Design Method of Hydraulic Valve Block for Tunnel Boring Machine
-
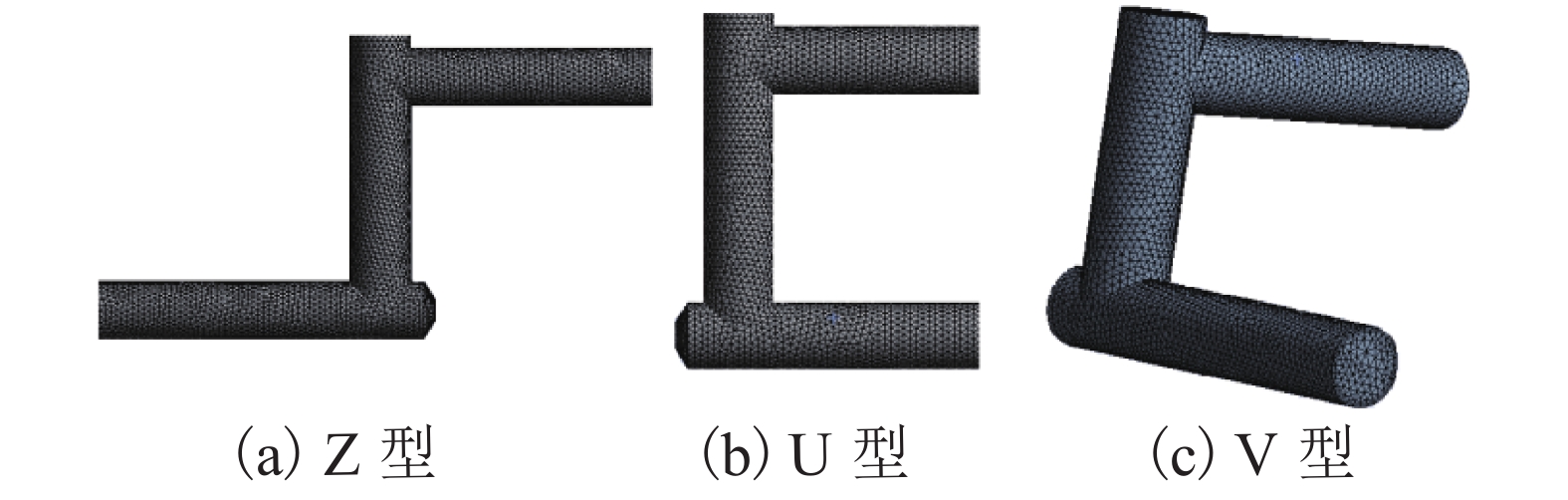
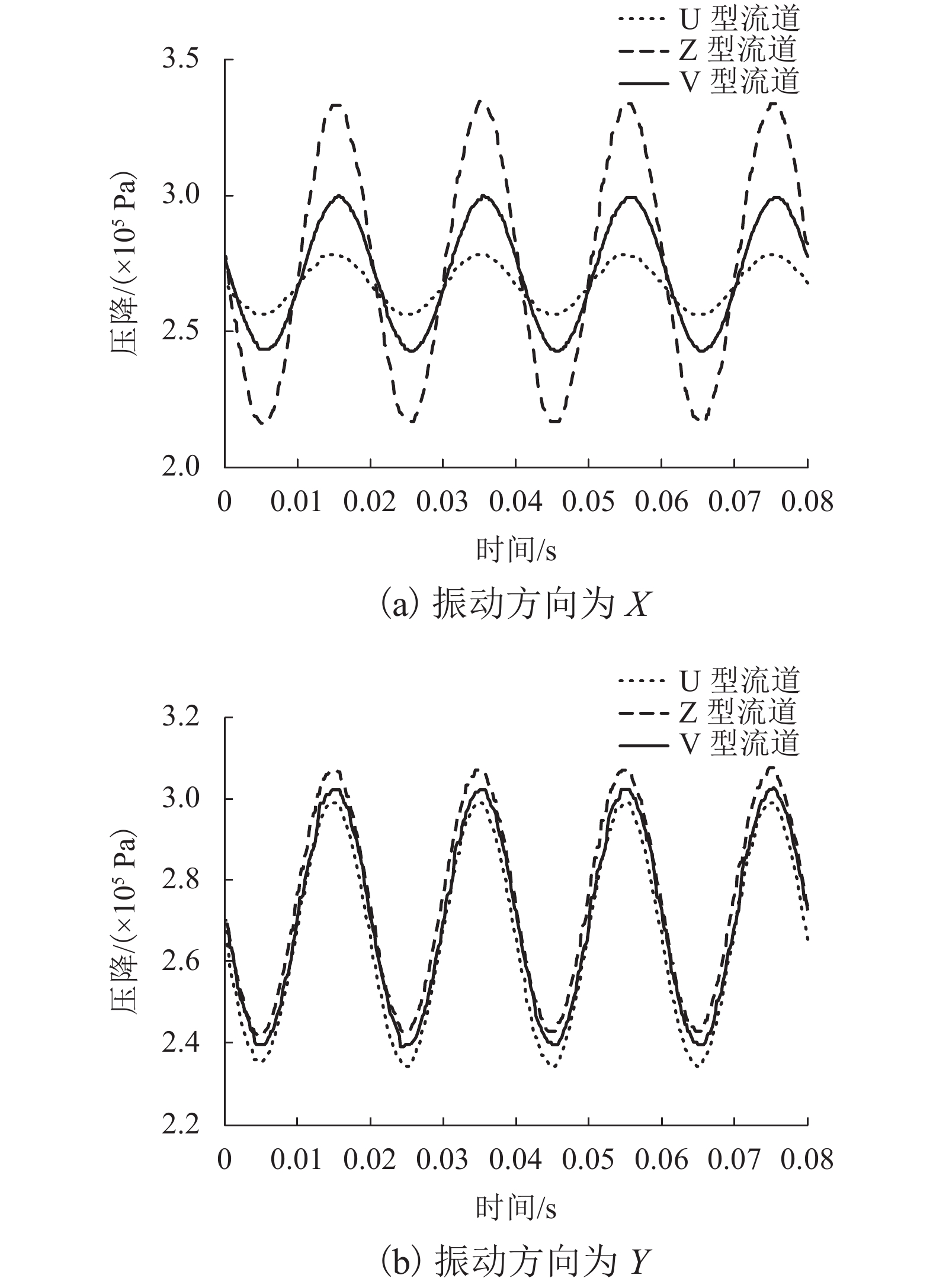
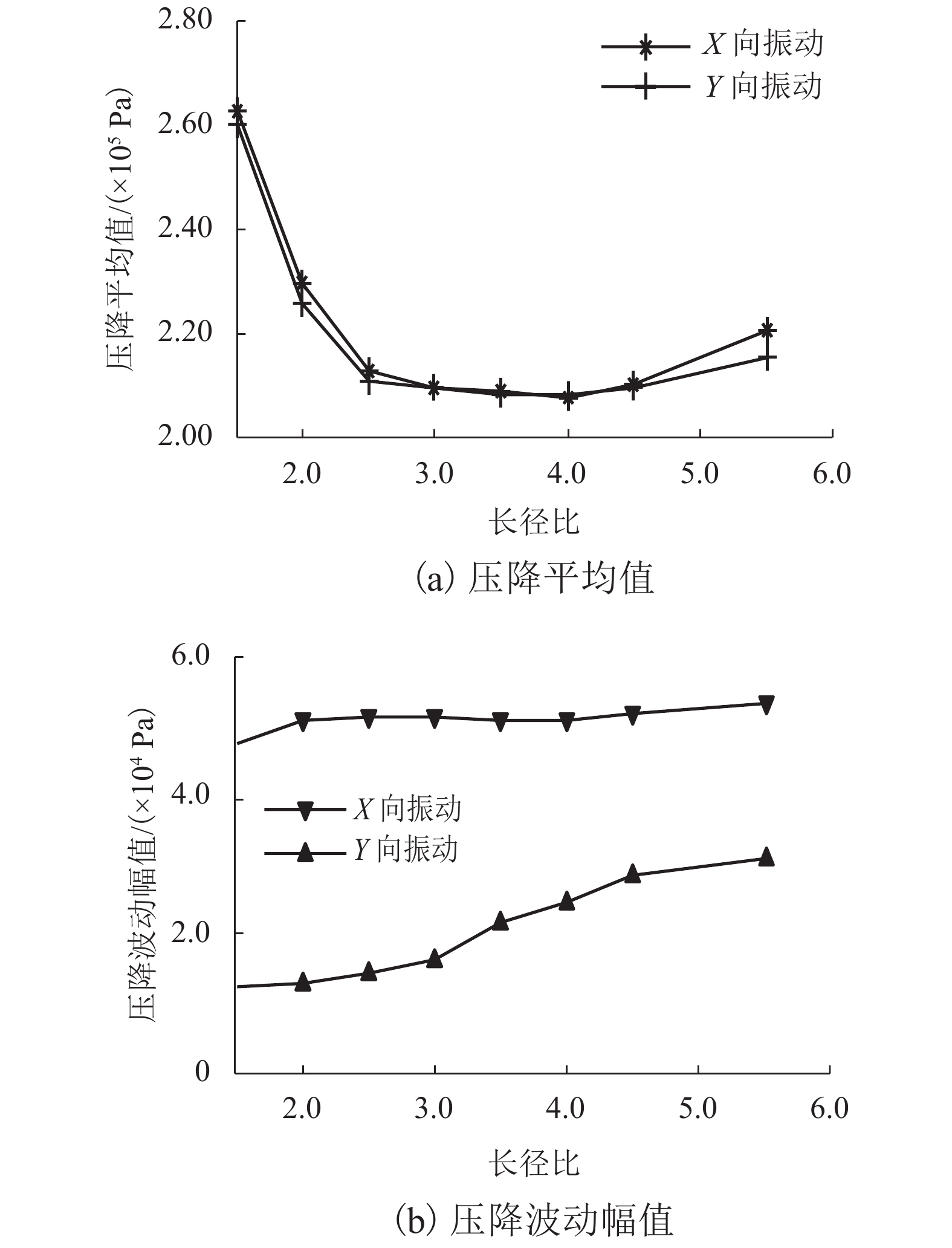
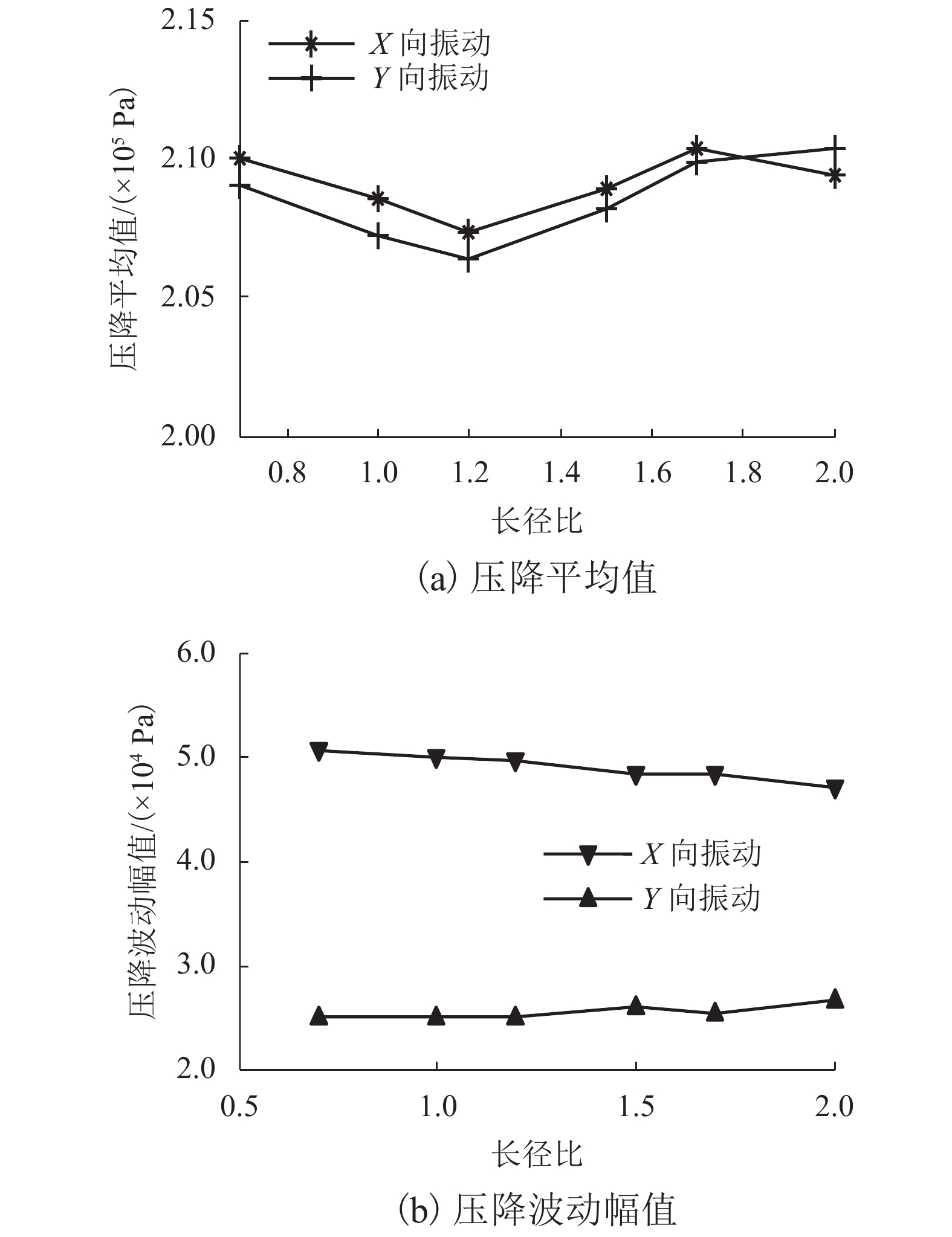
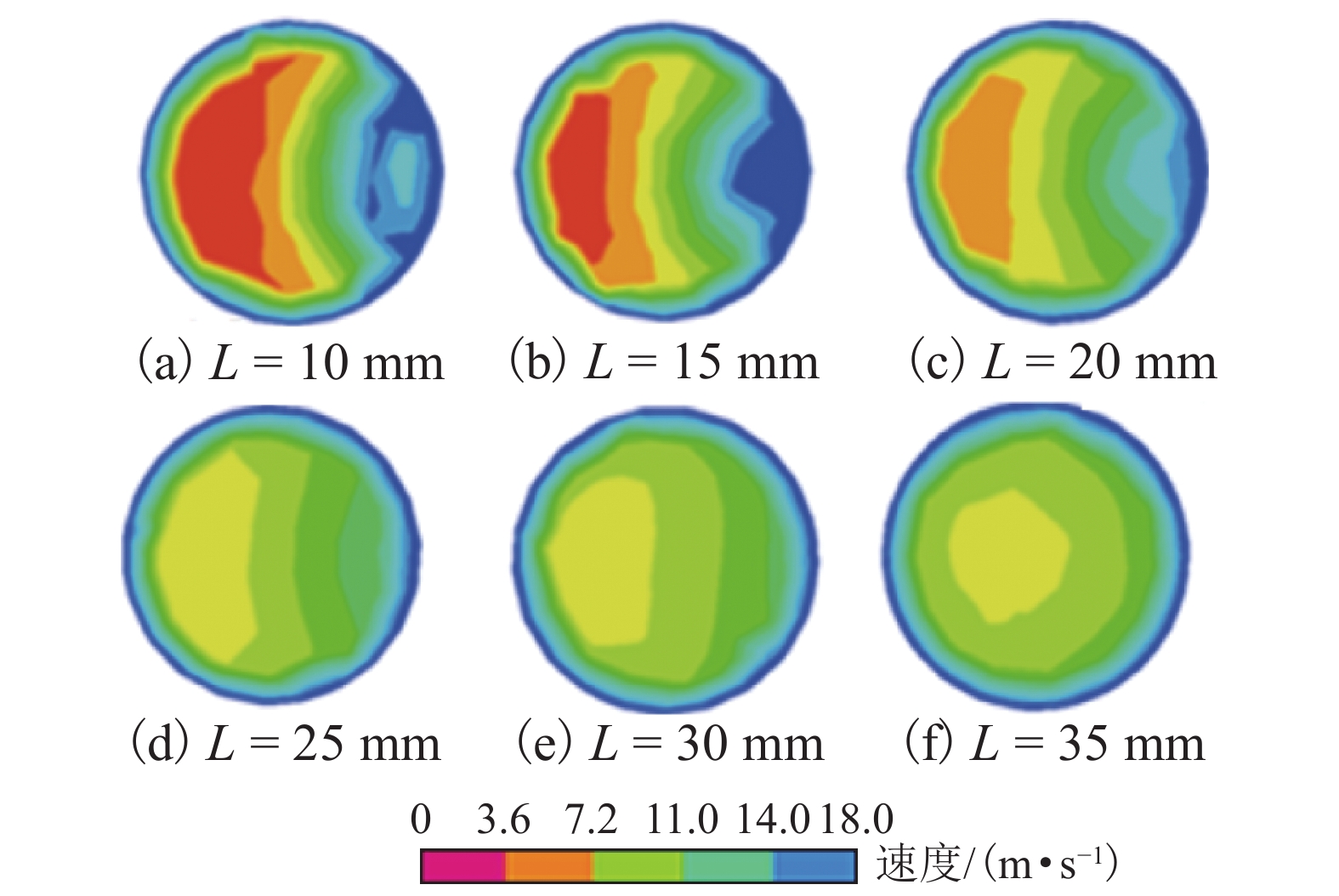
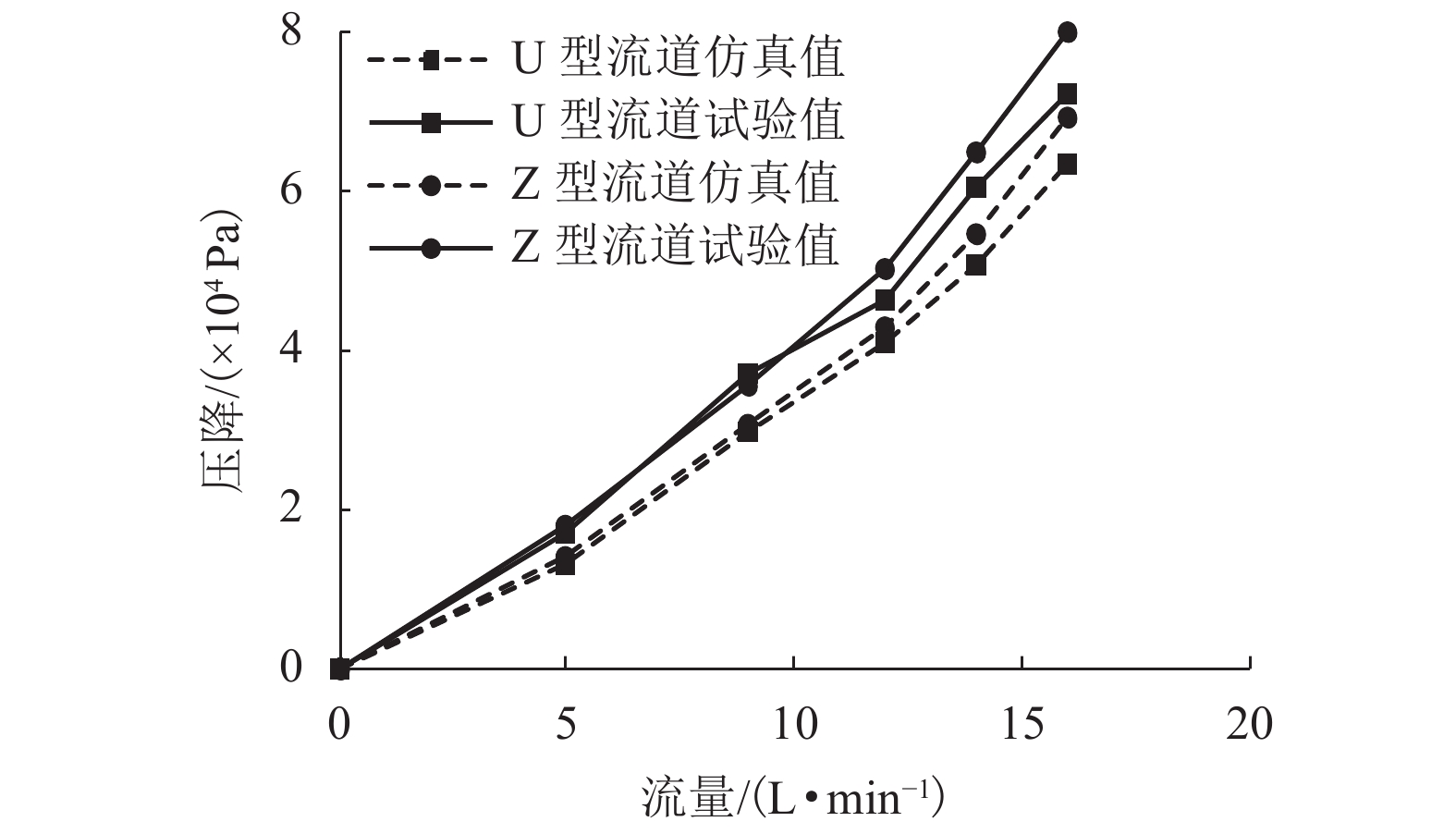
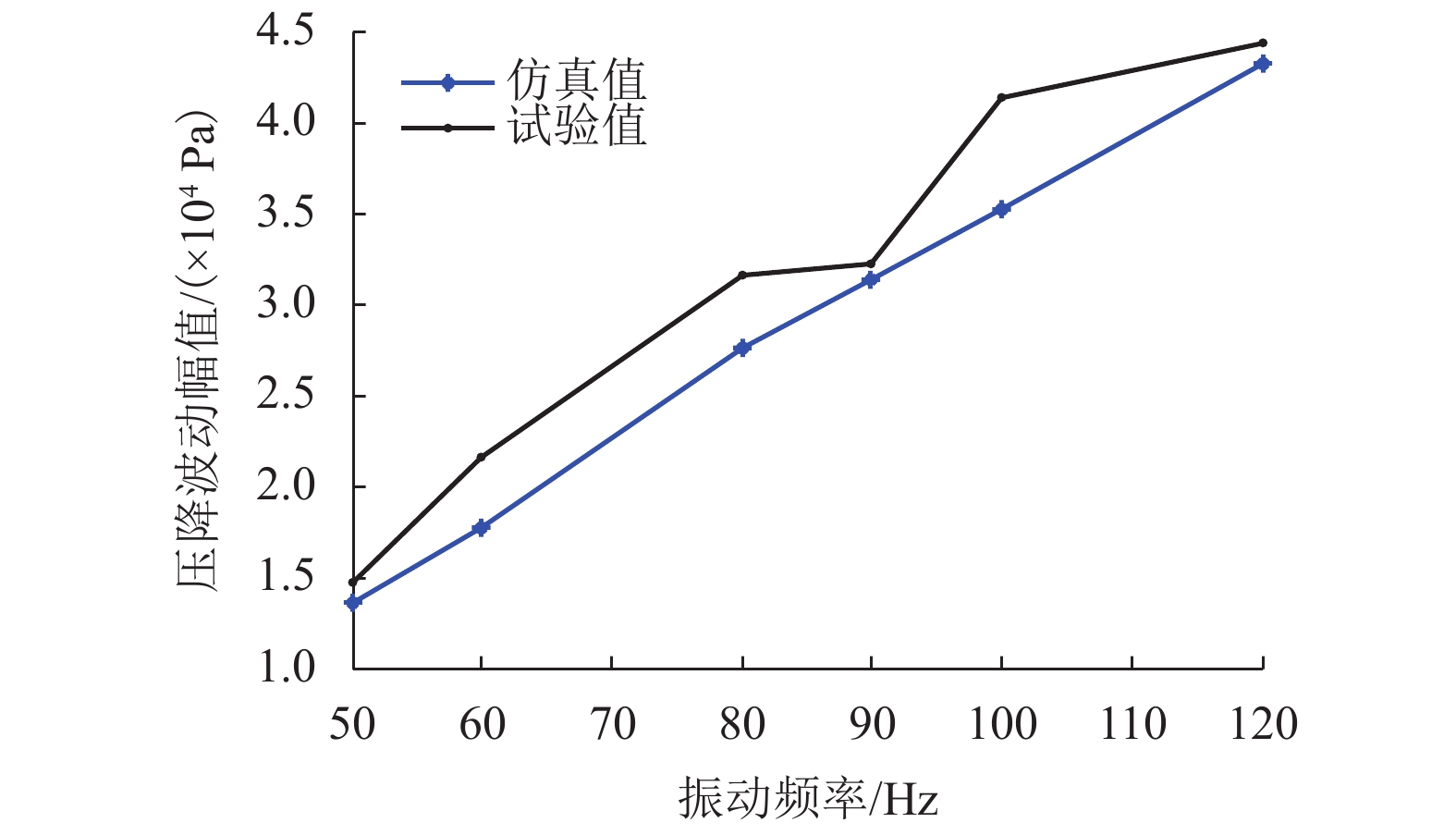
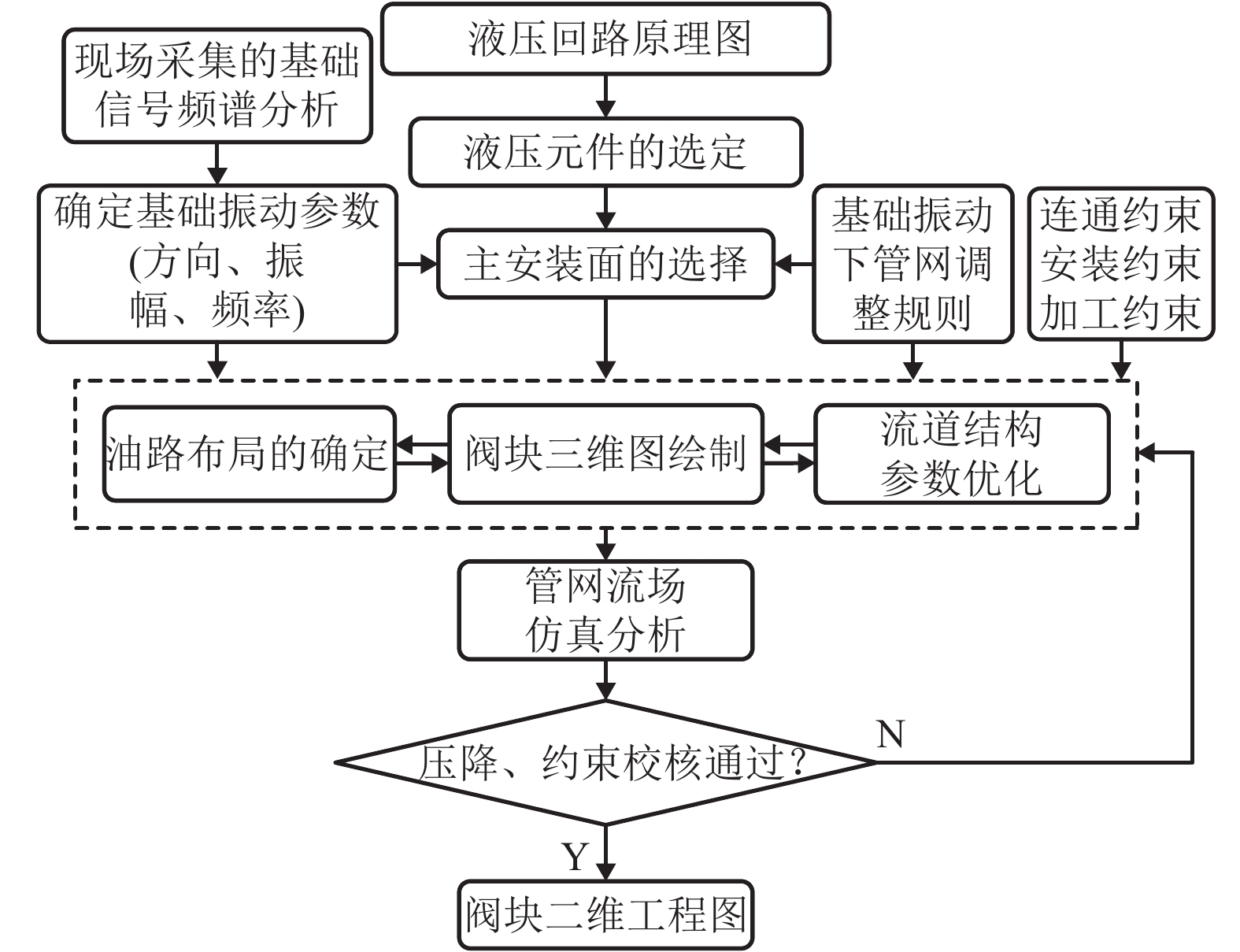
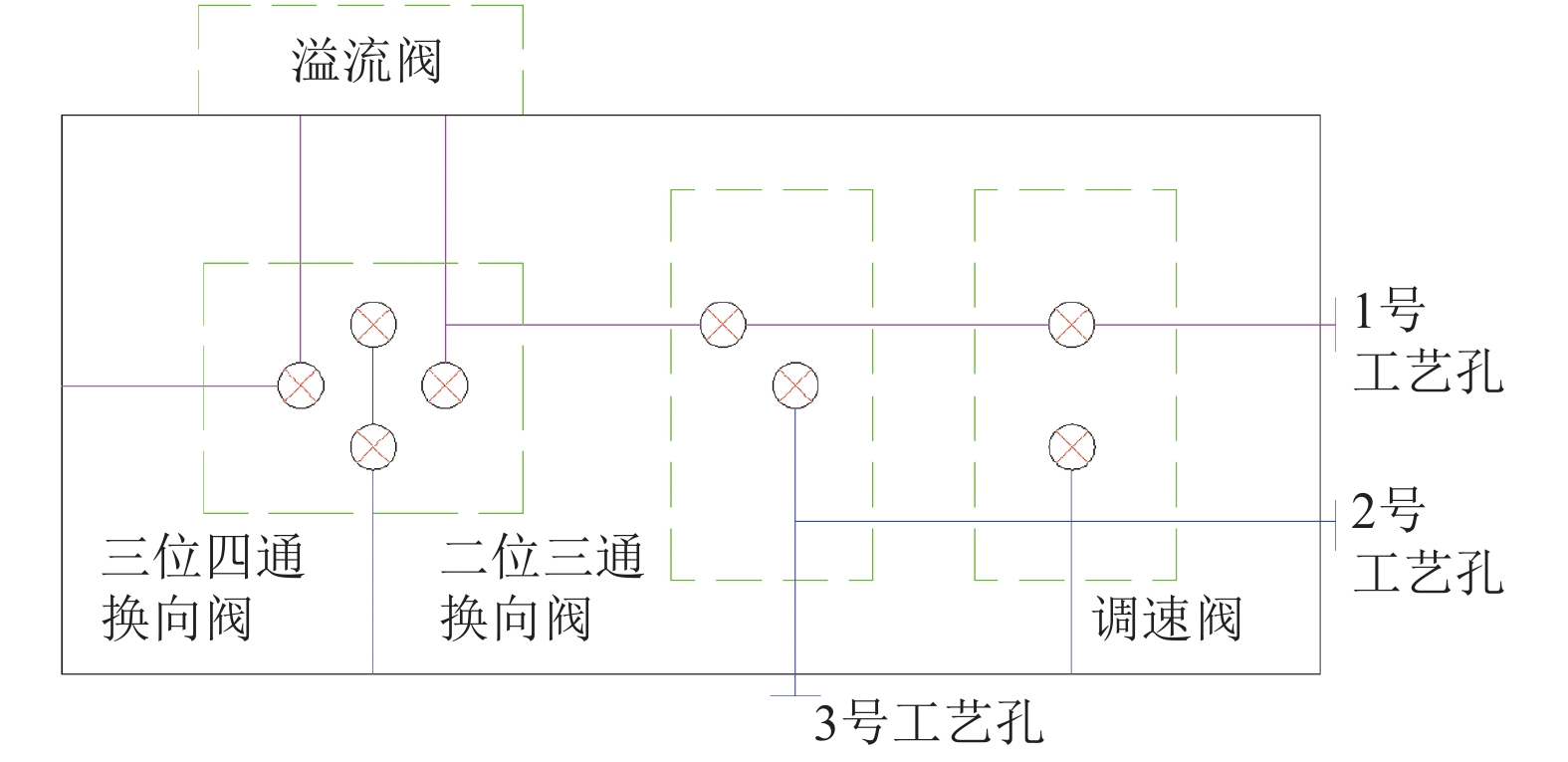
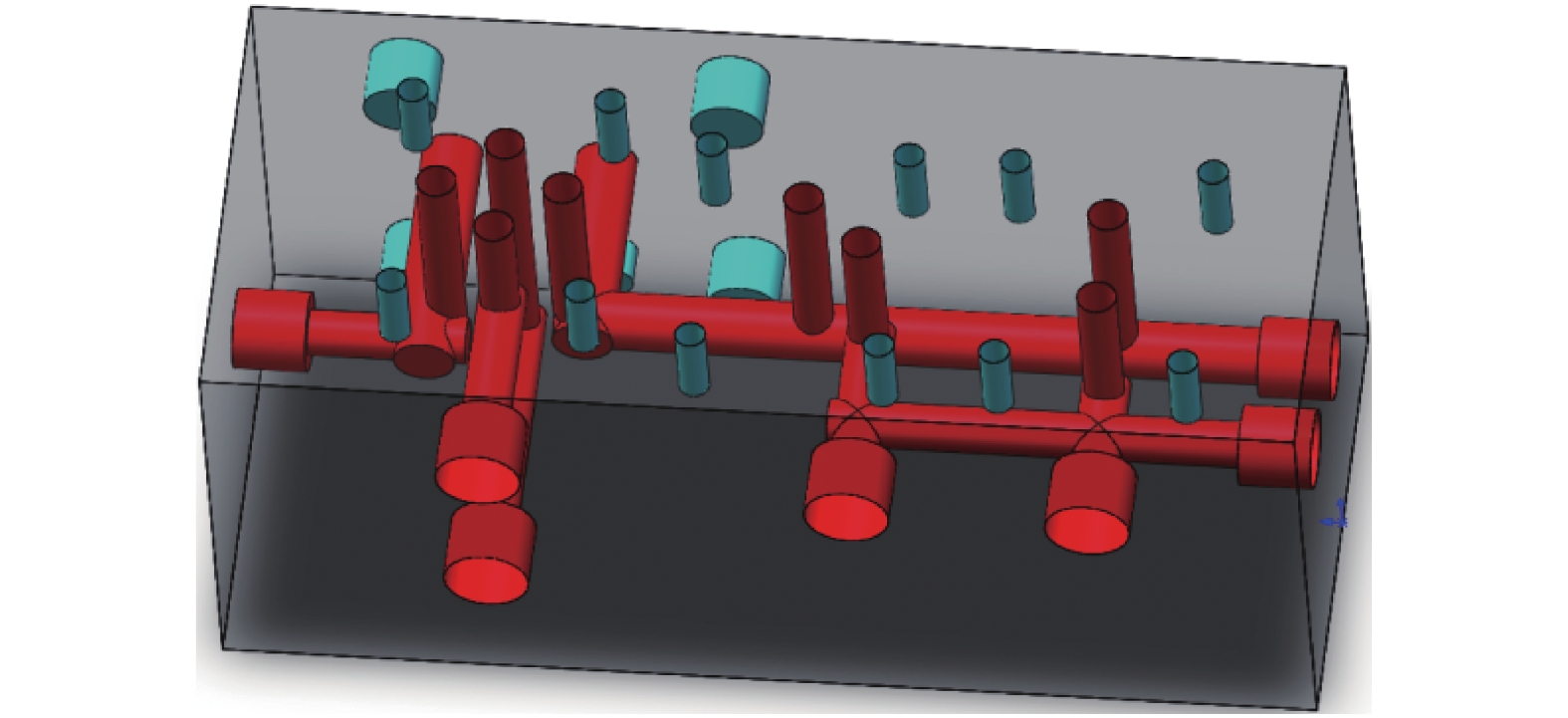
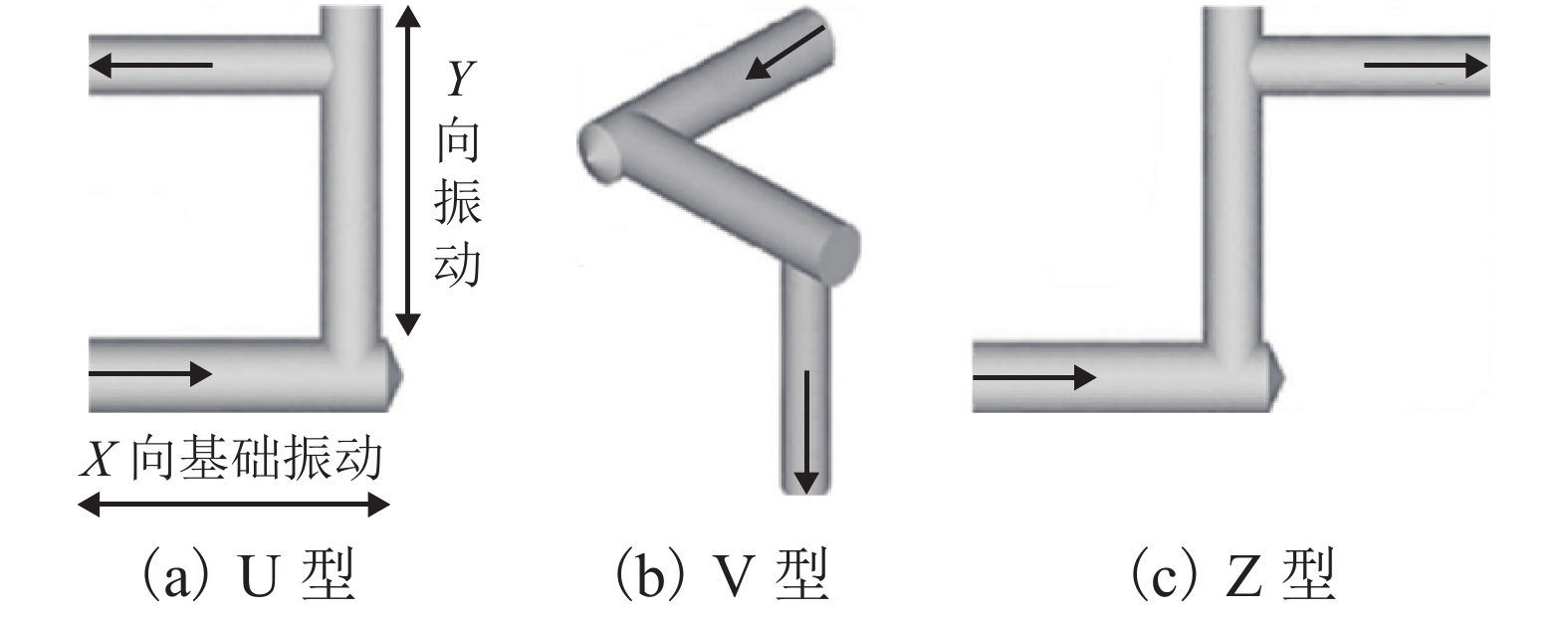
摘要: 为了改善基础振动下液压阀块流道流通品质,基于有限元原理建立了基础振动下流道的仿真模型并验证了仿真模型的正确性;分析了基础振动下不同流道的布局方式,工艺孔结构参数,进出口流道长度对流道压降特性的影响;提出了基础振动下液压阀块的设计流程. 研究结果表明:基础振动下U型流道压降特性最好,Z型流道最差;U型流道工艺孔长度越短,流道压降平均值和压降波动越小;Z型流道工艺孔长度为3.5倍工艺孔直径,V型流道的工艺孔长度为3倍工艺孔直径时,流道压降平均值和压降波动较小;工艺孔直径略大于进出口流道直径时,有利于减小基础振动的影响;出口流道的长度在3倍出口流道直径以上时,有利于避免流道出口处于转弯后流场的恢复区. 新的设计方法能够有效减小阀块内流体压降大小,提高压力稳定性.Abstract: In order to improve the flow quality of flow channels in hydraulic valve block under foundation vibration, a simulation model of flow channels under foundation vibration was established based on finite element theory and the correctness of the simulation model was verified. The effects of the different flow channels layout, process holes structure parameters, import and export flow length on the pressure drop characteristics of flow channels were analyzed under the foundation vibration. The design flow of hydraulic valve block under the foundation vibration was put forward. The results show that the U-shaped flow channel has the best pressure drop characteristics and Z-shaped has the worst pressure drop characteristics under the foundation vibration; the shorter U-shaped groove hole length is, the smaller the pressure drop average and the pressure drop fluctuating is; when the length of Z-shaped flow channel fabrication hole is 3.5 times the diameter of fabrication hole, the length of V-shaped flow channel fabrication hole is 3 times the diameter of fabrication hole, the average and fluctuating of pressure drop are less; it is helpful to reduce the impact of foundation vibration when the diameter of fabrication hole is bigger than the diameter of import and export flow channel; when the length of the export flow channel is over 3 times the diameter of export flow channel, it is beneficial to avoid recovery area after the outlet flow channel in turn flow field. The new method can effectively reduce the pressure drop in valve block and improve the pressure stability.
-
Key words:
- valve block /
- pressure drop characteristic /
- structure parameter /
- design method
-
表 1 流体介质参数
Table 1. Parameters of fluid
介质类型 密度/(kg•m – 3) 动力粘度/(kg•(m•s)−1) 热传导系数/(W•(m•k)−1) 比热容/(J•(kg•k)−1) 46号液压油 870 0.039 15 0.12 1 700 表 2 液压元件类型
Table 2. Types of hydraulic element
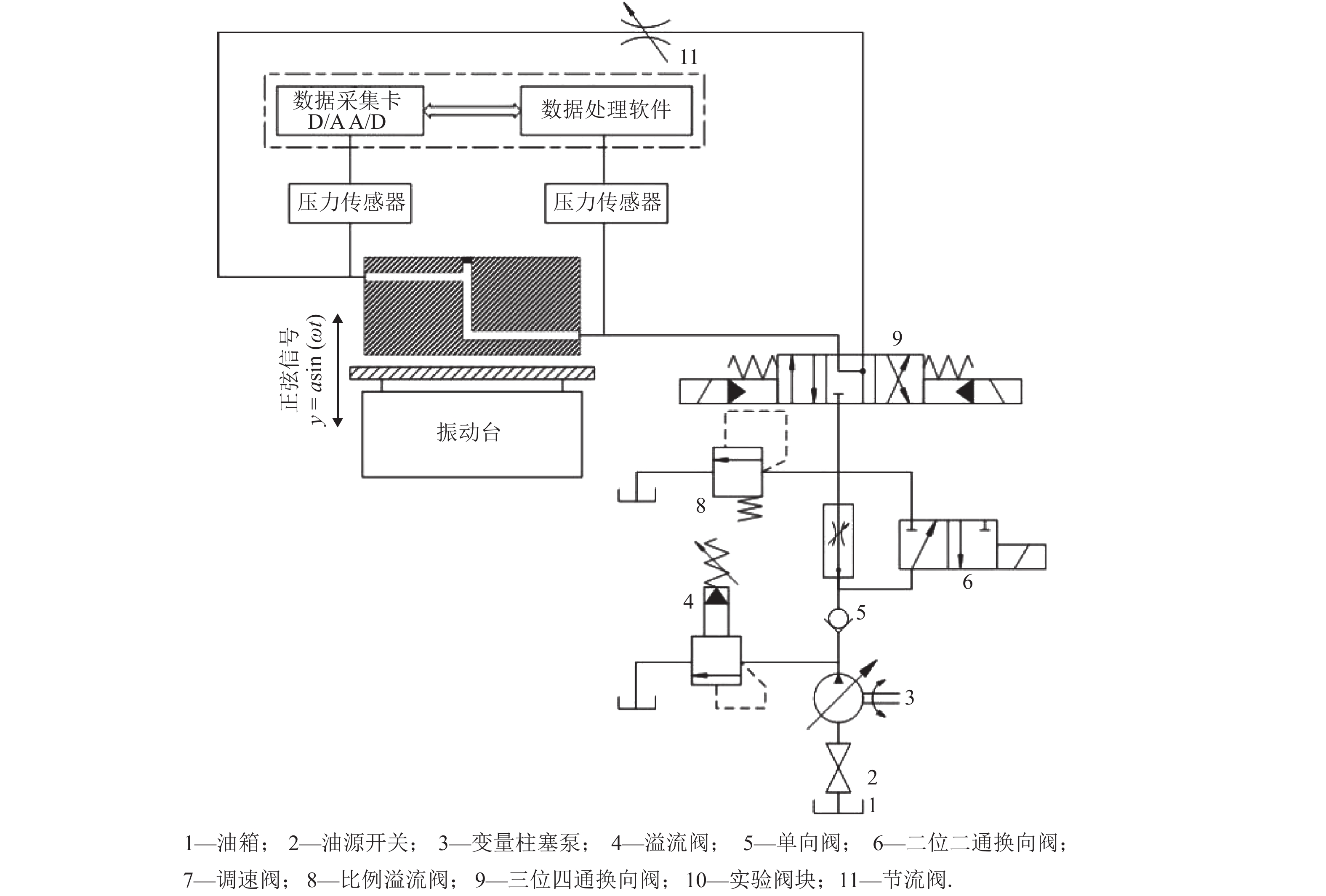
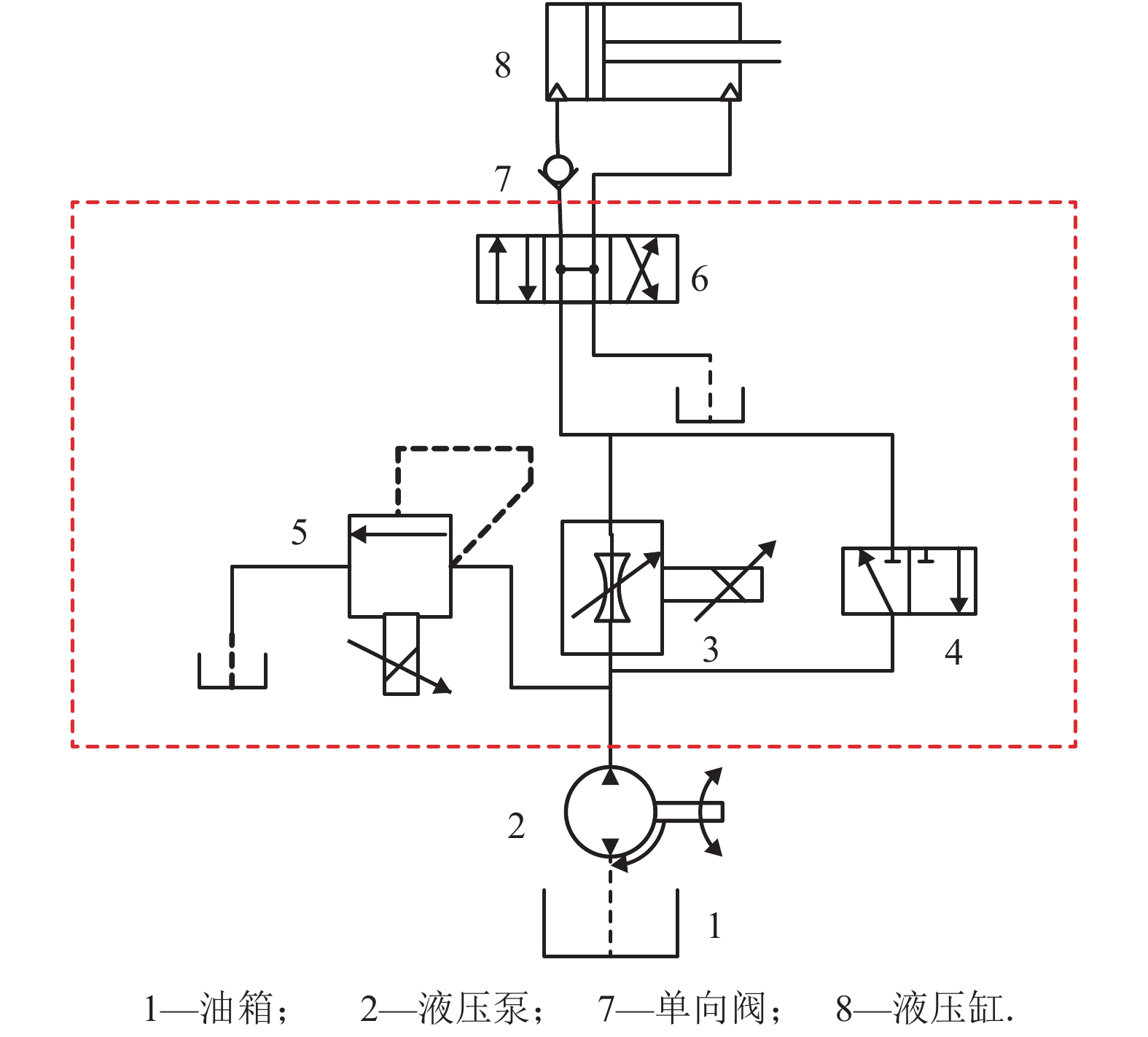
标号 名称 型号 3 比例调速阀 RPCED1-25/T3 4 二位二通换向阀 DS3-TA23/10N 5 比例溢流阀 RPCED10-350/10N-D24K1 6 三位四通换向阀 DS3-S3/10N-D24K1 -
LI X H, YU H B, YUAN M Z, et al. Study on the linear dynamic model of shield TBM cutterhead driving system[C]//IECON 2011: the 37th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2011: 3864-3871. KOYAMA Y. Present status and technology of shield tunneling method in Japan[J]. Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, 2003, 18(2): 145-159. ZHANG K, YU H, LIU Z, et al. Dynamic characteristic analysis of TBM tunnelling in mixed-face conditions[J]. Simulation Modeling Practice and Theory, 2010, 18(7): 1019-1031. doi: 10.1016/j.simpat.2010.03.005 陈炳瑞,冯夏庭,曾雄辉,等. 深埋隧洞TBM 掘进微震实时监测与特征分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(2): 275-283.CHEN Bingrui, FENG Xiating, ZENG xionghui, et al. Deep buried tunnel TBM tunneling microseismic monitoring and real-time characteristics analysis[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(2): 275-283. IBERALL A S. Attenuation of oscillatory pressures in instrument lines[J]. Journal of Research, National Bureau of Standards, 1950, 45(5): 85-108. BROWN F T. The transient response of fluid lines[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1962, 84(4): 547-553. TAYLOR A M, WHITE LAW J H. Curved ducts with strong secondary motion-velocity measurements of developing laminar and turbulent flow[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1982, 104(15): 350-359. 万会雄,黄辉,黄海波. 超长液压管道压力损失的计算与试验分析[J]. 液压与气动,2009,86(10): 23-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4858.2009.10.008WAN Huixiong, HUANG Hui, HUANG Haibo. Super long hydraulic pipe pressure loss calculation and experimental analysis[J]. Journal of Hydraulic and Pneumatic, 2009, 86(10): 23-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4858.2009.10.008 侯占勇. 混凝土泵泵送系统阀块流道的压力损失研究及优化[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2013. 贺尚红,谭文成,何志勇. 复杂液压管网压力脉动特性建模与仿真[J]. 液压与气动,2012,62(9): 156-162.HE Shanghong, TAN Wencheng, HE Zhiyong. The modeling and simulation of complex hydraulic pipe network pressure pulsation characteristics[J]. Journal of Hydraulic and Pneumatic, 2012, 62(9): 156-162. CHAMBON R, CHEVALIER P M, DESCOTTE Y. An expert system for object placing in 3D space[J]. Computer Aided Engineering Journal, 1988(21): 51-59. CHAMBON R, TOLLENAERE M. Automated AI-based mechanical design of hydraulic manifold blocks[J]. Computer Aided Design, 1991, 23(3): 213-222. doi: 10.1016/0010-4485(91)90091-A TOLLENAERE M. Benefits of an object based approach for the development of an intelligent CAD system[J]. Proceedings Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Engineering, 1992(2): 127-135. 田树军,李利,冯毅. 基于计算智能的液压集成块优化设计[J]. 中国机械工程,2003,14(17): 1492-1495. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2003.17.017TIAN Shujun, LI Li, FENG Yi. Based on computational intelligence optimization design of hydraulic manifold blocks[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2003, 14(17): 1492-1495. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2003.17.017 田树军,张宏. 液压管路动态特性的 Simulink 仿真及其应用[J]. 系统仿真学报,2006,18(5): 1136-1138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2006.05.013TIAN Shujun, ZHANG Hong. The dynamic characteristics of hydraulic line Simulink simulation and its application[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2006, 18(5): 1136-1138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2006.05.013 张宏. 基于管网液流特性仿真的液压集成块优化设计[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2006. 张怀亮,彭玲,周井行. TBM液压阀块流道压降特性研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2017,45(9): 34-39, 66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2017.09.005ZHANG Huailiang, PENG Ling, ZHOU Jingxing. Research on pressure drop characteristics of the flow channel in hydraulic valve block for TBM[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(9): 34-39, 66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2017.09.005 -




 下载:
下载: