Optimization of Structural Setting Based on Forced Ventilation Method in Tunnel Under Construction
-
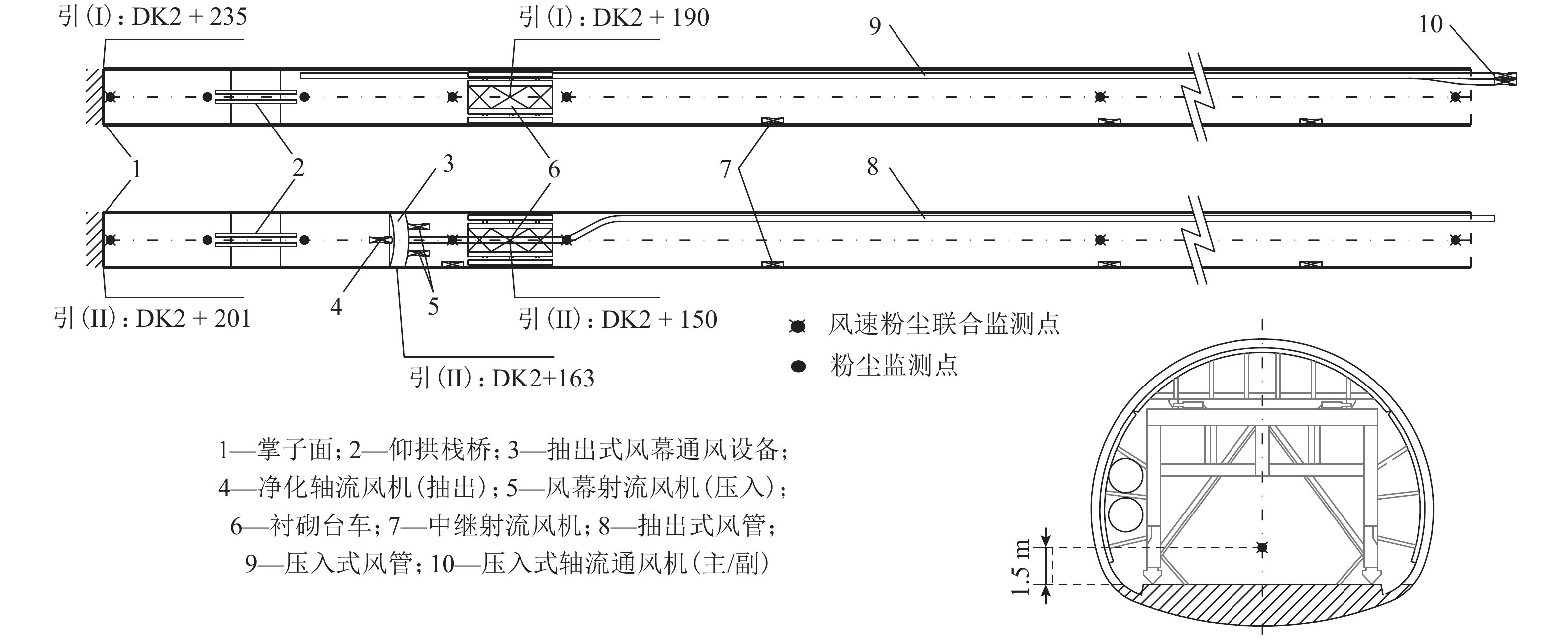
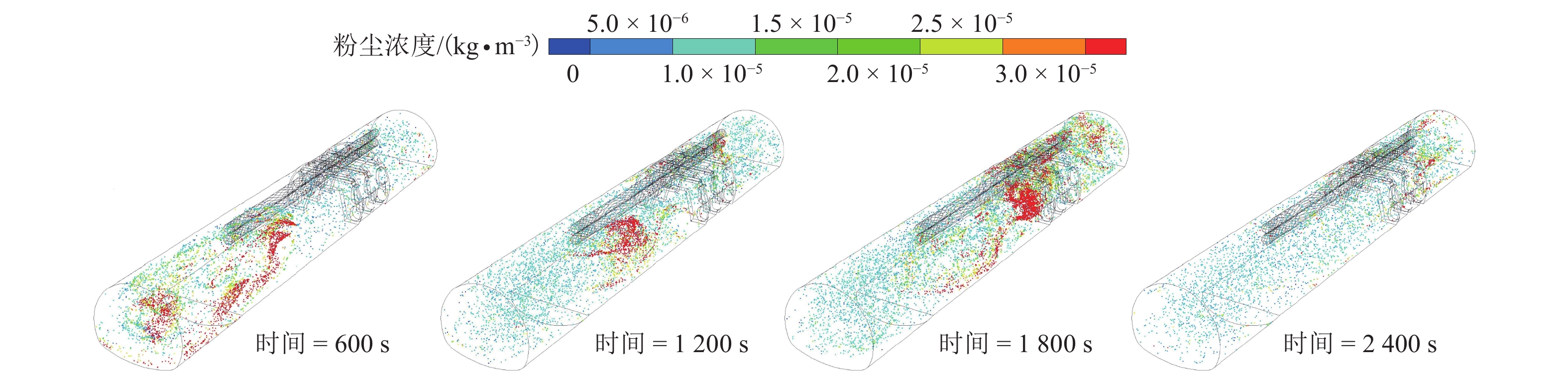
摘要: 针对钻爆法施工隧道中压入通风方式造成的隧道内空气质量差、排尘久等缺点,在传统通风方式的基础上进行结构优化改进,形成抽出式风幕通风方式. 以吴家岭二级水电站新建I号、II号引水隧道为试验隧道,对两种通风方式条件下隧道内风速及游离SiO2粉尘扩散特点进行现场监测与对比分析,并应用有限元Ansys-CFD软件对游离SiO2粉尘浓度场演化特征进行了模拟分析. 研究结果表明:在抽出式风幕通风条件下通风35 min后,施工作业区内游离SiO2粉尘浓度即可达标,洞身区只存在少量极低浓度SiO2粉尘,作业区内SiO2粉尘浓度最大净化率较压入式通风方式提高了25.93%,隧体内施工环境大为改善.Abstract: Considering the disadvantages of poor air quality and prolonged dust removal caused by the forced ventilation mode in tunnel construction using drilling and blasting methods, the extractive and air curtain ventilation mode was developed by structure optimization and improvement over the traditional ventilation mode. Diversion tunnels I and II of Wujialing second stage hydropower station were used as the research site, with wind speed and characteristics of free SiO2 dust diffusion monitored and comparatively analysed on site. Moreover, the evolution characteristics of the free SiO2 dust concentration field were simulated and analysed using Ansys-CFD. The results indicate that the concentration of free SiO2 dust in the working area can reach the standard after ventilating for 35 min under the extractive and air curtain ventilation mode, with little free SiO2 dust and a low concentration of dust in the tunnel body area. In addition, the maximum purification rate of SiO2 dust in the working area is 25.93% higher than that in the forced ventilation mode, and the construction environment in the tunnel is greatly improved.
-
表 1 通风机标定技术参数
Table 1. Specifications of ventilators
型号 档位 风量/
(m3•min–1)风压/
kPa功率/
kW风速/
(m•s–1)SDF(C)
—14高速 3 200 6.8 360 5.24 中速 2 000 3.1 120 3.28 低速 1 600 1.7 50 2.62 SDF(C)—13.5 高速 2 600 5.9 260 4.26 中速 1 900 2.7 80 3.11 低速 1 400 1.4 34 2.30 高速 2 100 4.6 145 3.44 SDZ—11.5 中速 1 500 2.1 45 2.46 低速 1 100 1.1 20 1.80 SSF—12.5 定速 2 000 2.5 75 3.27 表 2 监测设备标定技术参数
Table 2. Specifications of monitoring equipment
参数类型 风速测量 粉尘监测 仪器型号 QY—JL24型 LD—3C型 测量范围 0~60 m/s 低:0.01~300 mg/m3
高:0.001~10 mg/m3灵敏度 — 低:0.010 mg/m3
高:0.001 mg/m3精度 ± 0.1 m/s ± 10% 重复误差 1% 2% 测定时间 1~24 h 手动设置 设备存储 6 999组
数据循环99组
数据表 3 Ansys-CFD求解器与流场边界条件设置
Table 3. Solver settings and boundary conditions of the flow field in Ansys-CFD
求解器参数 类型 时间状态 离散项 模型 物质名称 总质量流率/(kg•s–1) 定义 基于压力 非定常 开启 κ-epsilon SiO2 0.848 边界类型 风幕喷口 通风管口 隧道壁/掌子面 衬砌台车 壁面类型 隧道口 定义 速度入口 速度入口 壁面 壁面 捕捉 流量出口 -
ZHANG Xuejin, ZHOU Chaoyue. Construction ventilation of tongluoshan expressway tunnel[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 838/839/840/841: 1234-1239 郭春,孙志涛,王明年. 特长TBM施工隧道环境粉尘安全控制研究[J]. 工业安全与环保,2015,4(7): 63-66GUO Chun, SUN Zhitao, WANG Mingnian. Study on the dust control of the construction environment safety in extra-long tunnel driven by TBM[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2015, 4(7): 63-66 曹建生. 新线铁路隧道施工粉尘危害及治理措施的探讨[J]. 铁道劳动安全卫生与环保,1998,25(4): 254-257CAO Jiansheng. The discussion of the harm and control measures about dust in new railway tunnel[J]. Labor Safety Health and Environmental Protection In Railway, 1998, 25(4): 254-257 孙忠强. 公路隧道钻爆法施工粉尘运移规律及控制技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2015 蒋志阳. 自动喷淋降尘系统在煤矿中的使用[J]. 信息系统工程,2016,5(4): 74-75JANG Zhiyang. The usage of automatic sprinkler system in coal mine[J]. China CIO News, 2016, 5(4): 74-75 王晓奎,令孤勇生. 大秦铁路花果山隧道通风降尘设计试验研究[J]. 铁道建筑,2014(11): 85-87WANG Xiaokui, LINGHU Yongsheng. Experimental study on the design of ventilation and dust removal in Huaguoshan tunnel of daqin railway[J]. Railway Engineering, 2014(11): 85-87 冷廷双. 宋存义. 布袋除尘器处理高浓度粉尘的试验研究[J]. 环境工程,2014,6(12): 83-87LENG Tingshuang, SONG Cunyi. Research on the treatment of high concentration dust with bag filter[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 6(12): 83-87 吴应豪. 巷道粉尘沉降规律与转载点喷雾降尘系统研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2007 GAO Jianliang. Simulation of thermal environment conditions in heading face with forcing auxiliary ventilation[J]. Shigen to Sozaiv, 2002: 118-119 陈华腾, 钮强等. 爆破计算手册[M]. 辽宁: 辽宁科学技术出版社, 1991: 45-100 中华人民共和国国家职业卫生标准. 工作场所空气质量测定: GBZ/T192.1—2007[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国卫生部. 2007 谭信荣,陈寿根. 空气质量测试在长大隧道施工中的应用[J]. 安全与环境学报,2012,6(2): 103-107TAN Xinrong, CHEN Shougen. The application of air quality test in the construction of growing tunnel[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2012, 6(2): 103-107 谭信荣,陈寿根. 钻爆法施工隧道空气质量现场测试[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2016,12(2): 567-572TAN Xinrong, CHEN Shougen. Air quality field testing in tunnel construction with the drilling and blasting method[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2016, 12(2): 567-572 ZHANG Xiantang, YI Bai. Study and application on dust comprehensive prevention and control technology in tunnel excavation by blasting[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 549: 931-635 CHEN Junsheng. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of ventilation effect of a large cross-section cable tunnel[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 10: 1404-1410 中华人民共和国行业标准. 工作场所粉尘容许浓度: BGZ2—2002[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2002 中华人民共和国水利行业标准. 水工建筑物地下开挖工程施工规范: SL378—2007[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国水利部, 2008 张秀华. 回采爆破空间中炮烟扩散规律模拟与分析[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010 牛伟,蒋仲安,王晓珍,等. 综放工作面粉尘浓度分布规律的数值模拟[J]. 中国矿业,2008,17(12): 77-80NIU Wei, JIANG Zhongan, WANG Xiaozhen, et al. Numerical simulation of distribution regularities of dust concentration in fully mechanized top-coal caving face[J]. China Mining, 2008, 17(12): 77-80 李艳强,吴超,易斌,等. 受限空间内粉尘流动的浓度分布模型及其数值模拟[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2007,17(10): 50-55LI Yanqiang, WU chao, YI bin, et al. Mathematical models and numerical simulation of concentration distribution of dust flowing in limited space[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2007, 17(10): 50-55 岑可法, 樊建人. 工程气固多相流动的理论及计算[M]. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 1990: 24-26 任玉新, 陈海昕. 计算流体力学基础[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006: 66-67 四川省泰坤建筑工程有限公司. 吴家岭二级水电站新建引水隧道空气净化阶段报告[DB/OL]. [2017-9-2]. http://wenku.baidu.com/view/45efc789eb172ded630b1c9864 -






 下载:
下载: