Fatigue Evaluation and Crack Propagation Characteristics of Rib-to-Deck Welded Joints in Steel Bridge Decks
-
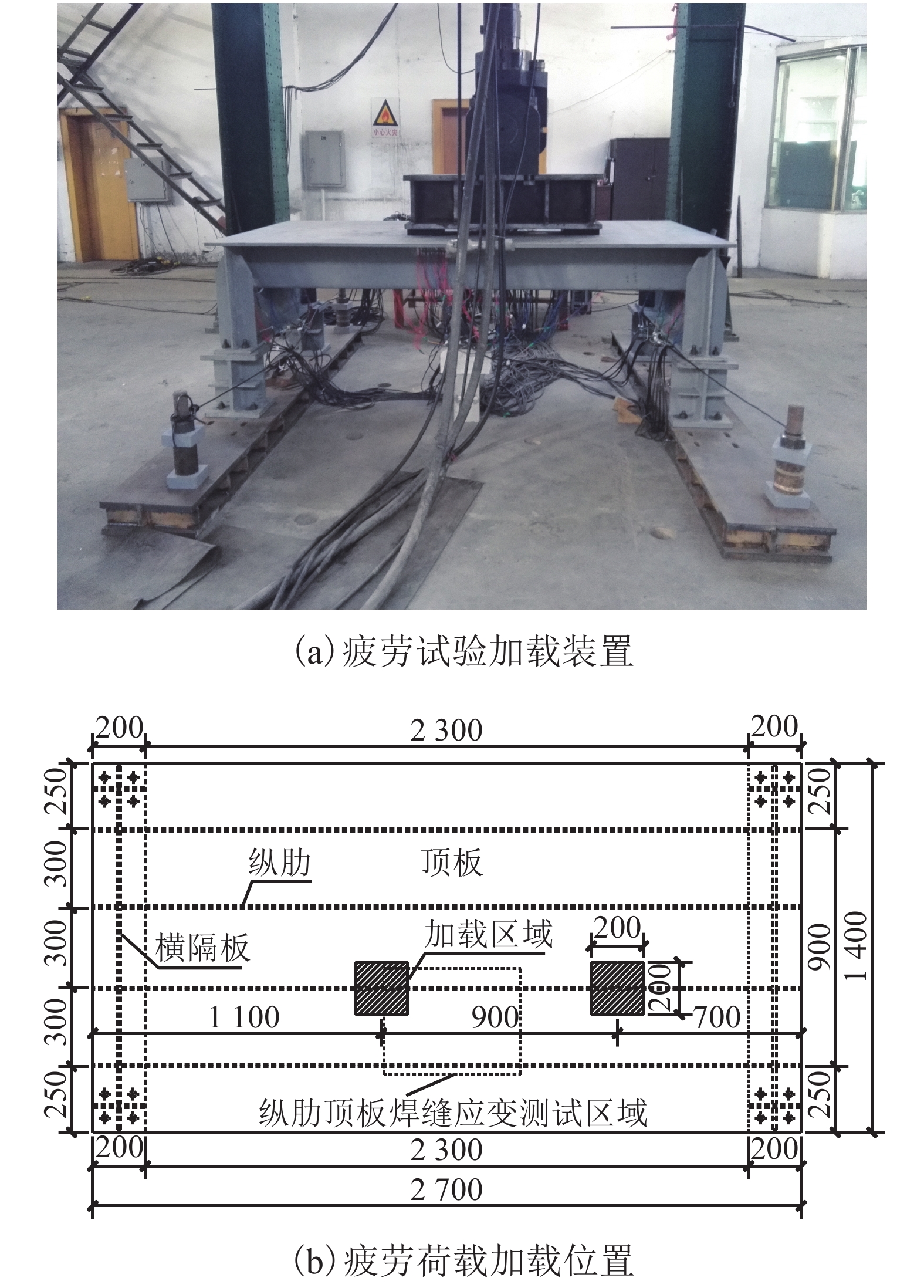
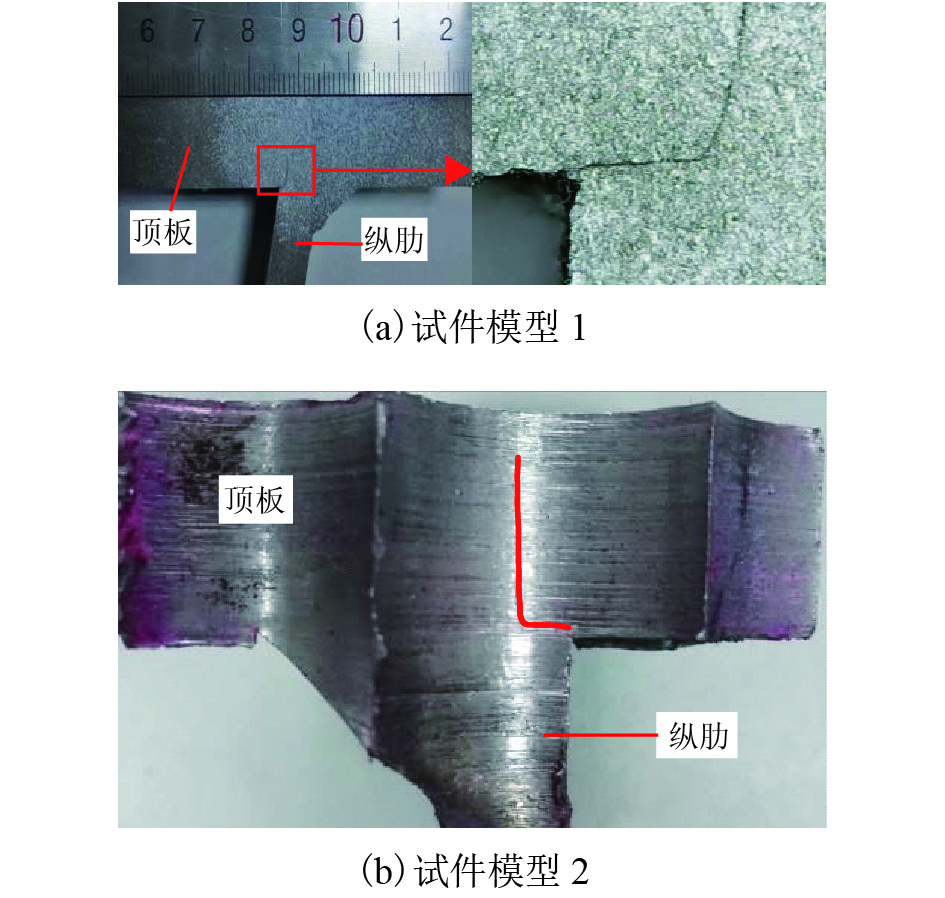
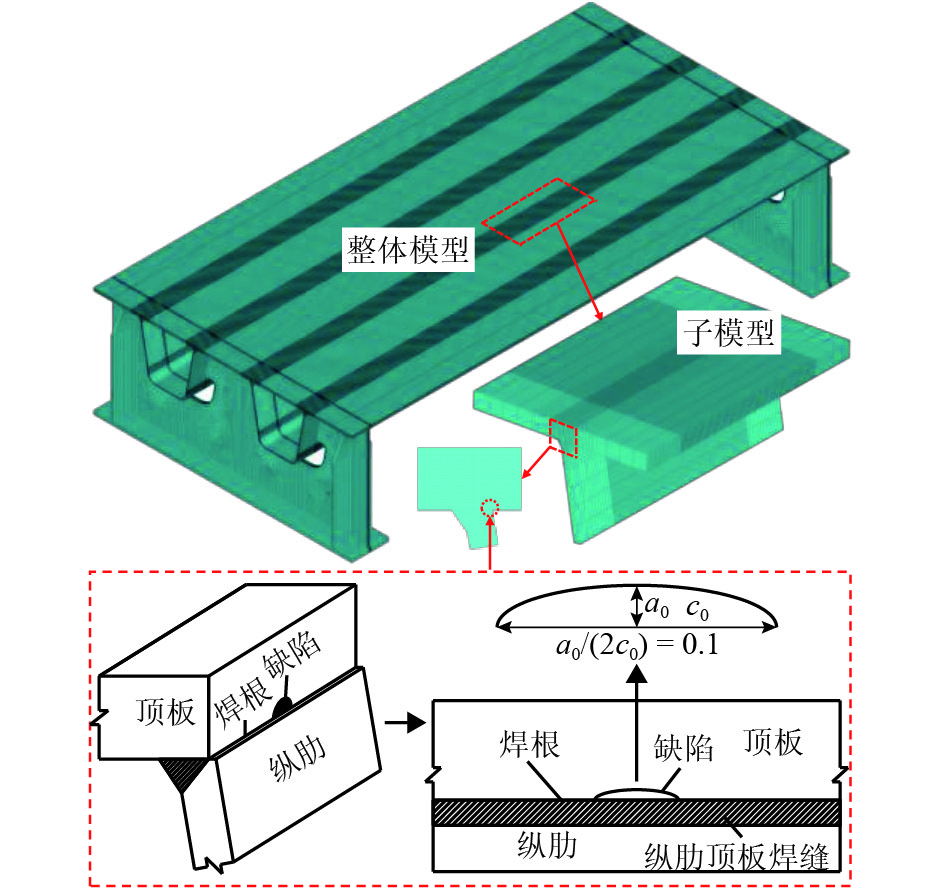
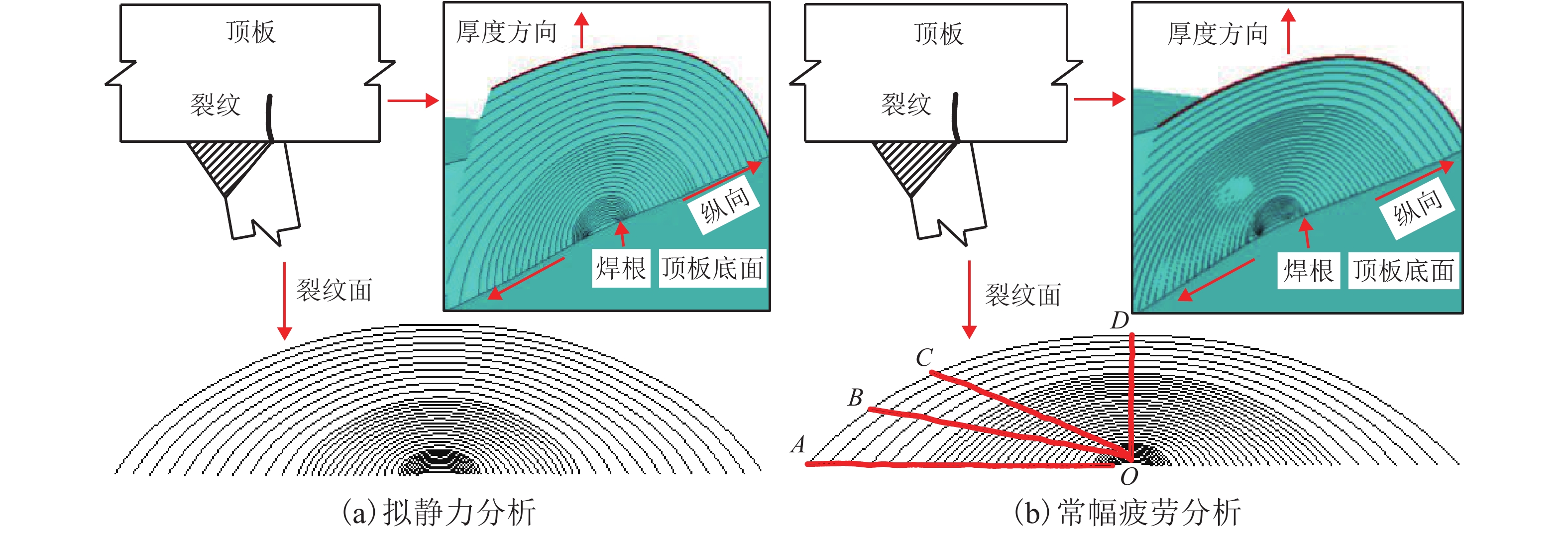
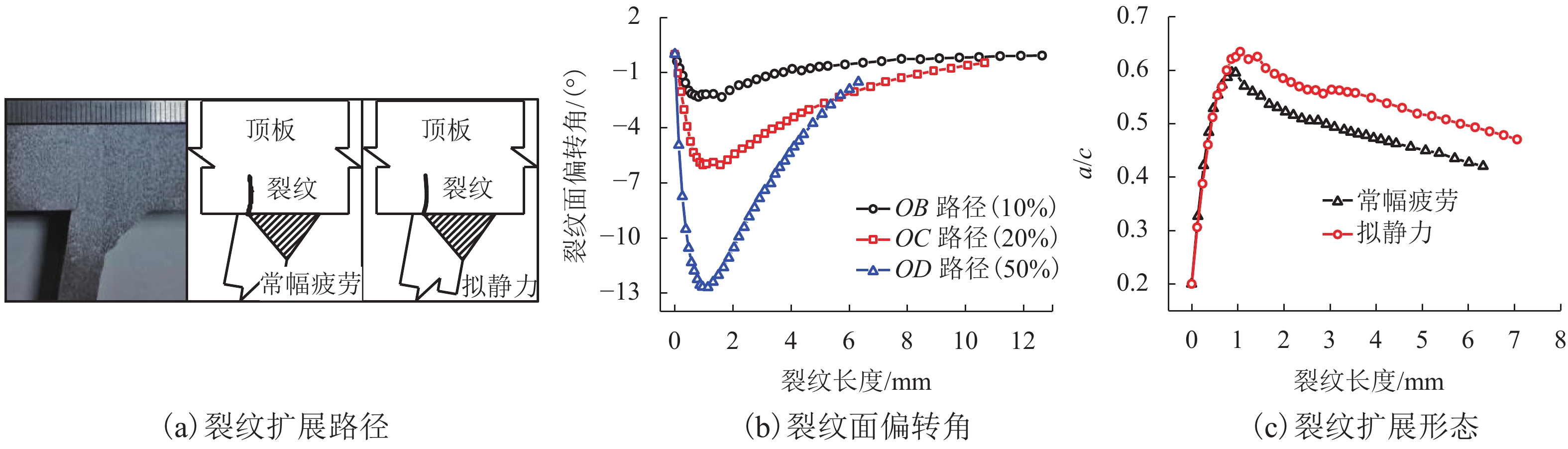
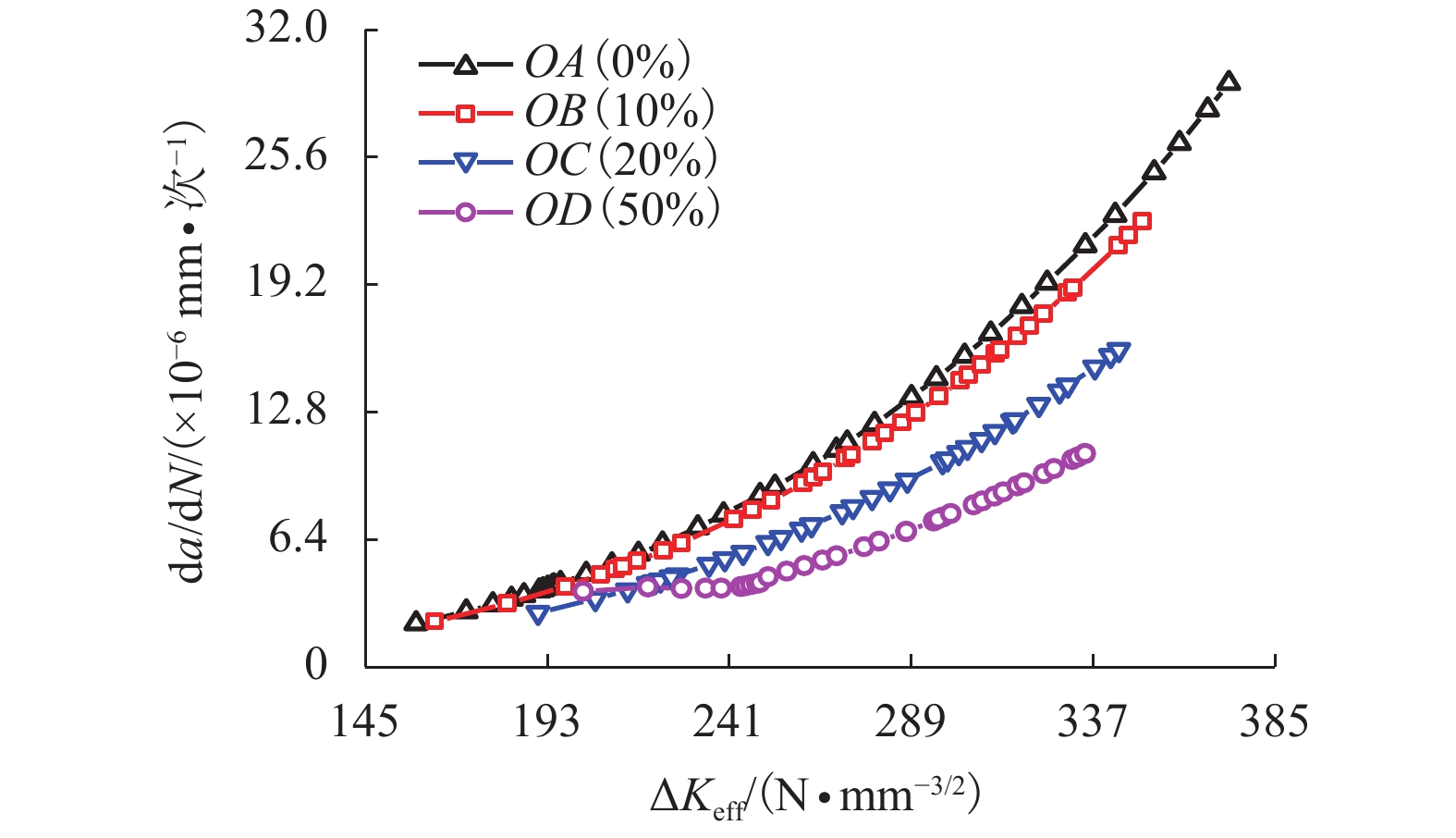
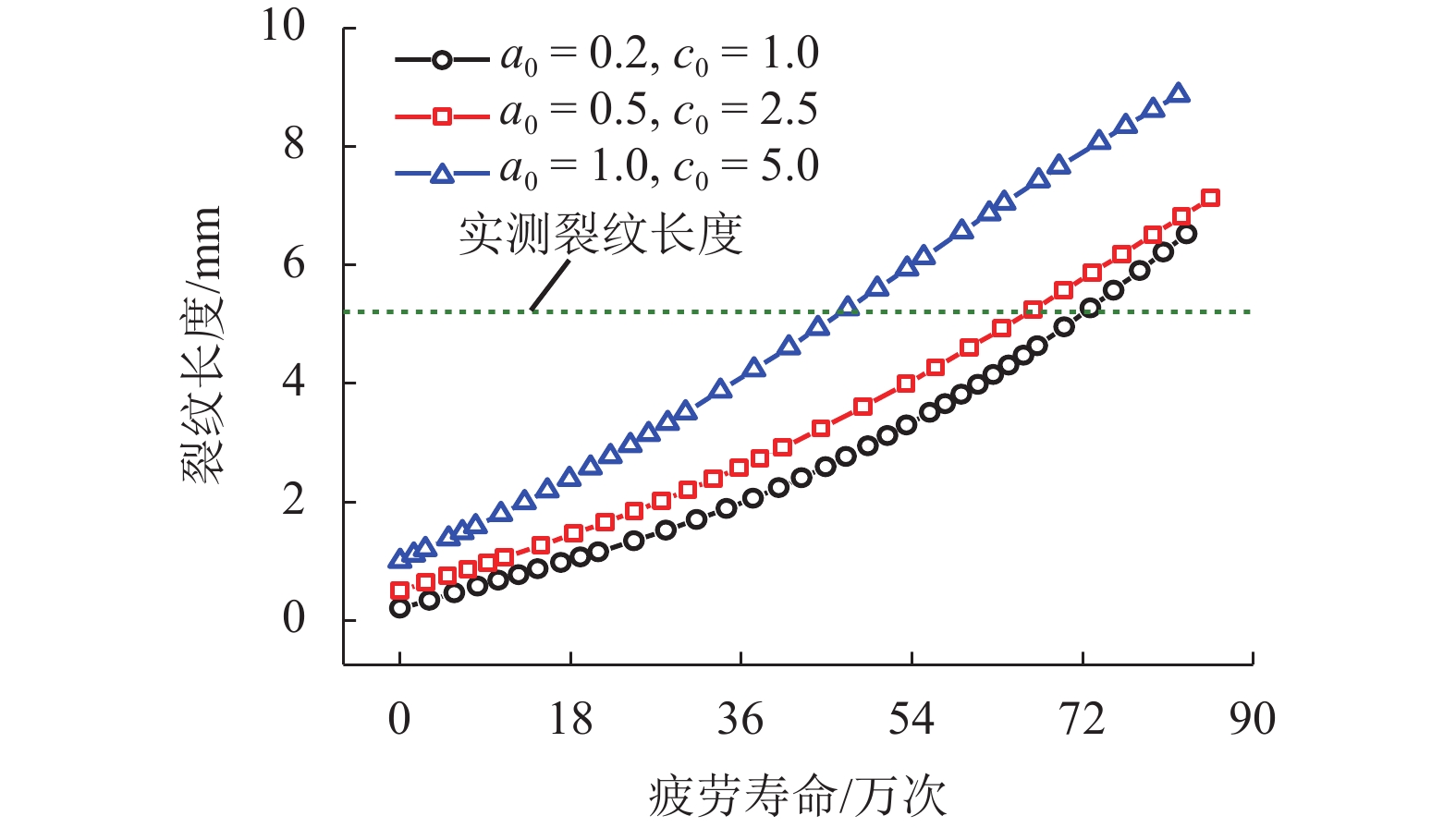
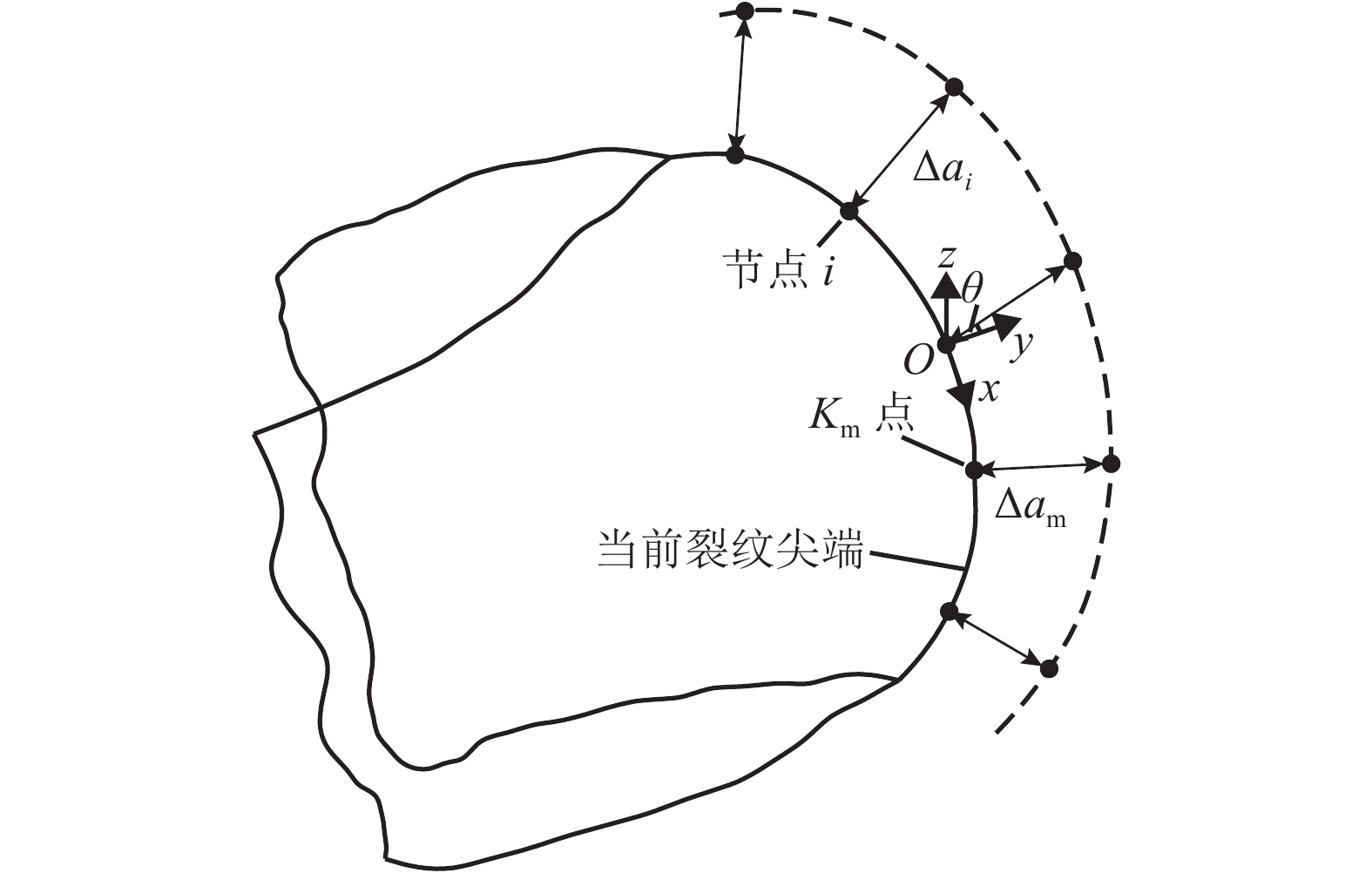
摘要: 为研究正交异性钢桥面板纵肋与顶板连接焊缝的裂纹扩展特性并建立相应的疲劳寿命评估方法,考虑裂纹扩展模拟方法以及材料特性等因素对于裂纹扩展过程与疲劳寿命预测的影响,以某长江公路大桥重载交通钢桥面板为研究对象,进行了疲劳模型试验和理论研究. 综合运用疲劳试验与断裂力学数值模拟研究起始于焊根位置裂纹的疲劳寿命评估问题,探明了疲劳裂纹的扩展特性. 研究结果表明:基于常幅疲劳加载的寿命预测结果与试验实测值间的相对误差小于10%,且预测结果偏于安全;裂纹扩展路径及裂纹面空间形态等扩展特性与疲劳试验相吻合;裂纹扩展模拟方法、扩展角计算准则、材料特性和初始裂纹深度是疲劳寿命预测的关键影响因素;起始于焊根的疲劳裂纹属于Ⅰ型主导的复合型裂纹,疲劳寿命评估应考虑Ⅱ型与Ⅲ型裂纹的影响;裂纹面呈现出典型的空间曲面特征,其深度与长度之比介于0.20~0.63之间,最大扩展角为12.7°;疲劳寿命评估结果对于初始裂纹深度取值较为敏感,应结合工程实际确定合理取值.Abstract: To investigate the fatigue crack growth characteristics and establish a fatigue life evaluation method for rib-to-deck (RTD) welded joints in orthotropic steel decks (OSDs), the influence of different simulation methods of fatigue crack propagation and material properties were considered. The OSD under heavy traffic in a highway bridge crossing the Yangtze River was taken as the research object, and fatigue tests and numerical simulation based on fracture mechanics were carried out. The fatigue life of RTD welded joints corresponding to cracks that originated from weld roots was reasonably predicted, and associated fatigue crack growth characteristics were revealed. The research results show that the relative errors between the predicted fatigue life under constant amplitude fatigue loading and measured values are less than 10%, and the assessment results tend to be safe. Fatigue crack growth paths and shape changes are basically consistent with those observed from fatigue testing. Simulation methods for fatigue crack growth, calculation criteria for kink angle, material parameter values, and initial crack depth are key factors that influence fatigue life prediction. Fatigue cracks initiated from weld roots are mixed-mode cracks dominated by mode I. The influence of mode II and mode III should be taken into account in fatigue life prediction. The crack shape shows the typical characteristic of a spatial curved surface with an aspect ratio between 0.20 and 0.63, and the maximum kink angle is 12.7°. The predicted fatigue life is fairly sensitive to the initial crack depth, which should be derived with reasonable consideration of engineering practice.
-
表 1 基于裂纹扩展分析的疲劳寿命评估
Table 1. Fatigue life assessment based on crack propagation analysis
裂纹扩展分析方法 扩展角计算准则 试件Ⅰ 试件Ⅱ 疲劳寿命/ 万次 相对误差/% 疲劳寿命/万次 相对误差/% 拟静力 MTS 86.0 7.5 138.9 6.8 GEN 88.7 10.9 147.4 13.3 SERR 85.3 6.6 141.0 8.4 常幅疲劳加载 MTS 75.3 –5.9 120.1 –7.7 GEN 73.8 –7.8 117.7 –9.5 SERR 74.9 –6.4 120.9 –7.1 表 2 材料特性参数推荐值
Table 2. Recommended values of material parameters
参 数 IIW BS7910 BS7608 JSSC $C$ 5.21 3.98 3.0 20 $n$ 3 2.88 3 2.75 注:参数$C$的单位为N•mm–3/2;BS7910对应的参 数值为2005版此规范双线性Paris公式中阶 段B取值. -
《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国桥梁工程学术研究综述·2014[J]. 中国公路学报,2014,27(5): 1-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2014.05.001Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review of china’s bridge engineering research:2014[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2014, 27(5): 1-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2014.05.001 DE JONG F B P. Renovation techniques for fatigue cracked orthotropic steel bridge decks[D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 2007 WOLCHUK R. Lessons from weld cracks in orthotropic decks on three European bridges[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1990, 116(1): 75-84. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1990)116:1(75) KOLSTEIN M H. Fatigue classification of welded joints in orthotropic steel bridge decks[D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 2007 张清华,卜一之,李乔. 正交异性钢桥面板疲劳问题的研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报,2017,30(3): 14-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.002ZHANG Qinghua, BU Yizi, LI Qiao. Review on fatigue problems of orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(3): 14-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.002 黄云. 基于损伤力学的正交异性板疲劳裂纹形成寿命研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2013 CHENG B, YE X, CAO X, et al. Experimental study on fatigue failure of rib-to-deck welded connections in orthotropic steel bridge decks[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2017, 103: 157-167. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2017.05.021 YA S, YAMADA K, SHIKAWA T. Fatigue evaluation of rib-to-deck welded joints of orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2013, 18(5): 492-499. MARTINSSON J. Fatigue assessment of complex welded steel structures[D]. Stockholm: Royal Institute of Technology, 2005 FISHER J W, BARSOM J M. Evaluation of cracking in the rib-to-deck welds of the Bronx-Whitestone Bridge[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 21(3): 1-10. XIAO Z G, YAMADA K, YA S, et al. Stress analyses and fatigue evaluation of rib-to-deck joints in steel orthotropic decks[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2008, 30(8): 1387-1397. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2007.10.008 卫星,姜苏. 基于断裂力学的钢桥面肋-板接头疲劳寿命预测[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(1): 16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.003WEI Xing, JIANG Su. Fatigue life prediction on rib-to-deck welded joints of steel bridge deck based on LEFM[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(1): 16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.003 BEGHINI M, BERTINI L, VITALE E. Fatigue crack growth in residual stress fields:experimental results and modelling[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 1994, 17(12): 1433-1444. AYGÜL M, AL-EMRANI M, BARSOUM Z, et al. Investigation of distortion-induced fatigue cracked welded details using 3D crack propagation analysis[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2014, 64(7): 54-66. 洪起超. 工程断裂力学基础[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 1987: 54-58 WARZYNEK P A, CARTER B J, BANKS-SILLS L. The M-integral for computing stress intensity factors in generally anisotropic materials[R]. Huntsville: NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, 2005 British Standards Institution. Guide on methods for assessing the acceptability of flaws in metallic structures: BS7910[S]. London: British Standard Institution, 2013 PARIS P C, ERDOGAN F. A critical analysis of crack propagation laws[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1963, 85(4): 528-533. doi: 10.1115/1.3656900 HOBBACHER A F. Recommendations for fatigue design of welded joints and components[M]. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 73-75 British Standards Institution. Fatigue design and assessment of steel structures: code of practice: BS7608[S]. London: British Standard Institution, 1993 RADAJ D, SONSINO C M, FRICKE W. Fatigue assessment of welded joints by local approaches[M]. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2006: 263-267 日本鋼構造物協会. 鋼構造物の疲労設計指針·同解説: JSS Ⅳ 09-2010[S]. 東京: 技報堂出版, 2012 -




 下载:
下载: