Parameters Analysis Based on Simplified Method to Solve Piled Embankment with Geogrid-Reinforcement
-
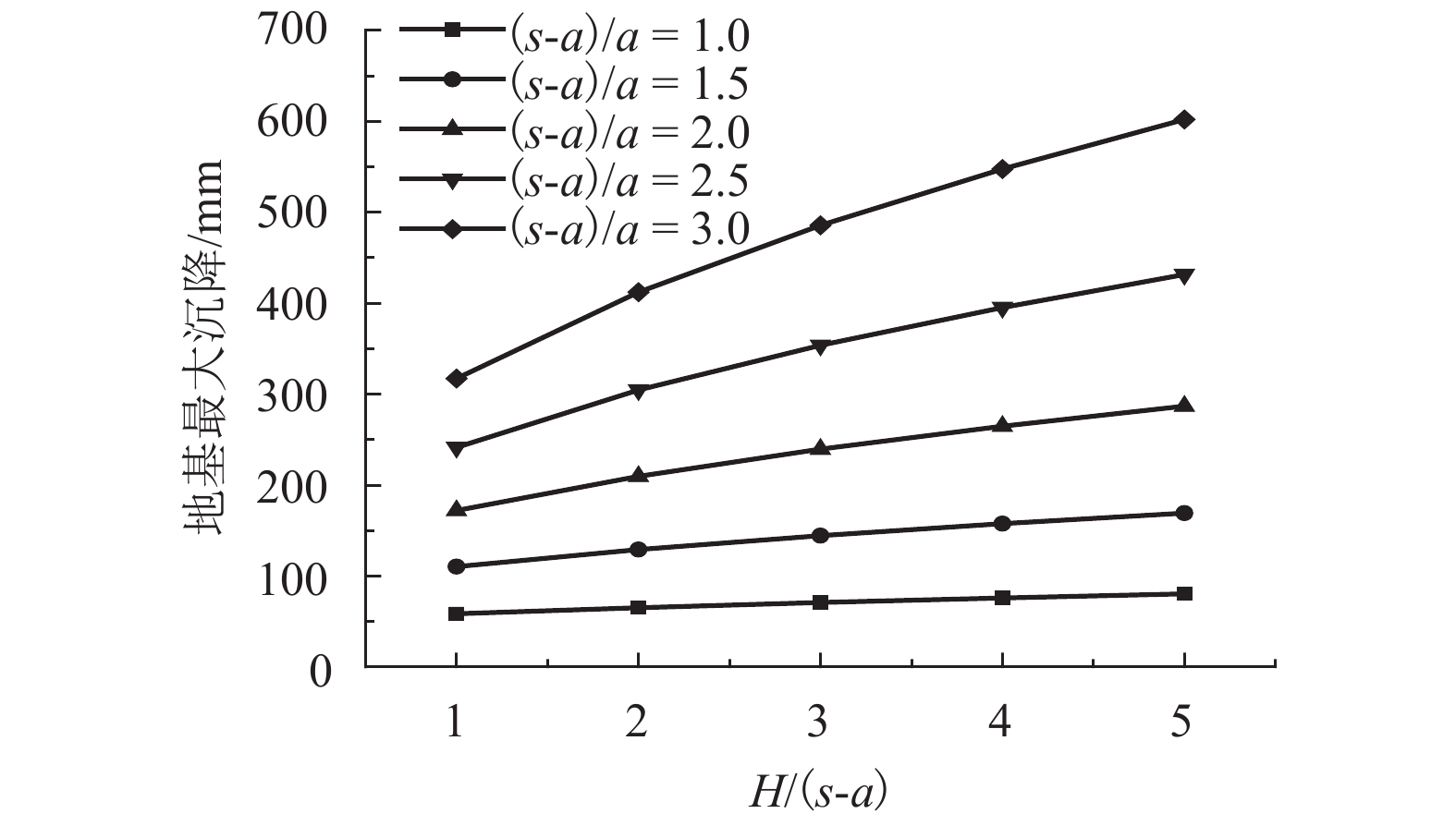
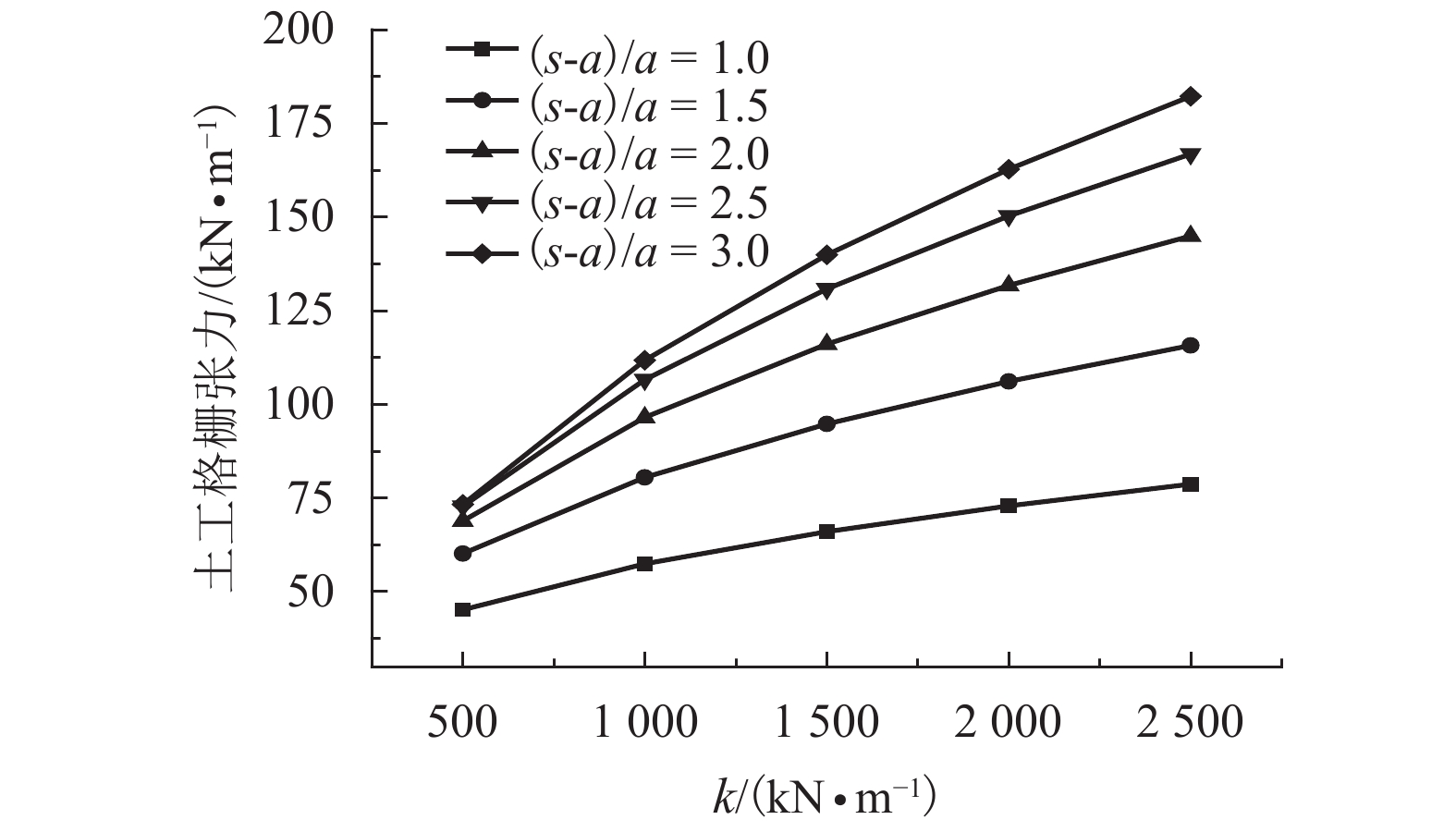
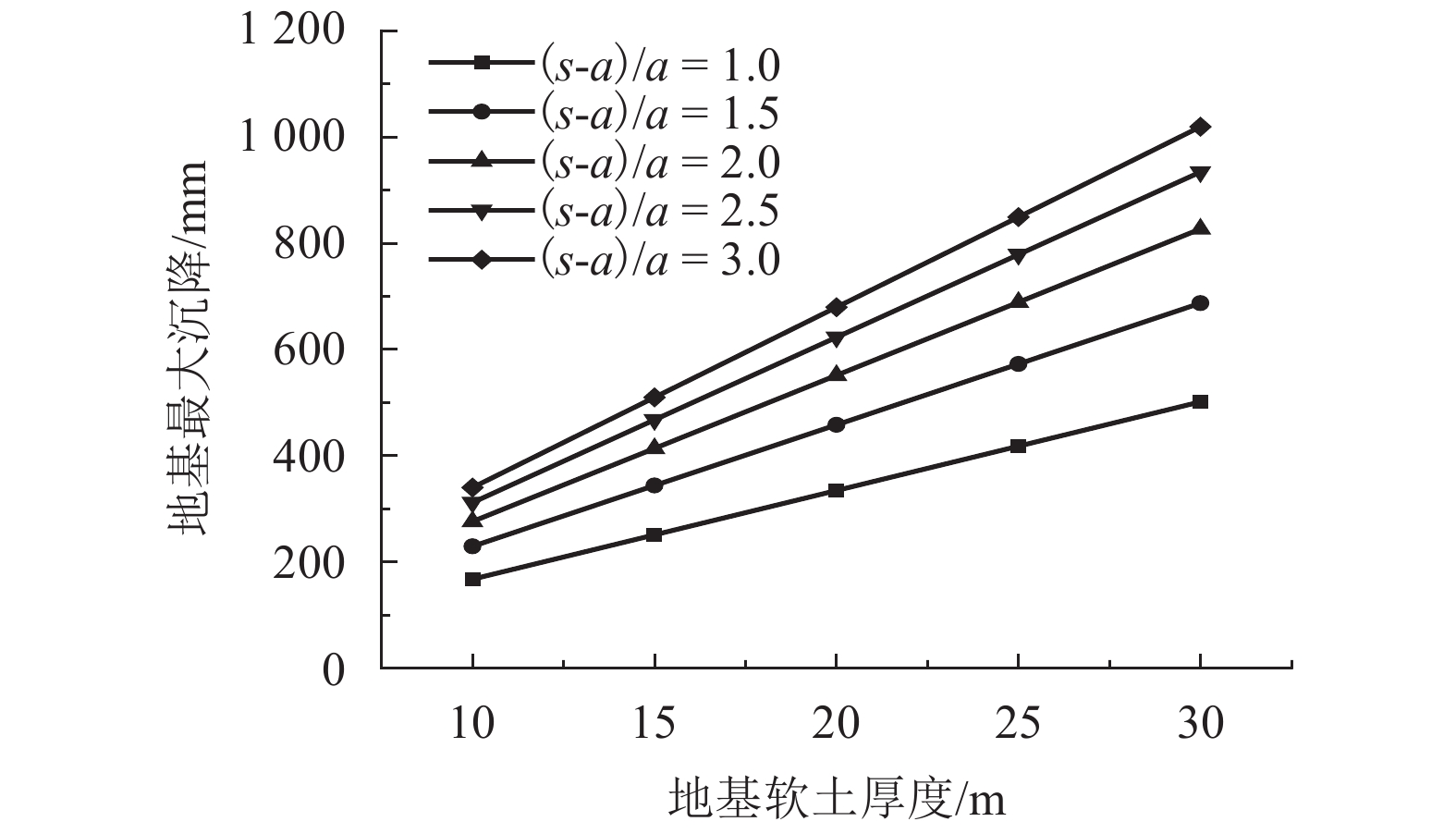
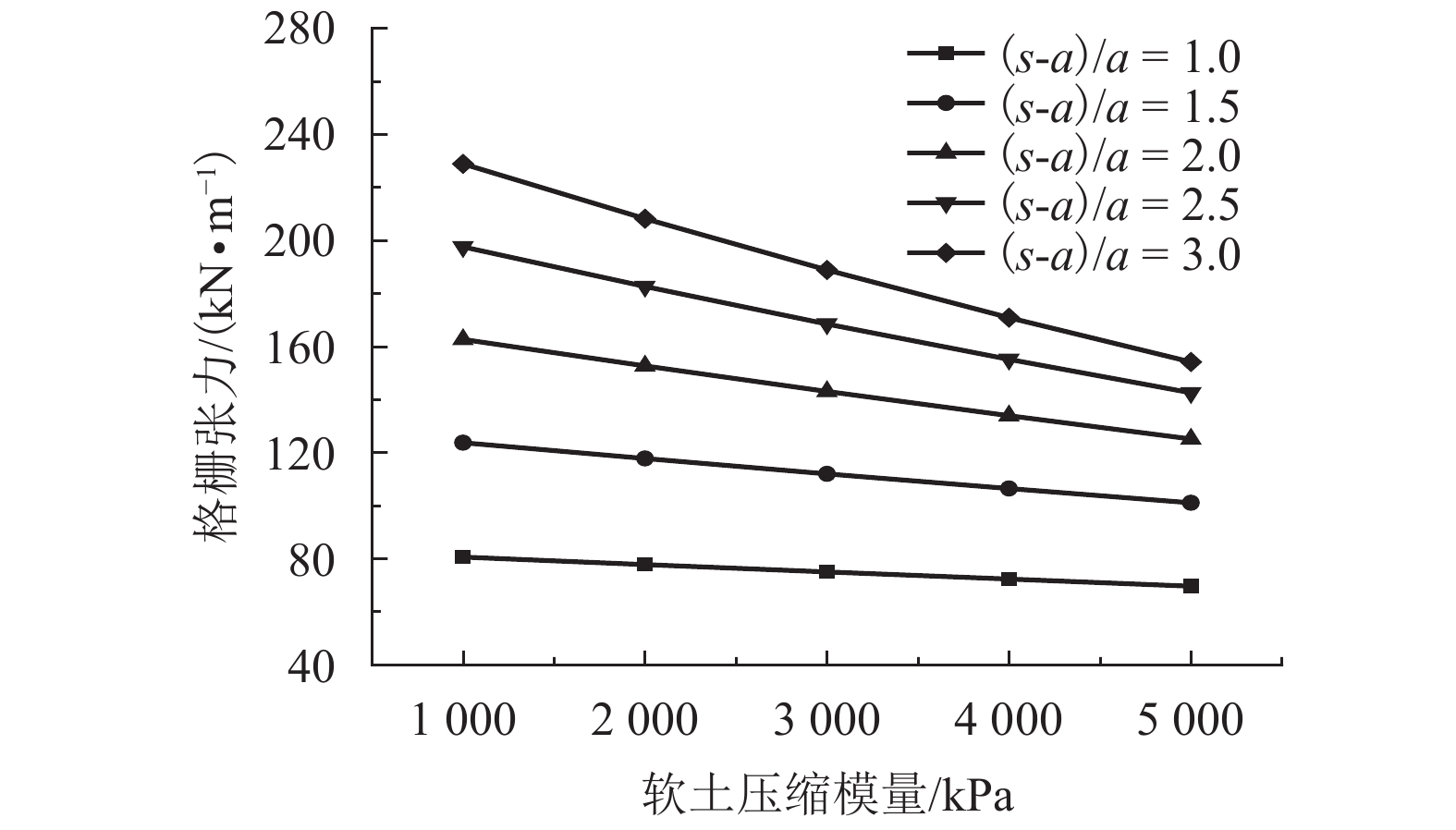
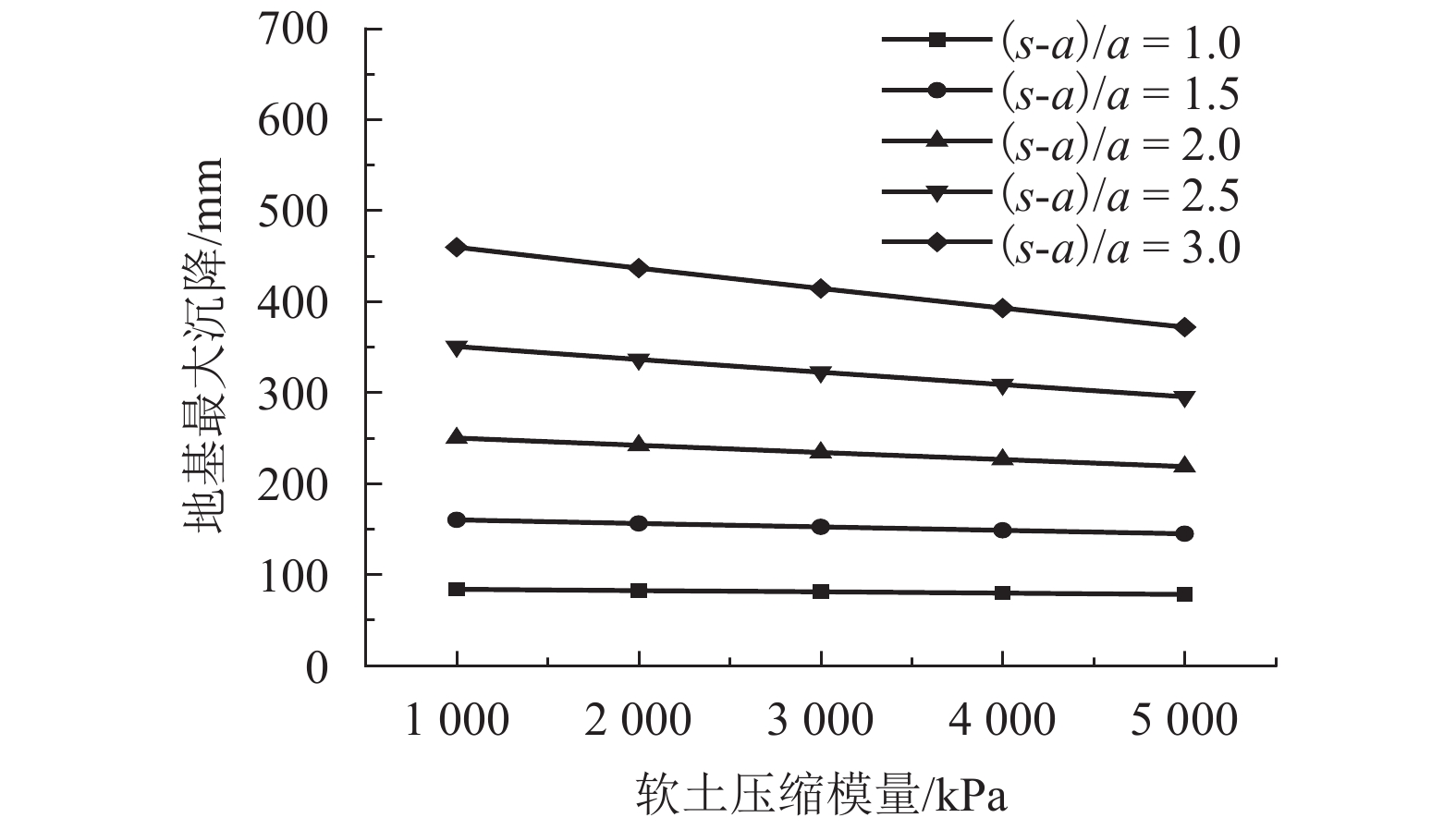
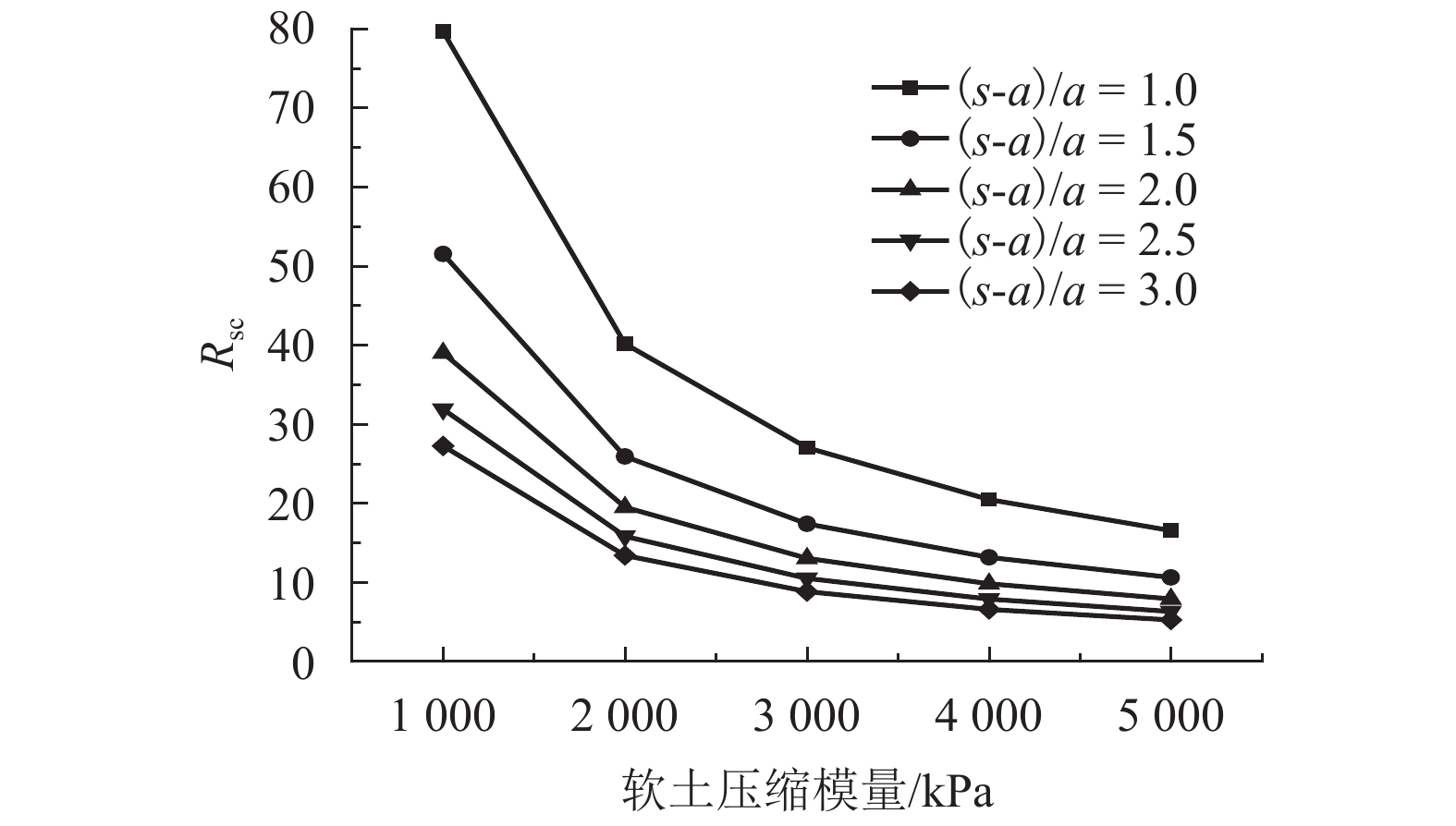
摘要: 为研究桩网路堤各影响参数对其传力机制与变形特性的影响,通过理论推导得出了桩网路堤简化分析方法,采用该方法对桩网路堤进行参数分析. 首先,综合考虑路堤填土土拱效应、地基支承作用和土工格栅效应,采用抛物线方程描述土工格栅变形,推导得到了针对正方形布桩型式的桩网路堤的分析方法;其次,通过与现场试验和目前主流设计方法对比分析,验证了本文计算方法结果可靠、计算过程简便;最后,采用该理论方法针对路堤高度、土工格栅刚度、地基软土厚度、软土模量对格栅张力、地基最大沉降和应力集中比的影响规律进行系统分析,在此基础上,引入非重复性二次方差分析对各参数的影响程度进行了量化对比. 研究结果表明:格栅张力与路堤填高、格栅刚度、地基软土厚度成正相关关系,与软土模量成负相关关系;地基沉降与路堤高度、软土厚度成正相关关系,与格栅刚度、地基软土模量成负相关关系;应力集中比与路堤高度、格栅刚度、地基软土厚度成正相关关系,与地基软土模量成负相关关系;降低地基软土厚度和增大软土模量是保证土工格栅正常工作情况下尽可能增大应力集中比的有效手段;缩小桩间距或采用大桩帽,其优化效果好于提高格栅抗拉刚度.Abstract: In order to analyze the influence of parameters on load transfer and deformation mechanisms of piled embankment with geogrid-reinforcement, a simplified method was proposed and employed for parameters analysis. A method including soil arching effect in granular material, subsoil resistance and membrane effect, is deduced and the deformation of the geogrid is expressed by Quadratic parabolic equation. Through comparative analysis with test data and other current design methods, it is found that the proposed method is conceptually and mathematically simple, and the results are reliable. The influence of embankment height, tensile stiffness of the geogrid, soft soil depth and compression modulus of soft soil on the tension of the geogrid, the settlement of soft ground and stress concentration ratio are studied using this method. The influence significance of these factors has been investigated by the evaluation theory of binary variance analysis of non-repeatability tests. The results show that the tension of geogrid is in proportion to embankment height, tensile stiffness of geogrid, soft soil depth, but in inversely proportion to compression modulus of soft soil. The settlement of soft ground is in proportion to embankment height, soft soil depth, but in inversely proportion to tensile stiffness, compression modulus of soft soil. Rsc is in proportion to embankment height, tensile stiffness, soft soil depth, but in inversely proportion to compression modulus of soft soil. Decreasing soft soil depth and improving compression modulus of soft soil are both the effective methods to transfer more load to piles. Larger pile caps and small pile spacing should be prior to adopting the geogrid with high tensile stiffness in promoting transferring more load to piles.
-
表 1 土体的物理力学性质
Table 1. Parameters of soil
土层 厚度/m 重度/(kN•m–3) 压缩模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/kPa 摩擦角/(°) 路堤 7.2 20.0 15.00 0.3 10.0 30.0 素填土 2.0 19.1 5.54 0.3 19.0 18.8 粉砂 7.0 18.4 9.97 0.3 10.0 24.1 中砂 10.0 18.9 25.00 0.3 28.8 密砂 5.0 18.9 32.60 0.3 28.9 表 2 实测结果与计算结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of test data and calculation results
方法 桩顶荷载/kPa 地基土表面荷载/kPa 格栅张力
/(kN•m–1)现场
实测240.7 73.7 4.3 计算
结果262.2 74.7 6.6 误差/% 8.9 1.3 34.8 表 3 路堤、桩(桩帽)、土工格栅以及土体的主要参数
Table 3. Parametes of embankment,pile(cap),geogrid and soil
名称 参数名称 数值 路堤 高度/m 1.39 重度/(kN•m–3) 20 内摩擦角/(°) 30 桩 桩帽宽度/m 1.13 桩间距/m 2.52 桩径/m 0.6 地基土 深度/m 25 重度/(kN•m–3) 17.5 弹性模量/MPa 2.2 内摩擦角/(°) 9 土工格栅 抗拉刚度/(kN•m–1) 1 700 表 4 不同方法计算结果
Table 4. Results of different methods
参数 本文计算方法 Low计算
方法[11]Abusharar计算
方法[10]BS8006计算
方法[14]BS8006修正
方法[15]Guido计算
方法[6]Lu计算
方法[9]桩顶竖向荷载/kPa 77.04 70.92 69.30 71.83 73.70 63.05 74.85 地基表层平均荷载/kPa 9.54 14.50 15.82 0 0 0 11.30 格栅张力/(kN•m–1) 47.40 34.00 39.18 44.40 64.30 30.55 38.71 土工格栅承担的
竖向荷载/kPa15.10 14.49 15.81 34.68 33.40 20.90 19.31 表 5 参数影响程度计算结果
Table 5. Influence degree of different parameters
结果 F分布 B为格
栅刚度B为软
土模量B为软
土厚度B为路
堤高度格栅
张力FA 12.8 25.8 9.9 14.3 FB 81.3 13.8 36.0 20.3 Rsc FA 44.1 9.6 24.3 25.1 FB 24.9 82.6 49.8 494.4 地基
沉降FA 37.3 34.5 29.0 22.7 FB 9.8 1.3 4.4 5.8 -
肖启航. 高速铁路CFG桩复合地基的沉降特性研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2010 张崇磊. 中等压缩性土地区短桩桩网复合地基路基荷载传递规律及沉降机理研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014 SHEN S L, CHAI J C, HONG Z S, et al. Analysis of field performance of embankments on soft clay deposit with and without PVD-improvement[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2005, 23(6): 463-485 张良,罗强,刘潇潇,等. 基于现场试验的桩网复合地基垫层效应分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2010,45(5): 787-793ZHANG Liang, LUO Qiang, LIU Xiaoxiao, et al. Cushion effect analysis of pile-net composite foudation based on field tests[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(5): 787-793 陈仁朋,汪焱卫,陈金苗. 桩网结构路基格栅加筋作用及其张力特性研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(6): 1080-1086CHEN Renpeng, WANG Yanwei, CHEN Jinmiao. Reinforcing mechanism and tension behaviors of geogrid in pile-supported reinforced embankment[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(6): 1080-1086 GUIDO V A, KNEUPPEL J D, SWEENEY M A. Plate loading tests on geogrid reinforced earth slabs[C]//Proceedings of the Geosynthetic’s 87. New Orleans: [s.n.], 1987: 216-225 ZHUANG Y, WANG K Y, LIU H L. A simplified methodto analyze the reinforced piled embankments[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2014, 42(2): 154-165 HELWETT W J, RANDOLPH M F. Analysis of piled embankment[J]. Ground Engineering, 1988, 21(3): 12-18 LU W H, MIAO L C. A simplified 2-D evaluation method of the arcing effect for geosynthetic-reinforced and pile-supported embankments[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2015, 65(65): 97-103 ABUSHARAR S W, ZHENG J J, CHEN B G, et al. A simplified method for analysis of a piled embankment reinforced with geosynthetics[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2009, 27(1): 39-52 LOW B K, TANG S K, CHOA V. Arching in piled embankments[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1994, 120(11): 1917-1938 JONES C J F P, LAWSON C R, AYRES D J. Geotexitile reinforced piled embankments[C]//Proceeding of 4th International Conference on Geotextiles: Geomembranes and Related products. Rotterdam: Balkema, 1990(1): 155-160 CHEN R P, CHEN Y M, XU Z Z. Interaction of rigid pile-supported embankment on soft soil[J]. ASCE Geotechinical Special Publication, 2006, 151: 231-238 British Standard. Code of Practice for Strengthened/Reinforced Soils and Other Fills: BS8006-1-2010[S]. British Standard Institution, 2010 VAN EEKELEN S J M, BEZUIJEN A, VAN TOL A F. Analysis and modi cation of the British Standard BS8006 for the design of piled embankments[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2011, 29(3): 345-359 汪荣鑫. 数理统计[M]. 西安: 西南交通大学出版社, 2005: 40-45 -






 下载:
下载: