System Dynamics Analysis Method of Evolutionary Game Dynamics for Supervision of High-Speed Railway Operation Safety
-
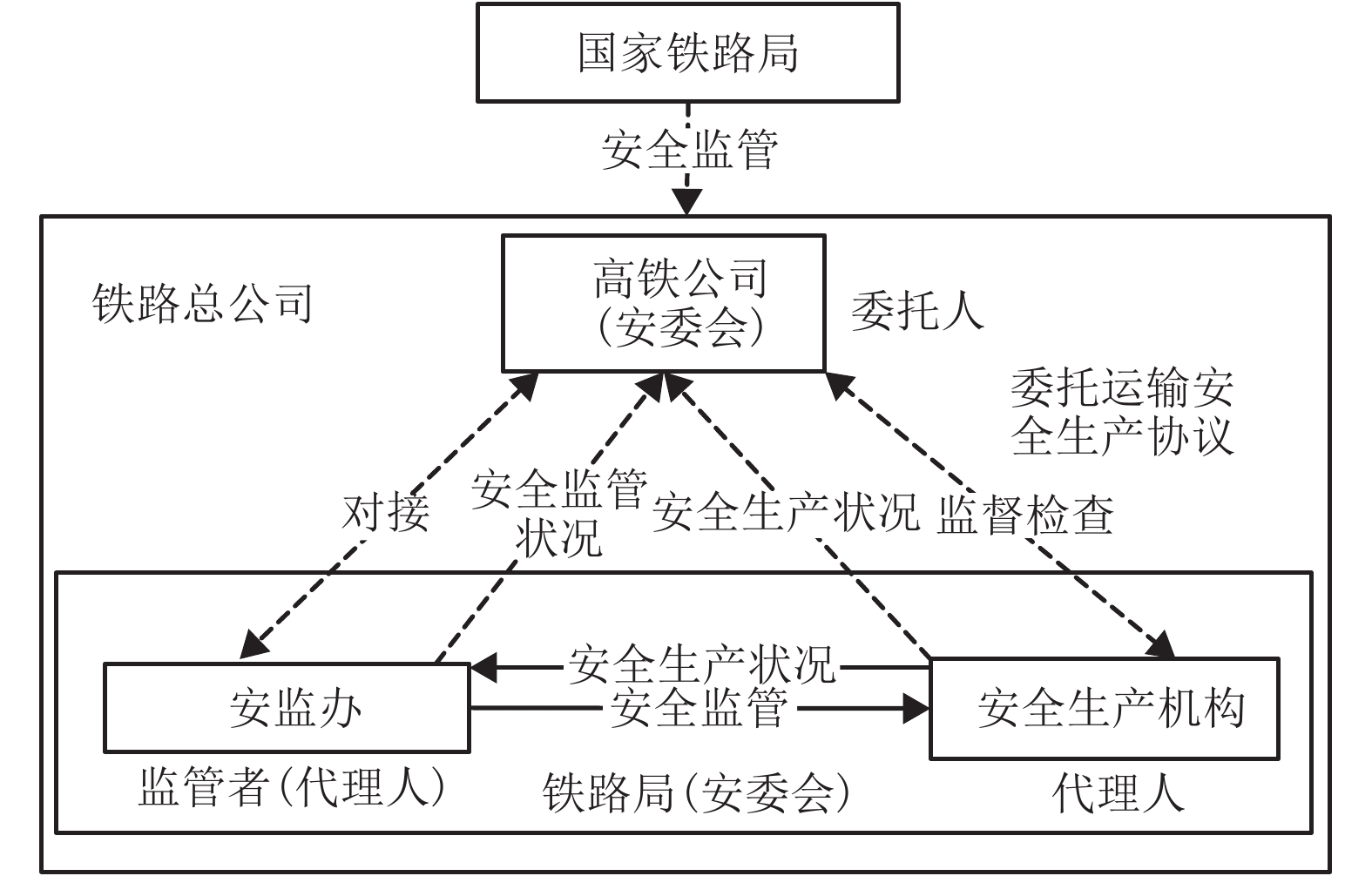
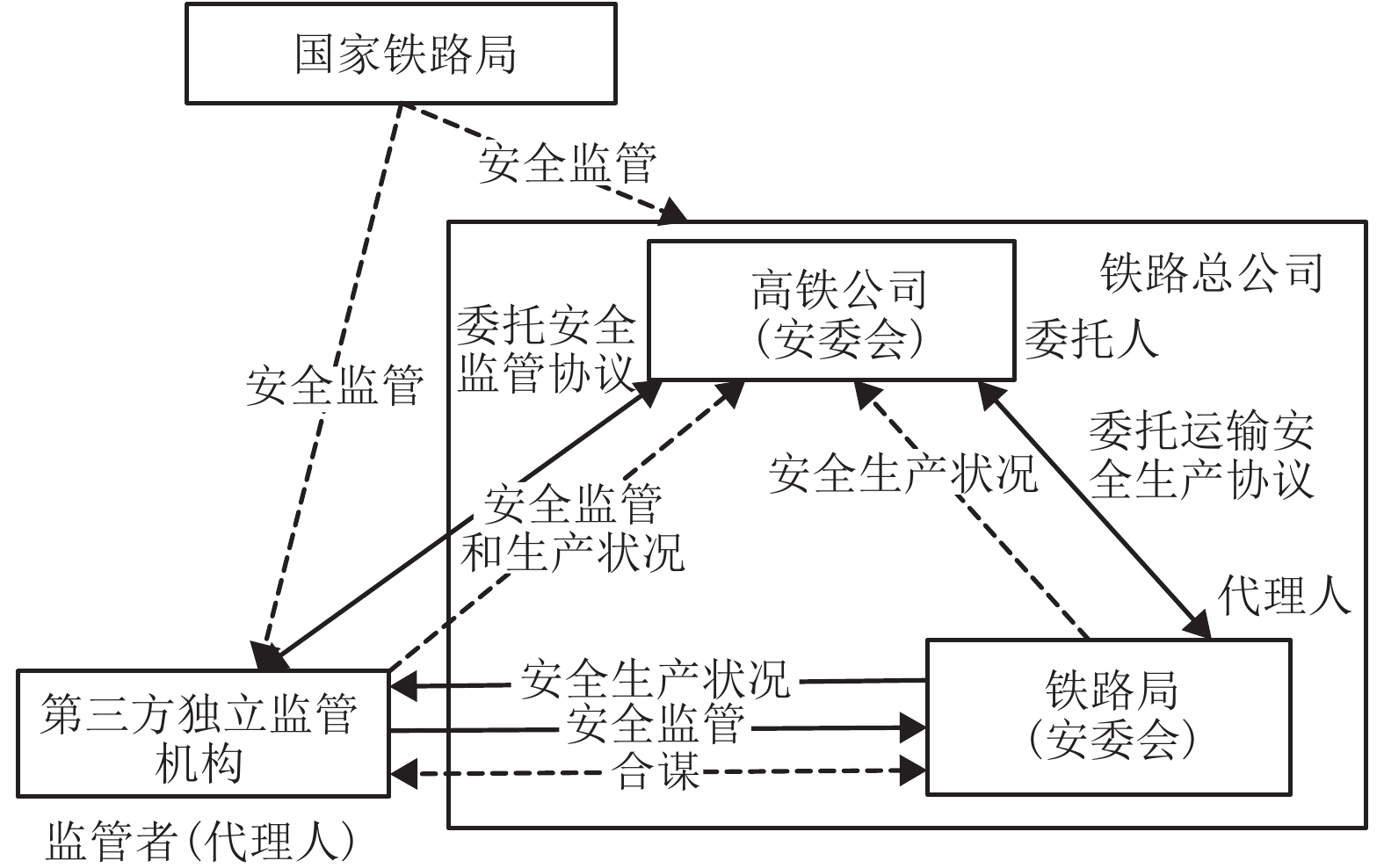
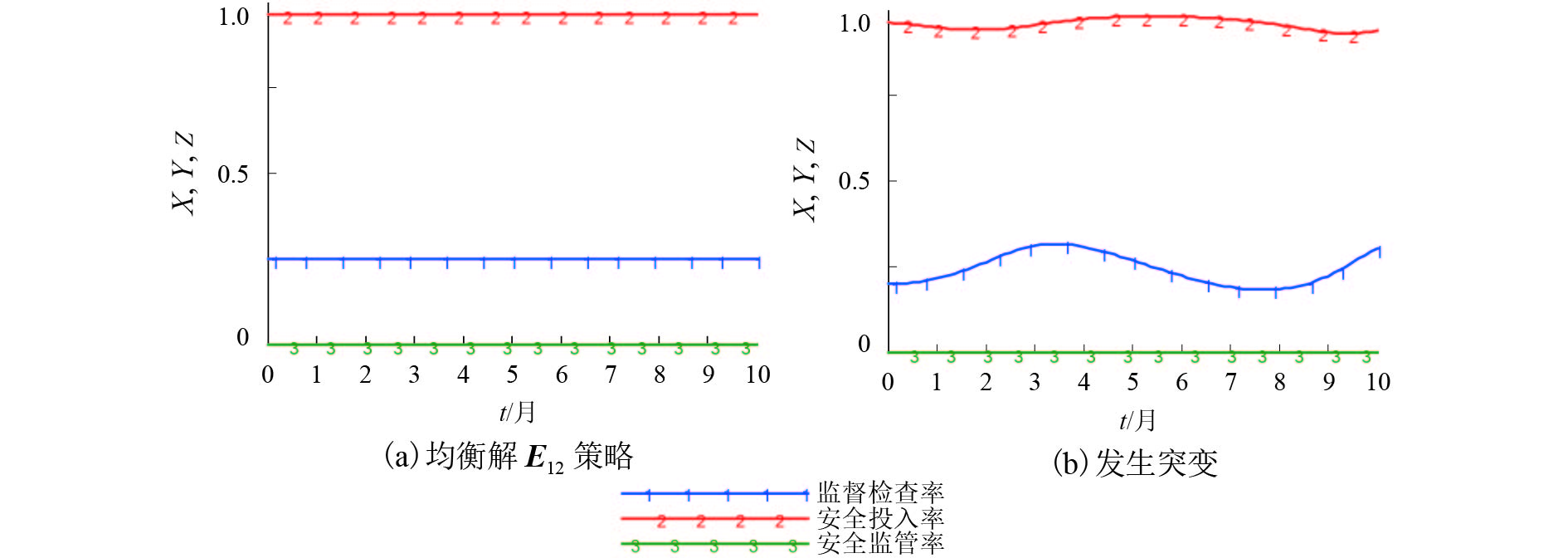
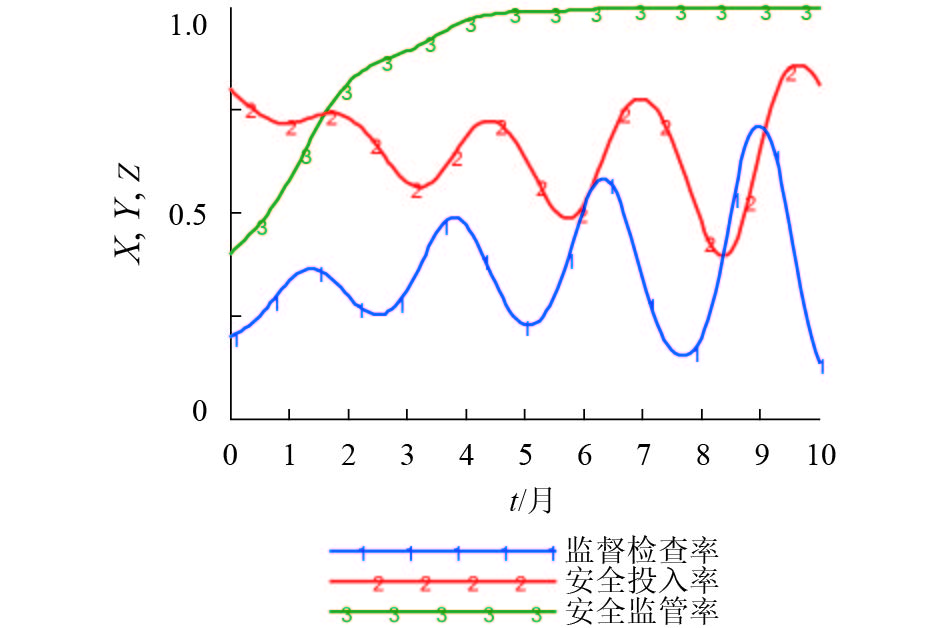
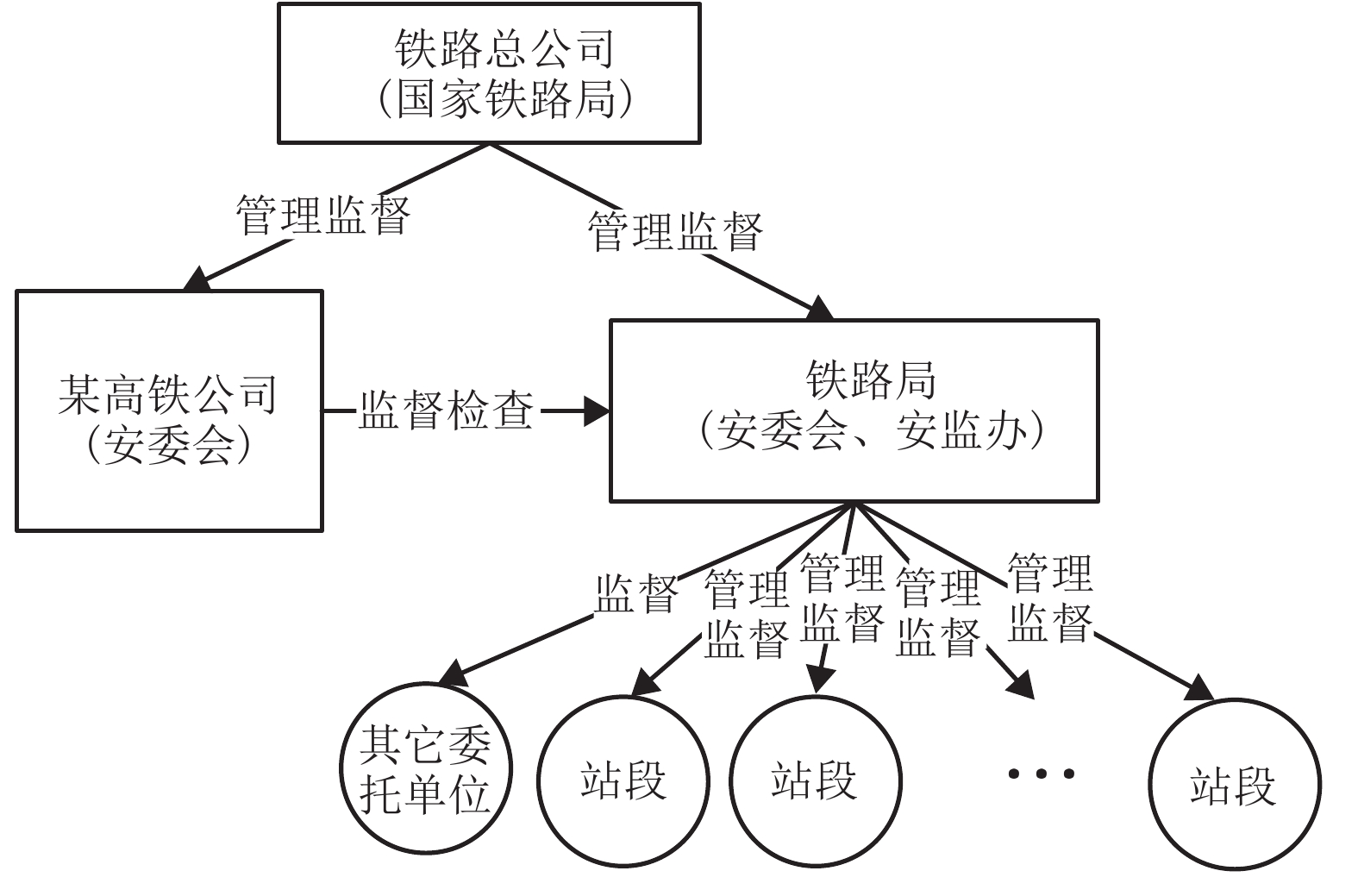
摘要: 针对我国高速铁路委托运输管理模式下,高铁运营安全监督系统存在监管机构不独立和考核奖惩措施不明确的问题,建立了高铁运营安全监督系统演化博弈模型. 该模型是通过分析系统现状和委托代理模式,基于增强高铁公司主体地位和权威性的优化假设条件下建立的,由高铁公司、第三方监管机构和委托路局三方组成,并通过演化博弈理论证明,结合系统动力学(system dynamic,SD)仿真,可以揭示高铁运营安全监督系统博弈各方进行决策的行为特征及其稳定状态. SD仿真结果表明:该模型的8个纯策略均衡解和2个混合策略均衡解都不是演化稳定策略均衡,在任意非均衡解初始策略下,高铁公司和委托路局的博弈演化过程虽然都出现了波动,但第三方监管机构的安全监管率将始终向实时监管的状态演化,说明通过引入第三方独立监管机构和明确安全监督检查考核奖惩措施,可以有效提高高铁运营安全监督系统的安全监管率.Abstract: On the issue of no-incentive restraint mechanism and the regulator not independent in the entrusted transportation management model of high-speed railways (HSR) in China, an evolutionary game model of the HSR operation safety supervision system has been established through the analysis of the current situation and principal-agent model of the system based on the optimization assumptions that enhance the status and authority of the HSR company. The system was composed of the HSR company, a third-party regulatory agency (RA), and commissioned railway bureau (RB). The results of the evolutionary game theory combined with system dynamics (SD) simulation revealed the behavioural characteristics and steady-state decision-making by the three parties in the system. The SD simulation results showed that eight pure strategy equilibrium solutions and two mixed strategy equilibrium solutions of the model did not comply with the evolutionary stable strategy. Under the initial strategy of any non-equilibrium solution, the game evolution process of both the HSR company and commissioned RB continually fluctuate; however, the safety regulation rate of the RA will always evolve towards the state of real-time supervision, indicating that the introduction of an independent third-party RA and a clear incentive restraint mechanism can improve the safety regulation rate of the HSR operations safety supervision system effectively.
-
Key words:
- high-speed railway /
- operation safety supervision /
- system dynamics /
- game theory /
- principal-agent
-
表 1 高铁公司、监管机构和委托路局的收益矩阵
Table 1. Payoff matrix of the high-speed railway company,regulatory agencies,and commissioned railway bureau
策略 监督检查 不监督检查 路局按协议
安全投入路局有违法
违规行为路局按协议
安全投入路局有违法
违规行为严格监管 (– CS – BR – BE,BR + πR,πE – CE + BE) (PR – CS – (1 – RE)BE + REPE,
CR + πR – PR – WNB,(1 – RE)(BE +
πE – CE) + RE(πE – CE – PE))(0,πR,πE – CE) (– LS,πR + CR – WNB,πE – CE) 不监管 (PE – CS – BR,BR + πR,
πE – LE – PE)(PR + PE – CS,πR + CR – PR – WB,πBE + πE – PE – LE) (0,πR,πE – LE) ( – LS,CR + πR – WB,πBE +
πE – LE)表 2 仿真参数设置
Table 2. Simulation parameter setting
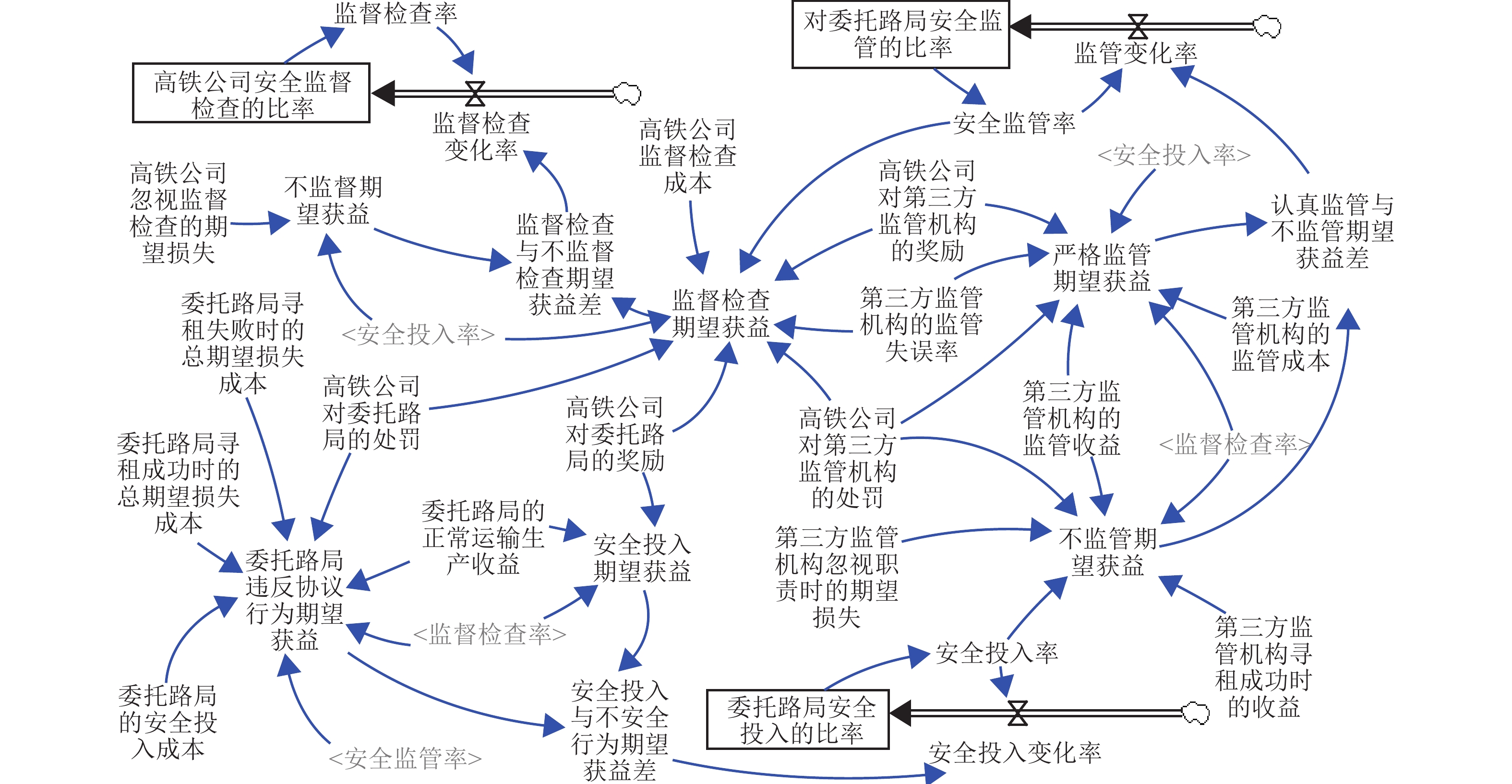
变量 变量含义 取值 变量 变量含义 取值 X 高铁公司监督检查率 [0,1] πR 委托路局的正常运输生产收益 11 Y 委托路局安全投入率 [0,1] CR 委托路局的安全投入成本(委托路局的违规操作收益) 5 Z 监管机构安全监管率 [0,1] WB 委托路局寻租成功时的总期望损失成本 3 CS 高铁公司监督检查成本 0.5 WNB 委托路局寻租失败时的总期望损失成本 2 LS 高铁公司忽视监督检查的期望损失 6 πE 第三方监管机构的监管收益 6 PR 高铁公司对委托路局的处罚 5 CE 第三方监管机构的监管成本 1 PE 高铁公司对第三方监管机构的处罚 3 LE 第三方监管机构忽视职责时的期望损失 1 BR 高铁公司对委托路局的奖励 3 RE 第三方监管机构的监管失误率 0.1 BE 高铁公司对第三方监管机构的奖励 2 πBE 第三方监管机构寻租成功时的收益 2 -
王东. 高速铁路委托运营管理模式研究[J]. 铁道运输与经济,2014,36(6): 12-14, 41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1421.2014.06.003WANG Dong. Study on the management mode of entrusted operation on high-speed railways[J]. Railway Transport and Economy, 2014, 36(6): 12-14, 41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1421.2014.06.003 陈茂莹. 关于合资铁路委托管理问题的思考[J]. 铁道经济研究,2011(5): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9746.2011.05.006CHEN Maoying. Reflections on the problems of entrusted management of joint-venture railway[J]. Railway Economics Research, 2011(5): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9746.2011.05.006 许浩平. 合资铁路委托运输管理的研究[J]. 铁道经济研究,2014(4): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9746.2014.04.007XU Haoping. Study on entrusted transport management of joint-venture railway[J]. Railway Economics Research, 2014(4): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9746.2014.04.007 韩世通. 加强合资铁路委托运输管理的探讨[J]. 铁道运输与经济,2015,37(10): 57-60.HAN Shitong. Discussion on strengthening entrusted transport management of joint venture railway[J]. Railway Transport and Economy, 2015, 37(10): 57-60. 彭辉,赵军锋,王爱云,等. 合资铁路委托运输管理激励兼容机制模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2013,13(6): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2013.06.003PENG Hui, ZHAO Junfeng, WANG Aiyun, et al. Incentive-compatible mechanism model of entrusted transportation management for joint-venture railway[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2013, 13(6): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2013.06.003 ZHENG Shiyuan, RUDY R N. Centralization or decentralization:a comparative analysis of port regulation modes[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2014, 69: 21-40. 贾璐. 基于SD的工程建设安全监管演化博弈研究[J]. 南昌大学学报 (工科版),2012,34(1): 42-48.JIA Lu. Study on the evolutionary game for project construction safety regulation based on system dynamics model[J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Engineering & Technology Edition), 2012, 34(1): 42-48. FAMA E F, JENSEN M C. Separation of ownership and control[J]. The Journal of Law and Economics, 1983, 26(2): 301-325. doi: 10.1086/467037 FAMA E F, JENSEN M C. Agency problems and residual claims[J]. The Journal of Law and Economics, 1983, 26(2): 327-349. doi: 10.1086/467038 FRIEDMAN D. On economic applications of evolutionary game theory[J]. Journal of Evolutionary Economics, 1998, 8(1): 15-43. doi: 10.1007/s001910050054 WEIBULL J W. Evolutionary game theory[M]. [S.l.]: MIT Press, 1997: 45 STERMAN J D. Business dynamics: systems thinking and modeling for a complex world[M]. New York: Irwin Mc Graw-Hill, 2000: 137 -




 下载:
下载: