Functional Relationships between Sound Powers Radiated from Noise Sources of High-Speed Train and Its Speed
-
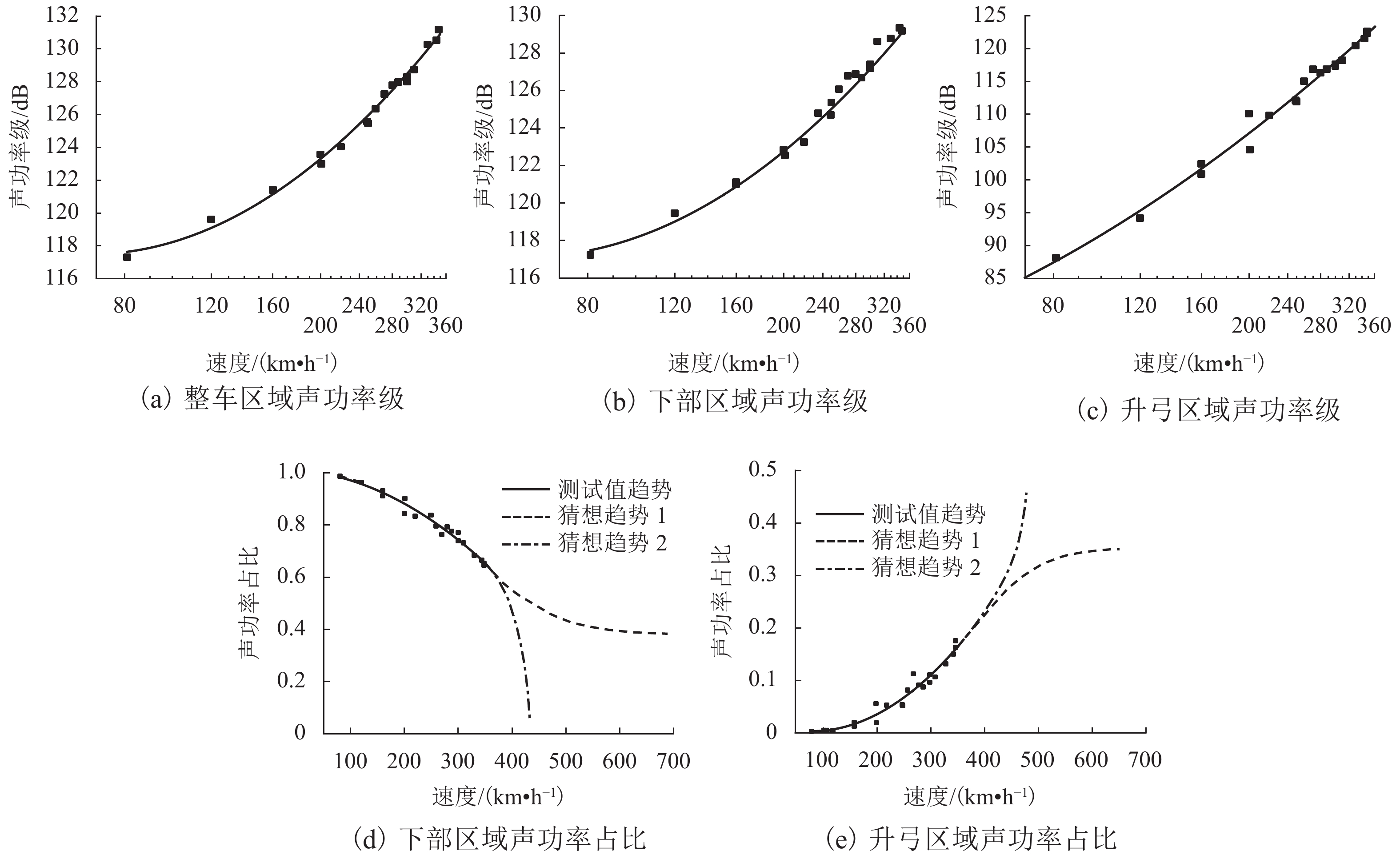
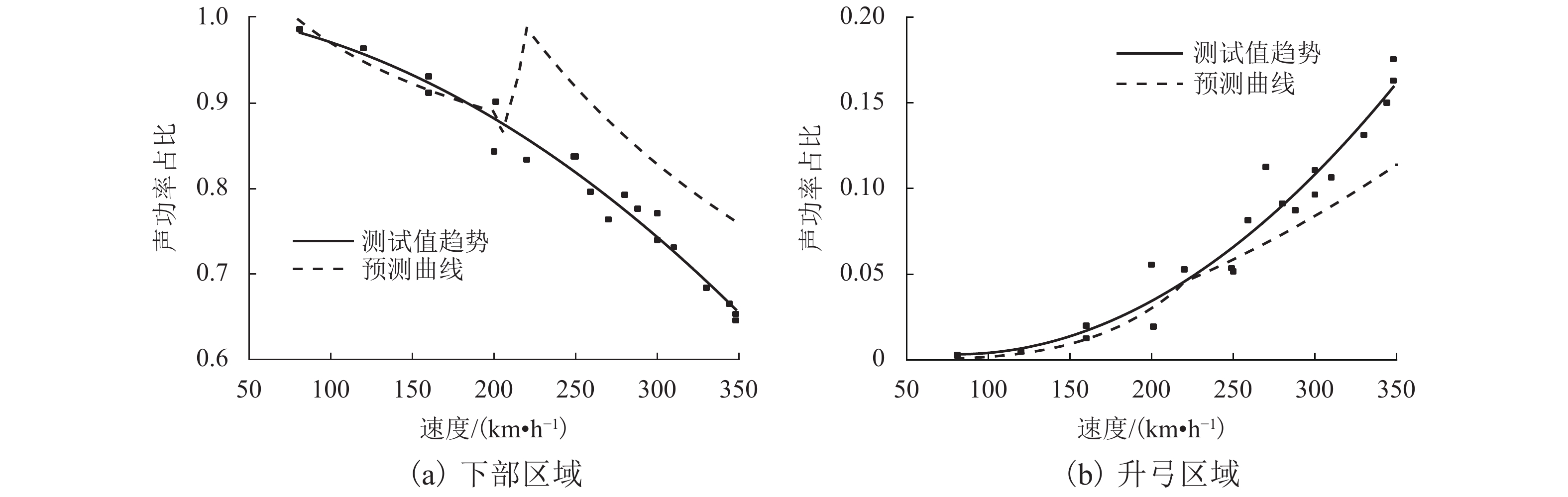
摘要: 为了解决既有对数经验公式无法拟合高速列车显著声源贡献率与速度的函数关系这一问题,使用轮辐声阵列进行高速列车车外声源识别试验;根据显著声源位置对列车表面进行区域划分,量化分析显著声源区域的声功率级和声功率贡献率与速度之间的关系;在既有对数经验公式的基础上,根据不同种类噪声声功率随速度的变化特性,建立新的拟合公式;结合列车噪声测试数据对新的拟合公式进行验证. 研究结果表明:列车以350 km/h运行时,下部区域对列车总辐射噪声的贡献率占70%以上,升弓区域对局部区域声功率的影响最显著,超过50%;随着速度的增长,下部区域的贡献率逐渐减小,弓网区域逐渐增大,显著声源区域的贡献率变化先快后慢,最后趋于稳定;利用新的拟合方法得出,列车声源区域的声功率级和声功率贡献率与速度的拟合度基本都在0.9以上.
-
关键词:
- 高速列车 /
- 车外噪声声源识别 /
- 声源声功率拟合与预测 /
- 轮轨噪声 /
- 气动噪声
Abstract: To solve the problem that the existing logarithm empirical formula cannot satisfactorily fit the relationship between the sources contribution rate and the speed, the microphone array was used to identify the external sound sources of a high-speed train at different speeds. Dividing the train surface into sub-regions with the location of the known main noise sources, the relationship between sound power level and its contribution rate of main noise sources sub-region and train speed were analyzed quantitatively. Then, according to the characteristic of different kinds of noise sound powers increment rate with speed, the new fitting formula was established based on the existing logarithm empirical formula. Finally, the new formula was verified on the noise data of different train. The results show that when the train runs at 350 km/h, radiated noise from the lower region of railway system dominate the total radiated noise, which account for more than 70%. The sound power of the rising pantograph region is significant in the local region as well, which account for more than 50%. With the speed increase, the contribution rate of lower region decrease and the pantograph regions increase, and each regions change rapidly first and then slowly, finally become stable. Using the advanced fitting method, the fitting degrees of sound power level and sound power contribution rate with speed in the source regions of the train are all above 0.9. -
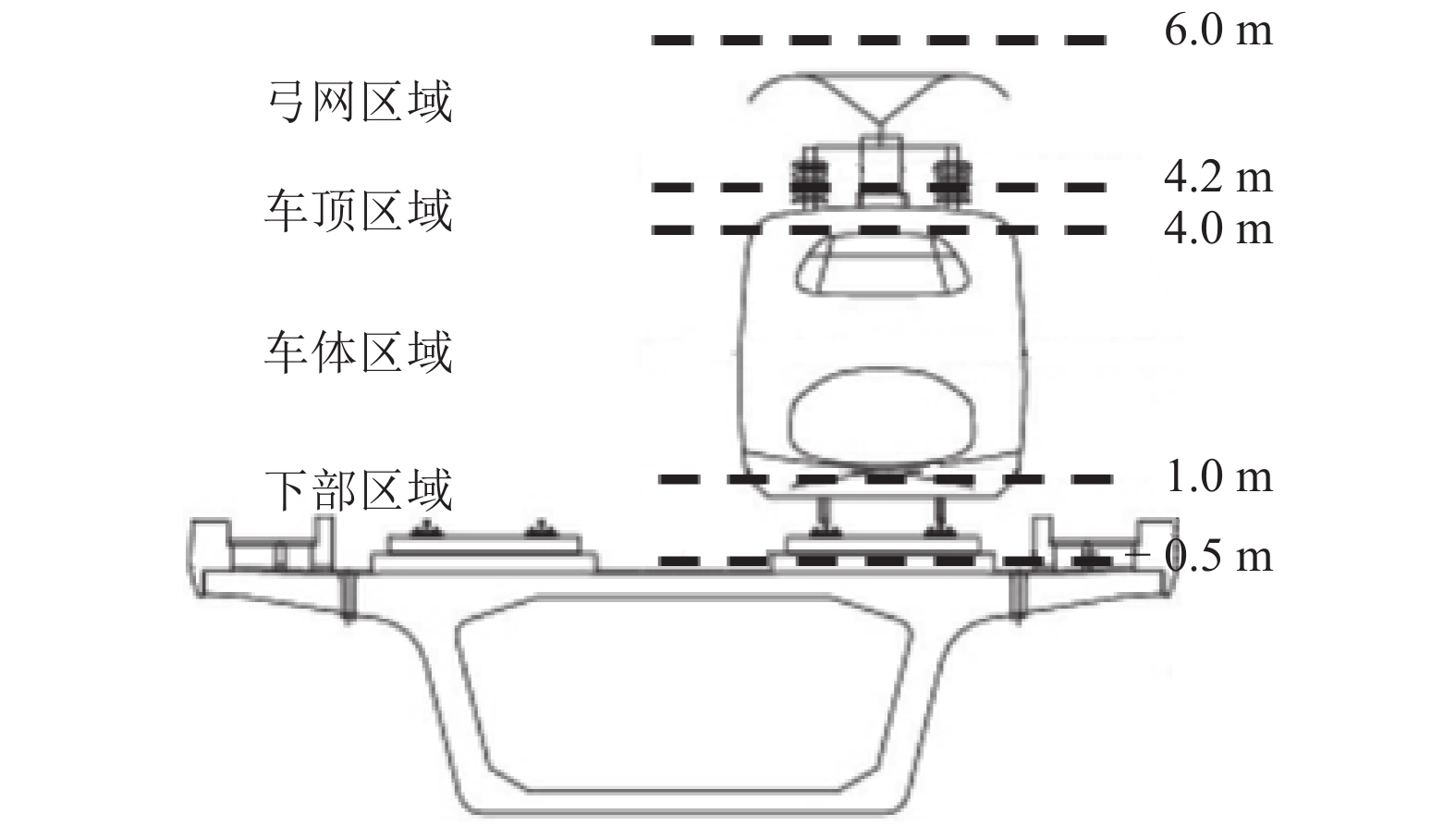
表 1 声源区域范围
Table 1. Regions of sound source
m 区域 高度方向 长度方向 下部 −0.5~1.0 0~212 车体 1.0~4.0 0~209 车顶 4.0~4.2 6~203 弓网 4.2~6.0 6~203 表 2 声源细化分区范围
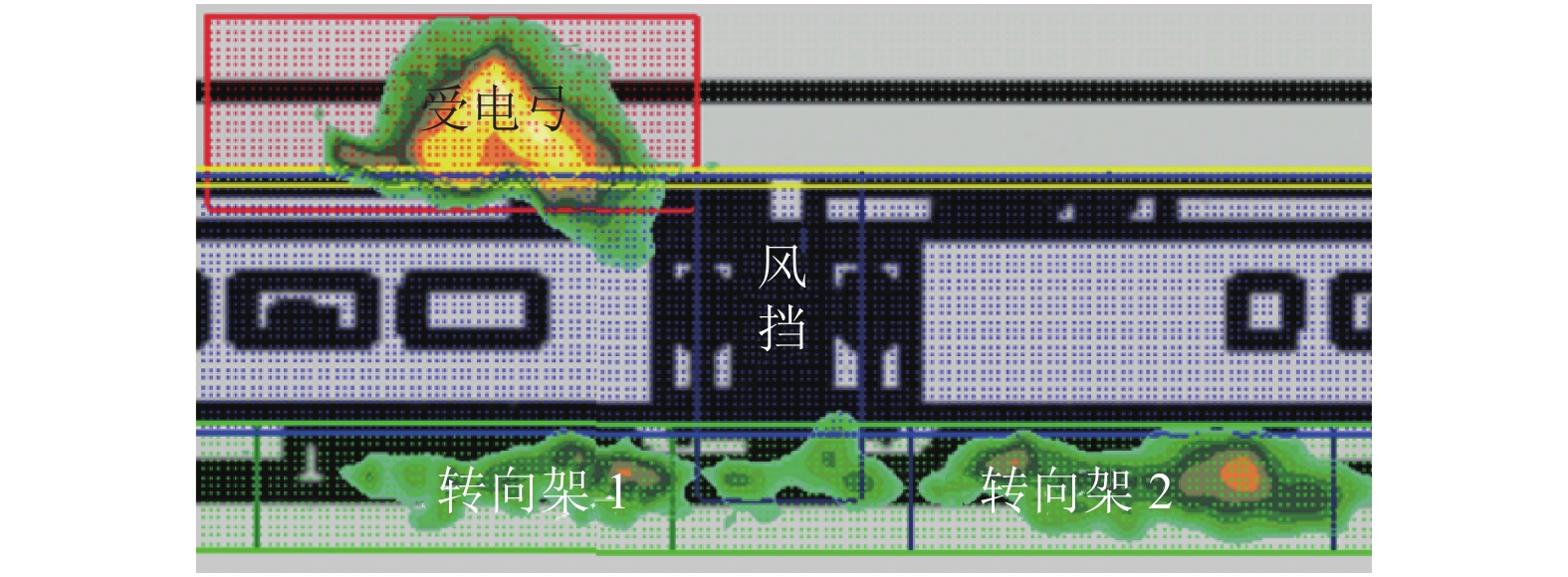
Table 2. Refined divided regions of sound source
区域 高度方向/m 长度方向 弓网 3.7~6.0 声强最大值前后 3.0 m 转向架 −0.5~1.0 转向架中心前后 2.5 m 排障器 −0.5~1.0 0 ~第一个转向架前 风挡 0.2~4.2 车厢连接中心前后 1.0 m 表 3 式(1)拟合参数
Table 3. Fitting parameters of eq. (1)
区域 速度范围/(km•h−1) Ai Bi 整车 45 ≤ V ≤ 220 15.51 87.48 220 < V ≤ 350 36.62 37.82 下部 45 ≤ V ≤ 220 13.91 90.56 220 < V ≤ 350 30.95 51.06 升弓 45 ≤ V ≤ 350 56.38 −21.87 表 4 新方法拟合参数表
Table 4. Fitting parameters of the new method
区域 ai/× 10−15 bi/× 10−17 ci 整车 3.92 24.00 0.50 下部 1.38 23.50 0.41 升弓 1.04 −1.04 0.03 -
翟婉明,赵春发. 现代轨道交通工程科技前沿与挑战[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 209-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.001ZHAI Wanming, ZHAO Chunfa. Frontiers and challenges of sciences and techologies in modern railway engineering[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 209-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.001 KURITA T. Development of external-noise reduction technologies for shinkansen high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Environment & Engineering, 2011, 6(4): 805-819. POISSON F, GAUTIER P E, LETOURNEAUX F. Noise sources for high speed trains:a review of results in the TGV case[J]. Notes on Numerical Fluid Mechanics, 2008, 99: 71-77. HE Bin, XIAO Xinbiao, ZHOU Qiang, et al. Investigation into external noise of a high-speed train at different speed[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Science A, 2014, 15(12): 1019-1033. DENG Yongquan, XIAO Xinbiao, HE Bin, et al. Analysis of external noise spectrum of high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(12): 4753-4761. doi: 10.1007/s11771-014-2485-3 胡文林,胡叙洪,齐春雨,等. 高速铁路噪声源区划及各区域声源贡献量分析[J]. 铁道标准设计,2016(3): 163-166.HU Wenlin, HU Xuhong, QI Chunyu, et al. Division and contribution analysis of high-speed railway noise sources[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2016(3): 163-166. MELLET C, LÉTOURNEAUX F, POISSON F, et al. High speed train noise emission:Latest investigation of the aerodynamic/rolling noise contribution[J]. Noise & Vibration Worldwide, 2007, 293(3/4/5): 535-546. THOMPSON D J. Railway noise and vibration:mechanisms,modelling and means of control[J]. Elsevier Science & Technology, 2008, 153(4): 21-25. EHRENFRIED K, KOOP L. Comparison of iterative deconvolution algorithms for the mapping of acoustic sources[J]. AIAA Journal, 2006, 45(7): 1-19. THOMPSON D J, GAUTIER P E. Review of research into wheel/rail rolling noise reduction[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers:Part F, 2006, 220(4): 385-408. doi: 10.1243/0954409JRRT79 杨新文,翟婉明. 高速铁路轮轨噪声理论计算与控制研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2011,32(1): 133-135.YANG Xinwen, ZHAI Wanming. Theoretical calculation and control study on the wheel/rail noises of high speed railway[J]. China Railway Science, 2011, 32(1): 133-135. THOMPSON D J, IGLESIAS E L, LIU X, et al. Recent developments in the prediction and control of aerodynamic noise from high-speed trains[J]. International Journal of Rail Transportation, 2015, 3(3): 119-150. doi: 10.1080/23248378.2015.1052996 刘加利,张继业,张卫华. 高速列车车头的气动噪声数值分析[J]. 铁道学报,2011,33(9): 19-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.09.003LIU Jiali, ZHANG Jiye, ZHANG Weihua. Numerical analysis on aerodynamic noise of the high-speed train head[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(9): 19-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.09.003 杜健,梁建英,田爱琴. 高速列车受电弓气动噪声特性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(5): 935-941. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.05.025DU Jian, LIANG Jianying, TIAN Aiqin. Analysis of aeroacousitcs characteristics for pantograph of high-speed[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(5): 935-941. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.05.025 CHU Zhigang, YANG Yang. Comparison of deconvolution methods for the visualization of acoustic sources based on cross-spectral imaging function beam forming[J]. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2014, 48(1/2): 404-422. -





 下载:
下载: