Analysis of Required Separation Distances of High-Pier Bridges Subjected to Non-stationary Ground Motions
-
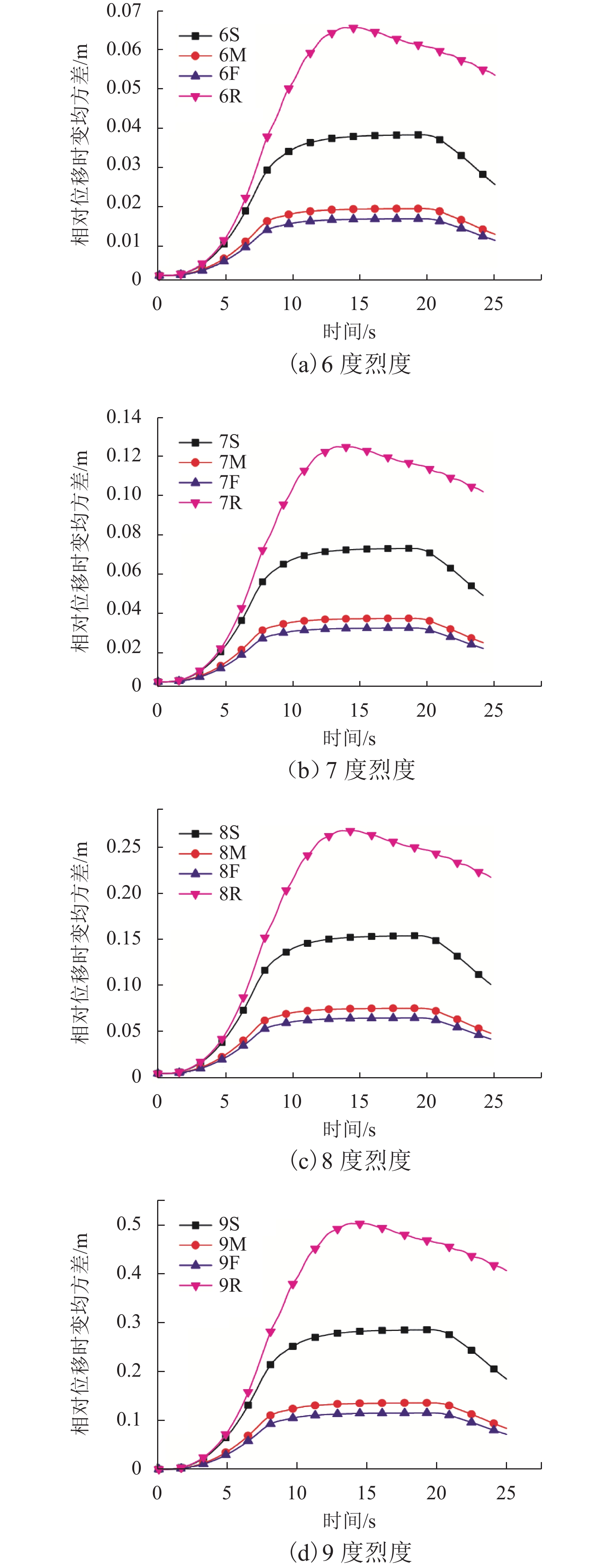
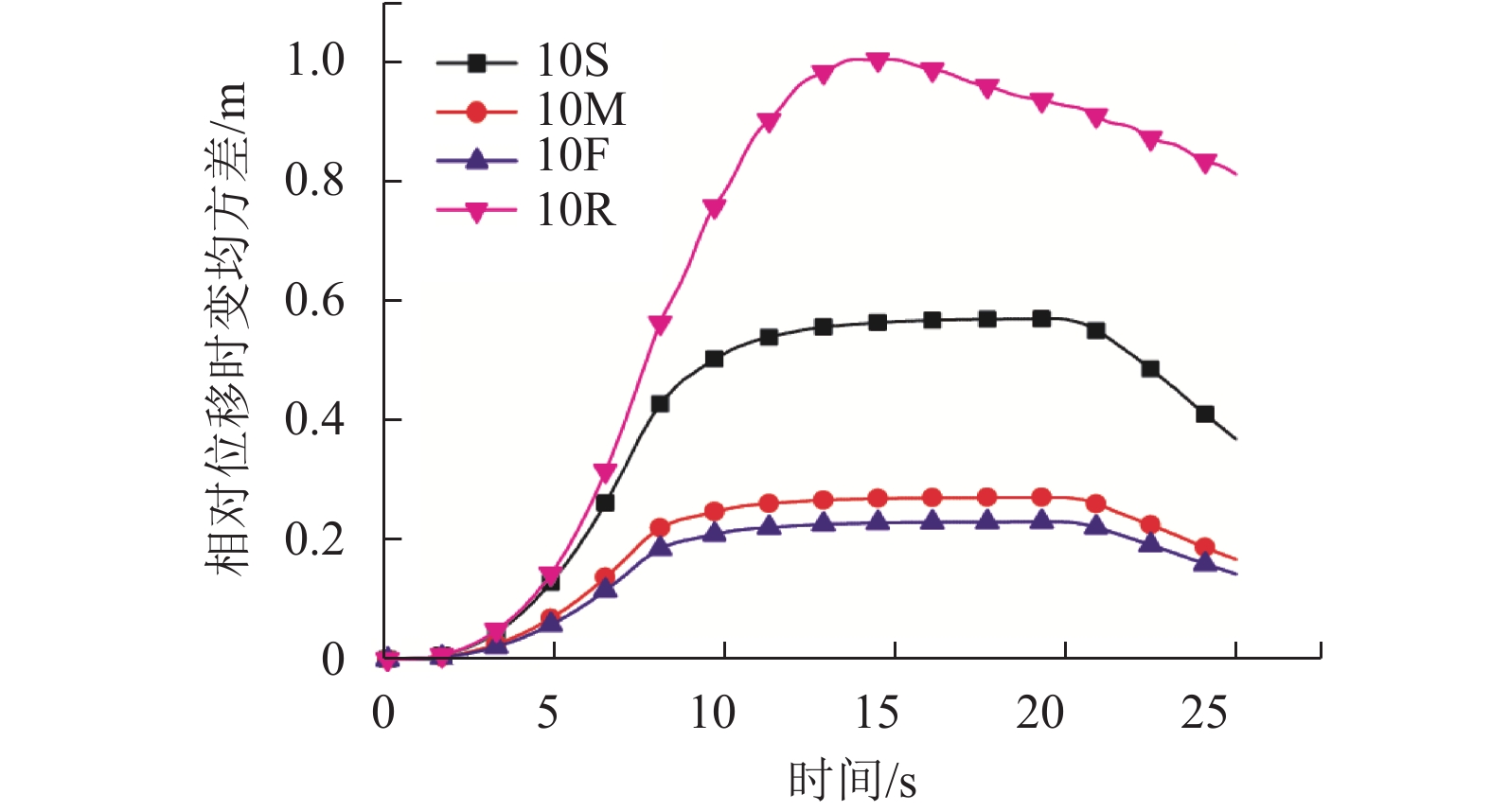
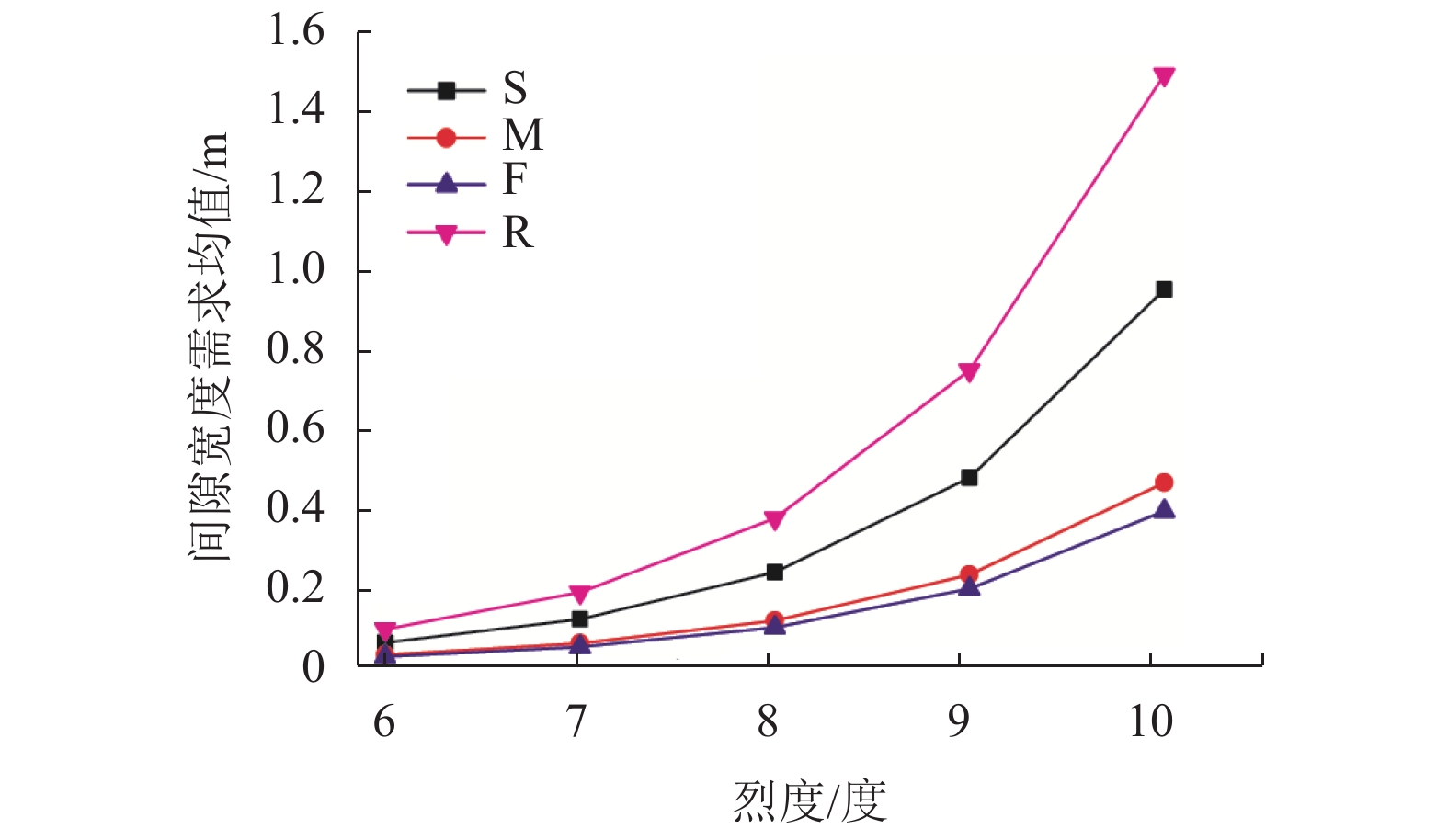
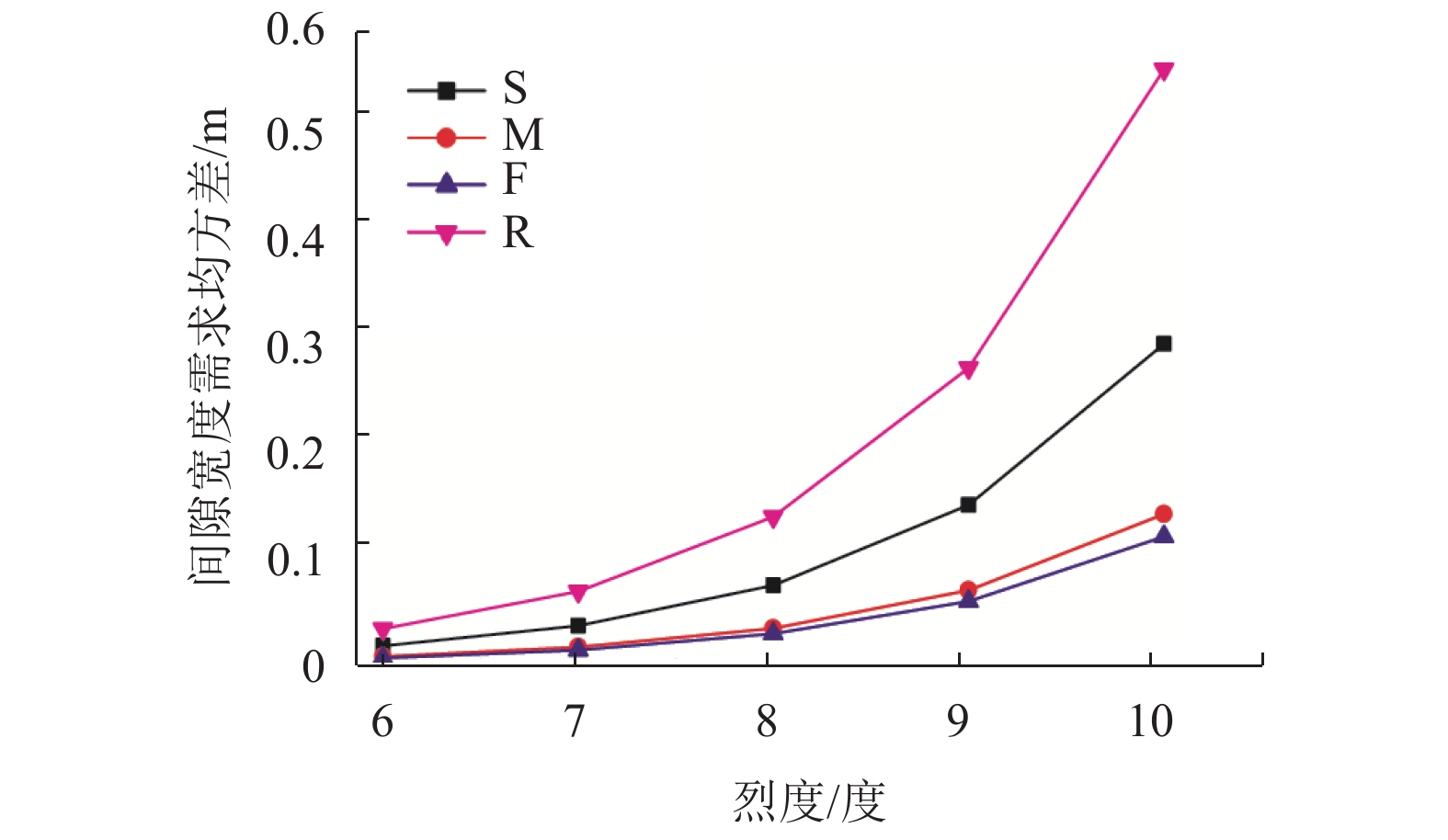
摘要: 为了研究非平稳地震作用下高墩桥梁体防撞间隙需求,基于随机振动理论及虚拟激励法,对不同烈度下场地条件对非平稳间隙需求的影响进行了分析. 首先,建立了非平稳地震作用下相邻梁体相对位移需求与烈度间的数学关系;其次,基于理论计算的梁体间最大相对位移,确定碰撞间隙宽度需求以达到防止梁体间发生碰撞的目的;最后,以某大跨度连续刚构-连续梁体系为实际工程算例,研究了非平稳地震作用下桥梁结构在一致场地和非一致场地(实际场地)条件下的碰撞间隙需求量,且获得了不同烈度下非平稳碰撞间隙需求谱. 研究结果表明:非平稳地震作用下,硬土场地条件时,相对位移时变均方差的峰值最小,实际场地条件最大,约为硬土场地的4倍;实际场地条件的各烈度下非平稳碰撞间隙宽度需求均值比软土场地、中土场地和硬土场地分别大36%、69%和73%,均方差分别大45%、74%和78%;平稳地震激励比非平稳地震激励时碰撞间隙需求量大20%~30%.Abstract: To investigate the influence of non-stationary ground motions on required separation distances, the influence of site conditions on non-stationary gap under different intensities was analysed based on the random vibration theory and pseudo excitation method. First, the mathematical formulation clarifying the relationship between the required relative displacement and earthquake intensity was derived. Second, the minimum gap required between two adjacent girds to prevent seismic pounding was determined from the maximum relative displacement based on theoretical analysis. Finally, a real continuous rigid bridge was used to obtain the required gap length spectrum between two adjacent decks for considering non-stationary seismic excitations with different intensities under different local site conditions. Furthermore, the influence of actual site conditions and uniform site conditions on the required separation distance was investigated. Numerical results reveal that actual site conditions have the most obvious effect on the time-dependent mean square deviation of relative peak displacement, which is four times the corresponding value for firm site conditions. The mean values of the required separation distance for different intensities are larger than the corresponding values for uniform site conditions by 36%, 69%, and 73% for soft sites, median sites, and firm sites, respectively, whereas the mean square deviation is 45%, 74%, and 78%, respectively. The required separation distance under stationary seismic excitations is 20%–30% larger than that under non-stationary seismic excitations.
-
表 1 3类场地类型参数
Table 1. Type parameters for three sites
场地类型 ${\omega _{\rm{g}}}$ ${\xi _{\rm{g}}}$ ${\omega _{\rm{f}}}$ ${\xi _{\rm{f}}}$ 硬土 15.0 0.6 1.5 0.6 中土 10.0 0.4 1.0 0.6 软土 5.0 0.2 0.5 0.6 表 2 地震动强度比例因子
Table 2. Scale factor of ground motion intensity
场地类型 烈度/度 6 7 8 9 10 硬土 3.69 14.77 59.08 236.31 945.13 中土 3.97 15.89 63.53 254.07 1 016.17 软土 5.22 20.87 83.45 333.76 1 334.86 表 3 墩底工况分析
Table 3. Analysis of pier bottom condition
工况编号 烈度/度 1# 墩 2# 墩 3# 墩 4# 墩 5# 墩 6S 6 S S S S S 6M 6 M M M M M 6F 6 F F F F F 6R 6 M S F M S 7S 7 S S S S S 7M 7 M M M M M 7F 7 F F F F F 7R 7 M S F M S 8S 8 S S S S S 8M 8 M M M M M 8F 8 F F F F F 8R 8 M S F M S 9S 9 S S S S S 9M 9 M M M M M 9F 9 F F F F F 9R 9 M S F M S 10S 10 S S S S S 10M 10 M M M M M 10F 10 F F F F F 10R 10 M S F M S -
李乔, 赵世春. 汶川大地震工程震害分析[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2008: 18-27 KAWASHIMA K, UNJOH S, HOSHIKUMA J, et al. Damage of bridges due to the 2010 Maule,Chile,earthquake[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 2011, 15(7): 1036-1068 CHOUW N, HAO H. Pounding damage to buildings and bridges in the 22 February 2011 Christchurch earthquake[J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2012, 2(3): 123-140 HE L, SHRESTHA B, HAO H, et al. Experimental and three-dimensional finite element method studies on pounding responses of bridge structures subjected to spatially varying ground motions[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2017, 20(1): 105-124 doi: 10.1177/1369433216646009 HAO H. A parametric study of the required seating length for bridge decks during earthquake[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2015, 27(1): 91-103 RUANGRASSAMEE A, KAWASHIMA K. Relative displacement response spectra with pounding effect[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2001, 30(10): 1511-1538 白凤龙. 空间变化地震动激励下大跨度结构的反应研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2010 CHOUW N, HAO H. Significance of SSI and non-uniform near-fault ground motions in bridge response I:effect on response with conventional expansion joint[J]. Engineering Structures, 2008, 30(1): 141-153 CHOUW N, HAO H. Significance of SSI and non-uniform near-fault ground motions in bridge response II:effect on response with modular expansion joint[J]. Engineering Structures, 2008, 30(1): 154-162 李忠献,周莉,岳福青. 地震动空间效应与土-基础相互作用效应对隔震桥梁临界碰撞间隙的影响[J]. 土木工程学报,2010,43(7): 85-90LI Zhongxian, ZHOU Li, Yue Fuqiang. Effects of spatial variation of ground motion and siol-foundation interaction on critical pounding gap length of seismic isolated bridges[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering, 2010, 43(7): 85-90 李忠献,岳福青,周莉,等. 基于随机振动理论确定桥梁地震碰撞的临界间隙[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2006,26(4): 156-161LI Zhongxian, YUE Fuqing, ZHOU Li, et al. Determination of critical gap length of seismic pounding for bridges based on random vibration theory[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2006, 26(4): 156-161 BI K, HAO H, CHOUW N. Influence of ground motion spatial variation,site condition and SSI on the required separation distances of bridge structures to avoid seismic pounding[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2011, 40(9): 1027-1043 贾宏宇,杜修力,李晰,等. 地震作用下高墩铁路桥梁梁体碰撞间隙宽度需求机理分析[J]. 工程力学,2017,34(2): 207-215JIA Hongyu, DU Xiuli, LI Xi, et al. Demand mechanism analysis on pounding separation distance of high pier railway bridges subjected to earthquake excitations[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34(2): 207-215 JIA H Y, ZHANG D Y, ZHENG S X, et al. Local site effects on a high-pier railway bridge under tridirectional spatial excitations:Nonstationary stochastic analysis[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2013, 52(6): 55-69 doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2013.05.001 RUIZ P, PENZIEN J. Probabilistic study of the behavior of structures during earthquake[Z]. University of California, Berkeley: Earthquake Engineering. Research Center, 1969 ZHANG D Y, JIA H Y, ZHENG S X, et al. A highly efficient and accurate stochastic seismic analysis approach for structures under tridirectional nonstationary multiple excitations[J]. Computers & Structures, 2014, 145(C): 23-35 LIN J, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y. Accurate and highly efficient algorithms for structural stationary/non-stationary random responses[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2001, 191(1): 103-111 doi: 10.1016/S0045-7825(01)00247-X DAVENPORT A G. Note on the distribution of the largest value of a random function with application to gust loading[J]. Process Institute Civil Engineering, 2015, 28(2): 187-196 江近仁,洪峰. 功率谱与反应谱的转换和人造地震波[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,1984,4(3): 1-11JIANG Jinren, HONG Feng. Conversion between power spectrum and response spectrum and artificial earthquakes[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 1984, 4(3): 1-11 -




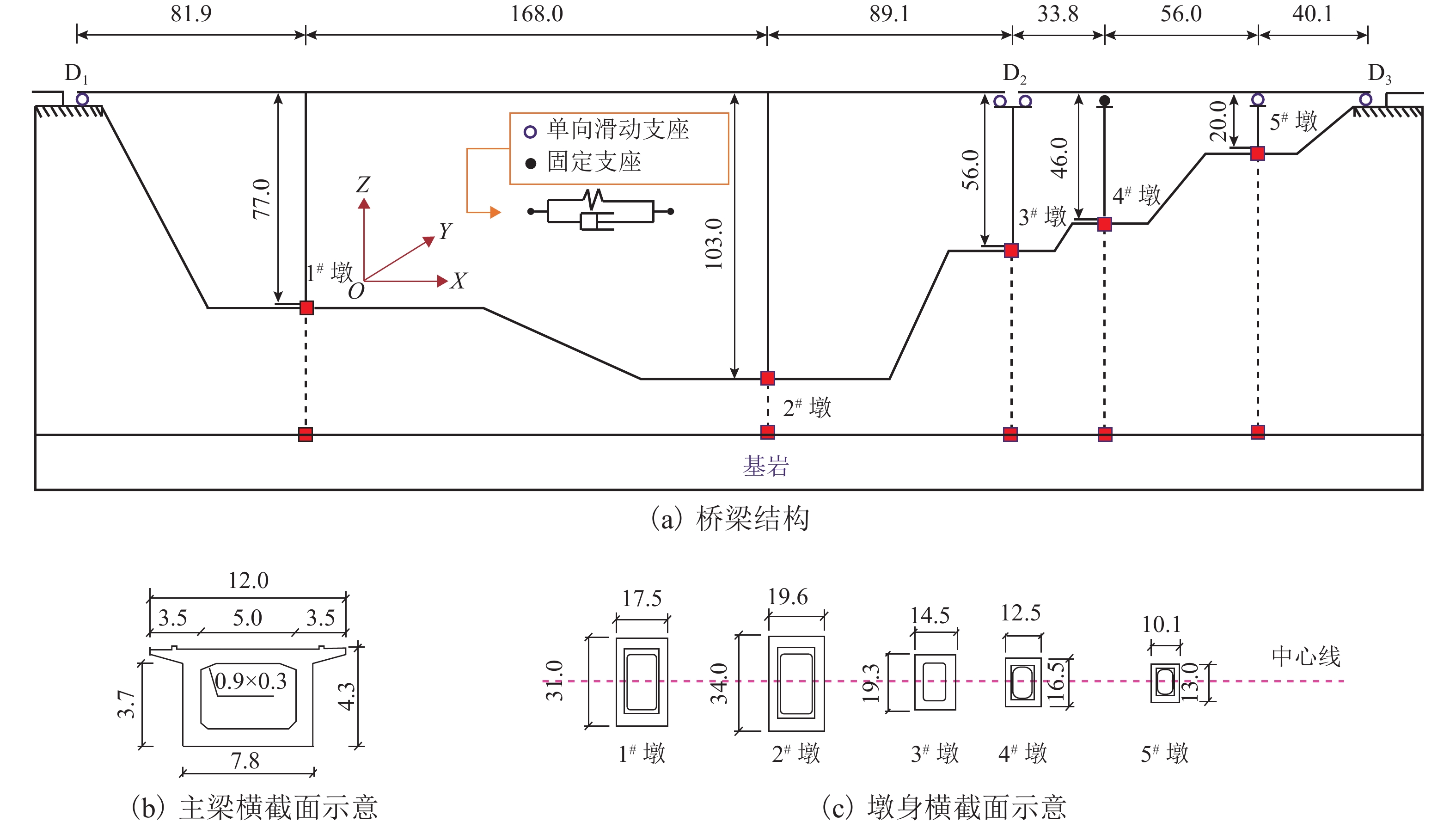
 下载:
下载: