Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructures and Properties of Wire and Arc Additive-Manufactured Bainite Steel
-
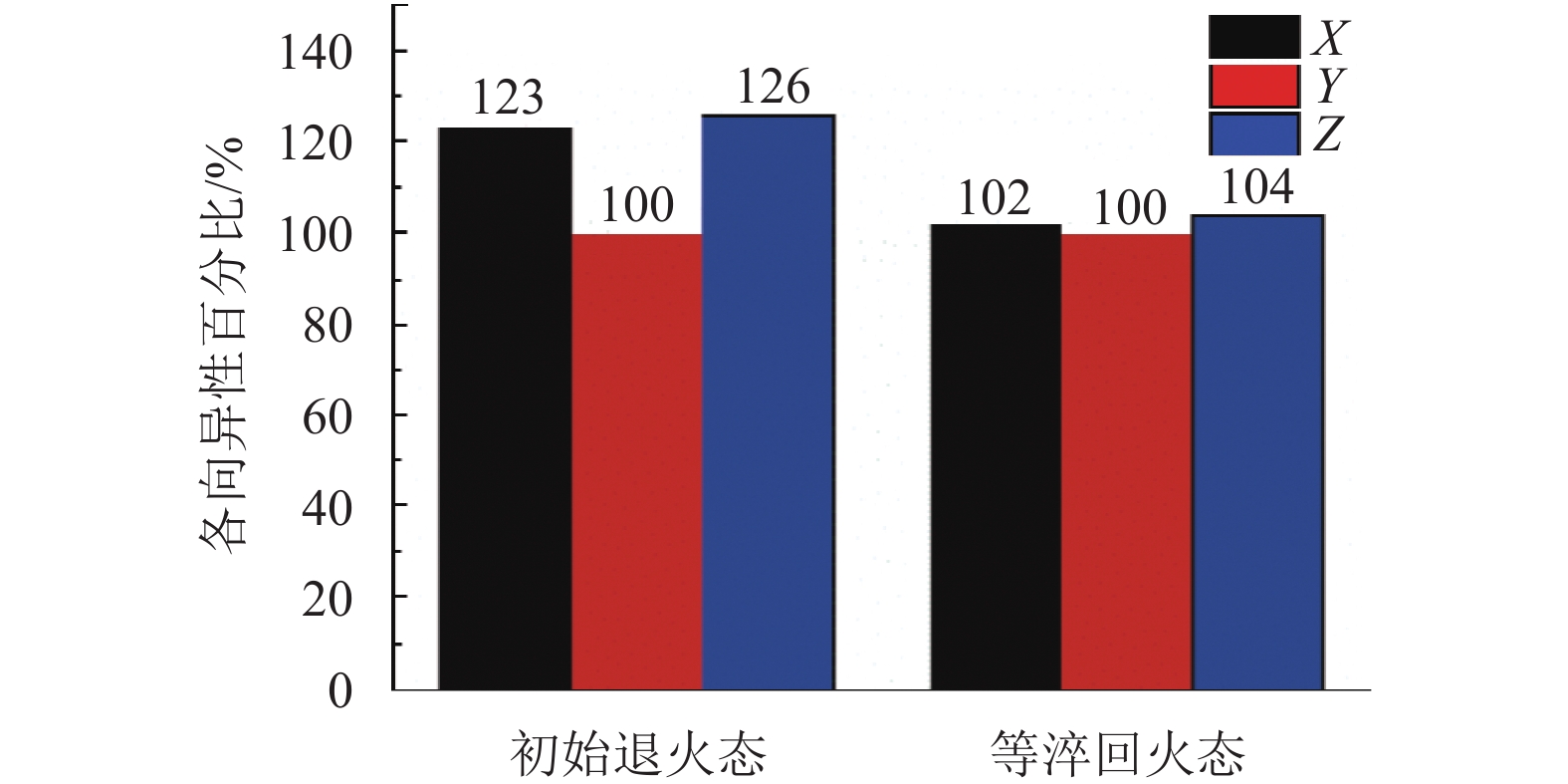
摘要: 针对金属电弧增材制造过程热循环在线控制困难,导致成形组织不均、力学性能低下的问题,以辙叉用贝氏体钢为成形材料,研究了不同整体后热处理工艺对其电弧增材制造试样组织及性能的影响,并对热处理工艺进行了优化.研究结果表明:去应力退火后的电弧增材制造试样力学性能较差,且存在各向异性,经290 ℃等温淬火与280 ℃回火处理后,试样微观组织由回火索氏体转变为下贝氏体+回火马氏体,抗拉强度提升39%,屈服强度提升61%,断后延伸率提升29%,冲击韧性提升17%,硬度提升20%,且各向异性特征大大缓解,材料组织趋于均匀.Abstract: It is difficult to actively control the thermal cycle in wire and arc additive manufacturing(WAAM), resulting in uneven microstructures and poor mechanical properties. Therefore, an anisothermal quenching and tempering process for bainite steel deposition is presented herein. The microstructures and properties were analysed and optimised after a series of heat treatments. The results show that the annealed microstructures change from tempered sorbite to lower bainite and tempered martensite after posttreatment, and the anisotropy is evidently weakened. After isothermal quenching at 290 ℃/oil cooling followed by tempering at 280 ℃/air cooling, the WAAM bainite steel shows more homogeneous microstructures and better mechanical properties, with increases in the tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, impact toughness, and hardness, by 39%, 61%, 29%, 17%, and 20%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- heat treatment /
- bainite steel /
- additive manufacturing /
- microstructures and properties
-
表 1 贝氏体钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of bainite steel
化学成分 C Si Mn Cr Ni Mo Ti Cu 其他 wB/% 0.231 1.918 1.651 1.294 0.360 0.433 0.089 0.110 — 表 2 不同热处理条件下试样的力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties under different conditions
热处理条件 力学性能 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 延伸率/% 冲击韧性/(J•cm–2) 硬度/HRC 初始退火态 933 1 258 11.0 30 41 290 ℃等淬,2 min/mm 1 078 1 686` 14.6 35 49 330 ℃等淬,2 min/mm 1 218 1 610 10.0 31 48 370 ℃等淬,2 min/mm 1 230 1 796 4.9 28 50 420 ℃等淬,2 min/mm 1 142 1 595 3.7 25 48 290 ℃等淬,1 min/mm 1 135 1 977 9.4 30 51 290 ℃等淬,3 min/mm 1 224 1 746 15.1 36 50 290 ℃等淬,2 min/mm,+280 ℃回火 1 499 1 749 14.2 35 49 290 ℃等淬,2 min/mm,+350 ℃回火 1 480 1 657 10.8 33 48 290 ℃等淬,2 min/mm,+420 ℃回火 1 203 1 583 6.9 26 47 -
耿海滨,熊江涛,黄丹,等. 丝材电弧增材制造技术研究现状与趋势[J]. 焊接,2015(11): 17-21GENG Haibin, XIONG Jiangtao, HUANG Dan, et al. Research status and trends of wire and arc additive manufacturing[J]. Welding, 2015(11): 17-21 熊俊,薛永刚,陈辉,等. 电弧增材制造成形控制技术的研究现状与展望[J]. 电焊机,2015,45(9): 45-50XIONG Jun, XUE Yonggang, CHEN Hui, et al. Status and development prospects of forming control technology in arc-based additive manufacturing[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2015, 45(9): 45-50 黄春平,黄硕文,刘奋成. 增材制造专题:金属材料增材制造技术[J]. 金属加工:热加工,2016(2): 33-38HUANG Chunping, HUANG Shuowen, LIU Fencheng. Topic of additive manufacturing:additive manufacturing technology of metal materials[J]. Metal Working:Hot Working, 2016(2): 33-38 田彩兰,陈济轮,董鹏,等. 国外电弧增材制造技术的研究现状及展望[J]. 航天制造技术,2015(2): 58-60TIAN Cailan, CHEN Jilun, DONG Peng, et al. Current state and future development of the wire arc additive manufacture technology abroad[J]. Aerospace Manufacturing Technology, 2015(2): 58-60 王桂兰,符友恒,梁立业,等. 电弧微铸轧复合增材新方法制造高强度钢零件[J]. 热加工工艺,2015,44(13): 24-26WANG Guilan, FU Youheng, LIANG Liye, et al. New hybrid additive manufacturing method for forming high strength parts by weld-rolling[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2015, 44(13): 24-26 董博伦,柏久阳,林三宝,等. 激光/电弧增材制造金属的热处理工艺研究现状与发展[J]. 焊接,2016(4): 17-22DONG Bolun, BAIJ iuyang, LIN Sanbao, et al. Current state and future development of heat treatment of metals deposited by laser/arc based additive manufacturing[J]. Welding, 2016(4): 17-22 WANG Y D, TANG H B, FANG Y L, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser melting deposited 1Cr12Ni2WMoVNb steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2010, 528(1): 474-479 BRANDL E, SCHOBERTH A, LEYENS C. Morphology,microstructure,and hardness of titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) blocks deposited by wire-feed additive layer manufacturing (ALM)[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2012, 532(3): 295-307 吕耀辉,徐富家,刘玉欣,等. 固溶温度对等离子快速成形Inconel 625合金组织的影响[J]. 材料科学与工艺,2013,21(2): 14-19LÜ Yaohui, XU Fujia, LIU Yuxin, et al. Effect of solution temperature on the microstructure of Inconel 625 alloy fabricated by PAW rapid prototyping[J]. Materials Science & Technology, 2013, 21(2): 14-19 WAUTHLE R, VRANCKEN B, BEYNAERTS B, et al. Effects of build orientation and heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V lattice structures[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2015, 5: 77-84 熊师兵,栾道成,张仁进,等. 不同热处理方式对贝氏体钢组织性能的影响[J]. 科学与财富,2015(19): 99-100XIONG Shibing, LUAN Daocheng, ZHANG Renjin, et al. Effect of different heat treatments on the microstructure and properties of bainitic steel[J]. Sciences & Wealth, 2015(19): 99-100 张仁进,栾道成,田翰林,等. 等温处理对辙叉用新型贝氏体钢接触疲劳性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理,2015,40(12): 106-109ZHANG Renjin, LUAN Daocheng, TIAN Hanlin, et al. Effect of isothermal treatment on contact fatigue of a new bainite steel for frog[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2015, 40(12): 106-109 BAUFELD B, BIEST O V D, GAULT R. Additive manufacturing of Ti–6Al–4V components by shaped metal deposition:microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Materials & Design, 2010, 31(Sup.1): 106-111 WANG F, WILLIAMS S, COLEGROVE P, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of wire and arc additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 2013, 44(2): 968-977 张萍,刘德波,师建行,等. TIG增材制造TC4钛合金力学性能及工艺参数的影响规律[J]. 焊接,2015(10): 45-48ZHANG Ping, LIU Debo, SHI Jianxing, et al. Mechanical properties of TC4 components produced by additive manufacturing with TIG welding[J]. Welding, 2015(10): 45-48 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 王伟,赵飞,匡祯辉,白振华,刘勇. 基于聚类和GBDT的镀锌钢卷力学性能预测. 重型机械. 2024(02): 54-58 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 周凡,顾介仁,王克鸿,柴权赢. 等离子弧增材低碳贝氏体钢组织与性能分析. 焊接学报. 2023(05): 117-121+135-136 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 熊鹏,赵雷杰,张孜,王艳辉,岳赟,郝晓歌. 无碳化物贝氏体钢摩擦磨损性能研究进展. 技术与市场. 2022(11): 52-54+58 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 江易林,方金祥,董世运,潘亮. 无碳化物贝氏体钢的研究进展. 热加工工艺. 2020(22): 16-21 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-






 下载:
下载:





 百度学术
百度学术
