Multi-objective Indoor Path Planning Method with Dynamic Environment Awareness
-
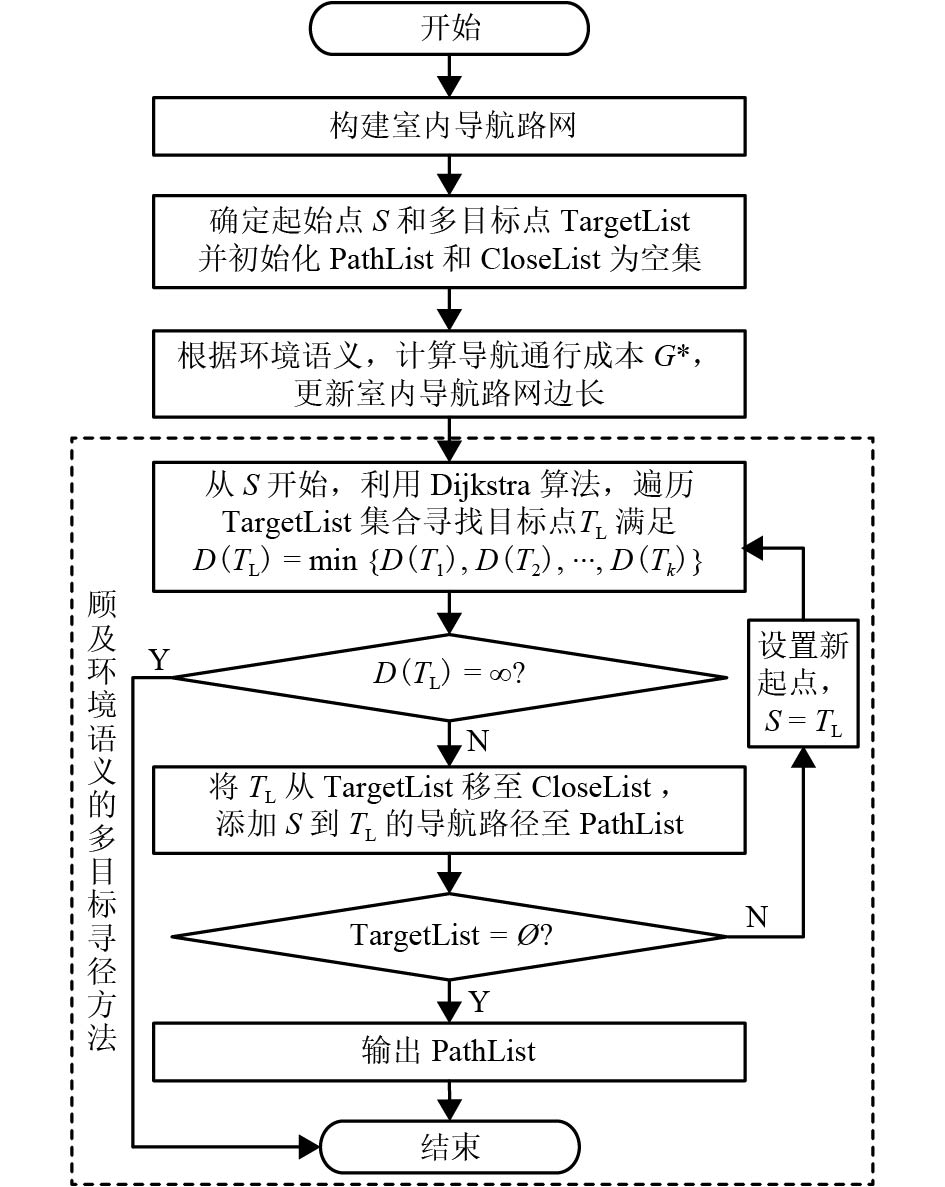
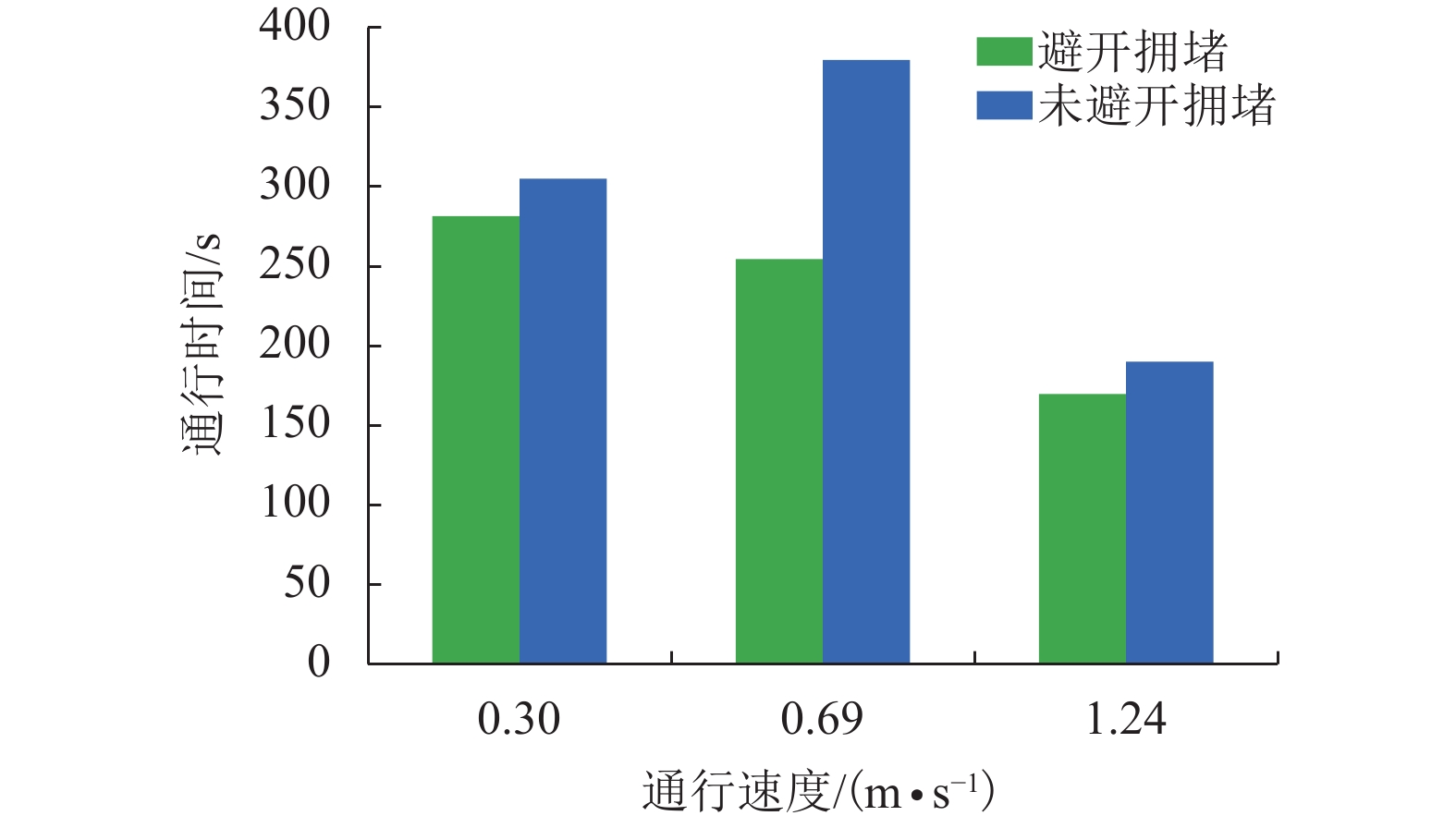
摘要: 为了满足复杂室内环境中用户的多目标导航需求,提出了动态环境感知的多目标室内路径规划方法. 该方法顾及室内路径复杂度、拥挤程度与阻断事件等多维室内环境语义,扩展了节点-边表示的室内导航路网模型,通过量化表征多维室内环境语义,建立了能够综合感知室内环境语义变化的导航通行成本函数,然后,将顾及室内动态环境语义的导航通行成本函数值作为室内导航路网模型的边长,设计实现了基于Dijkstra的多目标室内路径规划算法. 通过模拟实验分析比较室内路径规划结果,实验结果表明:由于扩展后的室内导航路网模型增加了具有方向性语义的垂直组件,考虑了阻断事件因素,导航路径规划能够避开不可用连接边;在路径拥挤程度分别为轻度、缓慢和堵塞情况下,由于考虑了路径复杂度和拥挤程度,节约的通行时间平均提升了17%.
-
关键词:
- 环境语义感知 /
- 路径规划 /
- Dijkstra算法 /
- 室内导航
Abstract: A dynamic environment-aware multi-objective indoor path planning method is proposed, aimed at satisfying the multi-objective navigation requirements of users in complex indoor environments. Multi-dimensional indoor environment semantics such as indoor path complexity, the degree of congestion, and blocking events were take into account. The node-edge representation indoor navigation network model was also expanded, and a navigation traffic cost function was established by precisely quantifying the multi-dimensional indoor environment semantics. The value of the navigation traffic cost function was then taken as the side length of the model, and a multi-objective indoor path planning algorithm based on Dijkstra was designed and implemented. The results of the simulation show that navigation path planning can avoid unavailable connection edges by adding the vertical components with directional semantics and considering the blocking events factor in the extended indoor navigation network model. After the path complexity and traffic congestion were considered, the travel time is saved by an average of 17% in three traffic patterns, i.e., light, mild and heavy congestion.-
Key words:
- environmental semantic awareness /
- path planning /
- Dijkstra algorithm /
- indoor navigation
-
表 1 拥挤程度与人流量对应情况
Table 1. Degree of crowdedness and corresponding flow density
拥挤程度 畅通 轻度 缓慢 堵塞 人流密度
/(人•m–2)[0,0.75] (0.75,2.00] (2.00,3.50] >3.50 通行速度
/(m•s–1)>1.40 (1.08,1.40] (0.30,1.08] ≤0.30 表 2 经典最优路径规划算法
Table 2. Classic optimal path planning algorithms
算法 优点 缺点 Dijkstra 算法简单,全局最优解 长距离路径规划的效率较低 A* 启发式搜索效率高 局部最优解 Floyd 支持负权边,用于有向图 算法复杂度过高 BF 支持负权边,可用于所有图 算法复杂度过高 表 3 实验1环境语义
Table 3. Environment semantics of experiment 1
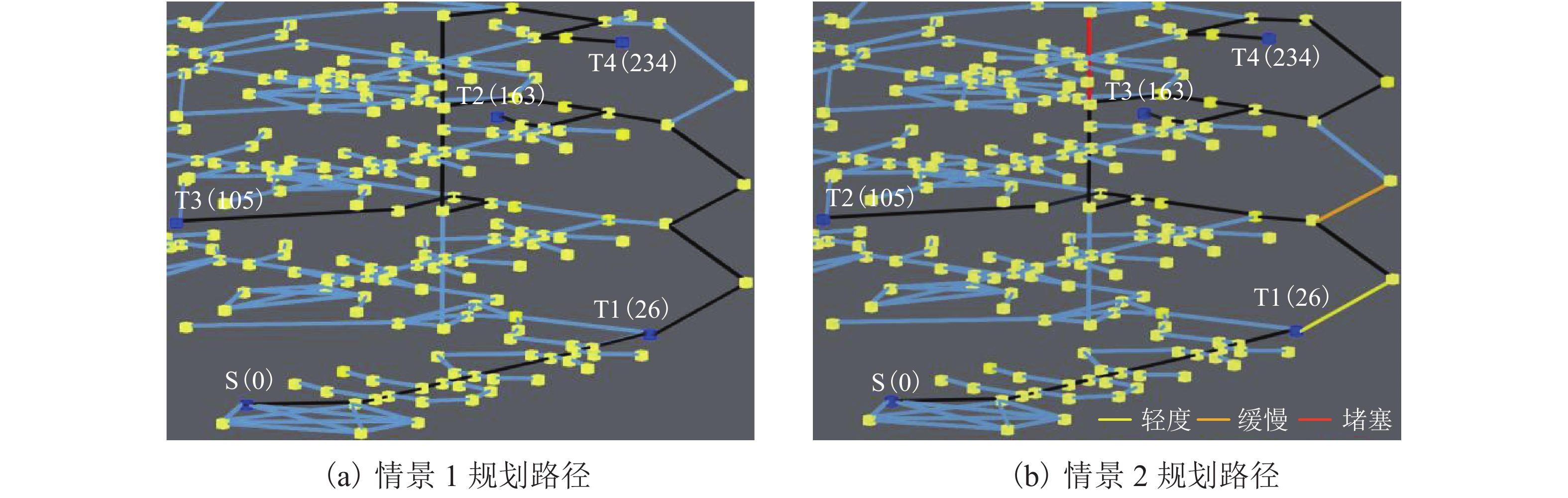
情景编号 请求时间 拥挤区域 拥挤程度 起点 终点访问顺序 1 任意时刻 无 无 0 26-163-105-234 2 t1时刻 无 无 0 26 t2时刻 1楼到2楼楼梯区域 轻度 26 105 t3时刻 2楼到3楼楼梯区域 缓慢 105 163 t4时刻 3楼到4楼电梯区域 堵塞 163 234 表 4 实验2环境语义
Table 4. Environment semantics of experiment 2
情景编号 请求时间 拥挤区域/拥挤程度 事件/上下行 起点 终点访问顺序 1 任意时刻 无 无 24 28-102-159-234 2 任意时刻 无 无/下行 24 28-102-159-234 3 t1时刻 1楼黄色区域/轻度 无 24 28 t2时刻 2楼橘色区域/缓慢 发生/无 28 159 t3时刻 4楼红色区域/堵塞 无 159 234 t4时刻 无 无 234 102 -
GUERRERO L A, FRANCISCO V, OCHOA S F. An indoor navigation system for the visually impaired[J]. Sensors, 2012, 12(6): 8236-8258. doi: 10.3390/s120608236 MAKRI A, ZLATANOVA S, VERBREE E. An approach for indoor wayfinding replicating main principles of an outdoor navigation system for cyclists[J]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry,Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2015, 40(4): 29-35. XIONG Qing, ZHU Qing, ZLATANOVA S, et al. Multi-level indoor path planning method[C]//International Archives of the Photogrammetry Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences. Tokyo: [s.n.], 2015: 19-23 VANCLOOSTER A, VIAENE P, VAN D W N, et al. Analyzing the applicability of the least risk path algorithm in indoor space[C]//Isprs Annals of the Photogrammetry Rotnote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences. Cape Town: [s.n.], 2013: 19-26 迟光华,谢君,李强,等. 一种用于制定多层多出口的室内应急疏散规划的方法[J]. 遥感信息,2013,28(6): 116-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2013.06.021CHI Guanghua, XIE Jun, LI Qiang, et al. A method for planning multilayer and multi-exit indoor emergency evacuation[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2013, 28(6): 116-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2013.06.021 KHAN A A, YAO Z, KOLBE T H. 3D geoinformation science[M]. 3D Geoinformation Science. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 175-192 LIN Y H, LIU Y S, GAO G, et al. The IFC-based path planning for 3D indoor spaces[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2013, 27(2): 189-205. doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2012.10.001 TSETSOS V, ANAGNOSTOPOULOS C, KIKIRAS P, et al. Semantically enriched navigation for indoor environments[J]. International Journal of Web & Grid Services, 2006, 2(4): 453-478. XU Y, WEN Z, ZHANG X. Indoor optimal path planning based on Dijkstra algorithm[C]//International Conference on Materials Engineering and Information Technology Applications. Paris: Atlantis Press, 2015: 309-313 LYARDET F, SZETO D W, AITENBICHLER E. Context-aware indoor navigation[C]//European Conference on Ambient Intelligence. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2008: 290-307 林雕,宋国民,游雄,等. 基于上下文感知的室内路径规划研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2016,32(3): 8-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2016.03.002LIN Diao, SONG Guomin, YOU Xiong, et al. Study on the context-aware indoor path planning[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2016, 32(3): 8-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2016.03.002 KARAS I R, BATUK F, AKAY A E, et al. Innovations in 3D Geo information systems[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 395-404 LEE J. A three-dimensional navigable data model to support emergency response in microspatial built-environments[J]. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 2008, 97(3): 512-529. YUAN W, SCHNEIDER M. Geospatial thinking[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2010: 299-313 SRIKULWONG M. Tactile displays for pedestrian navigation[D]. Bath: University of Bath, 2012 BALAKRISHNAN B, SUNDAR S S. Where am I? How can I get there? Impact of navigability and narrative transportation on spatial presence[J]. Human-Computer Interaction, 2011, 26(3): 161-204. DUCKHAM M, KULIK L. " Simplest” paths:automated route selection for navigation[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2003, 2825(1): 169-185. RICHTER K F, DUCKHAM M. Simplest instructions: finding easy-to-describe routes for navigation[C]//International Conference on Geographic Information Science. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2008: 274-289 GOLLEDGE R G, GARLING T. Handbook of transport geography and spatial systems[M]. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 2004: 501-512 TURNER A. Spatial information theory[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2009: 489-504 LO S M, FANG Z, LIN P, et al. An evacuation model:the SGEM package[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2004, 39(3): 169-190. doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2003.10.003 -





 下载:
下载: