Performance Analysis of Tri-state Boost Converter with Dynamic Reference Current Control
-
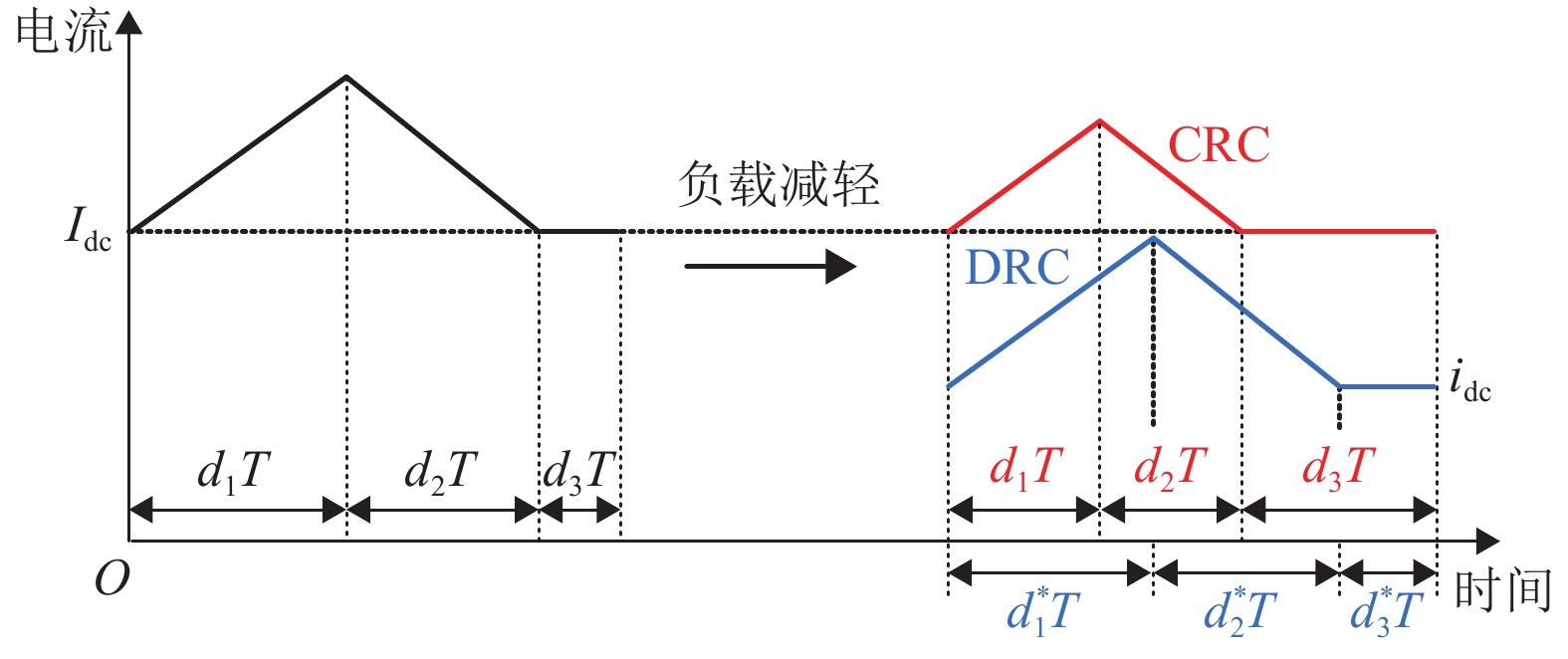
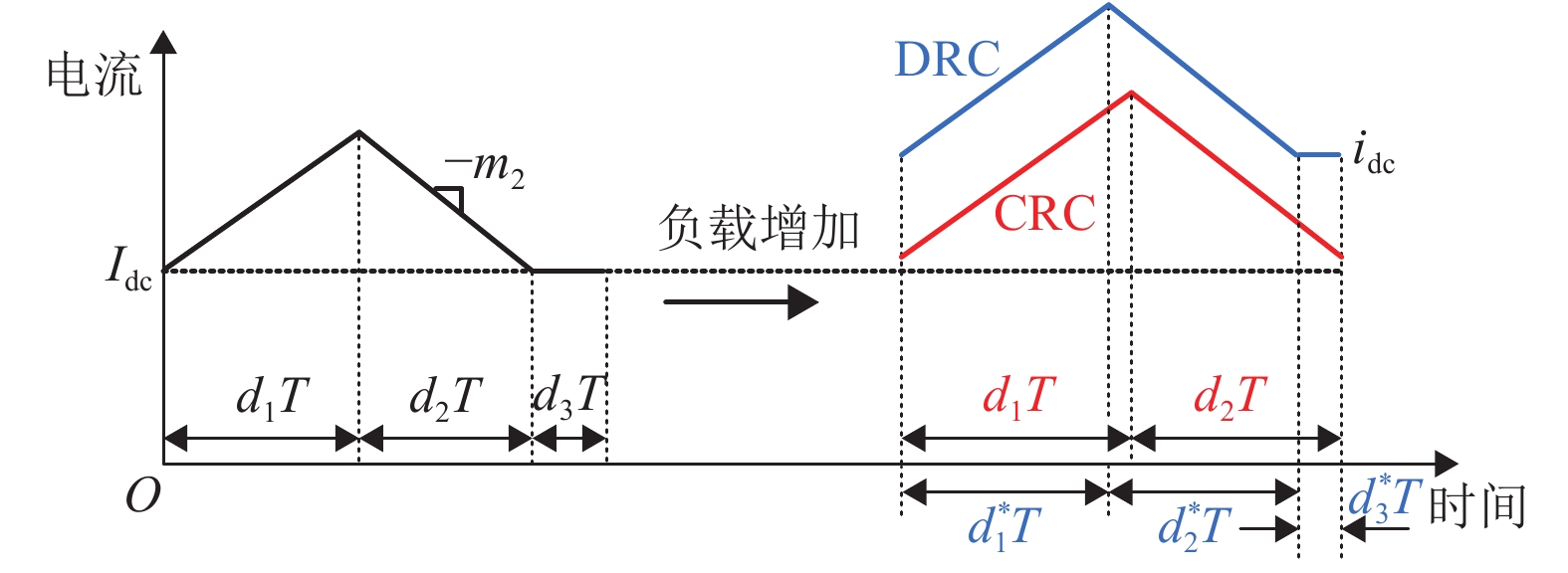
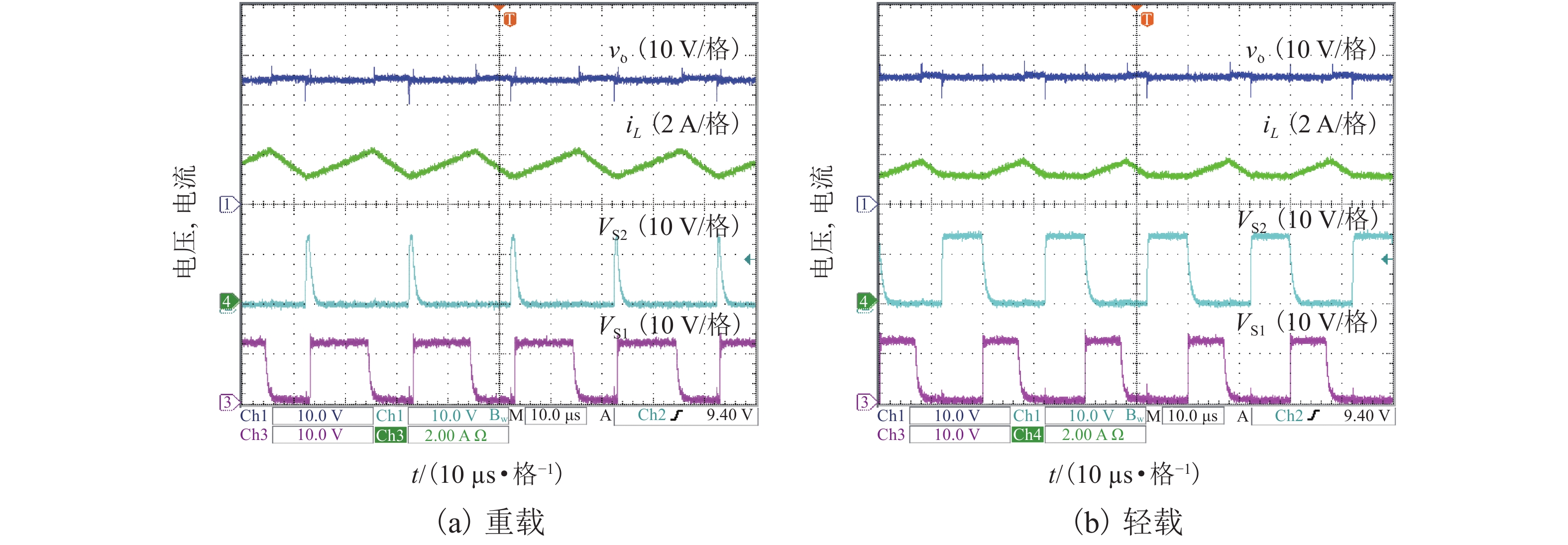
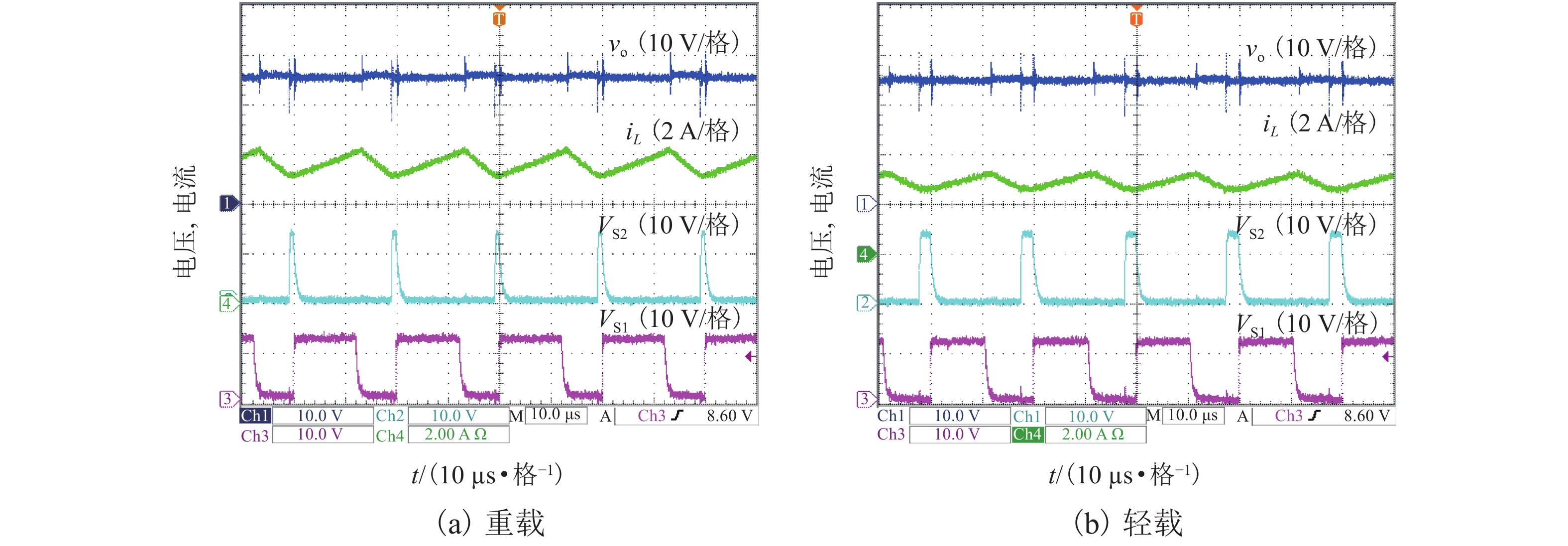
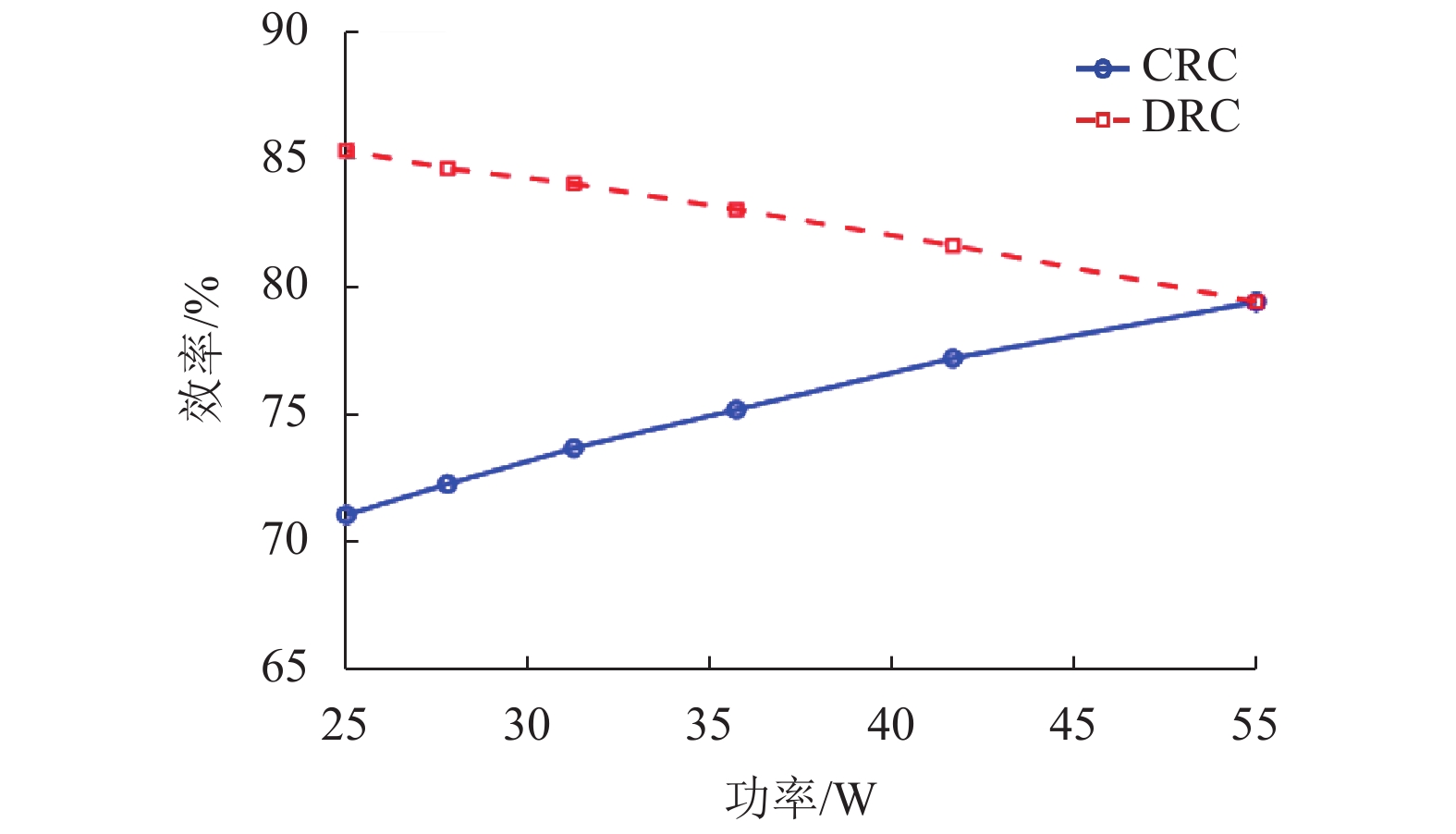
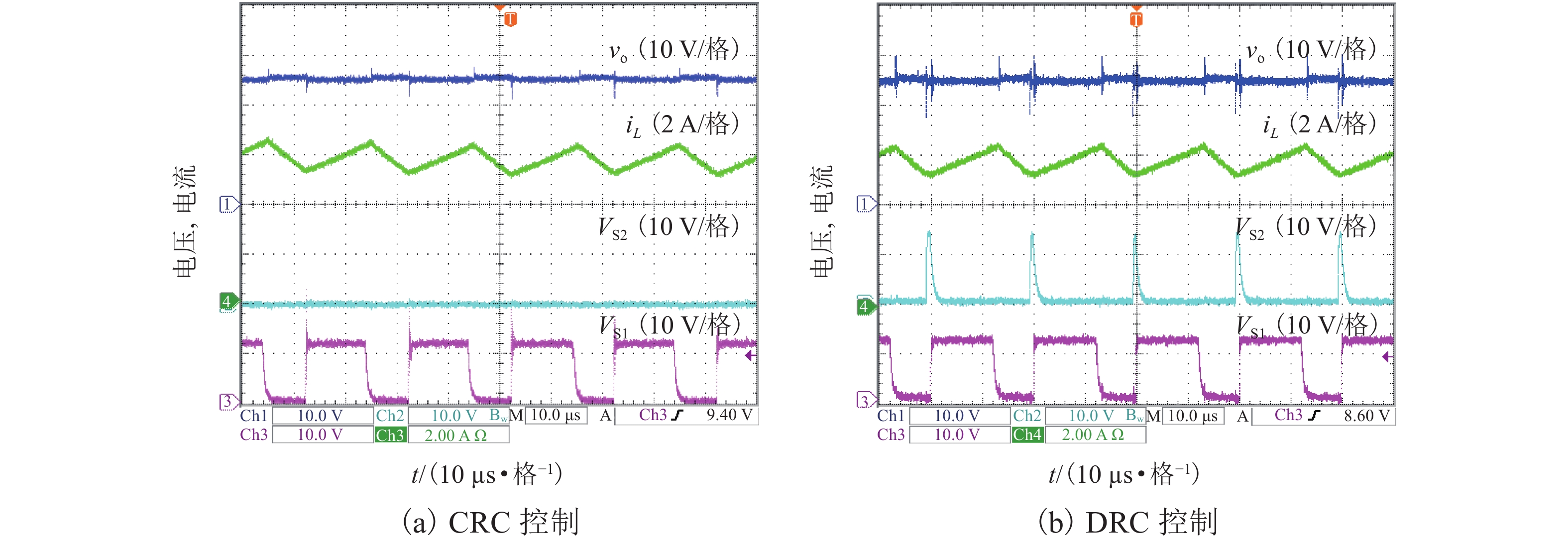
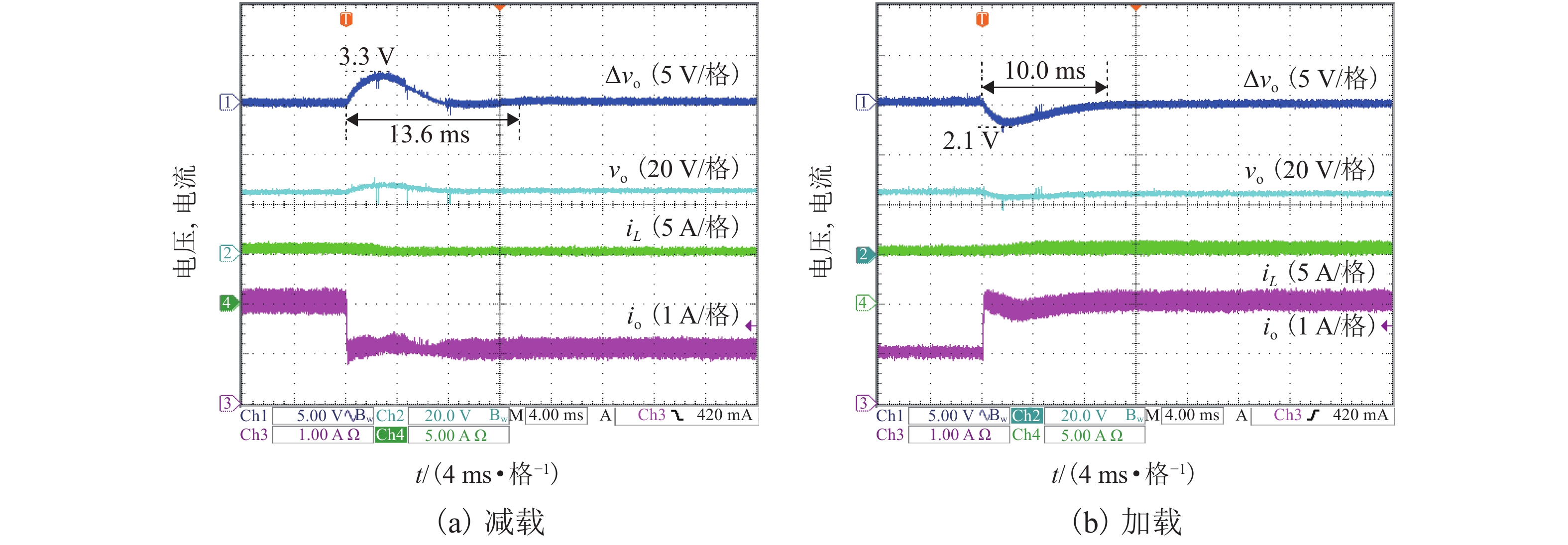
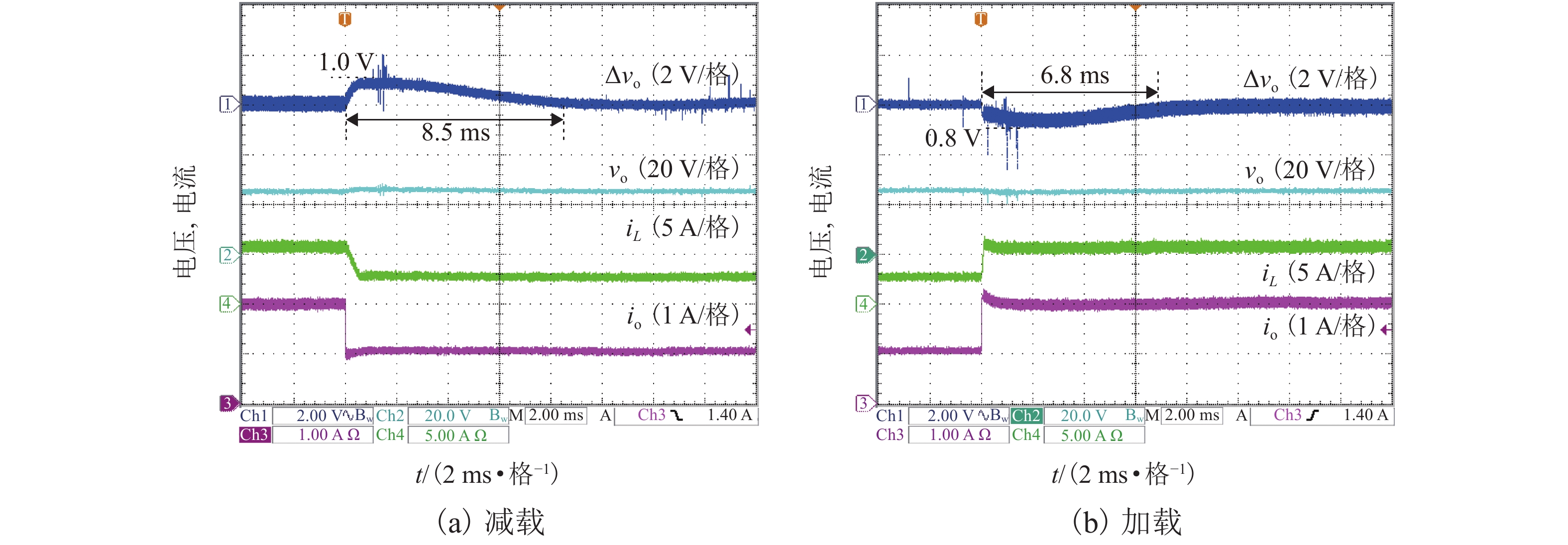
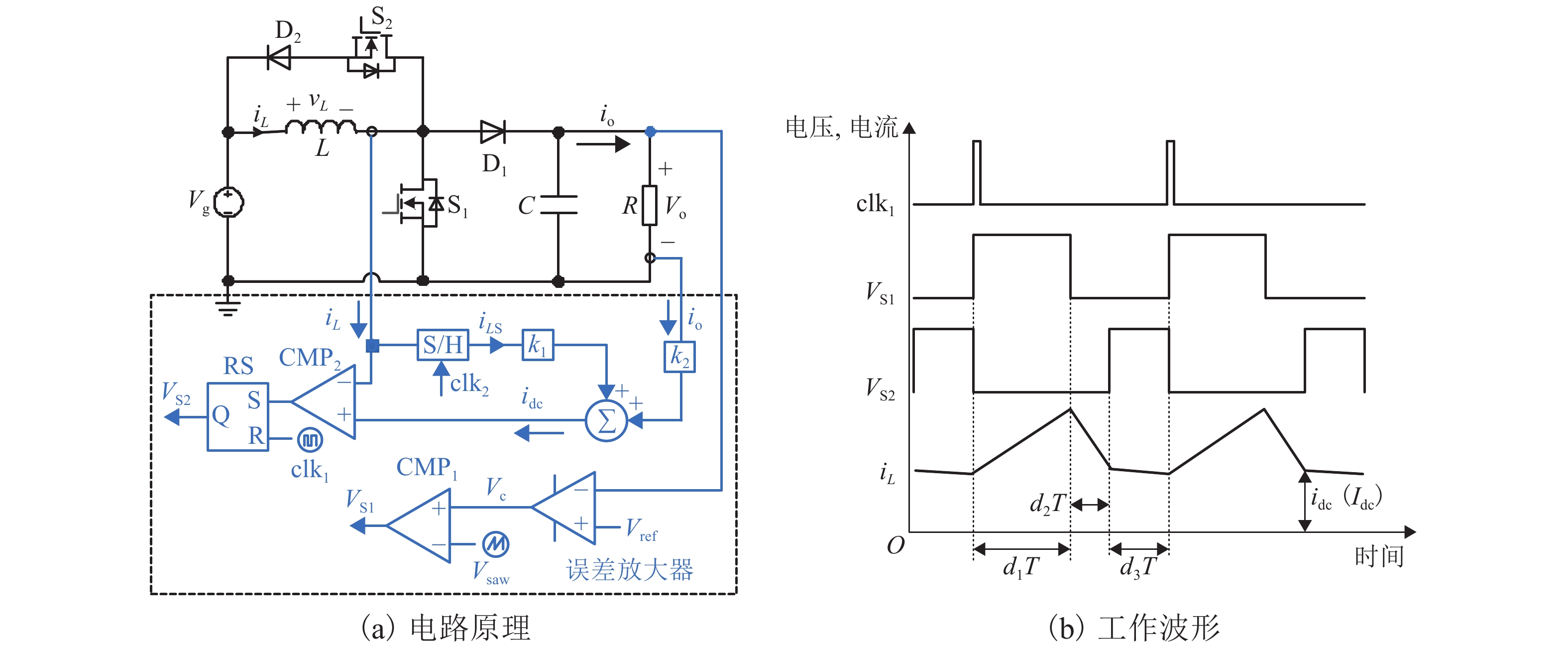
摘要: 为了提高工作于伪连续导电模式(pseudo continuous conduction mode,PCCM)的三态Boost变换器的效率、负载范围和瞬态响应性能,研究了一种动态参考电流(dynamic reference current,DRC)控制策略. 详细分析了DRC控制三态Boost变换器的工作原理,并比较了采用恒定参考电流(constant reference current,CRC)控制和DRC控制的三态Boost变换器的效率和负载瞬态响应性能,分别推导了它们的负载范围表达式,最后,通过实验对理论分析进行验证. 研究结果表明:与CRC控制相比,DRC控制三态Boost变换器的轻载效率提高了14%;在全负载范围内均能工作于PCCM模式,负载范围宽;负载减轻和增加时,调节时间分别减少了37.5%和32.0%,电压超调量分别减小了69.7%和61.9%,瞬态响应性能好.
-
关键词:
- 三态Boost变换器 /
- 动态参考电流控制 /
- 效率 /
- 负载范围 /
- 瞬态响应
Abstract: To improve the efficiency, load range, and transient response performance of a tri-state boost converter operating in the pseudo continuous conduction mode (PCCM), the dynamic reference current (DRC) control was studied. First, the principles of the DRC controlled tri-state boost converter were analysed. Further, its conversion efficiency and load transient response performance were compared with those of the tri-state boost converter with constant reference current (CRC) control. Furthermore, their corresponding load range expressions were deduced. Finally, the theoretical analyses were verified by experiment. The results show that the efficiency of the DRC controlled tri-state boost converter in the light-load condition is improved by 14% compared with that of the CRC controlled tri-state boost converter. Moreover, the DRC controlled tri-state boost converter can operate in PCCM within full-load range. When the load is reduced and increased, the regulation time is decreased by 37.5% and 32.0%, and the voltage overshoot is decreased by 69.7% and 61.9%, respectively. -
表 1 三态Boost变换器参数
Table 1. Parameters of the tri-state Boost converter
参数 物理量 取值 Vg 输入电压/ V 10 Vo 输出电压/ V 25 L 电感/μH 270 C 电容/μF 470 R 负载电阻/Ω 12.5~25.0 T 开关周期/μs 20 Idc 谷值参考电流/ A 5 k1 iL增益系数 0.5 k2 io增益系数 0.5 × 2.5 表 2 三态Boost变换器负载瞬态性能
Table 2. Load transient performance of tri-state boost converter
控制方法 调节时间/ms 超调量/V 减载 加载 减载 加载 电压型CRC 13.6 10.0 3.3 2.1 电压型DRC 8.5 6.8 1.0 0.8 -
YORK B, YU W S, LAI J S. An integrated boost resonant converter for photovoltaic applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2013, 28(3): 1199-1207. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2012.2207127 许建平,杨琦,刘雪山. 谐振式单开关多路输出Boost LED驱动电源[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(3): 475-486. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.03.007XU Jianping, YANG Qi, LIU Xueshan. Resonant single-switch multi-string Boost LED driver converter[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(3): 475-486. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.03.007 何圣仲,周国华,许建平,等. 谷值V2控制Boost变换器的频域与时域特性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(2): 218-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.02.003HE Shengzhong, ZHOU Guohua, XU Jianping, et al. Frequency-domain and time-domain characteristics of valley V2 controlled Boost converter[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(2): 218-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.02.003 SABLE D M, CHO B H, RIDLEY R B. Use of leading-edge modulation to transform Boost and flyback converters into minimum-phase-zero systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 1991, 6(4): 704-711. doi: 10.1109/63.97771 WU W C, BASS R M, YEARGAN J R. Eliminating the effects of right-half plane zero in fixed frequency Boost converters[C]//Power Electronics Specialists Conference. Fukuoka: IEEE, 1998: 362-366. HIMMELSTOSS F A, KOLAR J W, ZACH F C. Analysis of a Smith-predictor-based-control concept eliminating the right-half plane zero of continuous mode Boost and Buck-Boost DC/DC converters[C]//Industrial Electronics Conference. Kobe: IEEE, 1991: 423-428. VISWANATHAN K, ORUGANTI R, SRINIVASAN D. Tri-state Boost converter with no right half plane zero[C]//Power Electronics and Drive Systems International Conference. Denpasar: IEEE, 2001: 687-693. VISWANATHAN K, ORUGANTI R, SRINIVASAN D. A novel tri-state Boost converter with fast dynamics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2002, 17(5): 677-683. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2002.802197 KAPAT S, PATRA A, BANERJEE S. A novel current controlled tri-state Boost converter with superior dynamic performance[C]//International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. Seattle: IEEE, 2008: 2194-2197. GONG Huabin, WU Songrong, LIU Jie, et al. Bi-frequency control technology for pseudo continuous conduction mode switching DC-DC converter[C]// Propagation and EMC Technologies for Wireless Communications. Chengdu: IEEE, 2013: 684-690. VISWANATHAN K, ORUGANTI R, SRINIVASAN D. Dual-mode control of tri-state Boost converter for improved performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2005, 20(4): 790-797. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2005.850907 KAPAT S, PATRA A, BANERJEE S. A current-controlled tristate Boost converter with improved performance through RHP zero elimination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2009, 24(3): 776-786. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2008.2008994 刘锦波, 明文龙. 三态Boost型DC/DC变换器的数学模型及其输入/输出反馈线性化非线性控制方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2010, 30(增刊1): 171-177.LIU Jinbo, MING Wenlong. Mathematical model and its input/output feedback linearization control method of tri-state Boost type DC/DC converter[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2010, 30(S1): 171-177. 唐骐,王久和,胡经纬. 三态Boost型DC/DC变换器的无源控制方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2013,33(S1): 171-175.TANG Qi, WANG Jiuhe, HU Jingwei. Passivity-based control method of the tri-state Boost DC/DC converter[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(S1): 171-175. 崔恒丰,周国华,陈兴. 伪连续导电模式Buck变换器的动态参考电流控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报,2017,32(2): 246-254.CUI Hengfeng, ZHOU Guohua, CHEN Xing. Dynamic-reference-current control strategy for Buck converter in pseudo continuous conduction mode[J]. Transactions of China electrotechnical society, 2017, 32(2): 246-254. 李振华,周国华,刘啸天,等. 电感电流伪连续导电模式下Buck变换器的动力学建模与分析[J]. 物理学报,2015,64(18): 205-214.LI Zhenhua, ZHOU Guohua, LIU Xiaotian, et al. Dynamical modeling and analysis of Buck converter operating in pseudo-continuous conduction mode[J]. Acta Phys. Sin., 2015, 64(18): 205-214. VISWANATHAN K, ORUGANTI R, SRINIVASAN D. Design and evaluation of tri-state Boost converter[C]//Power Electronics Specialists Conference. Aachen: IEEE, 2004: 4662-4668. -




 下载:
下载: