Reliability Evaluation of Relay Protection for Traction Substation of Urban Rail Transit
-
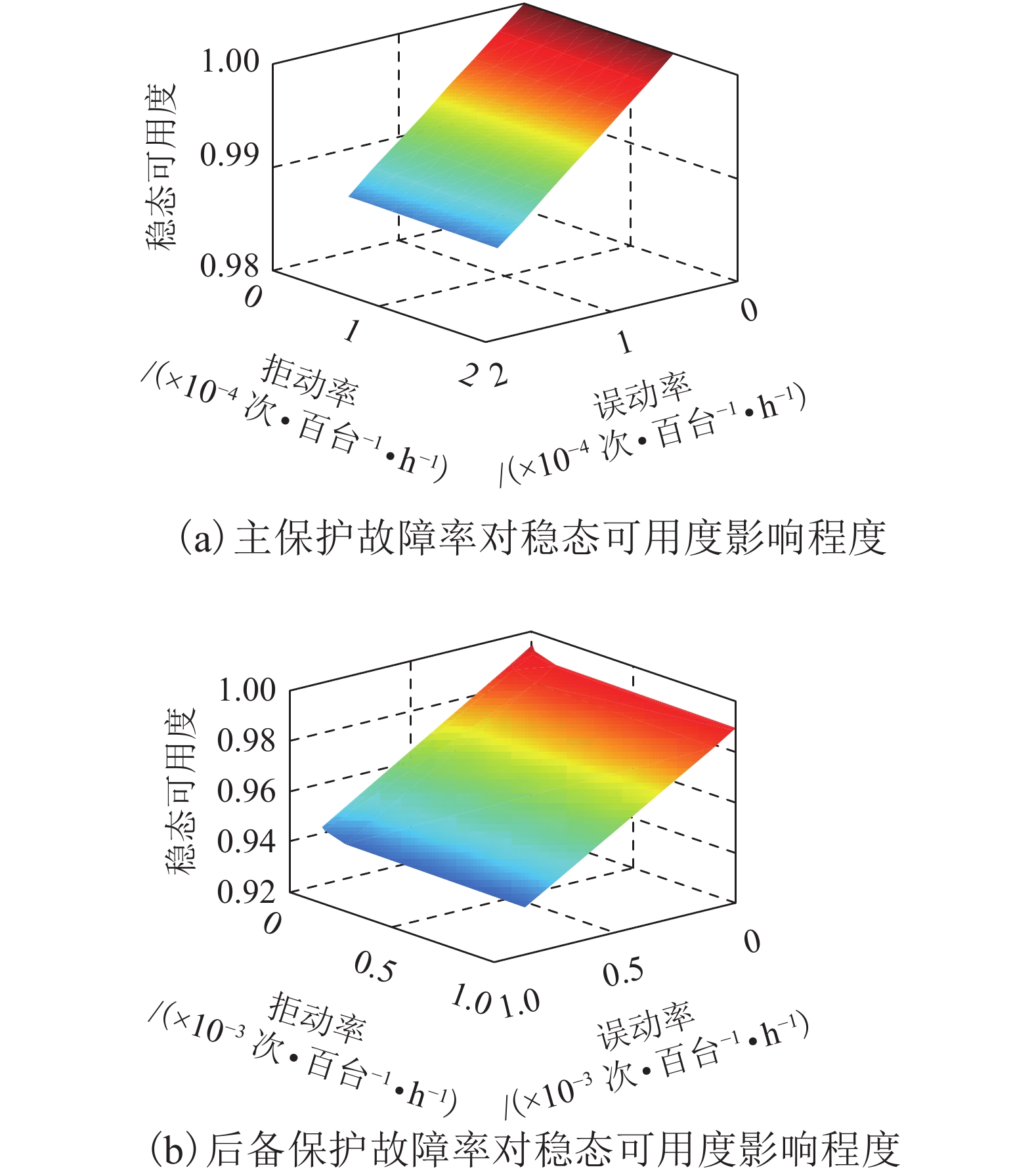
摘要: 为了掌握城市轨道交通牵引变电所继电保护可靠性,寻找继电保护系统薄弱环节,为故障排查提供指导,进行城市轨道交通牵引变电所继电保护可靠性评估研究. 首先针对城市轨道交通牵引变电所继电保护系统特点,确定可靠性指标;其次根据系统构成及其故障模式,建立继电保护装置故障树模型以及不同配置方案的保护系统故障树模型;最后考虑微机自检功能,基于马尔科夫理论及蒙特卡洛方法,仿真计算城市轨道交通牵引变电所继电保护可靠性指标. 研究结果表明:方法能够获取丰富的可靠性指标,进行牵引变电所继电保护可靠性评估,从而识别系统薄弱环节;自检率为0.9时,继电保护装置误动故障概率占装置故障概率比例高出拒动故障17.93%,装置误动及拒动自检成功率分别为86.09%与74.37%,保护装置可用度为99.88%;后备保护能够降低保护系统拒动概率,但由其误动造成的保护系统误动占比30%~50%,因此,在选用保护配置时需要考虑保护误动风险影响.Abstract: To understand the reliability and find the weaknesses in the relay protection system of urban rail transit traction substation to provide guidance for failure investigation, a reliability evaluation project of relay protection for urban rail transit traction substation was undertaken. First, the reliability index was determined according to the characteristics of the relay protection system of urban rail transit traction substation. Then, a fault tree model of the relay protection device and different configuration scheme protection systems were set up based on the system structure and failure mode. Finally, based on Markov theory and Monte Carlo method, the reliability index of relay protection of urban rail transit traction substation was calculated considering the self-test function of the microprocessor protection. The results show that the method can obtain sufficient reliability indicators to evaluate the reliability of traction substation relay protection to identify the protection system weaknesses. On the condition that the self-test success rate is 0.9, the relay protection device failure probability caused by the protection maloperation is 17.93% higher than that caused by the protection rejection. Meanwhile, the self-test success rates of maloperation and rejection are 86.09% and 74.37% respectively, and the availability of protection devices is 99.88%. Backup protection can reduce the rejection probability of the protection system, but backup protection caused about 30%–50% of the maloperation of the protection system. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the impact of protection maloperation when selecting the protection configuration.
-
Key words:
- relay protection /
- reliability /
- electric traction /
- fault tree analysis /
- Monte Carlo methods
-
表 1 继电保护装置硬件元件故障率
Table 1. Fault rate of hardware component of relay protection
元件类型 故障率 元件类型 故障率 元件类型 故障率 AI 22.562 CPU 36.738 MEM 36.738 DI 22.562 PSU 11.400 SC 7.000 DO 7.544 BT 7.544 表 2 可靠性指标
Table 2. Reliability index
类型 概率/
× 10–4频率/
( × 10–5次•h–1)tMTBF/h 硬件误动 5.055 8.523 可自检硬件误动 3.069 7.673 硬件拒动 2.994 5.092 可自检硬件拒动 1.626 4.066 硬件故障 7 338.9 不可自检硬件故障 53 266.0 软件子系统 130 550.0 装置误动 7.074 8.912 11 212.0 不可自检装置误动 80 619.0 装置拒动 4.923 5.467 18 283.0 不可自检装置拒动 71 348.0 装置故障 12.000 14.370 6 946.1 不可自检装置故障 37 836.0 表 3 不同自检率稳态可用度
Table 3. Steady state availability of different self-test rates
类型 c 0.82 0.86 0.90 0.94 0.98 误动 99.915 99.922 99.929 99.938 99.945 拒动 99.942 99.947 99.951 99.956 99.960 故障 99.857 99.869 99.880 99.894 99.904 表 4 不同自检率基本单元模式重要度
Table 4. Basic model importance of different self-test rates
基本单元 c 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 DO 0.020 0.017 0.015 0.009 BT 0.041 0.035 0.028 0.018 DI 0.116 0.102 0.086 0.058 AI 0.116 0.102 0.086 0.058 CPU 0.190 0.166 0.140 0.093 MEM 0.187 0.166 0.139 0.093 PSU 0.144 0.173 0.218 0.286 SOFT 0.187 0.238 0.289 0.387 表 5 不同配置方案可靠性基础数据
Table 5. Reliability data for different configuration schemes
保护类型 误动率/(× 10–5
次•百台–1•h–1)拒动率/(× 10–5
次•百台–1•h–1)修复率/
(次•h–1)主保护 10.261 10.274 0.019 后备保护 8.672 10.274 0.016 近后备保护 8.672 10.274 0.016 远后备保护 6.476 10.274 0.016 表 6 不同配置方案牵引变电所继电保护可靠性
Table 6. Relay protection reliability of traction substation with different configuration schemes
配置方案 误动概率
/× 10–2拒动概率
/× 10–5后备误动概率
/× 10–3两套主保护 1.07 2.76 一套主保护和
一套后备保护1.07 3.23 5.40 两套主保护和
一套后备保护1.60 430.00 5.40 两套主保护和
两套后备保护2.13 0* 10.70 两套主保护及远、
近后备保护2.00 0* 9.40 注:“0*”表示该值为无限接近于0的正数,非真 实数值0. -
宁晶洁. 城市轨道交通列车节能运行模型及算法研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2017 曹景雷. 基于GO法的地铁牵引供电系统可靠性研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2012 丁雪成,胡海涛,何正友,等. 计及维修因素的牵引变电站电气主接线可靠性分析[J]. 电网技术,2011,35(10): 117-123DING Xuecheng, HU Haitao, HE Zhengyou, et al. Analysis on reliability of main connection of traction substation considering influence of maintenance[J]. Power System Technology, 2011, 35(10): 117-123 薛安成,罗麟,景琦,等. 基于Markov模型的高压输电线继电保护装置风险评估[J]. 电网技术,2014,38(7): 1995-2000XUE Ancheng, LUO Lin, JING Qi, et al. Research on Markov Model based risk assessment of protective relaying for high voltage transmission line[J]. Power System Technology, 2014, 38(7): 1995-2000 JEDRZEJCZAK J, ANDERS G J. Transition rates assessment of protective relay reliability models with incomplete data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32(1): 809-816 王超,高鹏,徐政,等. GO法在继电保护可靠性评估中的初步应用[J]. 电力系统自动化,2007,31(24): 52-56WANG Chao, GAO Peng, XU Zheng, et al. Application of GO methodology in reliability assessment of protective relays[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2007, 31(24): 52-56 XIAO Fan, ZHANG Zhe, YIN Xianggen. Reliability evaluation of protection system in smart substation based on process layer network[C]// Proceedings of the 50th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC2015). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-5 HEYDT G T, GRAFF T J. Distribution system reliability evaluation using enhanced samples in a Monte Carlo approach[J]. IEEE Transaction on Power Systems, 2010, 25(4): 2006-2008 安灵旭,陈中伟,方华亮,等. 考虑运行时间和温度的继电保护可靠性分析[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报,2014,26(5): 7-11AN Lingxu, CHEN Zhongwei, FANG Hualiang, et al. Reliability analysis of potection system with conditions of operating time and operating temperature[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2014, 26(5): 7-11 郑风雷,吴杰康,黄强,等. 双重化继电保护系统可靠性的五状态空间模型与评估方法[J]. 电力系统自动化,2016,40(20): 26-31ZHENG Fenglei, WU Jiekang, HUANG Qiang, et al. Five-state space model and assessment method for reliability of dual-redundant relay protection system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(20): 26-31 李永丽,李致中,杨维. 继电保护装置可靠性及其最佳检修周期的研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2001,21(6): 63-71LI Yongli, LI Zhizhong, YANG Wei. Study of reliability and optimal routine test interval of protective relays[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2001, 21(6): 63-71 孙福寿. 复杂厂区电网继电保护智能化与可靠性研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2006 闫奇. 基于Markov过程的继电保护系统可靠性评估[D]. 保定: 华北电力大学, 2012 王世香,高仕斌. 蒙特卡罗方法在变电站综合自动化可靠性评估中的应用[J]. 电网技术,2006,30(5): 96-100WANG Shixiang, GAO Shibin. Application of Monte Carlo method in reliability evaluation of integrated substation automation[J]. Power System Technology, 2006, 30(5): 96-100 何洋阳, 黄康,王涛,等. 轨道交通牵引供电系统综述[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2016,13(2): 352-361HE Yangyang, HUANG Kang, WANG Tao, et al. Overview of traction power supply system for rail transportation[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2016, 13(2): 352-361 王艇. 地铁直流牵引供电保护技术与系统实现[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2006 戴志辉,王增平,焦彦军. 基于动态故障树与蒙特卡罗仿真的保护系统动态可靠性评估[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2011,31(19): 105-113DAI Zhihui, WANG Zengping, JIAO Yanjun. Dynamic reliability assessment of protection system based on dynamic fault tree and Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31(19): 105-113 MUSA J D. The measurement and management of software reliability[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1980, 68(9): 1131-1143 DAI Zhihui, WANG Zengping. Protection dynamic reliability analysis system based on 3RF technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2011, 26(3): 1137-1144 戴志辉. 继电保护可靠性及其风险评估研究[D]. 保定: 华北电力大学, 2012 吕佩韦. 地铁保护可靠性及最佳检修周期的研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2012 郑紫尧. 继电保护系统可靠性评估的研究[D]. 保定: 华北电力大学, 2013 -





 下载:
下载: