Study of Influencing Factors on Cone Factor for Cone Penetration in Marine Clay
-
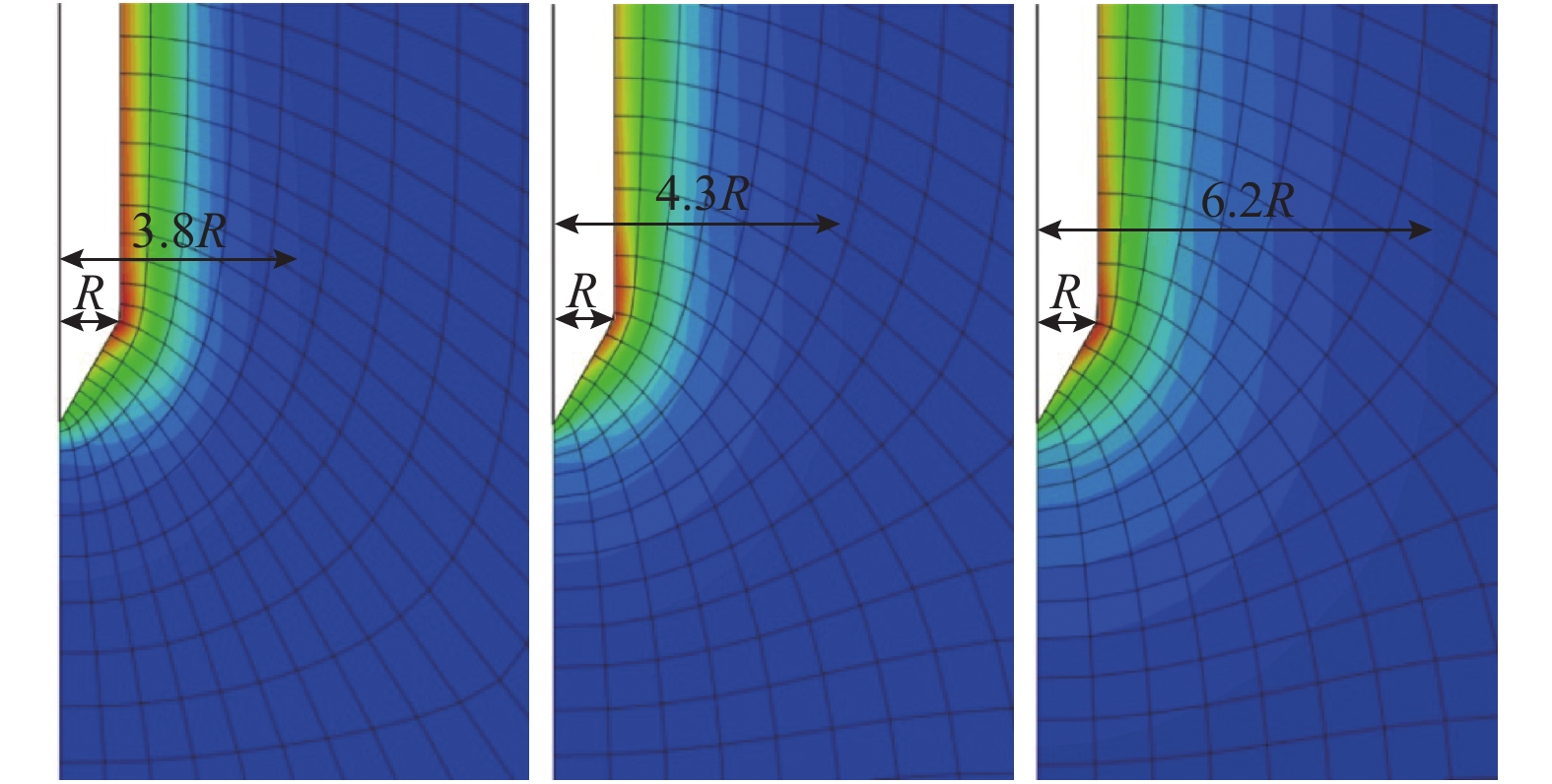
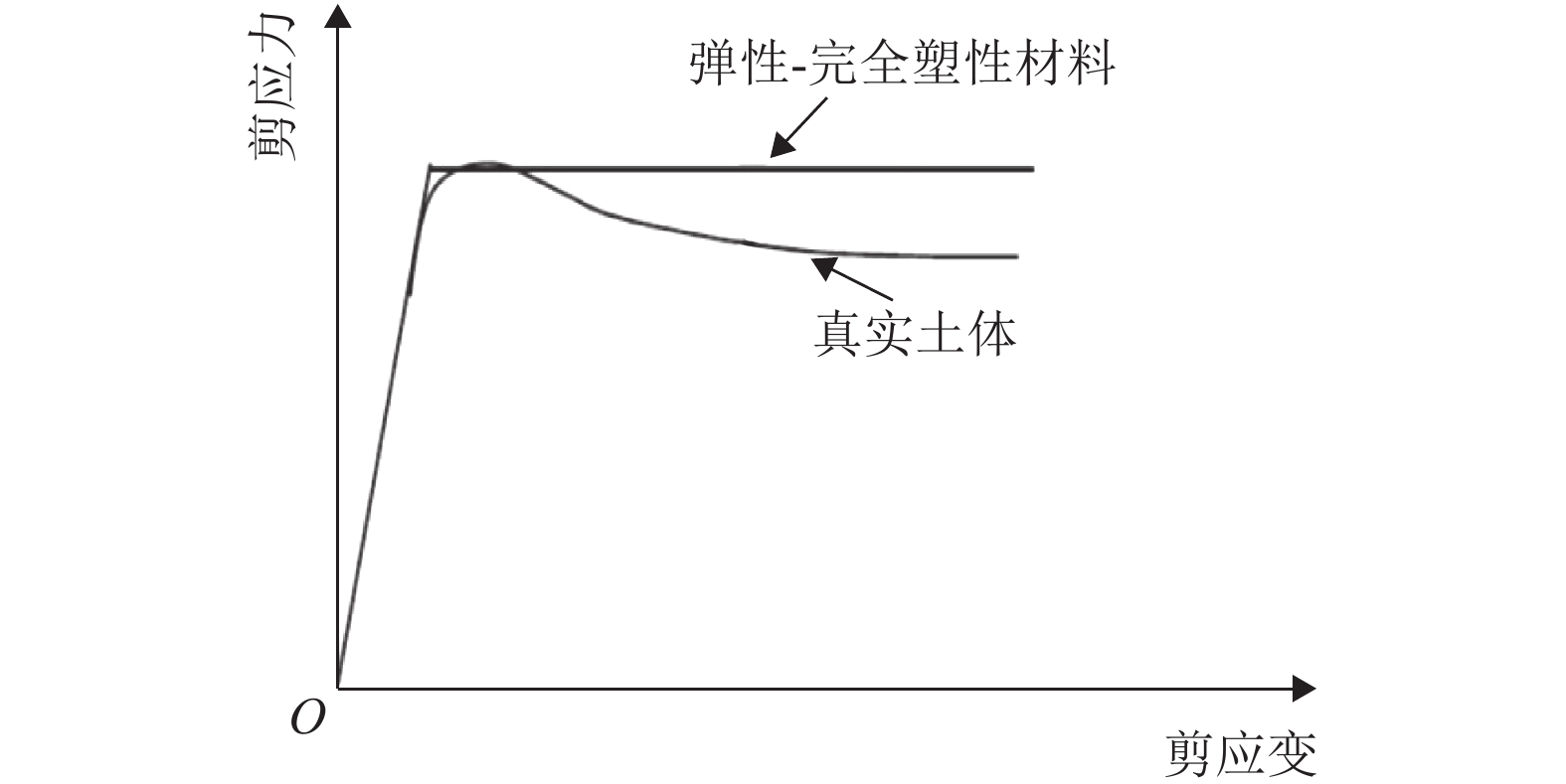
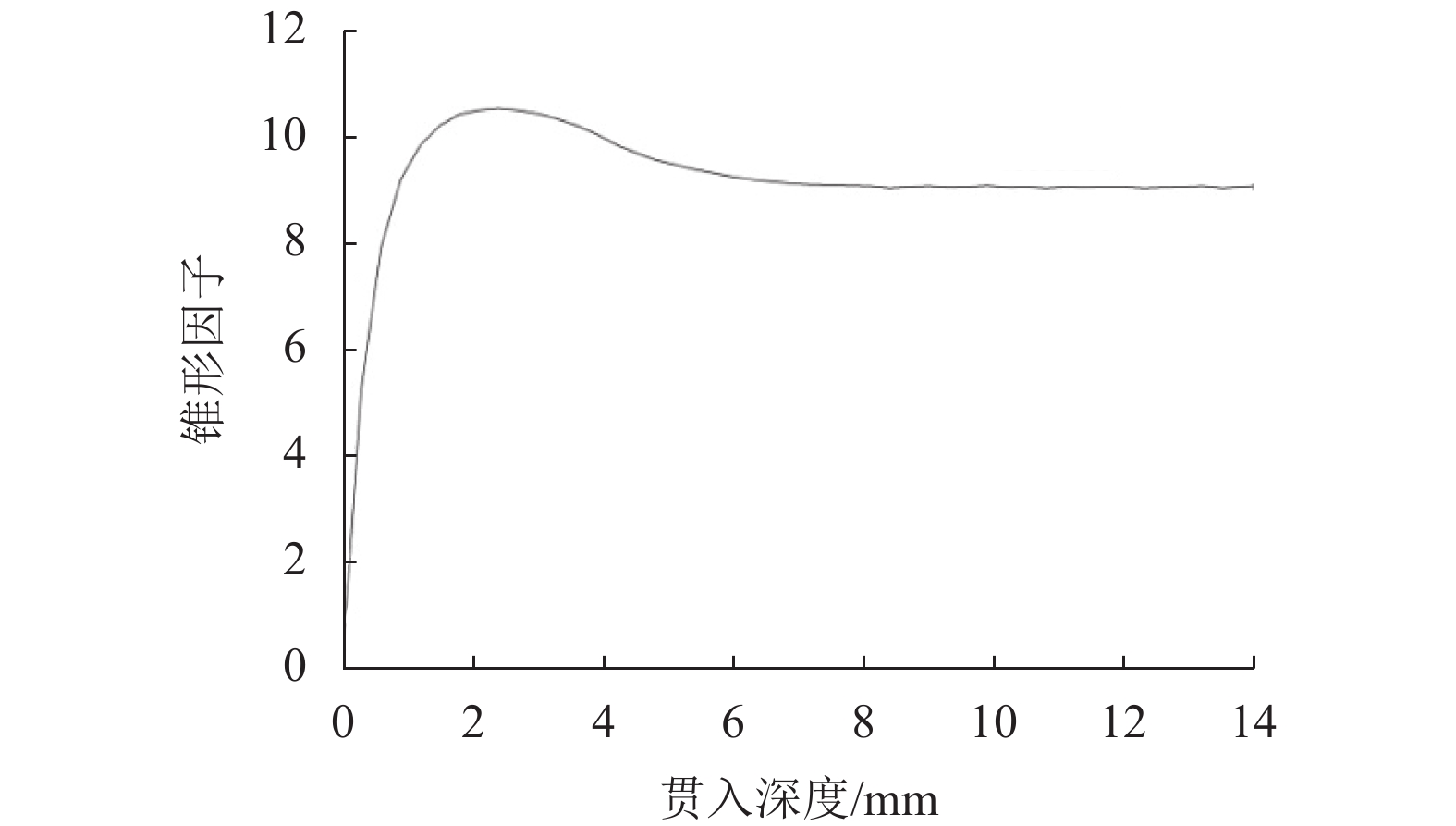
摘要: 为了研究土体刚度指数、应变软化和应变速率对海相黏土锥形因子的影响,利用有限元方法模拟了圆锥在黏土中的静力贯入,并采用任意拉格朗日-欧拉网格划分技术控制锥尖土体在大应变条件下的网格质量,讨论了稳定状态下传统小应变分析与大应变分析之间的差异性以及土体刚度指数对锥形因子与塑性区扩展的影响;引入土体应变软化参数和应变速率依赖性控制参数,分析了应变软化(灵敏度)和应变速率对锥形因子的影响,并建立了考虑土体刚度指数、应变软化和应变速率影响的锥形因子表达式. 结果表明:传统小应变分析会大大低估土体承载力,大应变极限承载力随着贯入深度的增大而增大,并在12D(D为探头外径)深度处达到稳定状态;锥形因子与塑性区均随着刚度指数的增大而增大,锥尖附近塑性区的径向扩张更接近于球形孔扩张;土体灵敏度随着应变软化参数的减小而增大,锥形因子出现小幅度减小;随着应变速率控制参数的增大,锥形因子出现大幅增加,但增量与灵敏度无关;锥形因子表达式量化了刚度指数、应变软化和应变速率对海相黏土的影响,有助于利用静力触探技术更准确的评价海相黏土抗剪强度.Abstract: To study the influence of the rigidity index, strain softening, and strain rate on the cone factor of marine clay, cone penetration in clay is simulated on the basis of the finite element method, and an arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) technique is adopted to control the quality of mesh under the condition of large strain. The difference between the traditional small-strain analysis and the ALE large-strain analysis under the steady state is discussed, and the influences of the rigidity index on the cone factor and the extension of the plastic zone are analyzed. The strain-softening parameters and the strain-rate-controlling parameter for the strain-rate dependency of soil are introduced to analyze the influence of strain softening (sensitivity) and strain rate on the cone factor. In addition, a cone factor expression is proposed considering the influence of the rigidity index, strain softening, and strain rate of the soft soil. The results show that the traditional small-strain analysis greatly underestimates the bearing capacity of clay, whereas the ultimate bearing capacity under large strain increases with penetration depth to finally reach steady state at 12D depth. Moreover, the cone factor and the plastic zone increase with an increase in the rigidity index, and the radial expansion of the plastic zone around the cone tip is closer to the spherical cavity expansion. The sensitivity of the soil increases and the cone factor decreases slightly with a decrease in the strain-softening parameter. The increase in the strain-rate-controlling parameter causes the cone factor to increase significantly, although the increment is independent of sensitivity. In this study, the influence of the rigidity index, strain softening, and strain rate on the cone factor of marine clay is quantified by this expression, which is helpful in evaluating the shear strength of marine clay using the static cone penetration technique.
-
Key words:
- cone penetration /
- large-strain finite element /
- cone factor /
- rigidity index /
- strain softening /
- strain rate
-
表 1 应变软化土体特征参数
Table 1. Characteristic parameters for strain-softening in soil
δrem A B C ${s_{{\rm{u min}}}}$ 0.86 0.05 10.54 245.10 0.004 30 0.57 0.05 3.77 132.28 0.002 85 0.38 0.05 1.93 101.63 0.001 90 0.24 0.05 1.04 86.81 0.001 20 0.13 0.05 0.51 77.88 0.000 65 -
邱延峻. 静力触探机理研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,1993,28(3): 46-52QIU Yanjun. Study of the mechanism of static penetration[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 1993, 28(3): 46-52 童立元,涂启柱,杜广印,等. 应用孔压静力触探(CPTU)确定软土压缩模量的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(2): 569-572TONG Liyuan, TU Qizhu, DU Guangyin, et al. Determination of confined compression modulus of soft clay using piezocone penetration tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(2): 569-572 刘松玉, 蔡国军, 童立元, 等. 现代多功能CPTU: 技术理论与工程应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 31-32 BISHOP R F, HILL R, MOTT N F. The theory of indentation and hardness tests[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society, 1945, 57(3): 7-8 YU H S, MITCHELI J K. Analysis of cone resistance:review of methods[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,ASCE, 1998, 124(2): 140-149 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1998)124:2(140) VESIC A S. Design of pile foundations[S]. Washington D. C.: National Cooperative Highway Research Program, Synthesis of Highway Practice 42, Transportation Research Board, National Research Council, 1977 LADANYI B, JOHNSTON G H. Behavior of circular footings and plate anchors embedded in permafrost[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1974, 11: 531-553 doi: 10.1139/t74-057 BALIGH M M. Theory of deep static cone penetration resistance[M]. Boston: Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, MIT, 1975: 75-56 BALIGH M M. Strain path method[J]. J. Geotech. Eng. ASCE, 1985, 111(9): 1108-1136 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:9(1108) LU Q, RANDOLPH M F, HU Y, et al. A numerical study of cone penetration in clay[J]. Geotechnique, 2004, 54(4): 257-67 doi: 10.1680/geot.2004.54.4.257 WALKER J, YU H S. Adaptive finite element analysis of cone penetration in clay[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2006, 1: 43-57 doi: 10.1007/s11440-006-0005-9 TOLOOIYAN A, GAVIN K. Modelling the cone penetration test in sand using cavity expansion and arbitrary lagrangian eulerian finite element methods[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2011, 38(4): 482-490 doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2011.02.012 EINAV I, RANDOLPH M F. Combining upper bound and strain path methods for evaluating penetration resistance[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2005, 63(14): 1991-2016 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0207 ZHOU H, RANDOLPH M F. Computational techniques and shear band development for cylindrical and spherical penetrometers in strain-softening clay[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2007, 7(4): 287-97 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1532-3641(2007)7:4(287) LIYANAPATHIRANA D S. Arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian based finite element analysis of cone penetration in soft clay[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2009, 36(5): 851-860 doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2009.01.006 ABU-FARSAKH M, TUMAY M, VOYIADJIS G. Numerical parametric study of piezocone penetration test in clays[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2003, 3(2): 170-181 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1532-3641(2003)3:2(170) YU H S, HERRMANN L R, BOULANGER R W. Analysis of steady state cone penetration in clay[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2000, 126(7): 594-605 SILVESTRI V. Strain-rate effects in self-boring pressuremeter tests in clay[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2006, 43(9): 915-27 doi: 10.1139/t06-047 -






 下载:
下载: