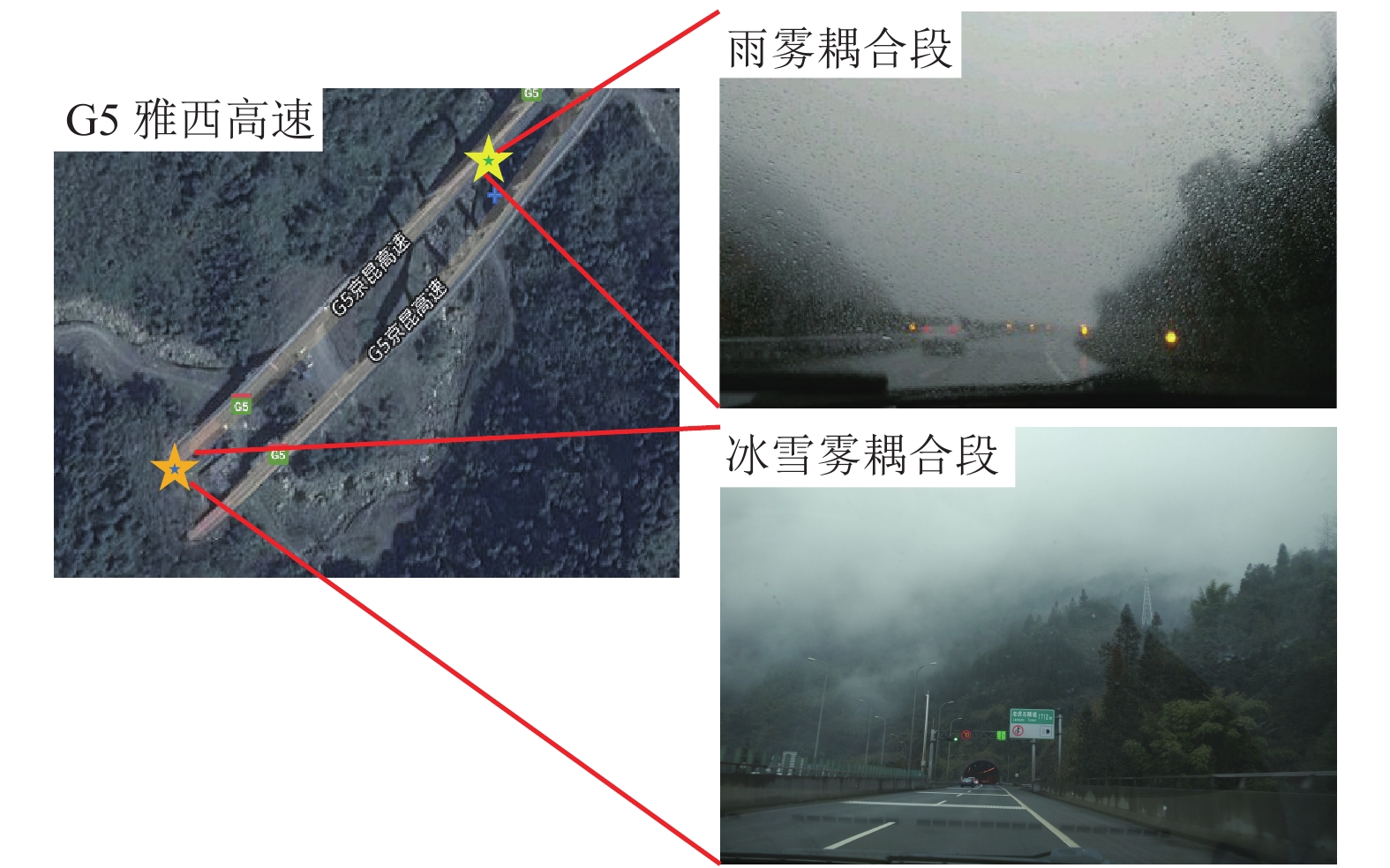
Probabilistic Risk Analysis of Multi-Climatic Coupling Sections of Expressway in Fog Area
-
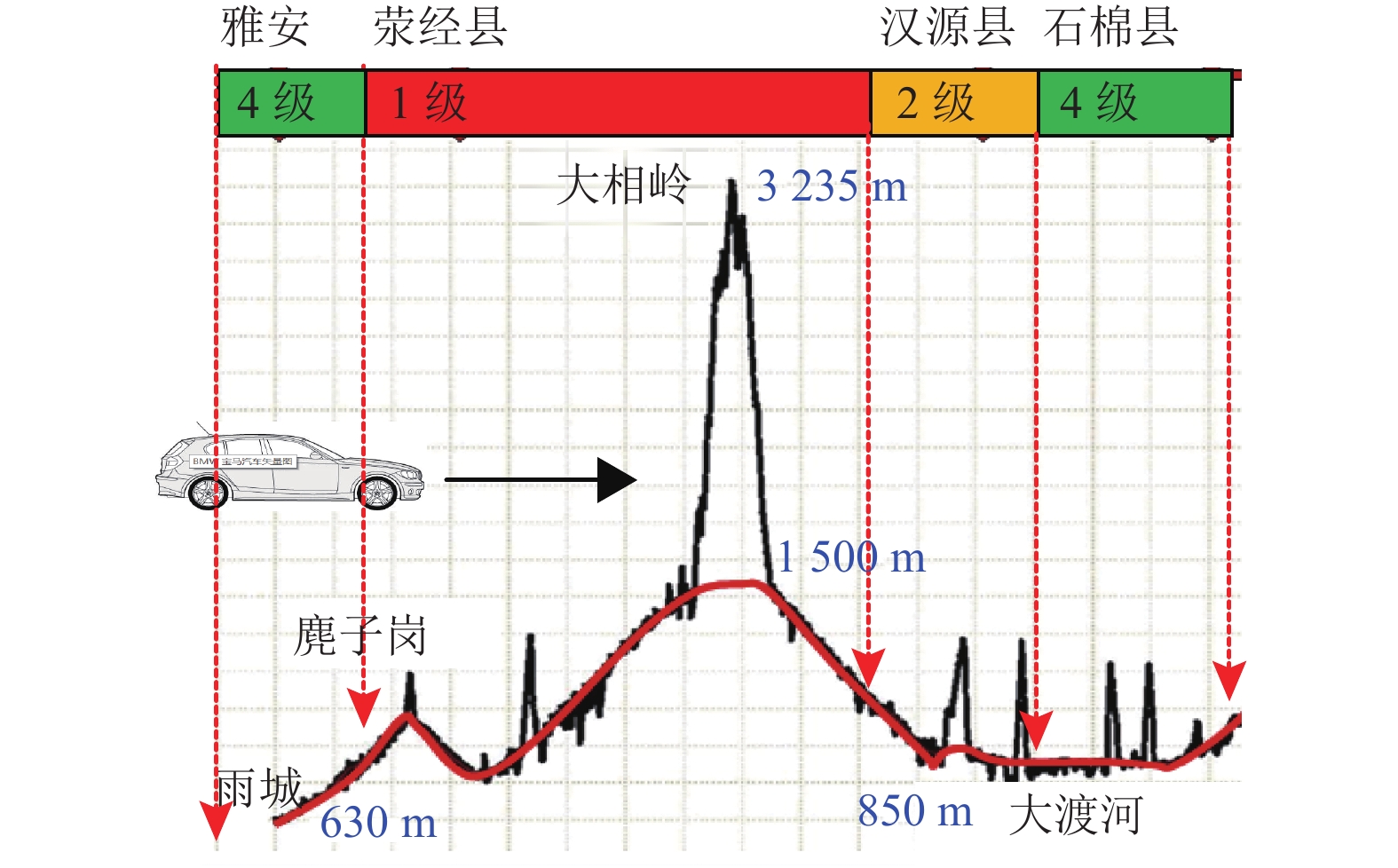
摘要: 高速公路雾区路段常伴随雨、冰、雪等复杂气候,综合考虑雾与雨、雪、冰等复杂因素耦合对高速公路事故风险评估具有重要意义. 引入“场”理论,构建高速公路雾区风险场模型,并基于模型对雾区多气候耦合路段的参数指标和道路风险进行分级研究. 首先,截取典型雾区路段进行栅格化分析,构建高速公路雾区风险场;然后引入PRA方法进行雾区风险场链式风险叠加分析,构建雾区风险场数值模型;最后以G5高速雅安至石棉段作为分析实例对模型进行验证,基于场理论给出了与当前国内气象预警分级相匹配的高速公路雾区耦合段风险分级指标,并将雾区路段的风险分级为四级,其中行车风险等级最高的为第1级.研究结果表明:场理论适用于多气候耦合的高速公路雾区段风险分析;高速公路雾区风险场是一种数量场和不稳定场,其不稳定性主要表现为雾区路段各气候参数的时变性;风险分级结果综合考虑了道路线形和环境特征以及基于时间变化的道路气候耦合特征,风险分级指标更符合基于时间动态变化的道路交通风险特性.Abstract: The fog sections of an expressway often experience fog accompanied by rain, ice, or snow, as well as other complex climatic conditions. Therefore, evaluating and researching the accident risk of an expressway with consideration of the coupling of complex factors such as fog, rain, snow, and ice has great significance. On the basis of field theory, a risk field model of an expressway in a fog area was established, and the parameters and risk classification of coupling sections in fog and multi-climate areas of the expressway were studied based on the model. First, rasterization of the typical fog sections of the expressway was performed to construct the risk field. Then, the method of probabilistic risk analysis (PRA) was used to analyse the risk field in the fog area and the chain risk, and the numerical model of the risk field in the fog area was constructed. Finally, the model was validated for the G5 Ya-an to Shi-mian expressway. The results show that field theory is more suitable for risk analysis of multi-climate-coupled fog areas of the expressway. The risk field in the fog area of the expressway is a number field as well as an unstable field, and its instability mainly manifests as the time variability of each climatic parameter in the fog area. Based on field theory, the risk classification index of the multi-climatic coupling section of the expressway in the fog area was provided, the index was matched with the current domestic meteorological warning classification, and the risk of the fog section was classified into four levels, with the traffic risk level being the highest.
-
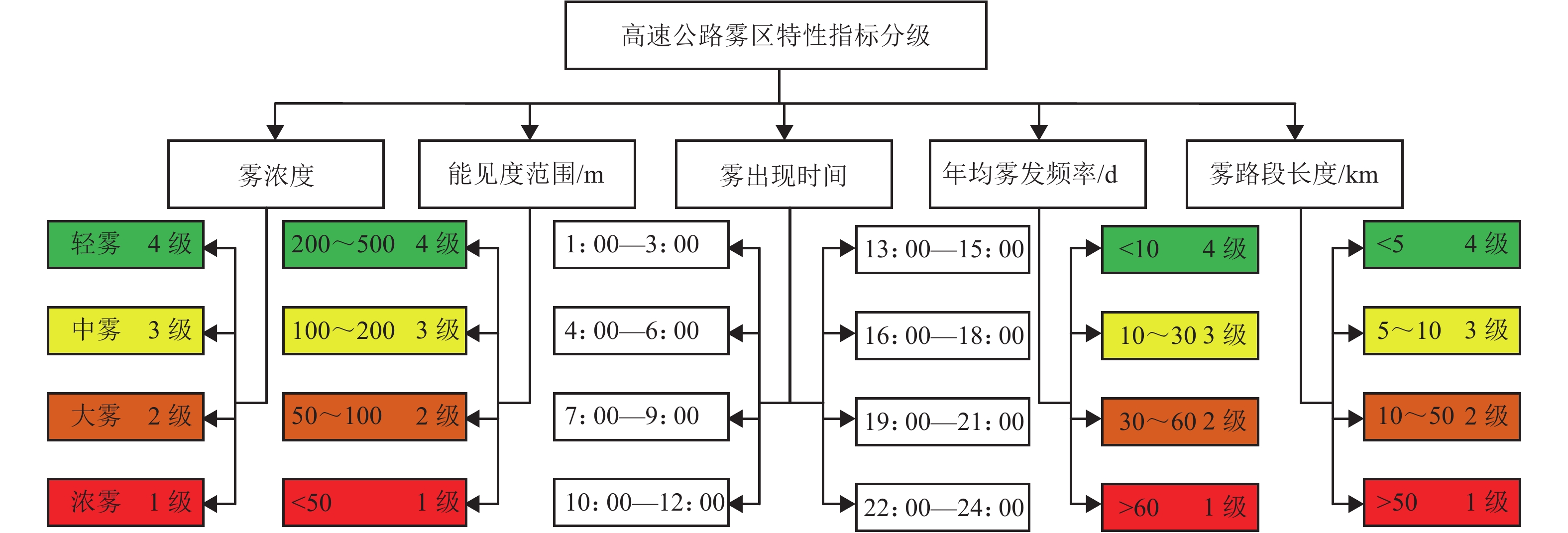
表 1 雾区多气候耦合风险参数
Table 1. Multi climatic coupling risk parameters in foggy area
气候耦合类型 耦合风险参数 能见度 路面 车身稳定性 温度 雾 ⊕ ⊕ 雨、雾 ⊕ ⊕ 风、雨、雾 ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ 雪、雾 ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ 雪、雾、冰 ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ 风、雪、雾、冰 ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ 表 2 雾区路段等级划分标准
Table 2. Grading standards of foggy sections
雾浓度 能见度/m 本文分级 中国
气象局公安部
分级能见度/m 雾区路段
分级浓雾雾墙 < 50 < 50 < 20 1级 20~50 2级 中等雾 200~500 100~200 50~100 3级 轻雾 > 500 > 200 100~200 4级 表 3 自然环境亮度级别划分
Table 3. Classification of natural environment brightness levels
时间度 级别 自然环境亮度I/(cd•m–2) 子夜 1级 I ≤ 0.001 夜晚 2级 0.001 < I ≤ 1 佛晓 3级 1 < I ≤ 10 白天 4级 10 < I ≤ 100 表 4 年雾发频次级别划分
Table 4. Grade division of fog frequency
级别 1级 2级 3级 4级 年雾发频次 > 60 30~60 10~30 < 10 -
交通部运输部公路局.公路交通气象服务效益评估(2011)[M].北京: 气象出版社, 2012: 2-15 陈艳艳,刘小明,任福田. 交通路网灾害风险系统影响分析[J]. 公路交通科技,2002,19(4): 79-81CHEN Yanyan, LIU Xiaoming, REN Futian. Disaster risk analysis of transportation infrastructure system[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2002, 19(4): 79-81 何寿奎. 基础设施公共安全风险评价方法研究[J]. 生态经济,2009(4): 186-189HE Shoukui. Community safety risk evaluating for infrastructures[J]. Ecological Environment, 2009(4): 186-189 涂辉招,孙立军,高子翔. 基于风险评估技术的城市快速路多匝道协调控制时机研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2015,28(7): 86-92TU Huizhao, SUN Lijun, Gao Zixiang. Study on control timing of coordinated multi-ramp for urban freeway corridors based on risk assessment technique[J]. China Highway Transportation, 2015, 28(7): 86-92 CHO H J, KIM K S. Development of hazardous road fog index and its application[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2005, 17(3): 390-396 马勇,付锐. 驾驶人视觉特性与行车安全研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报,2015,28(6): 82-94MA Yong, FU Rui. Research and development of driver’s visual behavior and driving safety[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(6): 82-94 李长城, 汤筠筠, 葛涛, 等. 恶劣气象条件下公路运行安全管理与保障技术[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2012: 23-49 EDWARDS B. J. The relationship between road accident severity an recorded weather[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2012, 29(4): 249-262 MUSK L F.Climate as a factor in the planning and design of new roads motorways[C]// Perry A H, Symons L J Highway Meteorology.London: E and FN Spon, 1991: 1-25 王炜,卢雪翠,解以扬. 雾的标准化危险性指数计算方法及其应用[J]. 气象与环境学报,2010,26(1): 16-20WANG Wei, LU Xuecui, XIE Yiyang. Normalized fog hazard index and its application[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2010, 26(1): 16-20 张振东,黄亮,于庚康,等. 宁沪高速公路雾事故特征及雾危险指数研究[J]. 灾害学,2016,31(4): 37-41ZHAND Zhendong, HUANG Liang, YU Gengkang, et al. Study on fog accident characteristics and fog risk index of nanjing shanghai expressway[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2016, 31(4): 37-41 王琰.公路网交通事故风险评估与安全管理技术[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2012: 12-56 郑恒.概率风险评价[M].北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011: 12-138 黄沿波,李剑峰,张斌,等. 基于风险场的评价理论研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2008,4(6): 101-105HUANG Yanbo, LI Jianfeng, ZHANG Bin, et al. There search of assessment theory based on risk field part theory model[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2008, 4(6): 101-105 张巍汉, 何勇, 刘洪启. 高速公路雾区交通安全保障技术[M].北京: 人民交通出版社, 2009: 34-120 刘洪启. 美国公路雾区预警系统建设与发展对我国的启示[J]. 中外公路,2007,27(4): 13-15LIU Hongqi. Enlightenment to China of expressway construction and development of fog zone warning systems in the U S[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2007, 27(4): 13-15 张继业,郑伟范. 交通流随机行为的研究进展[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(3): 534-545ZHANG Jiye, ZHENG Fanwei. Research on stochastic behavior of traffic flow[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(3): 534-545 史桂芳,袁浩,程建川. 雾天交通限速计算[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2010,45(1): 136-139SHI Guifang, YUAN Hao, CHENG Jianchuan. Calculation of speed limiton foggy days[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(1): 136-139 张铁军,周荣贵,唐琤琤,等. China RAP的海外之路[J]. 中国公路,2014(13): 54-55ZHANG Tiejun, ZHOU Ronggui, Tang Chengcheng, et al. China RAP’s oversea road[J]. China Highway, 2014(13): 54-55 刘君.不利天气道路交通安全风险评估与管控策略[M].气象出版社, 2016: 5-12 中华人民共和国公安部.关于加强低能见度气象条件下高速公路交通管理的通告[R].北京: 中华人民共和国公安部, 1997 SEINFELD J H, PANDIS S N. Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1998: 34-60 -





 下载:
下载: