Study of Large Deformation Classification Criterion for Layered Soft Rock Tunnels under High Geostress
-
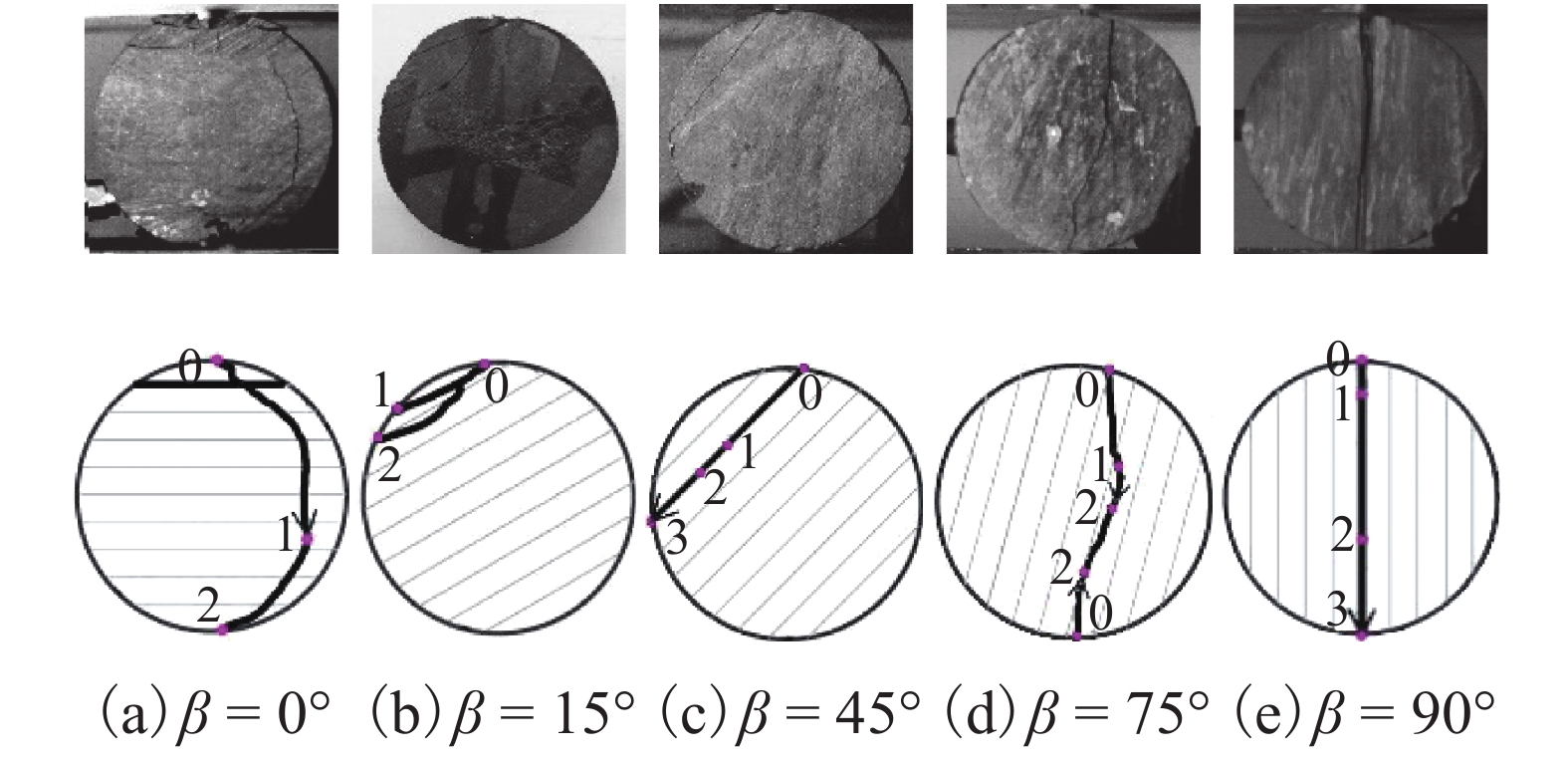
摘要: 为探明高地应力层状软岩隧道的非对称变形破坏规律及其支护结构的非对称受力特性,结合碳质千枚岩力学特性与变形破坏机制的各向异性特性,对层状软岩隧道围岩的非对称变形破坏特征进行了分析. 在93座典型高地应力层状软岩隧道变形数据的基础上,系统性地分析了隧道拱顶沉降、水平收敛、最大变形量与地应力、岩体抗压强度、隧道埋深之间的关系. 研究结果表明:高地应力层状软岩隧道的变形量与最大地应力、岩体抗压强度、埋深的分布较为离散,在一定地应力、岩体强度或埋深条件下,隧道变形量既存在于高值区间,也存在于低值区间;隧道变形量随地应力的增大、岩体强度的降低、埋深的升高逐渐向高值区间靠拢,高地应力层状软岩隧道大变形是高地应力、软弱围岩、层理弱面耦合作用的结果;基于隧道最大变形量与隧道强度应力比的幂指数变化规律,提出了高地应力层状软岩隧道的大变形预测分级指标.Abstract: The asymmetric deformation failure characteristics and asymmetric mechanical behaviour of supporting structures in layered soft rock tunnels under high geostress, combined with the anisotropic mechanical properties of carbonaceous phyllite, were investigated. Based on the deformation data of 93 layered soft rock tunnels under high geostress, the relationships between roof settlement, horizontal convergence, largest deformation and geostress, rock compressive strength, and overburden depth were systemically analysed. The results show that the deformations are discretely distributed according to the variations in geostress, rock compressive strength, and overburden depth. Under certain parameters of geostress, rock compressive strength, or overburden depth, the deformations are distributed in both the high- and low-value zones. With increasing geostress and overburden depth, and with decreasing rock compressive strength, the deformations gradually approach the high-value zone. This means that the large deformations of layered soft rock tunnels under high geostress are determined by the combined action of high geostress, weak surrounding rock, and a weak bedding plane. Based on the power exponent variation law between the largest deformation and the strength-stress ratio, a new classification criterion for large deformations is proposed for layered soft rock tunnels under high geostress.
-
表 1 典型高地应力条件下深埋长大层状软岩隧道统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of typical high geostress and layered soft rock tunnels
隧道名称 隧道
长度/m最大
埋深/m穿越地层
岩性最大主应力/MPa 围岩抗压强度/MPa 最大拱顶沉降/mm 最大水平收敛/mm 围岩与支护结构变形破坏特征 奥地利
陶恩6 400 1 000 绿泥石,
千枚岩27.00 1.70 1 200 500 世界上第1座知名的大变形隧道,施工中在层状软岩地层发生了大变形,最大位移速度达20 cm/d. 兰渝铁路木寨岭 19 068 715 薄层状炭质
板岩27.16 5.92 1 712 1 081 极高地应力软岩大变形隧道,开创小导洞应力释放+三层支护+长锚索+单层衬砌的“木寨岭模式”. 南昆铁路家竹菁 4 990 404 页岩,层状
煤层16.09 1.70 1 000 1 600 集高地应力、高瓦斯突出、高涌突水的铁路隧道,在高地应力条件下的层状软岩煤层中发生大变形. 成兰铁路茂县 25 000 675 绢云母千枚岩夹炭质千枚岩,陡倾 27.52 1.95 510 810 发生挤压性大变形,变形增长持续时间长,时间效应显著,岩层陡倾导致隧道水平收敛大于拱顶沉降. 兰新线乌鞘岭 20 050 1 100 千枚岩夹板岩 32.80 0.70~2.50 1 209 1 053 穿越挤压性断层,围岩整体稳定性较差,受强烈挤压变形,变形量大,初期变形速率快,变形时间长. 兰渝铁路两水 4 922 346 千枚岩与碳质板岩 10.50 2.90 750 543 变形迅速而强烈,且持续时间较长,混凝土大量开裂、掉块,部分钢拱架扭曲、断裂,支护结构失稳. 宜万铁路堡镇 11 600 630 炭质页岩 16.00 2.90 640 1 250 变形量大、变形发展快、持续时间长,且时空效应上具有明显的不对称性和不均匀性,顺层偏压严重. 西格二线关角 22 040 500 泥质片岩 22.04 5.00 505 460 隧道底部隆起和两侧边墙挤出,且变形持续时间长,通车不久后再次发生底部隆起,导致行车中断. 兰渝铁路新城子 9 164 749 薄层状碳质
板岩33.82 15.00 356 443 二衬受到强烈挤压产生不同程度的开裂、剥落、掉块现象,部分区段衬砌严重裂损,钢筋完全扭曲. 国道317
鹧鸪山4 423 1 000 薄层状碳质千枚岩,倾角40°~60° 20.00 12.00 300 300 围岩变形量较大,持续的时间长,表现为初期支护破裂、钢拱架扭曲,侵入隧道限界,易产生塌方. 兰渝铁路毛羽山 8 503 700 薄层状板岩,倾角70°~90° 21.28 5.63 540 1 200 围岩变形量大,变形速率快,具有显著的流变效应. 钢拱架严重扭曲、断裂,水平收敛远大于拱顶沉降. 渝沙高速共和 4 779 1 000 薄层状砂质页岩,倾角30°~40° 29.86 11.40 200 300 沿岩层法线方向的右拱肩和左拱脚部位的初期支护出现混泥土纵向开裂与钢架弯曲,围岩偏压严重. 表 2 高地应力层状软岩隧道的大变形分级指标
Table 2. Large deformatin classfication criterion for high geostress and layered soft rock tunnel
大变形等级 强度应力比 最大变形量/mm 无 > 0.80 < 100 轻微 (0.60,0.80] (300,100] 中等 (0.32,0.60] (500,300] 严重 (0.18,0.32] (800,500] 极严重 ≤ 0.18 ≥ 800 -
MENG L B, LI T B, JIANG Y, et al. Characteristics and mechanisms of large deformation in the Zhegu mountain tunnel on the Sichuan-Tibet highway[J]. Tunnelling & Underground Space Technology, 2013, 37(6): 157-164 李国良,刘志春,朱永全. 兰渝铁路高地应力软岩隧道挤压大变形规律及分级标准研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2015,52(1): 62-68LI Guoliang, LIU Zhichun, ZHU Yongquan. On the large squeezing deformation law and classification criteria for the Lanzhou–Chongqing railway tunnels in soft and high geostress rocks[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2015, 52(1): 62-68 赵福善. 兰渝铁路两水隧道高地应力软岩大变形控制技术[J]. 隧道建设,2014,34(6): 546-553ZHAO Fushan. Technologies to control serious deformation of soft rocks with high ground stress:case study on Liangshui tunnel on Lanzhou–Chongqing railway[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2014, 34(6): 546-553 李廷春. 毛羽山隧道高地应力软岩大变形施工控制技术[J]. 现代隧道技术,2011,48(2): 59-67LI Yanchun. Large deformation control technology for maoyushan tunnel in soft rock under high insitu stresses[J]. Modern Tunneling Technology, 2011, 48(2): 59-67 雷军,张金柱,林传年. 乌鞘岭特长隧道复杂地质条件下断层带应力及变形现场监测分析[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(5): 1367-1371LEI Jun, ZHANG Jinzhu, LIN Chuannian. Analysis of stress and deformation site-monitoring in fault zone of Wushaoling tunnel under complex geological conditions[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(5): 1367-1371 宋章, 蒋良文, 杜宇本, 等. 成兰铁路软岩隧道大变形特征及成因机制探析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(增刊1): 11-16SONG Zhang, JIANG Liangwen, DU Yunben, et al. Analysis on characteristic and formation mechanism of larger deformation for the tunnel of Chengdu–Lanzhou railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(Sup.1): 11-16 吴永胜, 谭忠盛, 李少孟. 挤压性大变形隧道围岩基本特性的试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2015, 48(增刊1): 398-402WU Yongsheng, TAN Zhongsheng, LI Shaomeng. Experimental study on the basic characteristics of tunnel in squeezing surrounding rock with large deformation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2015, 48(Sup.1): 398-402 梅志荣,李传富,张军伟,等. 成兰铁路高地应力软岩隧道大变形发生机理及控制技术[J]. 现代隧道技术,2014,51(增刊1): 11-18MEI Zhirong, LI Chuanfu, ZHANG Junwei. Occrence mechanism and control technology of large deformation in soft rock tunnels with high ground stress on Chengdu–Lanzhou railway[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2014, 51(Sup.1): 11-18 李鹏飞,田四明,赵勇,等. 高地应力软弱围岩隧道初期支护受力特性的现场监测研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2013,32(增刊1): 3509-3519LI Pengfei, TIAN Siming, ZHAO Yong, et al. In-situ monitoring study of mechanical characteristics of primary lining in weak rock tunnel with high geostress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(Sup.1): 3509-3519 刘高,张帆宇,李新召,等. 木寨岭隧道大变形特征及机理分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(增刊1): 5521-5526LIU Gao, ZHANG Fanyu, LI Xinzhao, et al. Research on large deformation and its mechanics of Muzhailing tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(Sup.1): 5521-5526 衡帅,杨春和,张保平,等. 页岩各向异性特征的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(3): 609-616HENG Shuai, YANG Chunhe, ZHANG Baoping, et al. Experimental research on anisotropic properties of shale[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(3): 609-616 刘志春,朱永全,李文江,等. 挤压性围岩隧道大变形机理及分级标准研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2008,30(5): 690-697LIU Zhichun, ZHU Yongquan, LI Wenjiang, et al. Mechanism and classification criterion for large deformation of squeezing ground tunnels[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2008, 30(5): 690-697 李永林,冯学钢,姜云,等. 隧道工程围岩大变形及预测预报研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2005,42(5): 49-54,62LI Yonglin, FENG Xuegang, JIANG Yun, et al. Large deformations encountered in the surrounding rocks of tunnels and their prediction[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2005, 42(5): 49-54,62 HOEK E, MARINOS P. Predicting tunnel squeezing problems in weak heterogeneous rock masses[J]. Tunnels and Tunneling International, 2000, 32(11): 45-51 -






 下载:
下载: