Numerical Simulation of Wind Characteristics at Bridge Sites in Complex Mountainous Terrains
-
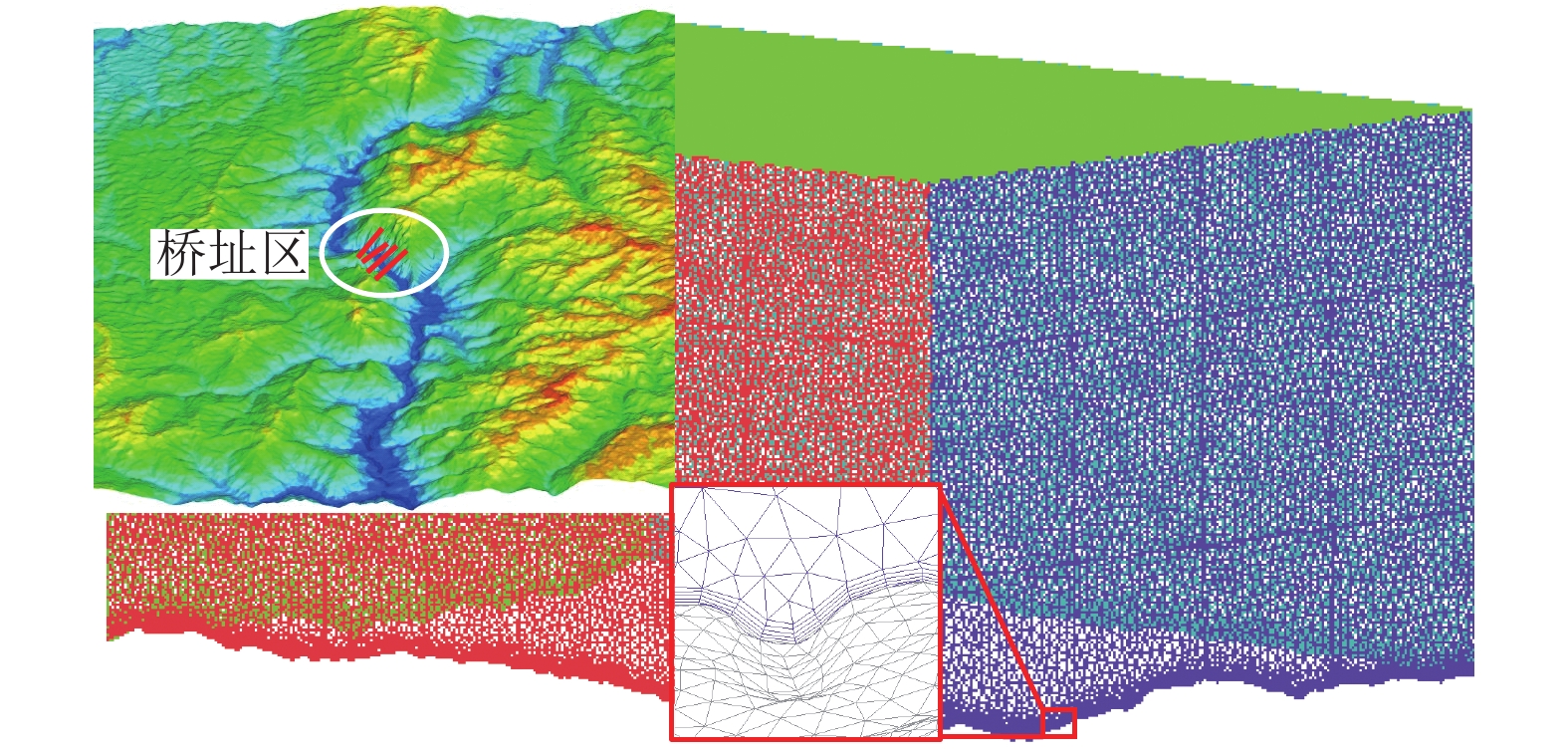
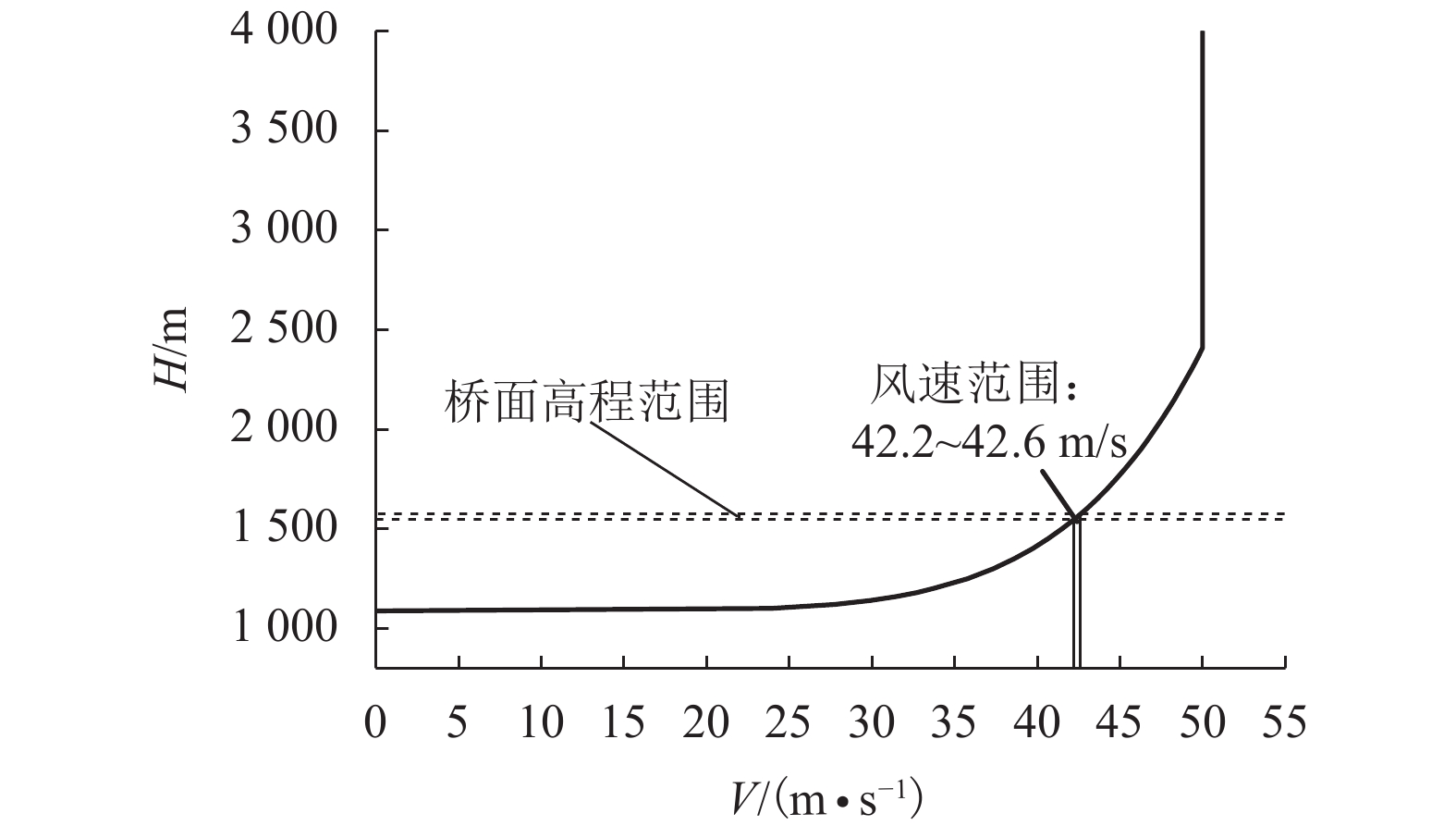
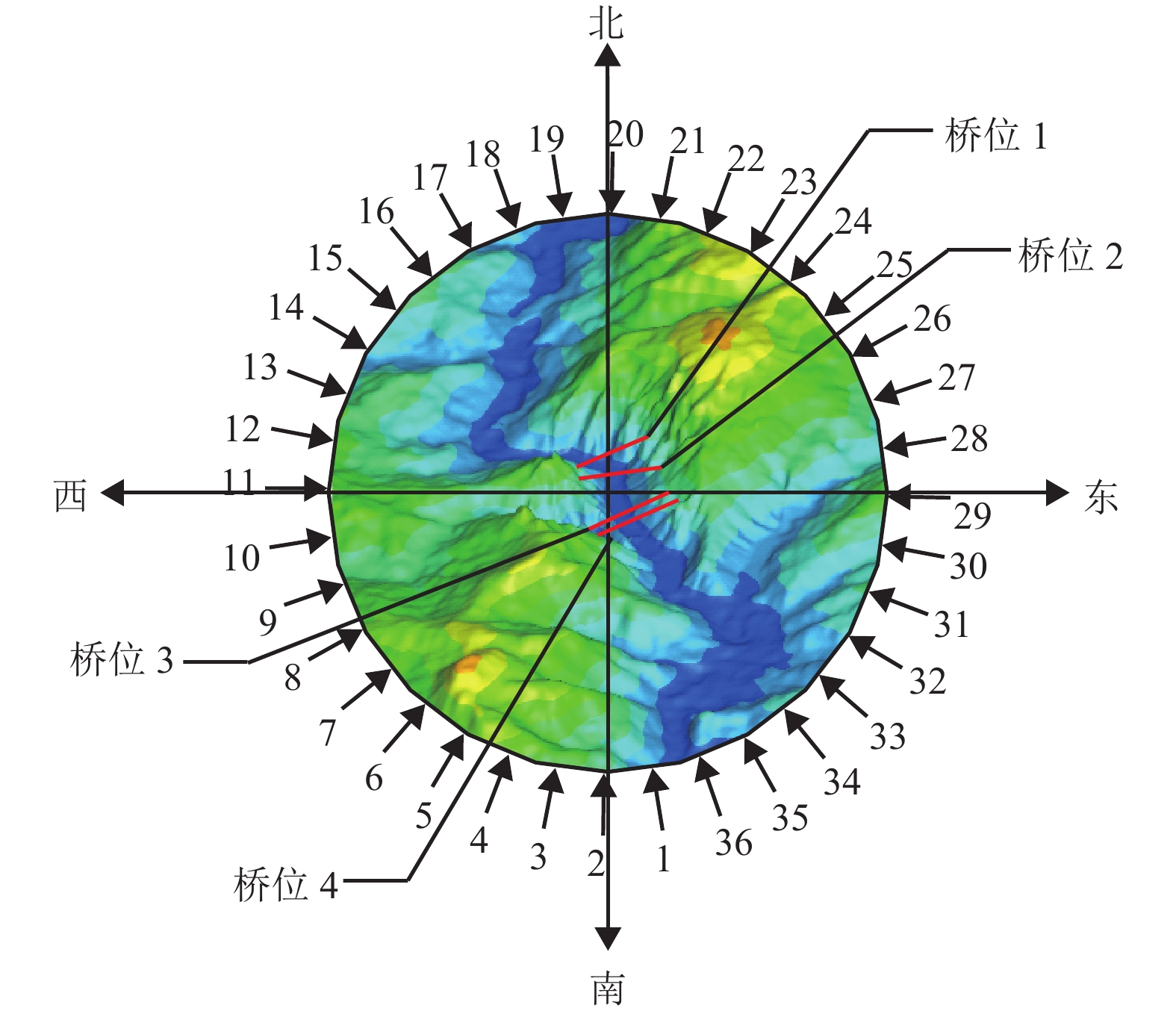
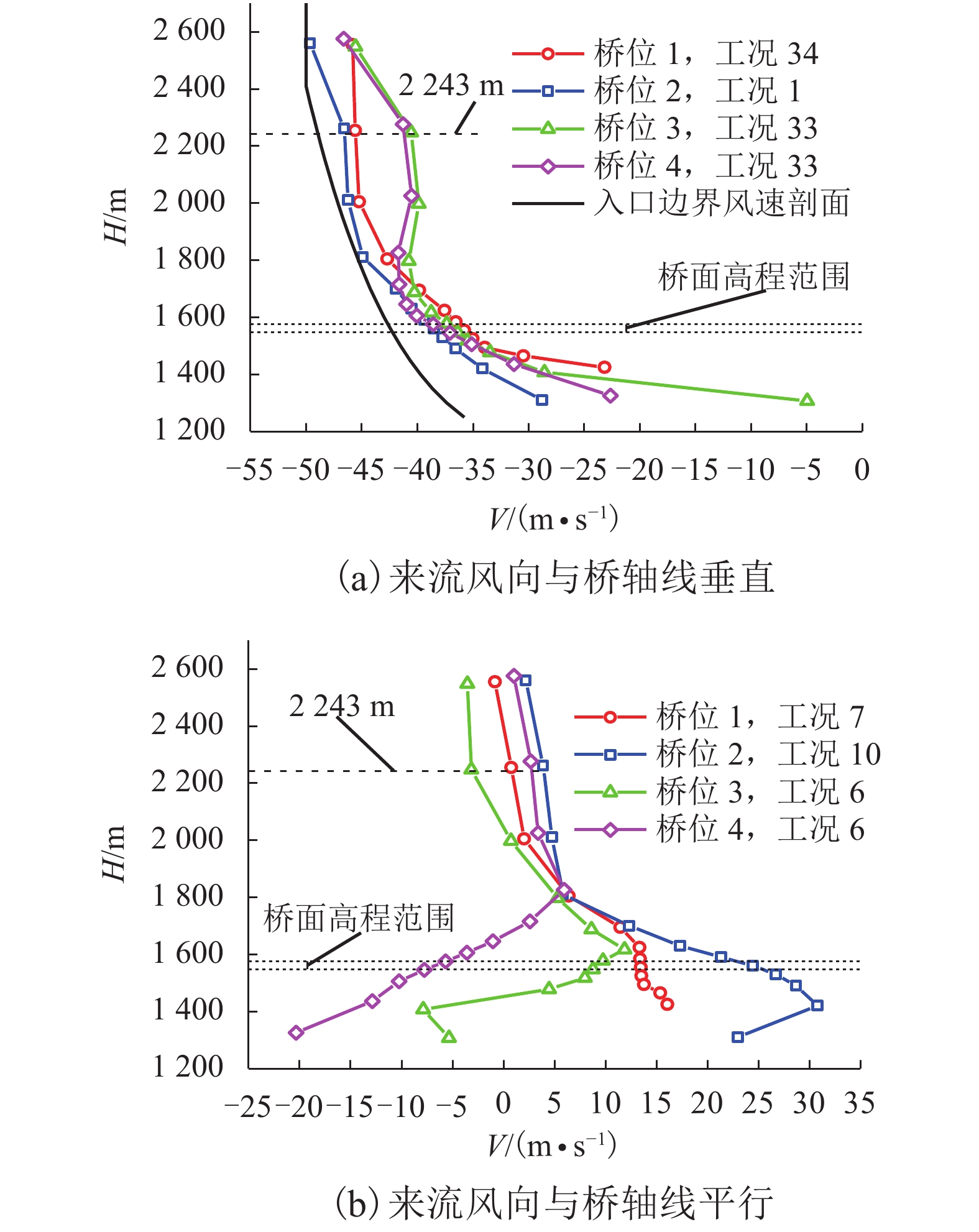
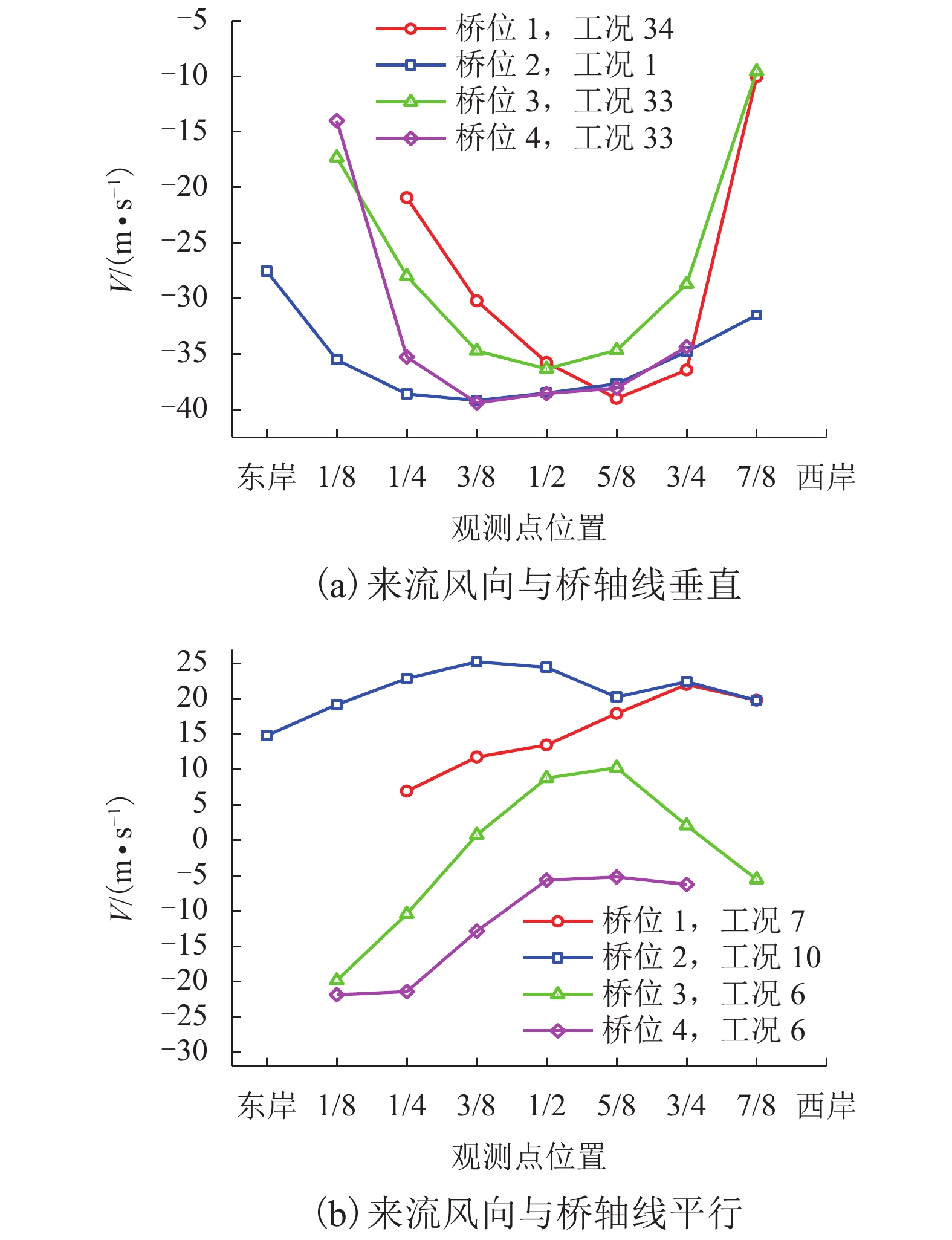
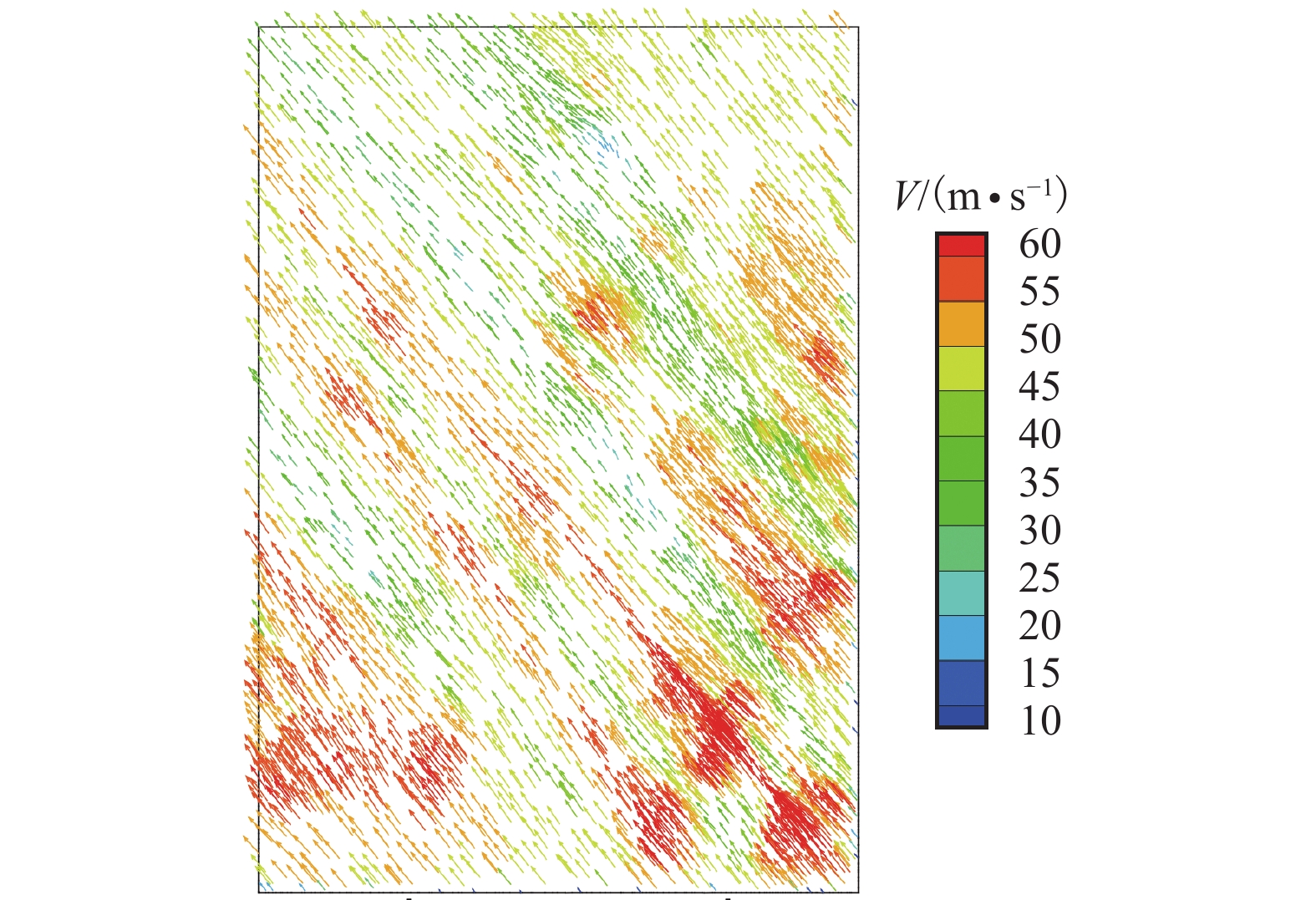
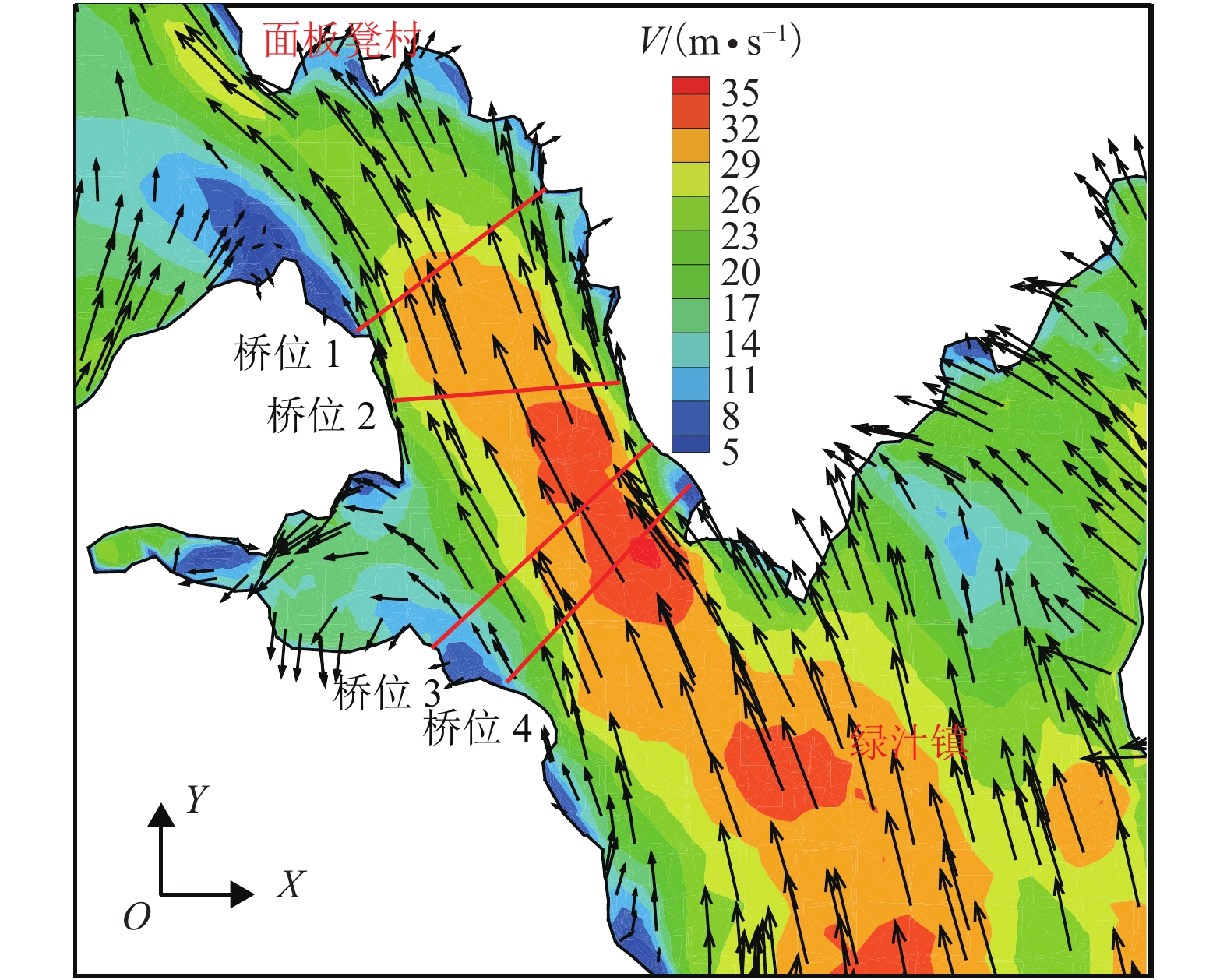
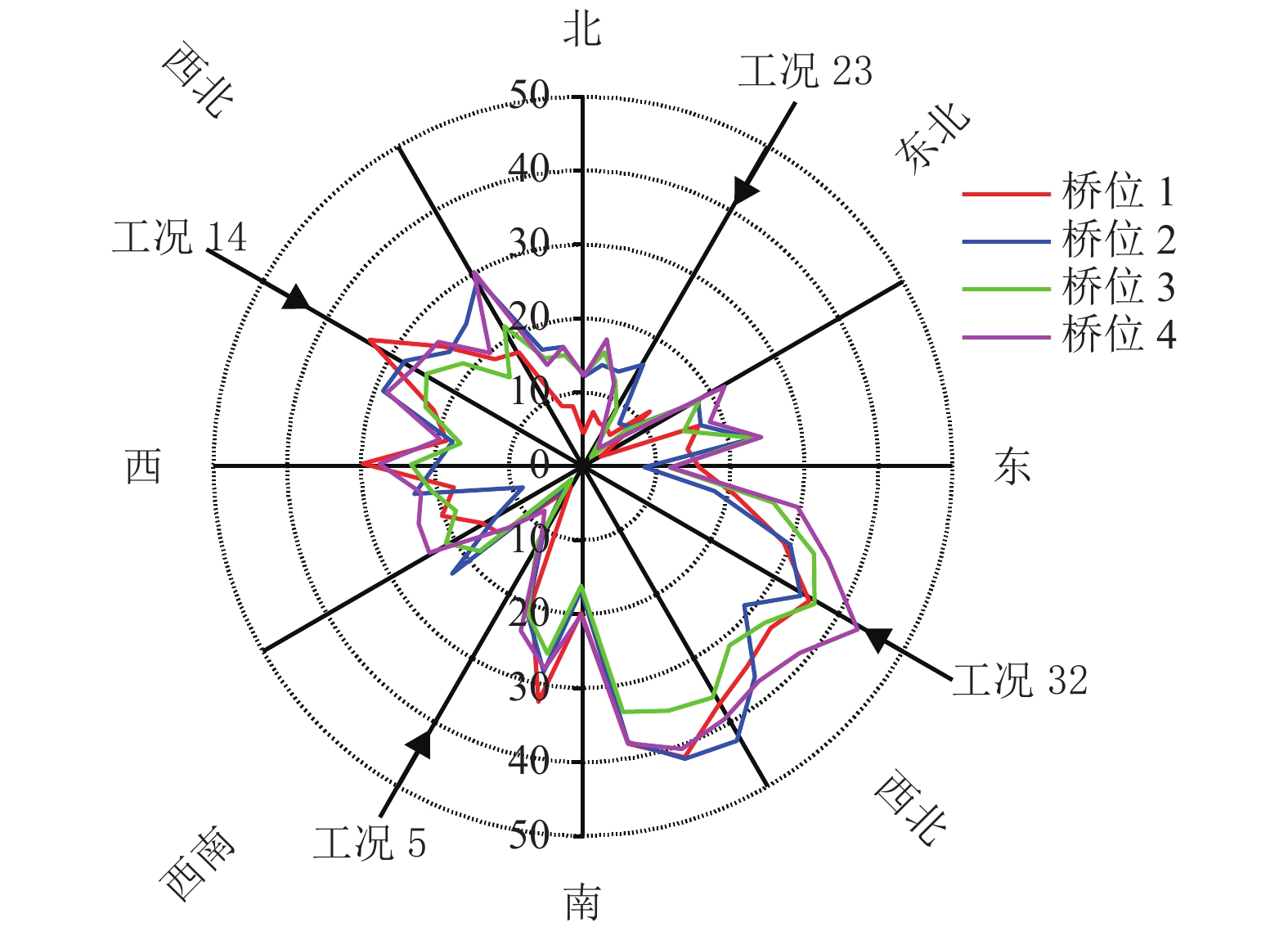
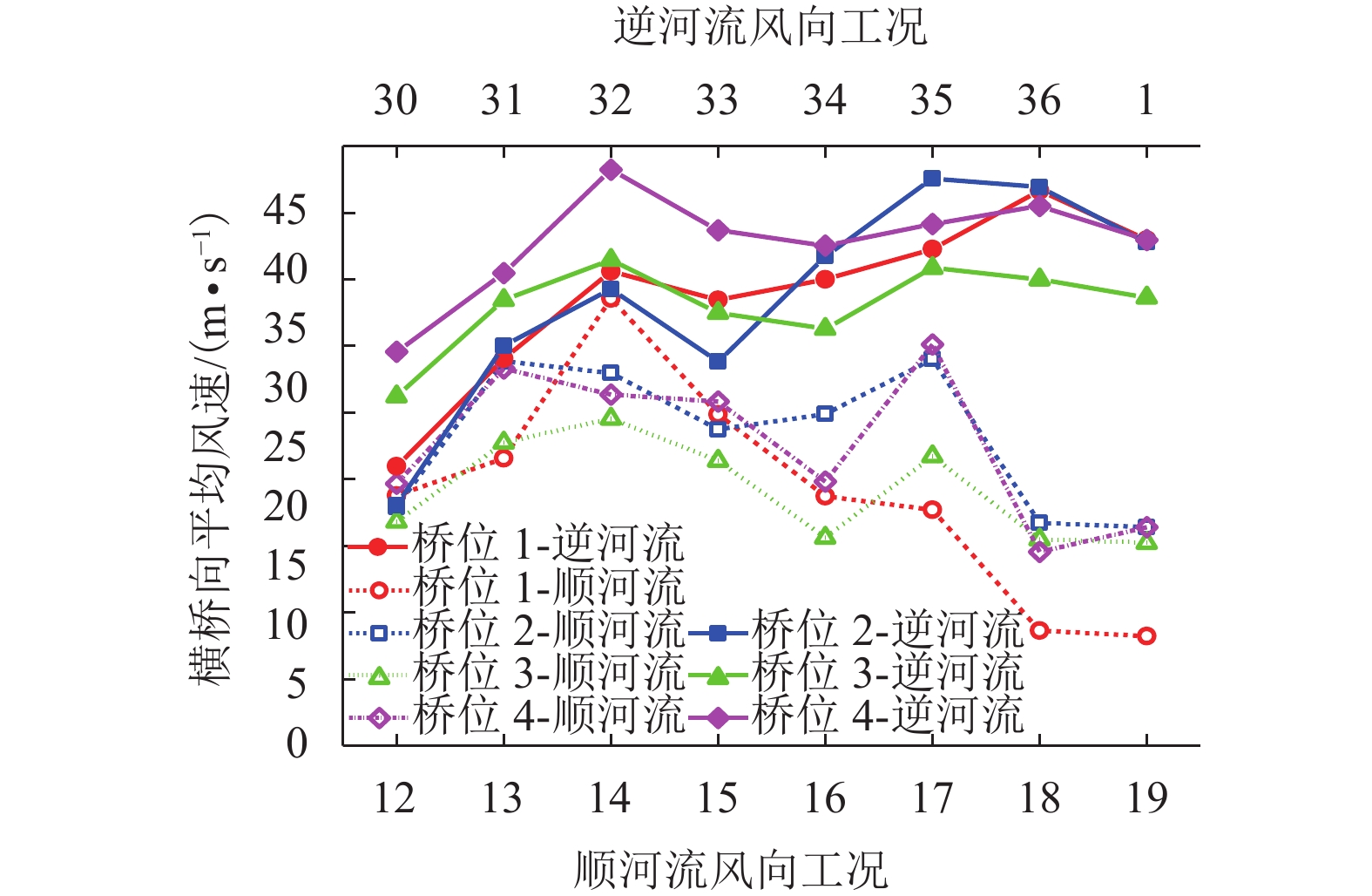
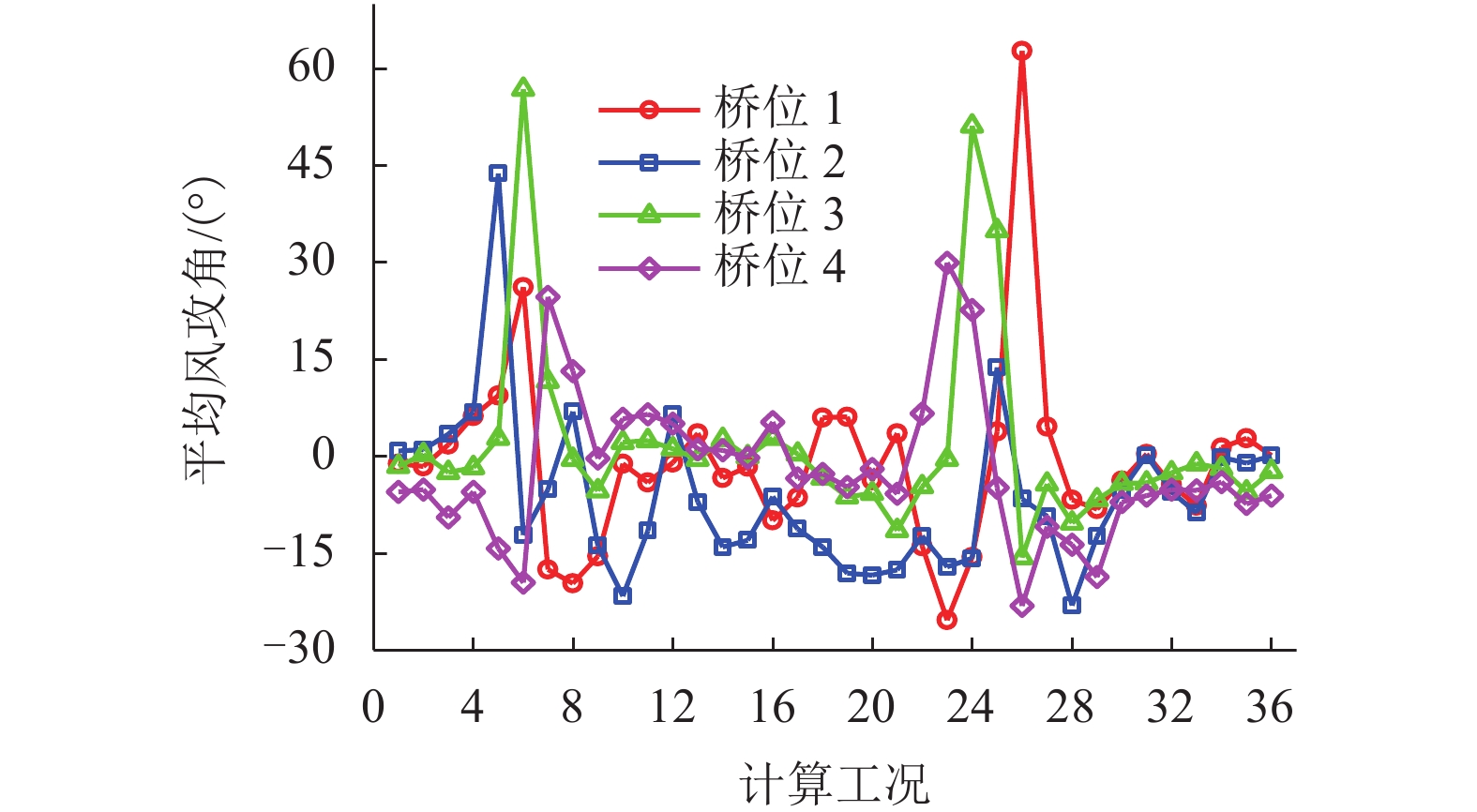
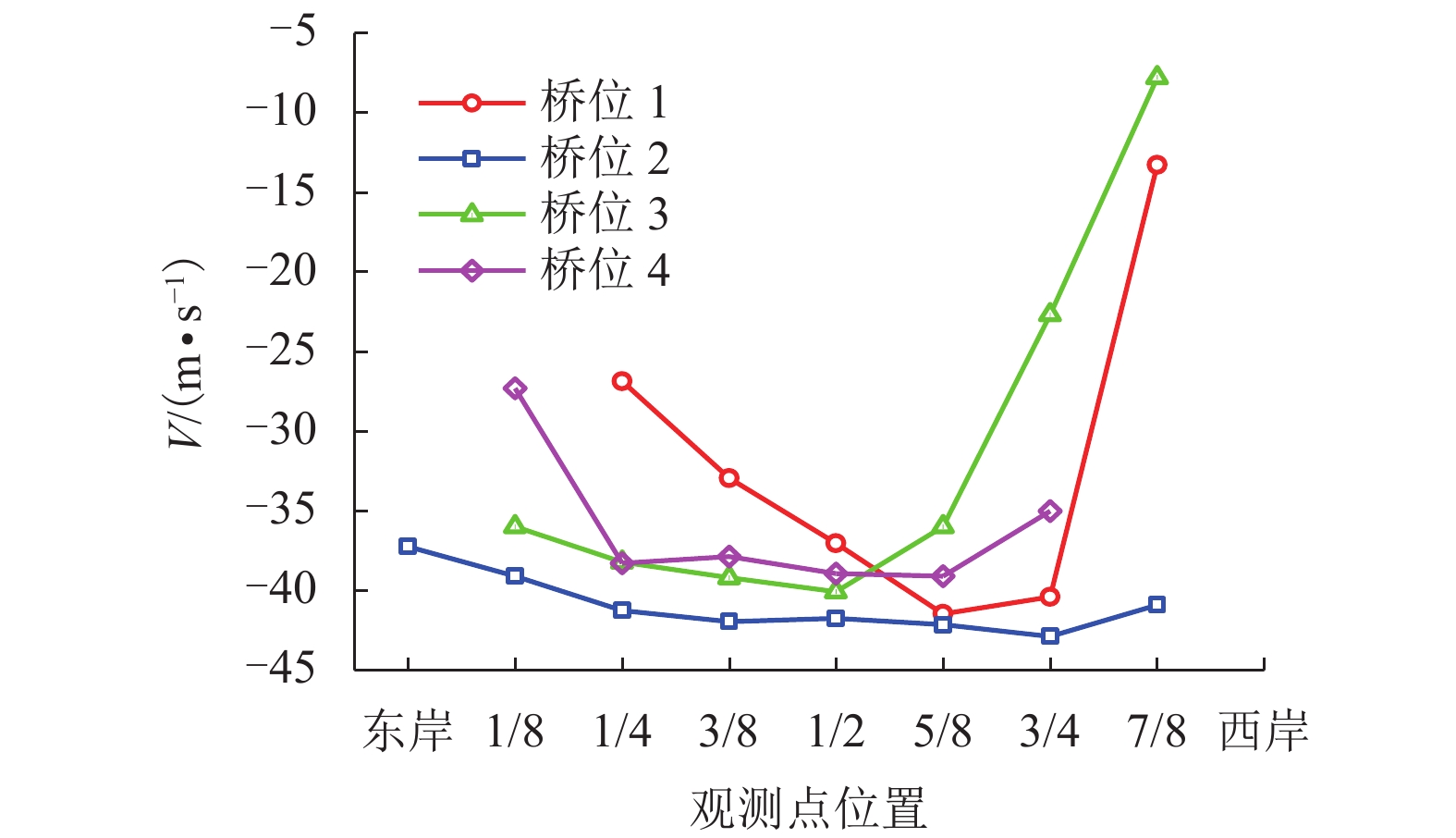
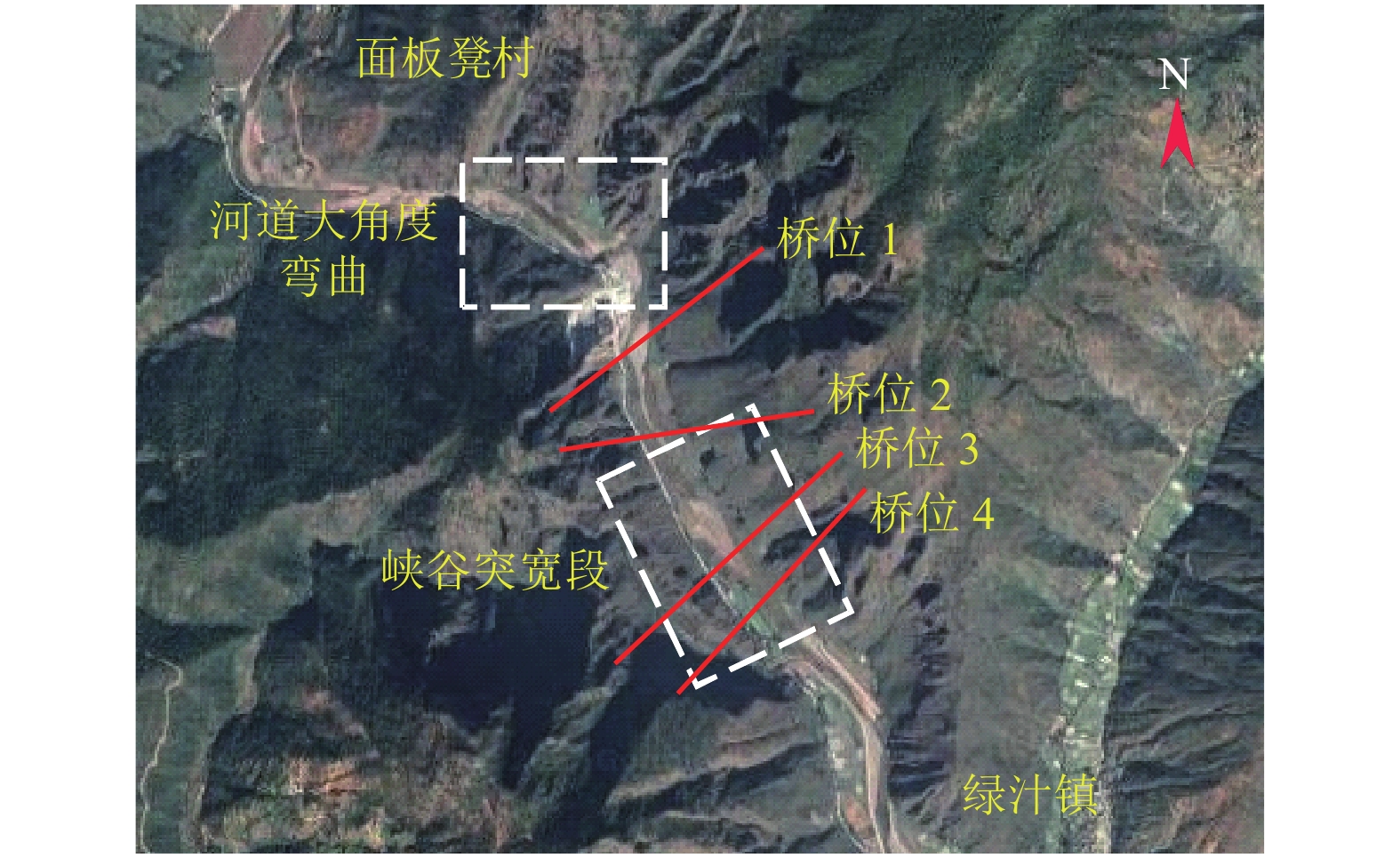
摘要: 为了研究复杂山区地形桥址区风场空间特性变化规律,以位于我国西南山区的绿汁江大桥为工程背景,利用FLUENT对山区地形风场特性进行数值模拟,通过36个风向工况的计算分析,得到复杂山区地形桥址区风场的空间分布特性. 结果表明:受复杂地形影响,各桥位平均风速风剖面曲线和沿主梁横桥向风速曲线差异较大,桥址区附近地形最高点以上400 m风场仍明显受地形影响;受河道大角度弯曲影响,桥址区形成类似“单向开口槽”的地形,顺河流风向的来流风受山体阻挡,各桥位处的风速低于逆河流风向,两个风向的风速差值的平均值达13.6 m/s,且各桥位风攻角以负攻角为主;峡谷突宽使谷内风场出现一定的分流,突宽区风速稍有减弱,风场的分流量有限,使得在渡过突宽段后的峡谷缩窄区,风速依旧较大.Abstract: In order to investigate the variation of spatial characteristics of the wind field at bridge sites in complex terrains, a mountainous terrain was built in FLUENT to simulate wind field characteristics. The Lvzhi River Bridge located at a gorge area in the southwest of China was chosen as the engineering background, in which 36 cases with different wind directions were analyzed. Under the influence of the complex terrain, the profiles of average transverse wind velocities along the height direction and bridge axes are quite different. The complex terrain still has an impact on the wind field at 400 m above the peak of the terrain near the bridge site. Affected by large angle bending of the river, the bridge site area forms a terrain similar to the " one-way open slot”. The incoming wind along the river downstream direction is blocked by the mountain, so the wind speed at each bridge is lower than that in the river upstream direction. The average of the velocity differences between these two directions reaches 13.6 m/s. The wind attack angles of all bridges are mainly negative. The suddenly widened gorge results in a part of limited distributary of the wind field and the wind speeds decrease slightly in the widening area. After crossing the widened section, the gorge narrows and the wind speeds remain large.
-
Key words:
- complex terrain /
- bridge site /
- curved river /
- wind characteristic /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 桥梁设计参数表
Table 1. Bridge design parameters
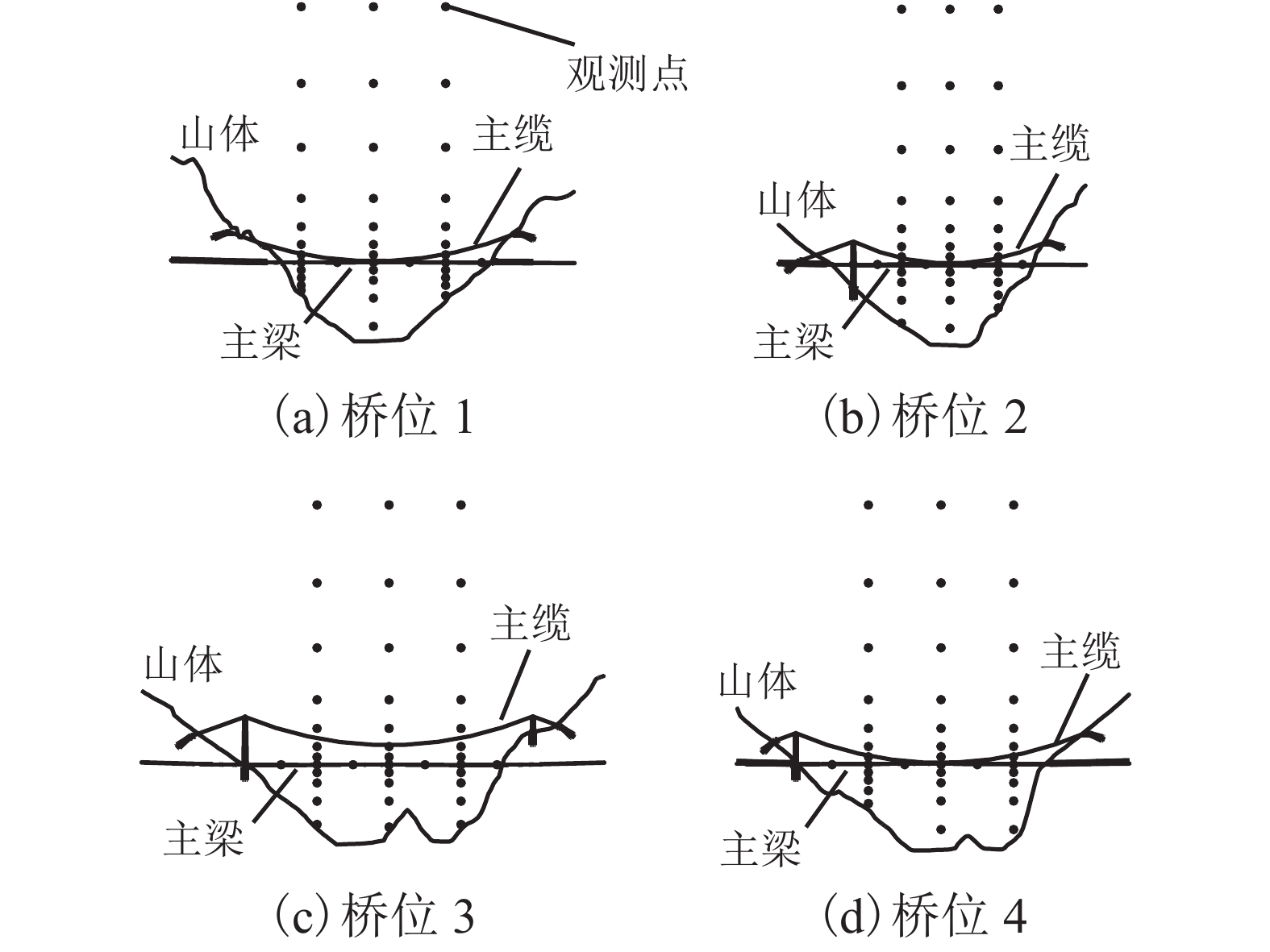
桥位 跨径/m 梁长/m 跨中标高/m 距谷底高度/m 1 1 300 828 1 554.8 308.8 2 750 699 1 560.0 318.0 3 1 100 993 1 547.4 307.3 4 1 120 966 1 575.6 333.6 -
李永乐,蔡宪棠,唐康,等. 深切峡谷桥址区风场空间分布特性的数值模拟研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2011,44(2): 116-122.LI Yongle, CAI Xiantang, Tang Kang, et al. Study of spatial distribution feature of wind fields over bridge site with a deep-cutting gorge using numerical simulation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2011, 44(2): 116-122. 陈万隆. 峡谷中风状况的分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 1979(增刊1): 29-34CHEN Wanlong. Analysis of wind conditions in the canyon[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 1979(S1): 29-34 庞加斌,宋锦忠,林志兴. 山区峡谷桥梁抗风设计风速的确定方法[J]. 中国公路学报,2008,21(5): 39-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2008.05.008PANG Jiabin, SONG Jinzhong, LIN Zhixing. Determination method for wind-resistant design wind speed of mountainous-valley bridge[J]. China Journal of Highway & Transport, 2008, 21(5): 39-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2008.05.008 ABDI D S, BITSUAMLAK G T. Wind flow simulations on idealized and real complex terrain using various turbulence models[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 75(8): 30-41. BLOCKEN B, HOUT A V D, DEKKER J, et al. CFD simulation of wind flow over natural complex terrain:case study with validation by field measurements for Ria de Ferrol,Galicia,Spain[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics, 2015, 147: 43-57. 肖仪清,李朝,欧进萍,等. 复杂地形风能评估的CFD方法[J]. 华南理工大学学报,2009,37(9): 30-35. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-565X.2009.09.006XIAO Yiqing, LI Chao, OU Jinping, et al. CFD approach to evaluation of wind energy in complex terrain[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology, 2009, 37(9): 30-35. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-565X.2009.09.006 NOMURA T. Prediction of large-scale wind field over complex terrain by finite element method[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics, 1997(67/68): 947-948. DHUNNY A Z, LOLLCHUND M R, RUGHOOPUTH S D D V. Wind energy evaluation for a highly complex terrain using computational fluid dynamics (CFD)[J]. Renewable Energy, 2017, 101: 1-9. YAN B W, LI Q S. Coupled on-site measurement/CFD based approach for high-resolution wind resource assessment over complex terrains[J]. Energy Conversion & Management, 2016, 117: 351-366. WAN F, PORTÉ-AGEL F. A large-eddy simulation study of turbulent flow over multiscale topography[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2011, 141(2): 201-217. doi: 10.1007/s10546-011-9648-7 遆子龙,李永乐,廖海黎. 地表粗糙度对山区峡谷地形桥址区风场影响研究[J]. 工程力学,2017,34(6): 73-81.TI Zilong, LI Yongle, LIAO Haili. Effect of ground surface roughness on wind field over bridge site with a gorge in mountainous area[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34(6): 73-81. 李永乐,遆子龙,汪斌,等. 山区Y形河口附近桥址区地形风特性数值模拟研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 341-348. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.013LI Yongle, TI Zilong, WANG Bin, et al. Numerical simulation of wind characteristics over bridge site near Y-shaped river junction in mountainous area[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 341-348. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.013 薛亚飞,刘志文. 复杂地形桥位风场空间分布特性数值模拟[J]. 公路交通科技,2016,33(5): 66-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2016.05.011XUE Yafei, LIU Zhiwen. Numerical simulation of spatial distribution feature of wind field over bridge site at complex terrain[J]. Journal of Highway & Transportation Research & Development, 2016, 33(5): 66-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2016.05.011 于舰涵,李明水,廖海黎. 山区地形对桥位风场影响的数值模拟[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(4): 654-662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.04.008YU Jianhan, LI Mingshui, LIAO Haili. Numerical simulation of effect of mountainous topography on wind field at bridge site[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(4): 654-662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.04.008 沈炼,韩艳,蔡春声,等. 山区峡谷桥址处风场实测与数值模拟研究[J]. 湖南大学学报,2016,43(7): 16-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2974.2016.07.003SHEN Lian, HAN Yan, CAI Chunsheng, et al. Experiment and numerical simulation for wind field of a long-span suspension bridge located in mountainous canyon[J]. Journal of Hunan University, 2016, 43(7): 16-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2974.2016.07.003 王云飞,汪斌,李永乐. 水库蓄水对岖桥址风特性的影响[J]. 西南交通大学,2018,53(1): 95-101,145.WANG Yunfei, WANG Bin, LI Yongle. Influence of reservoir water storage on wind chavacteristics over bridge site in mountainous area[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(1): 95-101,145. -




 下载:
下载: