368-378. EULER H-J, KEENAN R, ZEBHAUSER B, et al. Study of a simplified approach in utilizing information from permanent reference station arrays[C]//Proceedings of ION GPS 2001. Salt Lake City: ION, 2001: 11-14. EULER H J, ZEBHAUSER B E. The use of standardized network RTK messages in rover applications for surveying[C]//Proceedings of the 16th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. San Diego: ION, 2003: 22-24. WANNINGER L. The performance of virtual reference stations in active geodetic GPS-networks under solar maximum conditions[C]//Proceedings of ION GPS 1999. Budapest: ION, 1999: 1419-1427. RTCM special committee No.104. RTCM standard 10403.2 for differential GNSS services, version 3[S]. Arlington: Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services, 2013. 周乐韬. 连续运行参考站网络实时动态定位理论、算法和系统实现[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2007. 李成钢. 网络GPS/VRS系统高精度差分改正信息生成与发布研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2007. DAI Liwen, HAN Shaowei, WANG Jinling, et al. A study on GPS/GLONASS multiple reference station techniques for precise real-time carrier phase-based positioning[C]//Proceedings of ION GPS 2001. Salt Lake Lake: ION, 2001: 392-403. 吴北平. GPS网络RTK定位原理与数学模型研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学, 2003. 黄丁发,李成钢,吴耀强,等. GPS/VRS实时网络改正数生成算法研究[J]. 测绘学报,2007,36(3): 256-261. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.2007.03.003HUANG Dingfa, LI Chenggang, WU Yaoqiang, et al. Study of the real-time network correction generation approach for GPS/VRS technique[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2007, 36(3): 256-261. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.2007.03.003 黄丁发,周乐韬,李成钢,等. 增强虚拟参考站网络系统软件(VENUS)研制[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2008,33(2): 172-176.HUANG Dingfa, ZHOU Letao, LI Chengang, et al. Development of enhanced VRS network utility system[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2008, 33(2): 172-176. 张熙,黄丁发,廖华,等. 一种新的GNSS相对定位解算模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(3): 485-489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.03.016ZHANG Xi, HUANG Dingfa, LIAO Hua, et al. New mathematical model for GNSS relative positioning resolving[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(3): 485-489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.03.016 HAN Shaowei. Quality-control issues relating to instantaneous ambiguity resolution for real-time GPS kinematic positioning[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 1997, 71(6): 351-361. doi: 10.1007/s001900050103 张熙. 多星座CORS混合观测网络实时位置服务关键技术研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. 张熙,黄丁发,廖华,等. CORS网型结构对网络RTK服务性能的影响研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2015,40(7): 887-893.ZHANG Xi, HUANG Dingfa, LIAO Hua, et al. Impacts of CORS network structure for real-time differential positioning service performance[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2015, 40(7): 887-893. 张光华,张全德,门爱东. 基于共生调频数据广播的北斗地基增强系统设计和性能测试[J]. 测绘通报,2018(9): 74-78. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2018.0283ZHANG Guanghua, ZHANG Quande, MEN Aidong. Design and performance test of BDS ground-based augmentation system based on symbiotic FM data broad broadcasting[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2018(9): 74-78. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2018.0283 王海南. 常用无线电传播模型的对比分析及应用[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2011. -




 下载:
下载: