Effect of Rolling Direction on Contact Fatigue Damage of CL60 Wheel Steel
-
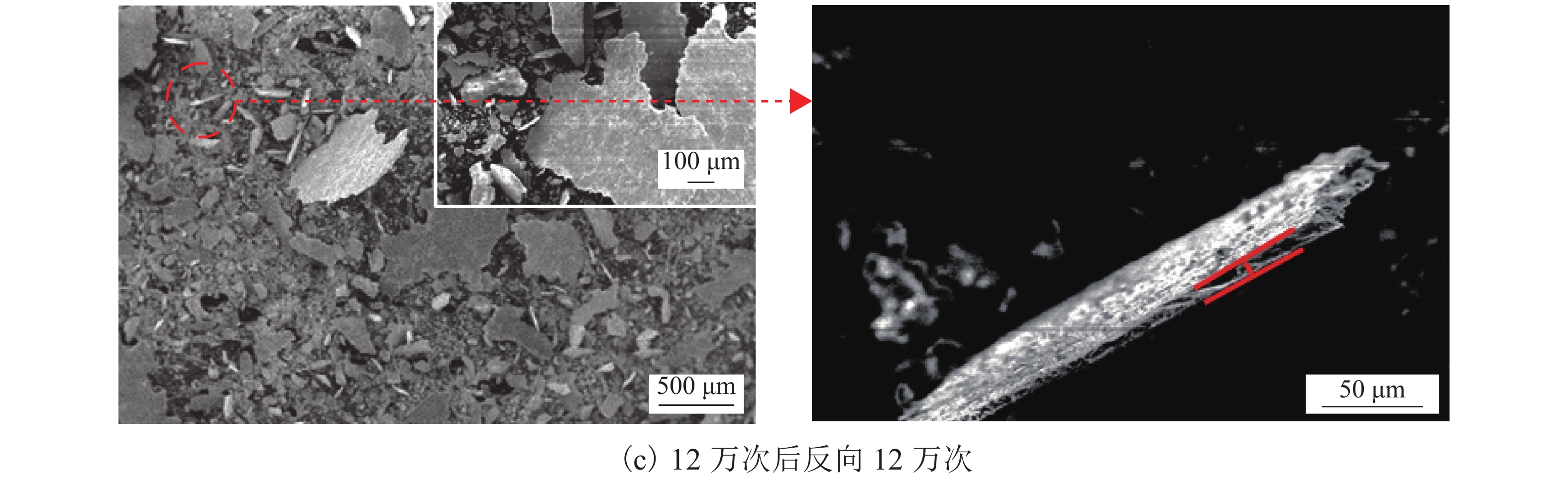
摘要: 为研究车轮滚动方向对车轮材料接触疲劳损伤的影响机制,利用WR-1滚动磨损试验机进行了车轮单向和双向运行滚滑磨损试验,使用光镜和扫描电镜分析了试验后车轮试样的表面磨损形貌、剖面疲劳裂纹形貌及磨屑尺寸,探究了换向运行工况下车轮表面损伤、裂纹扩展、磨屑尺寸随反向循环次数的演变规律. 研究结果表明:车轮表面损伤以起皮剥落为主,反向循环次数从1万次增加到12万次时,初始剥落逐渐消失,继而形成与原滚动方向相反的新剥落,相同循环次数下改变车轮滚动方向有利于减轻车轮材料疲劳损伤;车轮换向改变了表面微裂纹的扩展方向,形成4°~8° 的反向疲劳裂纹,并出现了裂纹扭曲和分支现象;单向滚动时,随循环次数增加,磨屑尺寸先增大后减小,反向后磨屑厚度先增大后减小,反向1万次时,磨屑厚度增大到10~12 μm,为单向时的两倍.Abstract: In order to investigate the effect of wheel rolling direction on rolling contact fatigue (RCF) damage of wheel steel, the rolling-sliding wear experiments under both unidirectional and bidirectional conditions were carried out on a rolling wear testing apparatus (WR-1, China). The wheel surface damage, section fatigue crack morphology and wear debris size were observed by optical microscope and scanning electron microscope, the evolution law of wheel surface damage, fatigue crack propagation and debris size with the number of reverse cycles under reversing operating conditions were investigated. The results show that the wheel surface damage is mainly caused by peeling. As the number of reverse cycles increases from 10 000 to 120 000, the initial peelings gradually wear off and then new peelings are formed opposite to the original rolling direction, changing wheel rolling direction is beneficial to reduce the RCF damage of wheel materials under the same test cycles. The propagation direction of surface microcracks is changed after wheel reverse rolling, forming reverse fatigue cracks of 4°−8°, and crack distortion and branching occur on the wheel samples. As the number of cycles increases, the debris size increases firstly and then decreases under unidirectional condition, after wheel reverse rolling, the debris thickness increases firstly and then decreases, the thickness increases to 10−12 μm after reversing 10 000 cycles, which is twice as much as under the unidirectional condition.
-
Key words:
- wheel steel /
- rolling direction /
- fatigue damage /
- crack propagation /
- debris size
-
表 1 轮轨试样化学成分质量百分数
Table 1. Mass percent chemical compositions of wheel and rail
% 项目 C Si Mn P S 车轮(CL60) 0.550~0.650 0.170~0.370 0.500~0.800 0.035 0.040 钢轨(U75V) 0.650~0.750 0.150~0.580 0.700~1.200 ≤ 0.025 ≤ 0.025 -
DONZELLA G, FACCOLI M, GHIDINI A, et al. The competitive role of wear and RCF in a rail steel[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2005, 72: 287-308. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2004.04.011 CANNON D F, PRADIER H. Rail rolling contact fatigue research by the European Rail Research Institute[J]. Wear, 1996, 191(1/2): 1-13. EKBERG A, KABO E. Fatigue of railway wheels and rails under rolling contact and thermal loading—an overview[J]. Wear, 2005, 258: 1288-1300. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2004.03.039 刘启跃, 何成刚,黄育斌,等. 轮轨疲劳损伤模拟实验研究及展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 282-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.008LIU Qiyue, HE Chenggang, HUANG Yubin, et al. Research and prospects of simulation experiment on wheel/rail fatigue damage[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 282-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.008 KAMMERHOFER C, HOHENWARTER A, PIPPAN R. A novel laboratory test rig for probing the sensitivity of rail steels to RCF and wear-first experimental results[J]. Wear, 2014, 316: 101-108. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2014.04.008 KRÁČALÍK M, TRUMMER G, DAVES W. Application of 2D finite element analysis to compare cracking behaviour in twin-disc tests and full scale wheel/rail experiments[J]. Wear, 2016, 346: 140-147. DIRKS B, ENBLOM R, BERG M. Prediction of wheel profile wear and crack growth:comparisons with measurements[J]. Wear, 2016, 366: 84-94. 李晓宇. 钢轨踏面斜裂纹扩展行为的仿真研究[D]. 北京: 铁道科学研究院, 2007. KAPOOR A, FLETCHER D I, FRANKLIN F J. The role of wear in enhancing rail life[J]. Tribology Series, 2003, 41: 331-340. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8922(03)80146-3 王文健. 轮轨滚动接触疲劳与磨损耦合关系及预防措施研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2008. 黄育斌,何成刚,马蕾,等. 干态下车轮材料表面疲劳裂纹萌生试验研究[J]. 摩擦学学报,2016,36(2): 194-200.HUANG Yubin, HE Chenggang, MA Lei, et al. Experimental study on initiation of surface fatigue crack of wheel material under dry condition[J]. Tribology Journal, 2016, 36(2): 194-200. 黄育斌. 轮轨材料表面疲劳裂纹形成机理与演变研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. FUJITA K, FUJITA A. The effect of changing the rolling direction on the rolling contact fatigue lives of annealed and case-hardened steel rollers[J]. Wear, 1977, 43(3): 315-327. doi: 10.1016/0043-1648(77)90128-4 TYFOUR W R, BEYNON J H. The effect of rolling direction reversal on fatigue crack morphology and propagation[J]. Tribology International, 1994, 27(4): 273-282. doi: 10.1016/0301-679X(94)90007-8 TYFOUR W R, BEYNON J H. The effect of rolling direction reversal on the wear rate and wear mechanism of pearlitic rail steel[J]. Tribology International, 1994, 27(6): 401-412. doi: 10.1016/0301-679X(94)90017-5 ASADI A L, KAPOOR A. An investigation to the influence of bogie direction reversal on equalizing rail vehicle wheel wear[J]. Wear, 2008, 265: 65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2007.08.023 ASADI A L, YOUNESIAN D, SCHMID F. Tangential force variation due to the bogie direction reversal procedure[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2007, 45(4): 359-373. doi: 10.1080/00423110600999912 MA L, SHI L B, GUO J, et al. On the wear and damage characteristics of rail material under low temperature environment condition[J]. Wear, 2018, 394: 149-158. LEWIS R, MAGEL E, WANG W J, et al. Towards a standard approach for the wear testing of wheel and rail materials[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2017, 231(7): 760-774. doi: 10.1177/0954409717700531 KAPOOR A. Wear by plastic ratcheting[J]. Wear, 1997, 212: 119-130. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1648(97)00083-5 WAGNER F, OUAREM A, GU C F, et al. A new method to determine plastic deformation at the grain scale[J]. Materials Characterization, 2014, 92: 106-117. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2014.03.007 TRUMMER G, MARTE C, DIETMAIER P, et al. Modeling surface rolling contact fatigue crack initiation taking severe plastic shear deformation into account[J]. Wear, 2016, 352: 136-145. SUH P N. The delamination theory of wear[J]. Wear, 1973, 25: 111-124. doi: 10.1016/0043-1648(73)90125-7 -




 下载:
下载: