Localization Algorithm for Mine Wireless Sensor Network Based on Rigid Cluster and Chicken Swarm Optimization
-
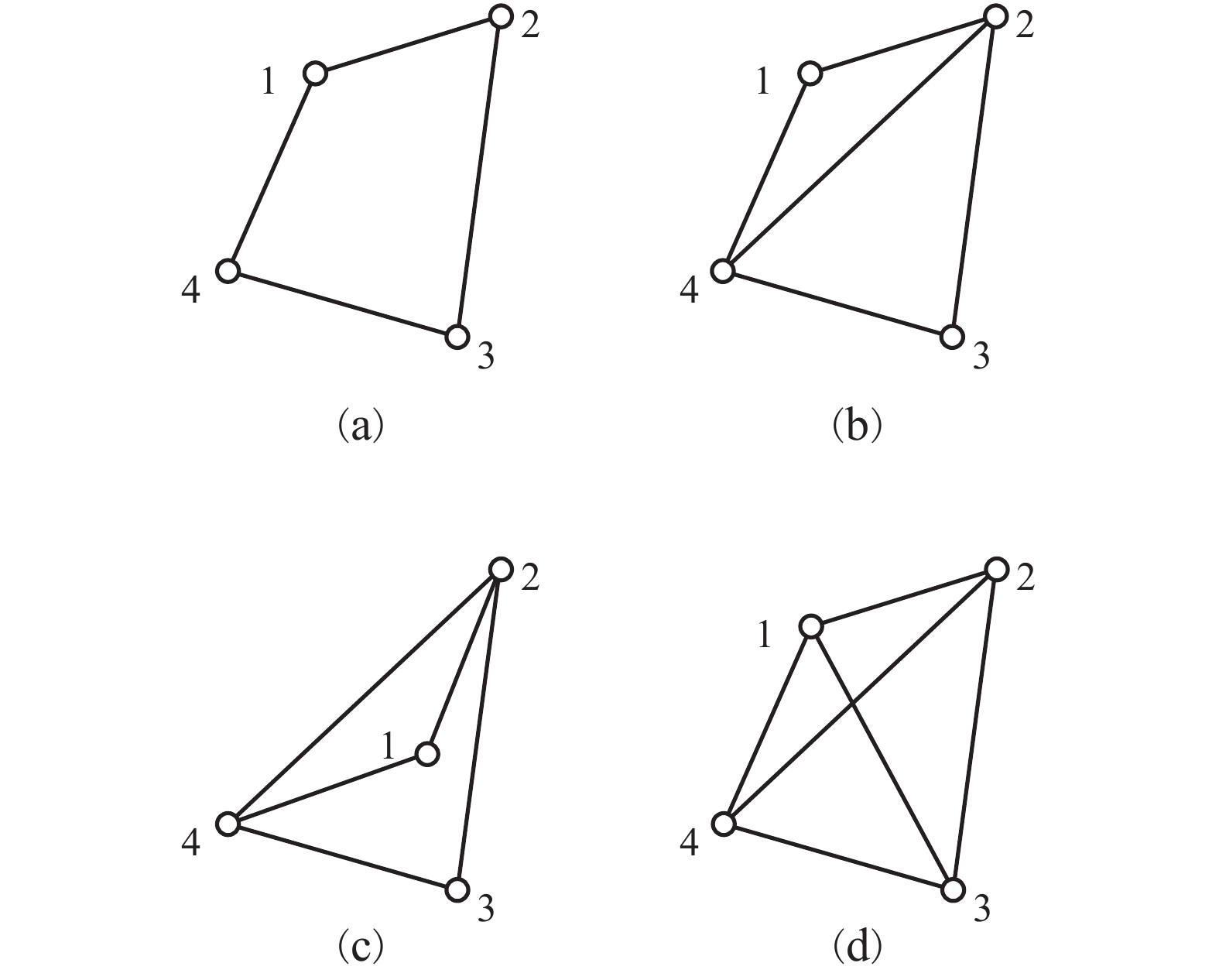
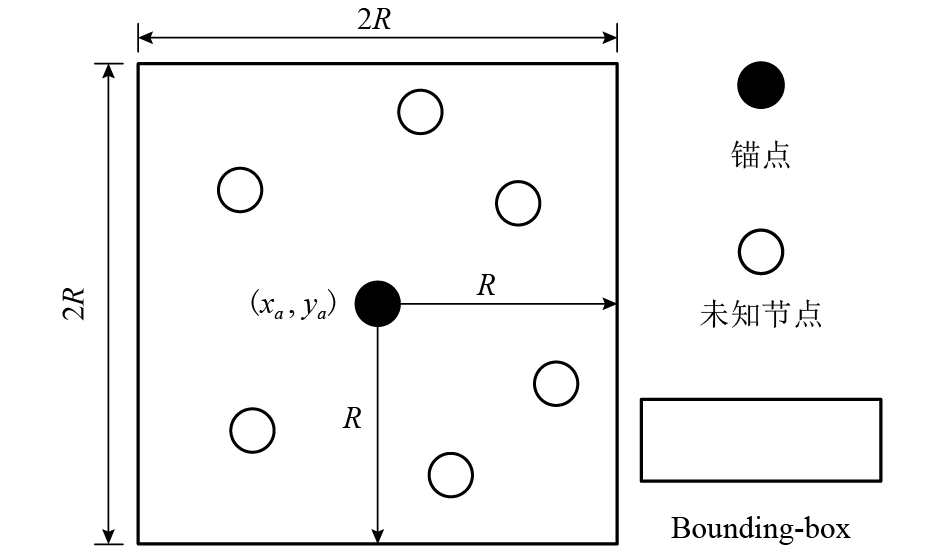
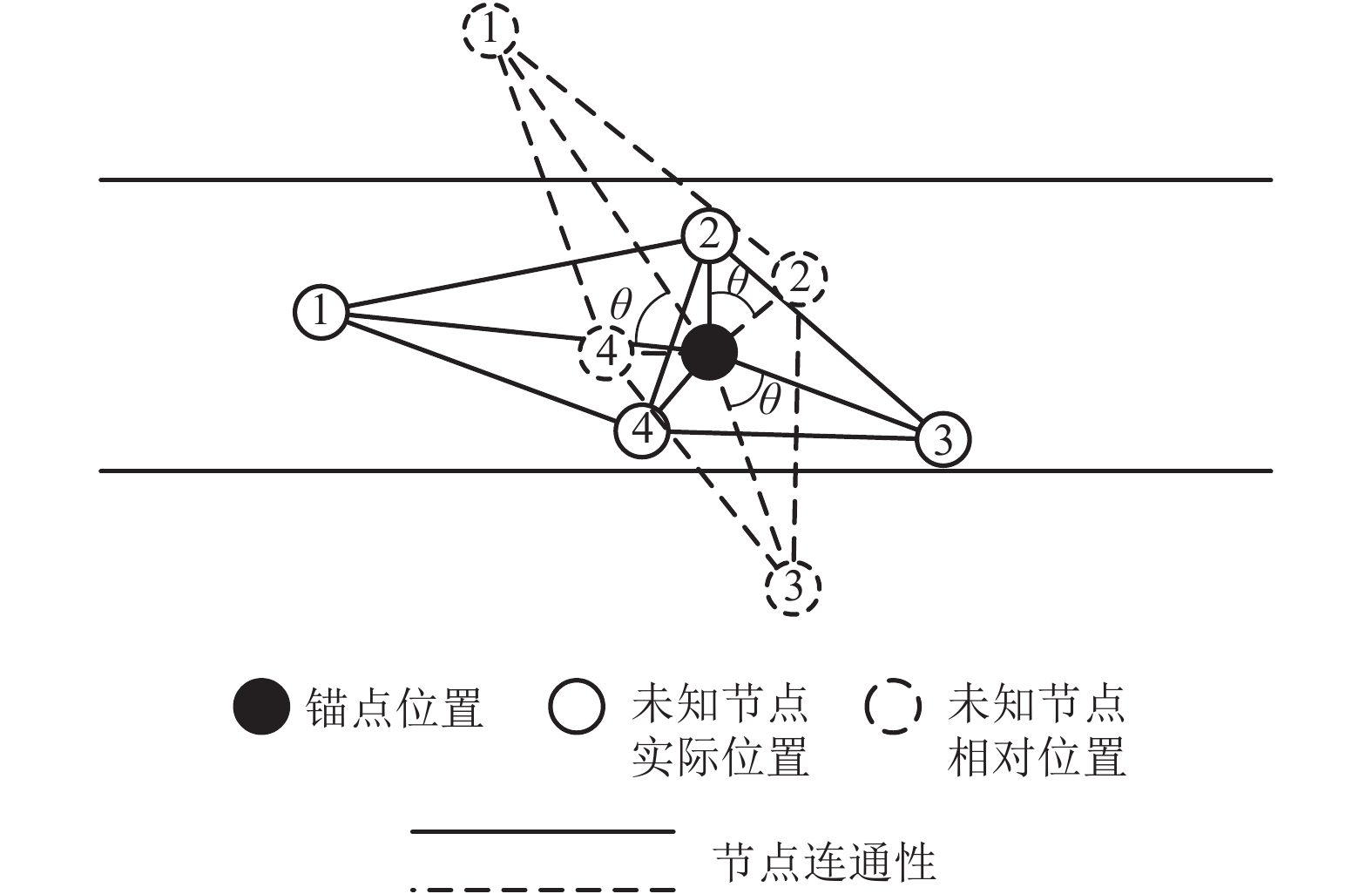
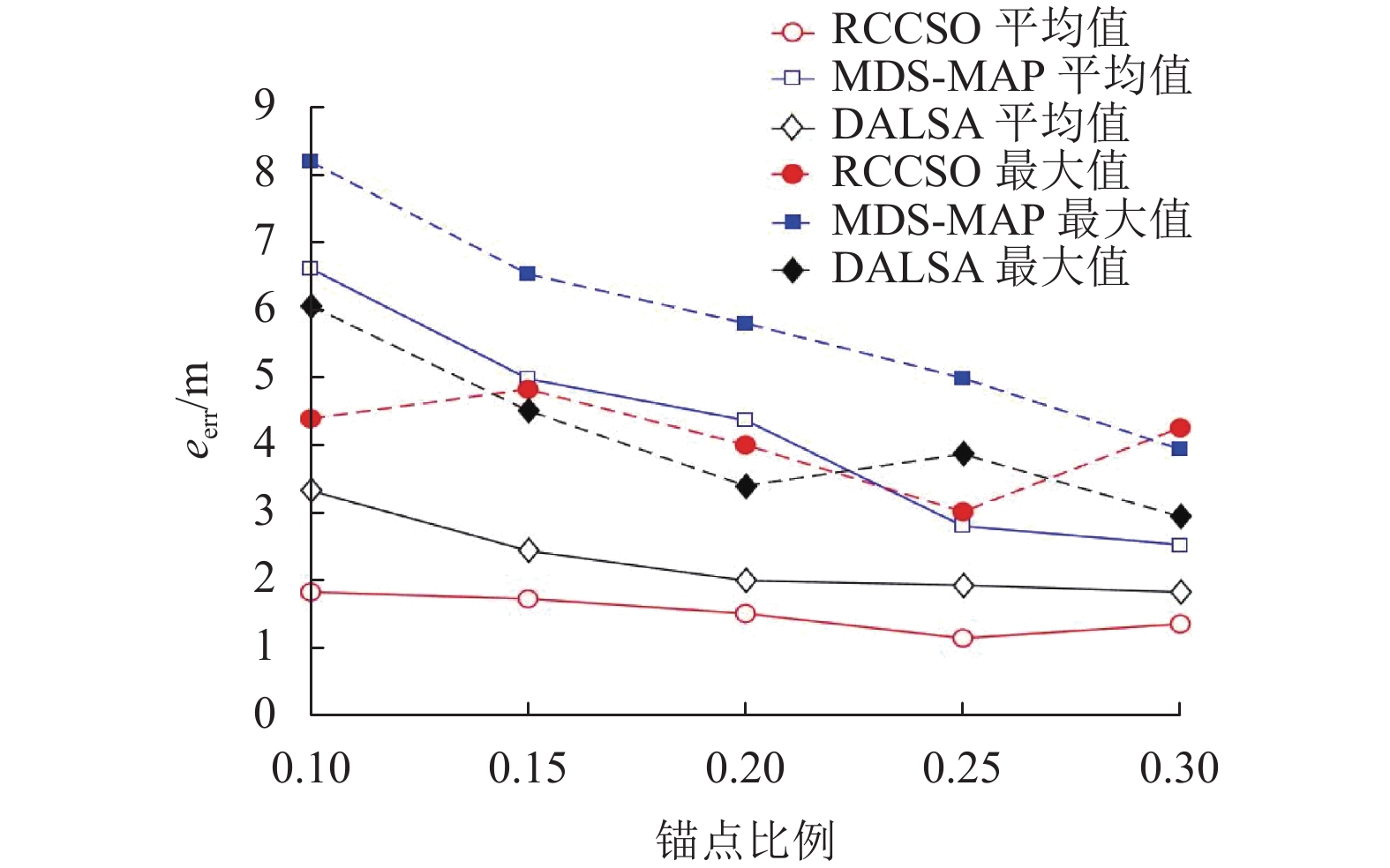
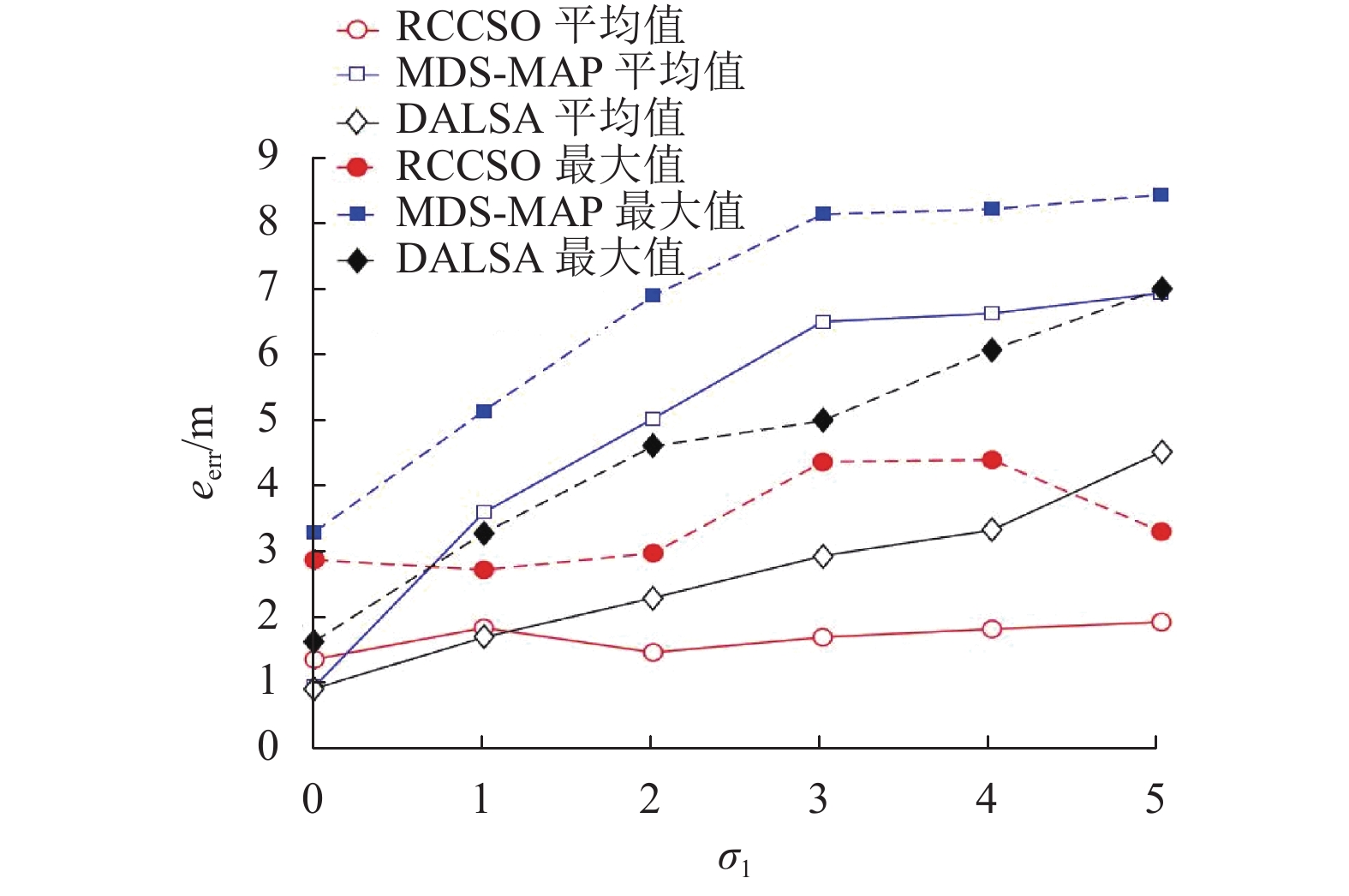
摘要: 针对矿井环境因素对无线传感器网络定位的制约,提出一种基于刚性分簇与鸡群优化的无线传感器网络定位算法(RCCSO). 首先,以传感网络中均匀分布的锚点为簇头,基于刚性图理论提出分簇算法对整个网络进行分簇并保证每个簇都是全局刚性的;其次,利用鸡群算法对簇内进行相对定位,求得簇内最优相对位置解集;再次,不同簇以锚点为旋转中心旋转不同角度,并利用鸡群算法求出旋转角度的最优解集,进而求得全局节点最优位置;最后,仿真结果显示,与多维标度MDS-MAP算法及自适应局部区域循环搜索DALSA相比,所提算法在精度上有较明显的提高.Abstract: In order to adapt to the restrain resulting in environment factor of mine to localization of wireless sensor network, a novel localization algorithm based on rigid cluster and chicken swarm optimization (RCCSO) is proposed. First, the clusters are set up centring on the uniformly distributed anchor nodes, expand the clusters based on rigid theory and get several clusters which are all globally rigid. Second of it, optimize the best relative position of the nodes in the same cluster by chicken swarm optimization, and get the solution sets of relative position. Then, centring on the anchor nodes, all the solution ratate for some different angle, and optimal the best solution set of ratation angles by chicken swarm optimization, and get the globally position of all the unknown nodes. Finally, Simulation comparison demonstrated that the accuracy of the new localization algorithm RCCSO is more precise than the MDS-MAP algorithm and DALSA algorithm.
-
Key words:
- wireless sensor network /
- mine localization /
- rigid cluster /
- chicken swarm optimization
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters of simulation
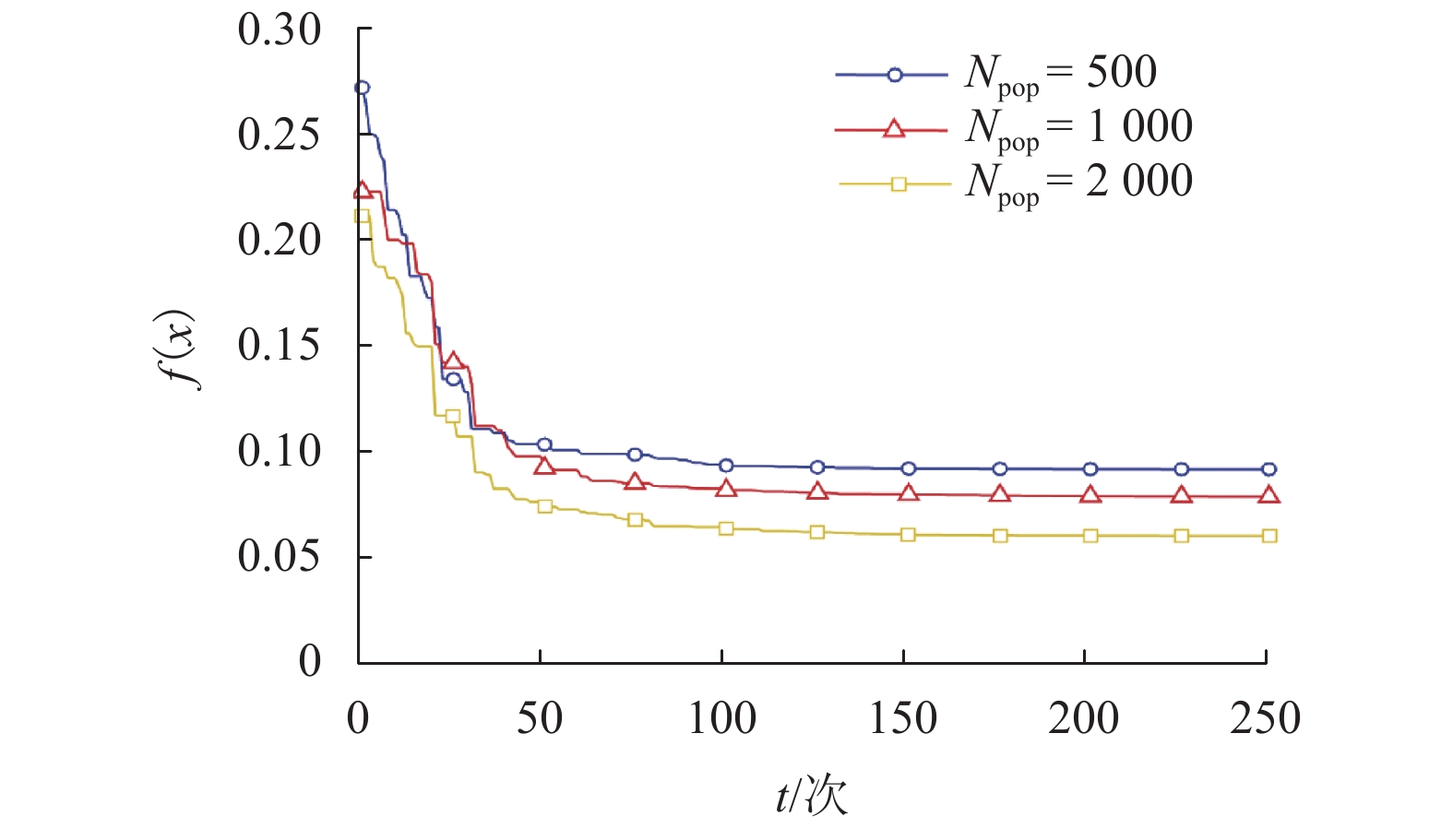
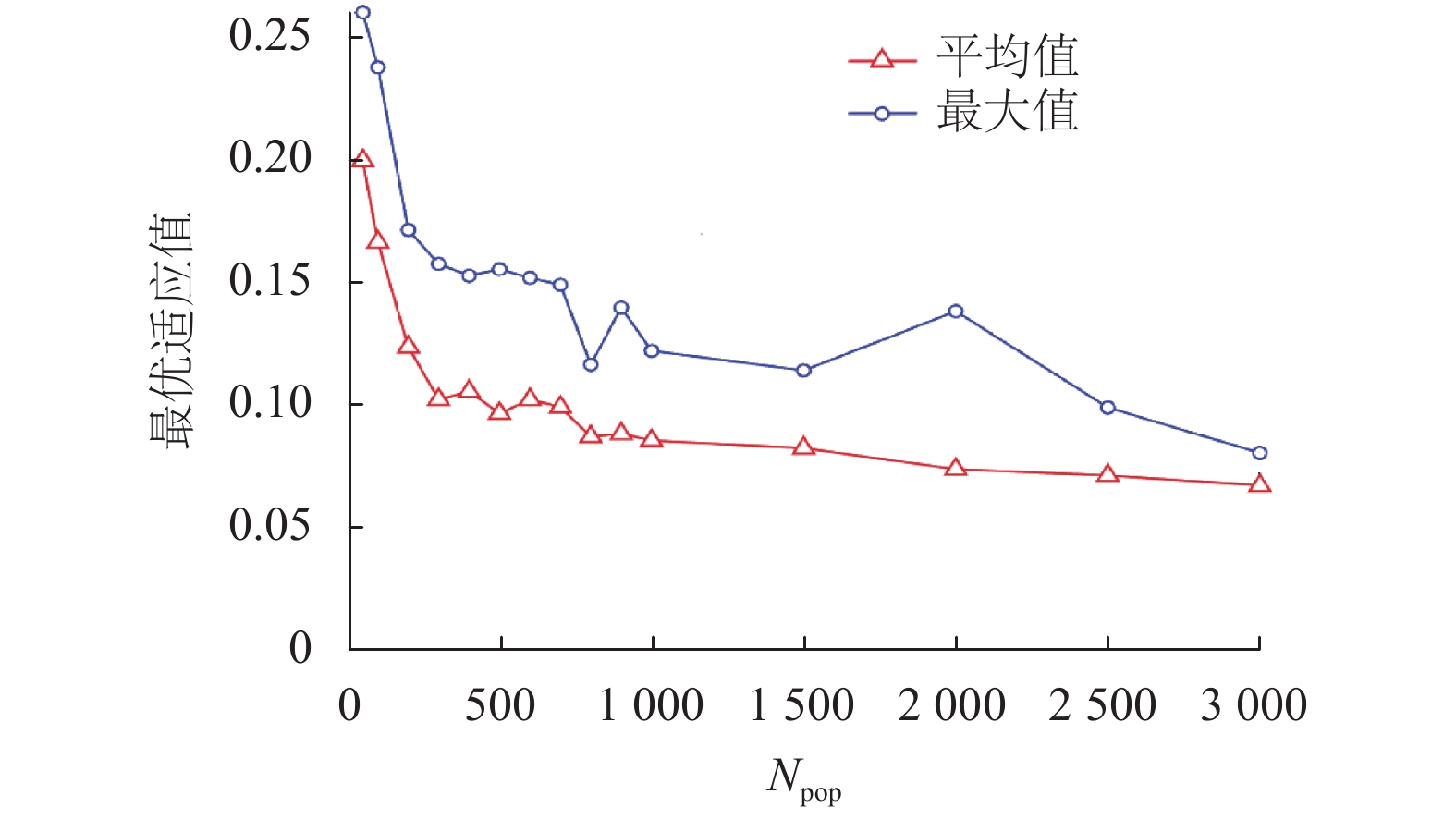
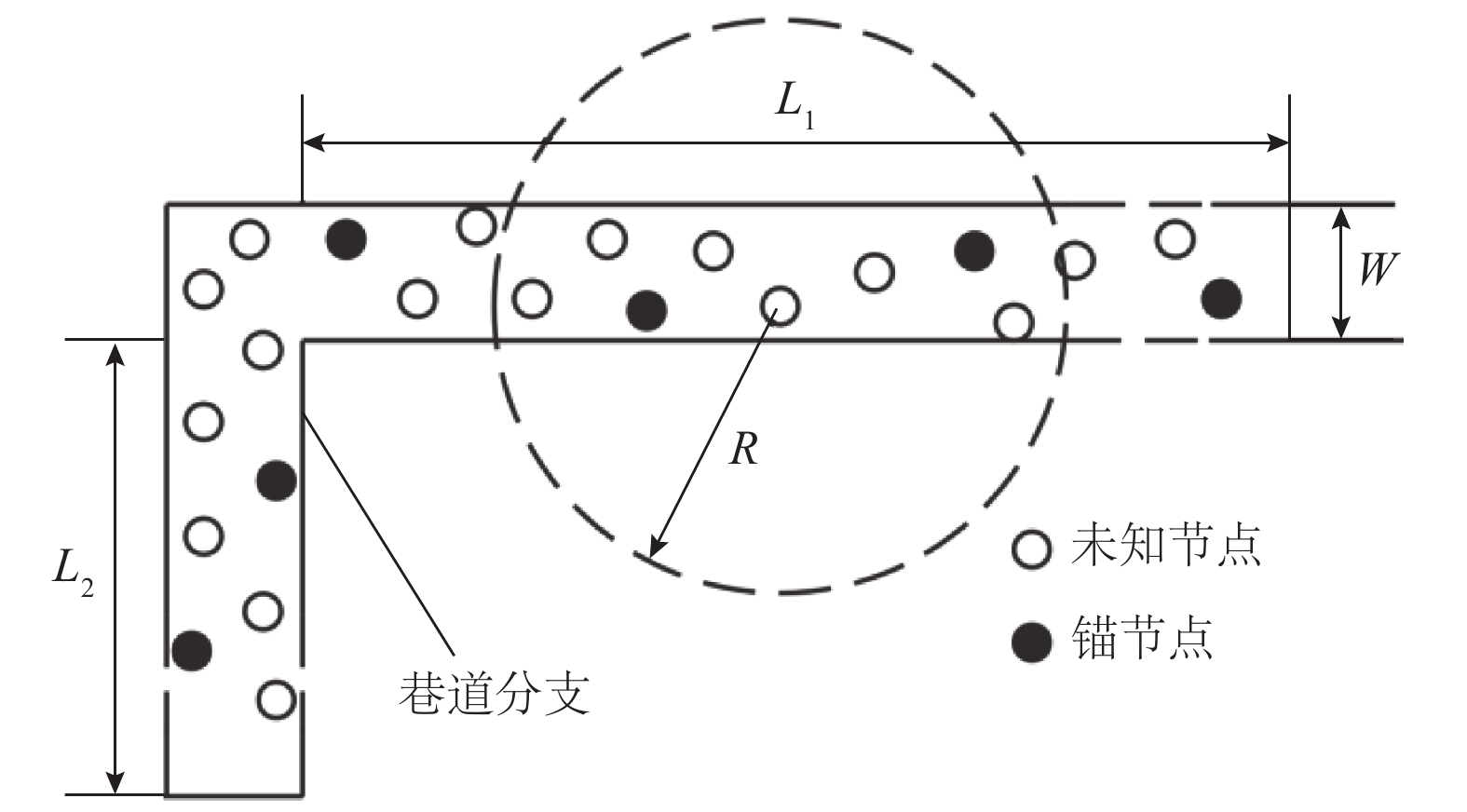
符号 含义 设定值 L1/m 巷道 1 长度 200 L2/m 巷道 2 长度 100 W/m 宽度 5 N 节点总数量 60 m/N 锚点比例 0.1~0.3 R/m 通信半径 25 IRSS(d0)/dBm d0 = 1 m 处 IRSS 值 –45 η IRSS 测距参数 4 σ1 IRSS 实际偏离标准差 0~5 tmax 最大轮次 100 Npop 鸡群中鸡的总数量 50~3 000 NR 公鸡比例 0.2 NH 母鸡比例 0.4 NC 小鸡比例 0.4 NM 鸡妈妈比例 0.4 ε RCCSO 设定参数 0.001 $\phi $ RCCSO 设定参数 0.5 -
HUANG Linqi, LI Xibing, DONG Longjun, et al. Relocation method of microseismic source in deep mines[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(11): 2988-2996. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64429-1 邓平,伍小梅. 一种基于粒子滤波的WSN自适应定位算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(2): 323-329. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.02.021DENG Ping, WU Xiaomei. An adaptive localization algorithm based on particle filter for wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(2): 323-329. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.02.021 BOUBRIMA A, BECHKIT W, RIVANO H. Optimal WSN deployment models for air pollution monitoring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(5): 2723-2735. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2658601 MARQUES B, RICARDO M. Energy-efficient node selection in application-driven WSN[J]. Wireless Networks, 2017, 23(3): 889-918. doi: 10.1007/s11276-016-1194-2 HAN S, GONG Z, MENG W, et al. Automatic precision control positioning for wireless sensor network[J]. Sensors Journal IEEE, 2016, 16(7): 2140-2150. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2506166 蒋伊琳,张芳园. 基于自然选择粒子群的时钟同步算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(3): 593-599. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.03.021JIANG Yilin, ZHANG Fangyuan. Clock synchronization algorithm based on particle swarm optimization with natural selection[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(3): 593-599. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.03.021 VANHEELl F, VERHAEVERT J, LAERMANS E, et al. Pseudo-3D RSSI-based WSN localization algorithm using linear regression[J]. Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing, 2015, 15(9): 1342-1354. 裴忠民,李贻斌,徐硕. 大规模无线传感器网络快速定位算法[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2013,42(2): 314-319.PEI Zhongmin, LI Yibin, XU Shuo. A fast localization algorithm for large-scale wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2013, 42(2): 314-319. 夏娜,王诗良,郑榕,等. 基于骨架提取的水下传感器网络刚性定位判别研究[J]. 计算机学报,2015,38(3): 589-601.XIA Na, WANG Shiliang, ZHENG Rong, et al. Study on localizablity judgement in underwater sensor networks based on skeleton extrication and rigid theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(3): 589-601. BOUKERCHE A, OLIVEIRA H A B F, AKAMURA E F, et al. A Voronoi approach for scalable and robust DV-Hop localization system for sensor networks[C]// International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks. [S.L.]: IEEE, 2017: 497-502 ZHAGN R, ZHOU F, RAN L, et al. A fuzzy graph theory based redundant node deployment algorithm for multi-hop WSN[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2011, 21(3): 223-227. 尚俊娜,刘春菊,岳克强,等. 基于改进双系统协同进化算法的无线传感器网络节点定位[J]. 计算机应用,2015,35(6): 1514-1518.SHANG Junna, LIU Chunju, YUE Keqiang, et. al. WSN nodes localization based on improved bi-system cooperative optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer Application, 2015, 35(6): 1514-1518. HERNANDEZ O O S, COTA-RUIZ J, GONZALEZ-LANDAETA R, et al. A distributed adaptive local searching algorithm for wireless sensor network localization[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2016, 12(10): 1-9. SHAYOKH M A, SHIN S Y. Bio inspired distributed WSN localization based on chicken swarm optimization[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2017, 97(4): 5691-5706. doi: 10.1007/s11277-017-4803-1 -




 下载:
下载: