Effects of Fastener Stiffness of Monolithic Bed Track on Vertical Rail Sound Power Characteristics
-
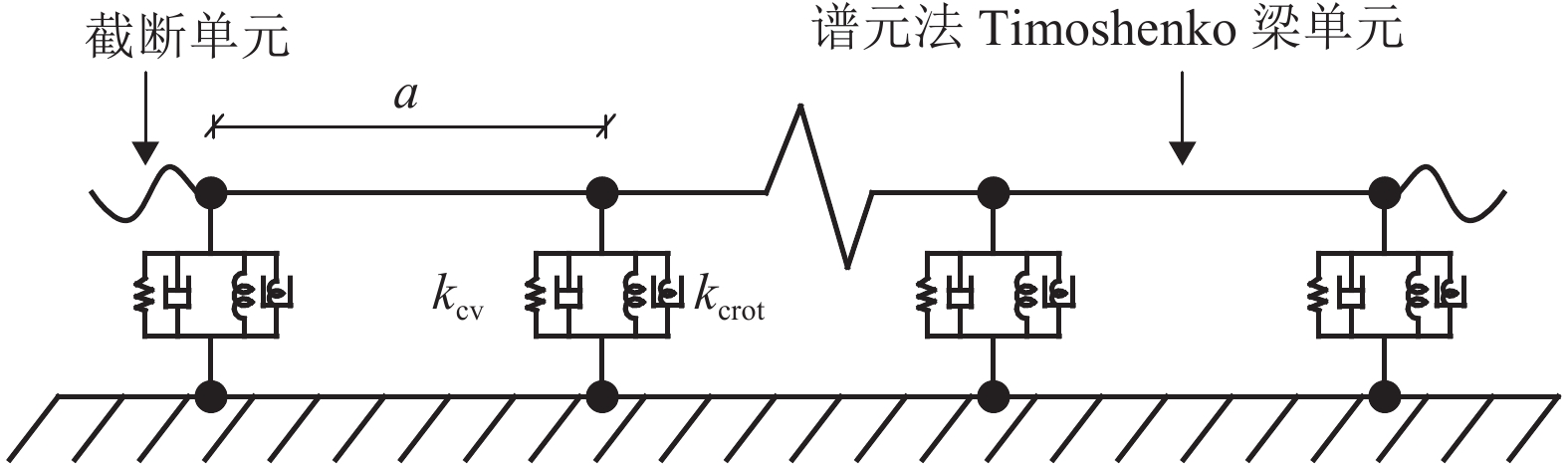
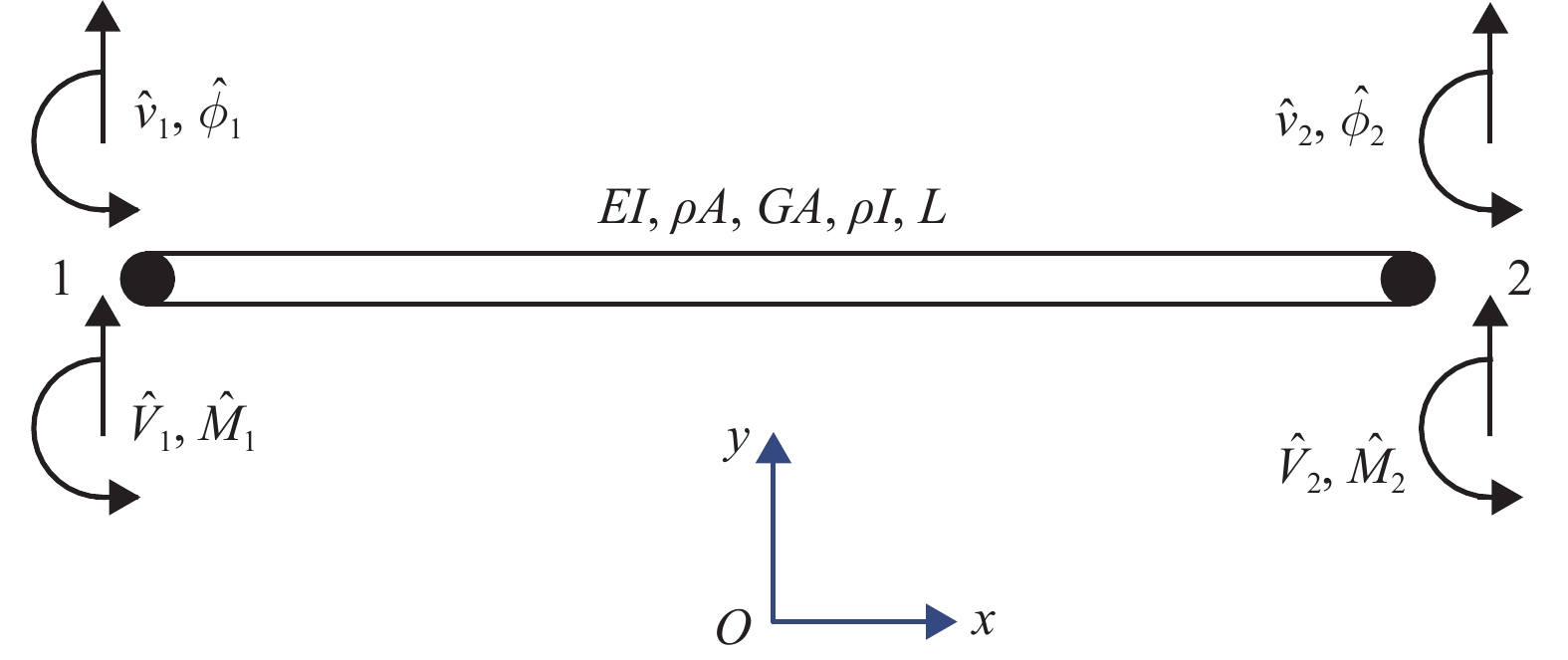
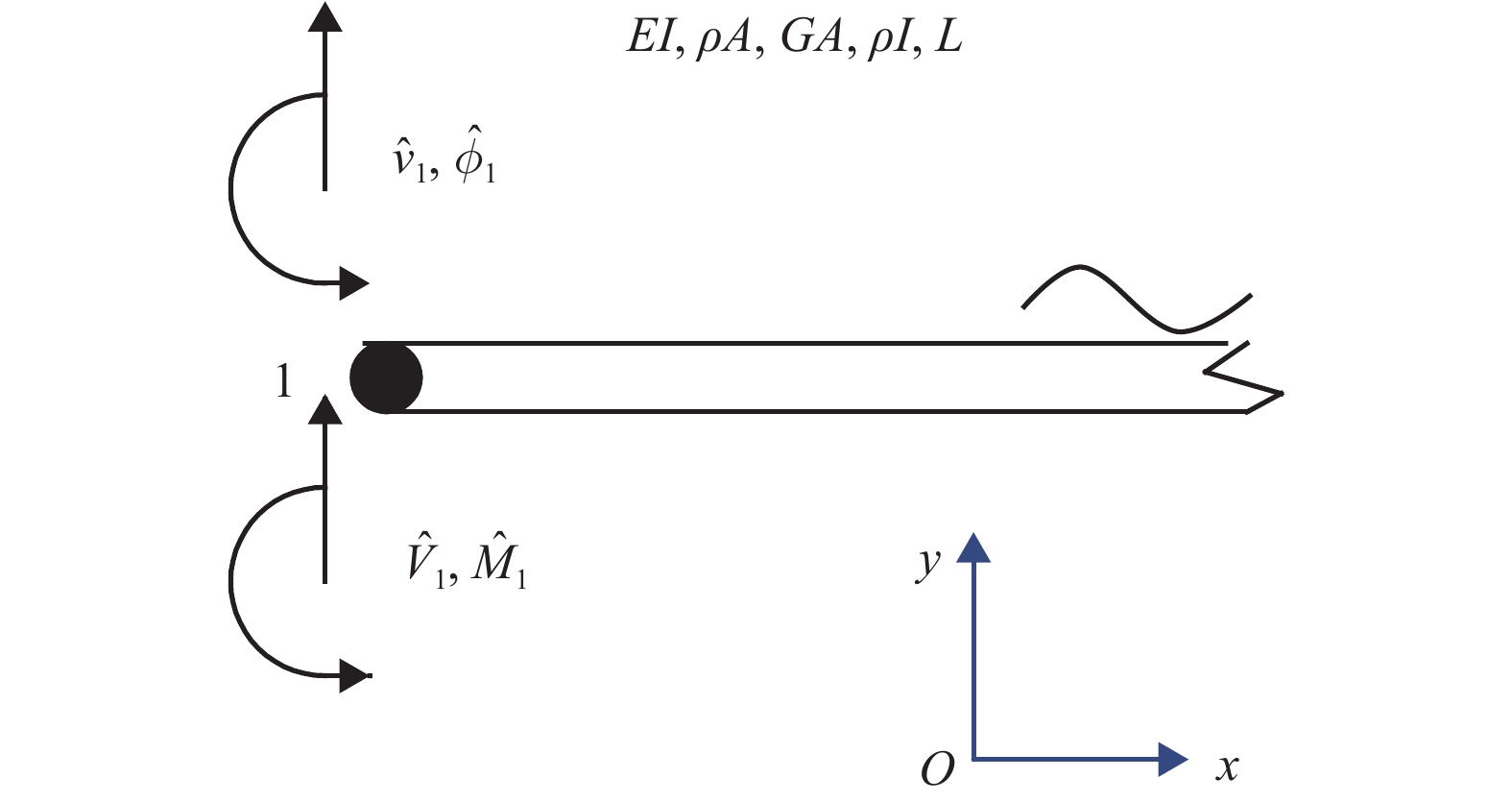
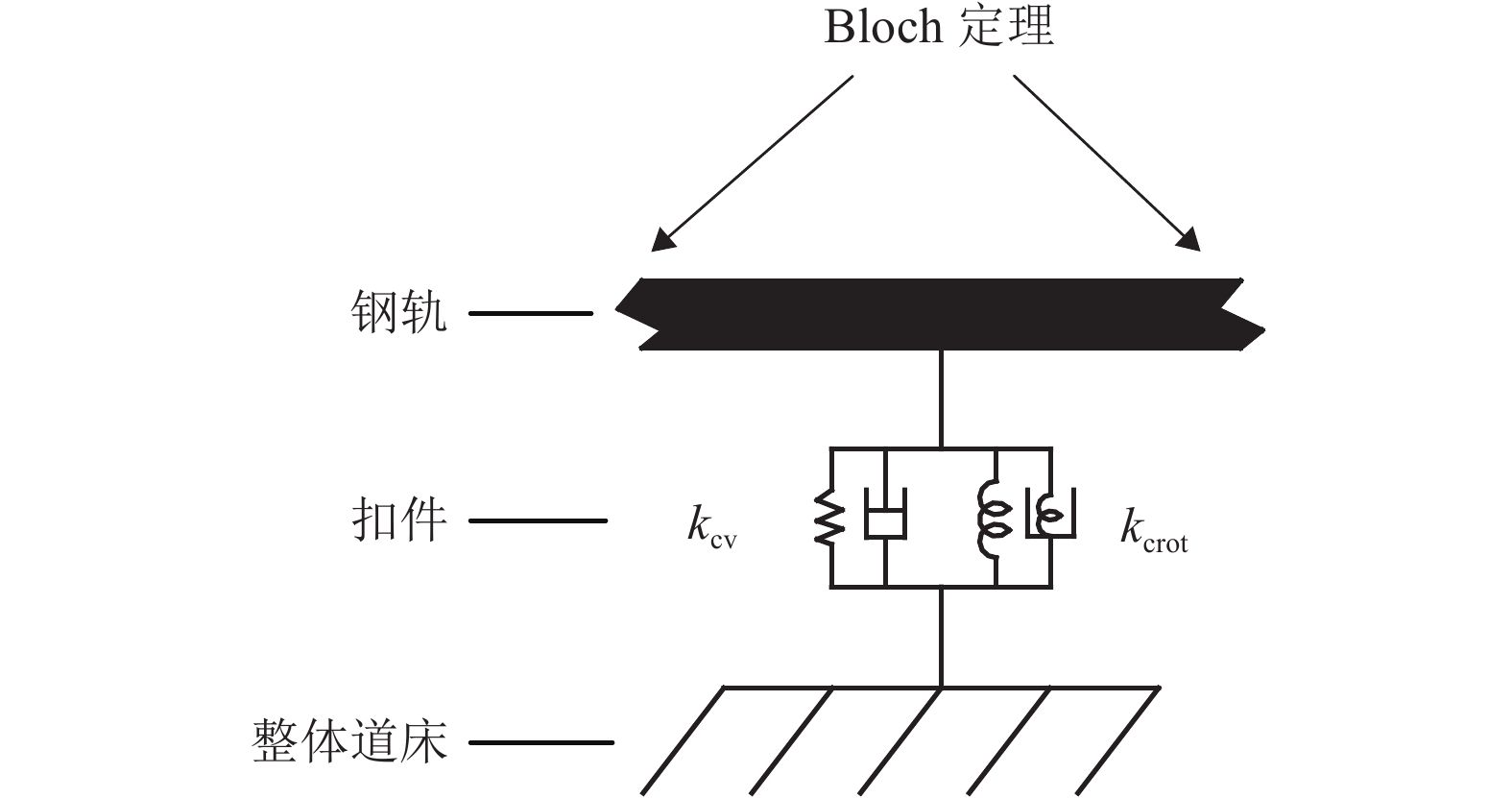
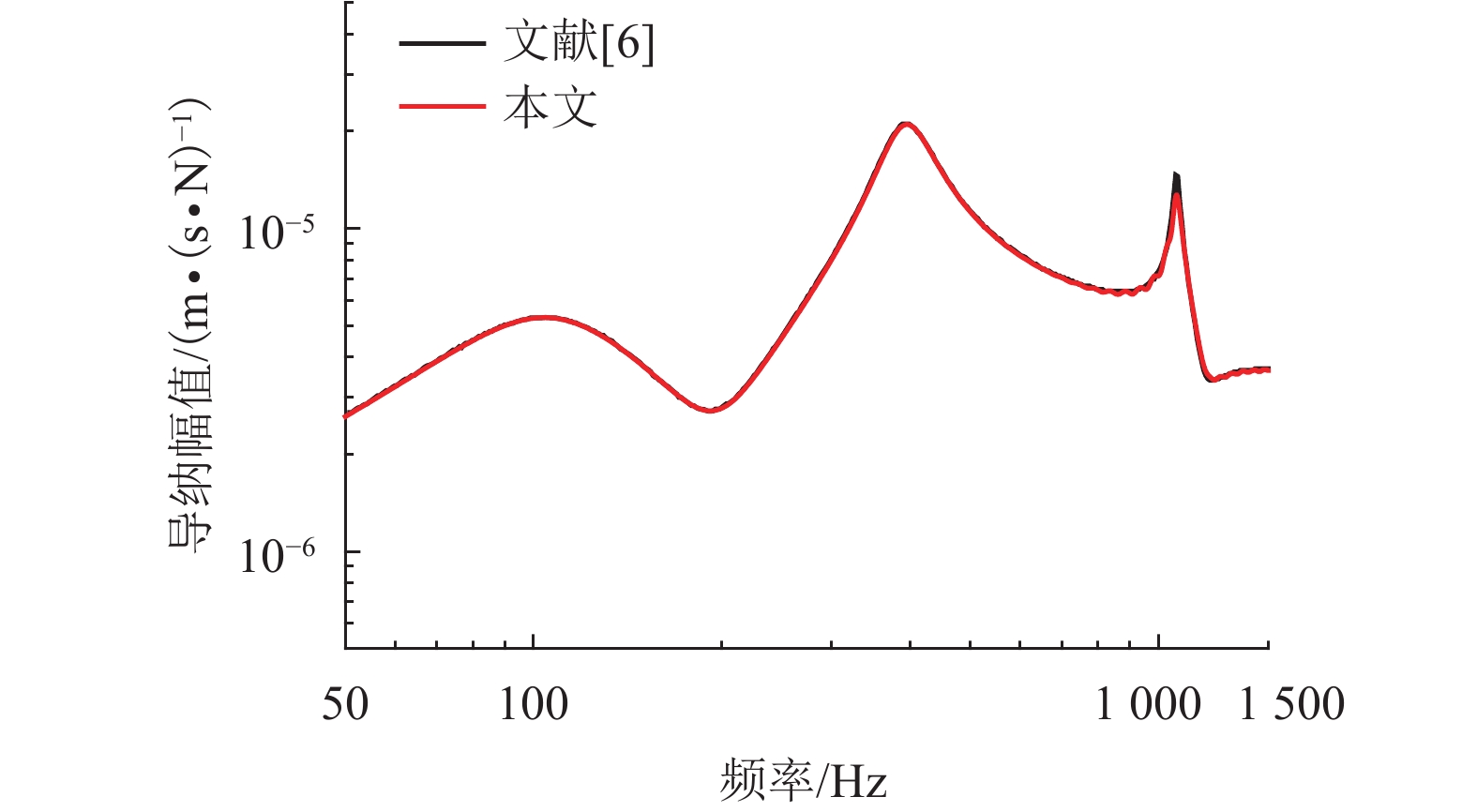
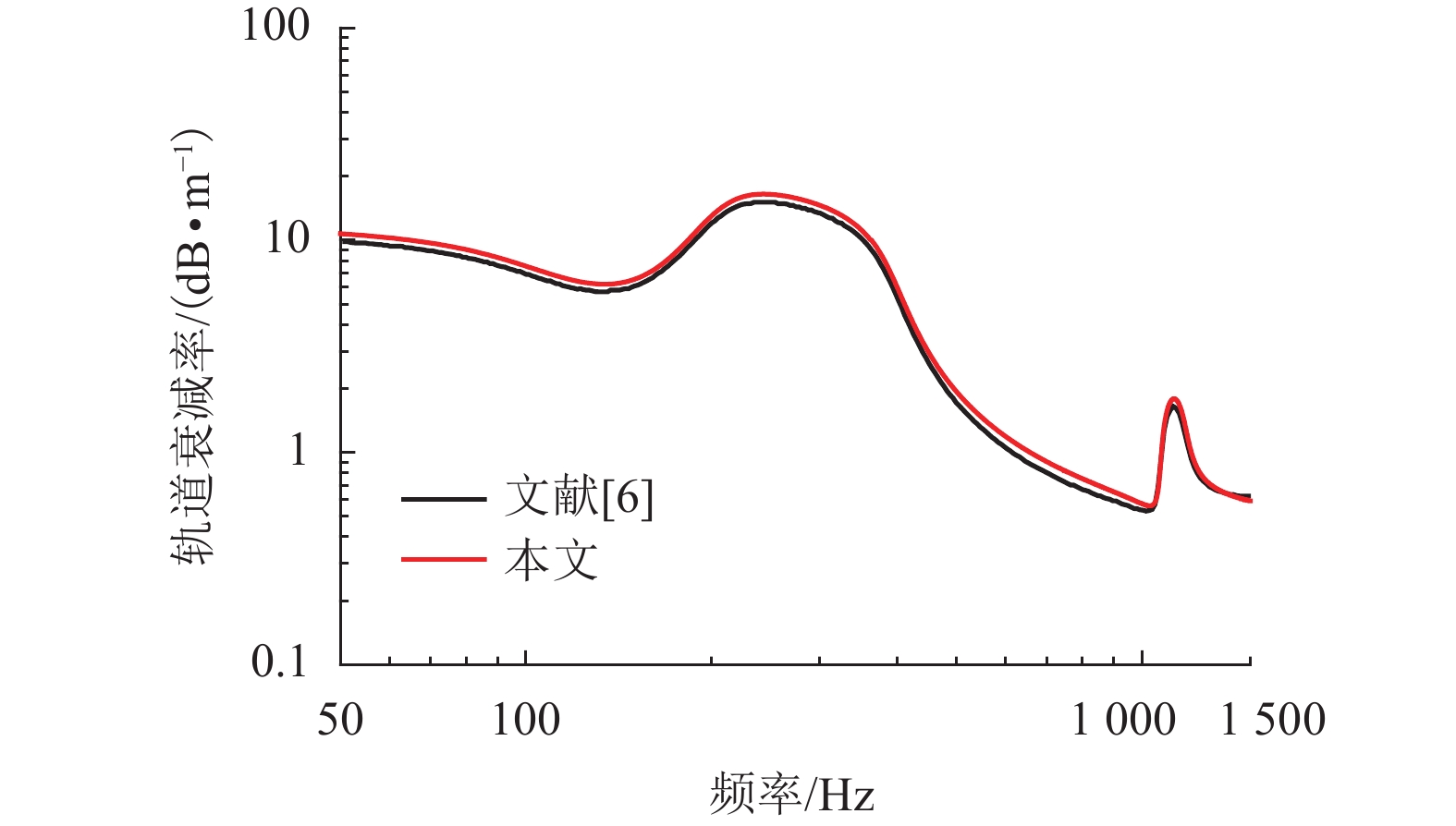
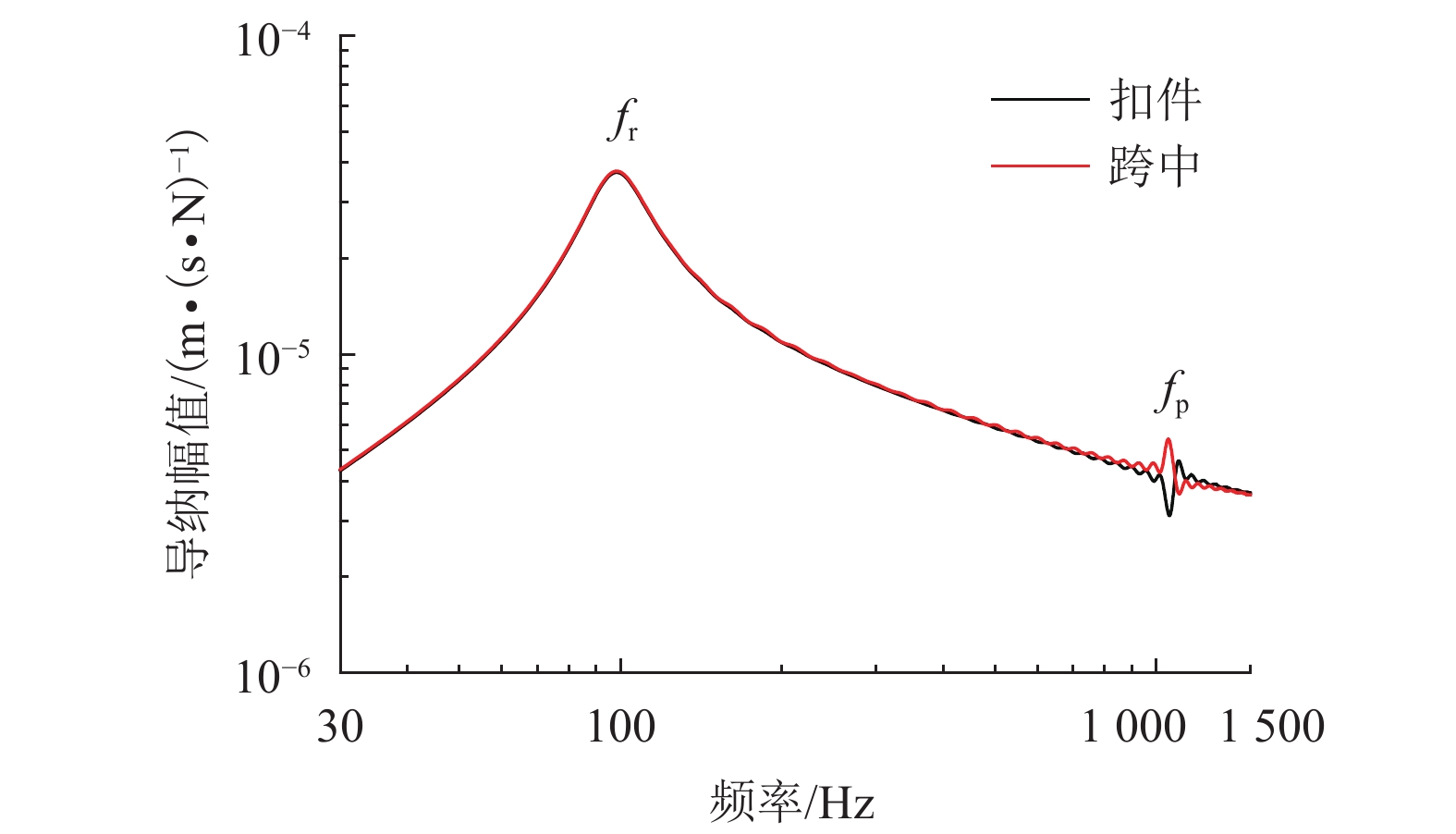
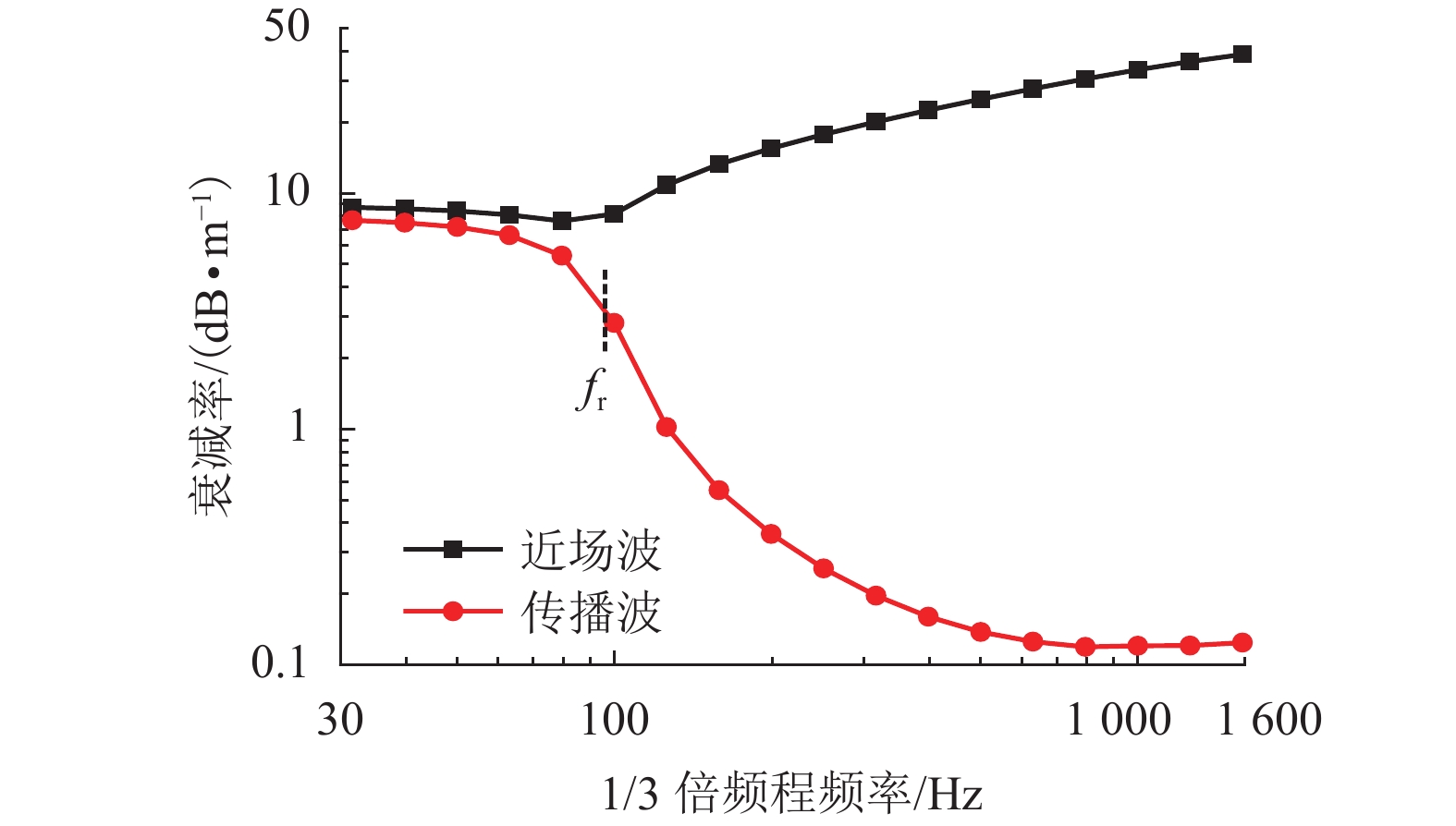
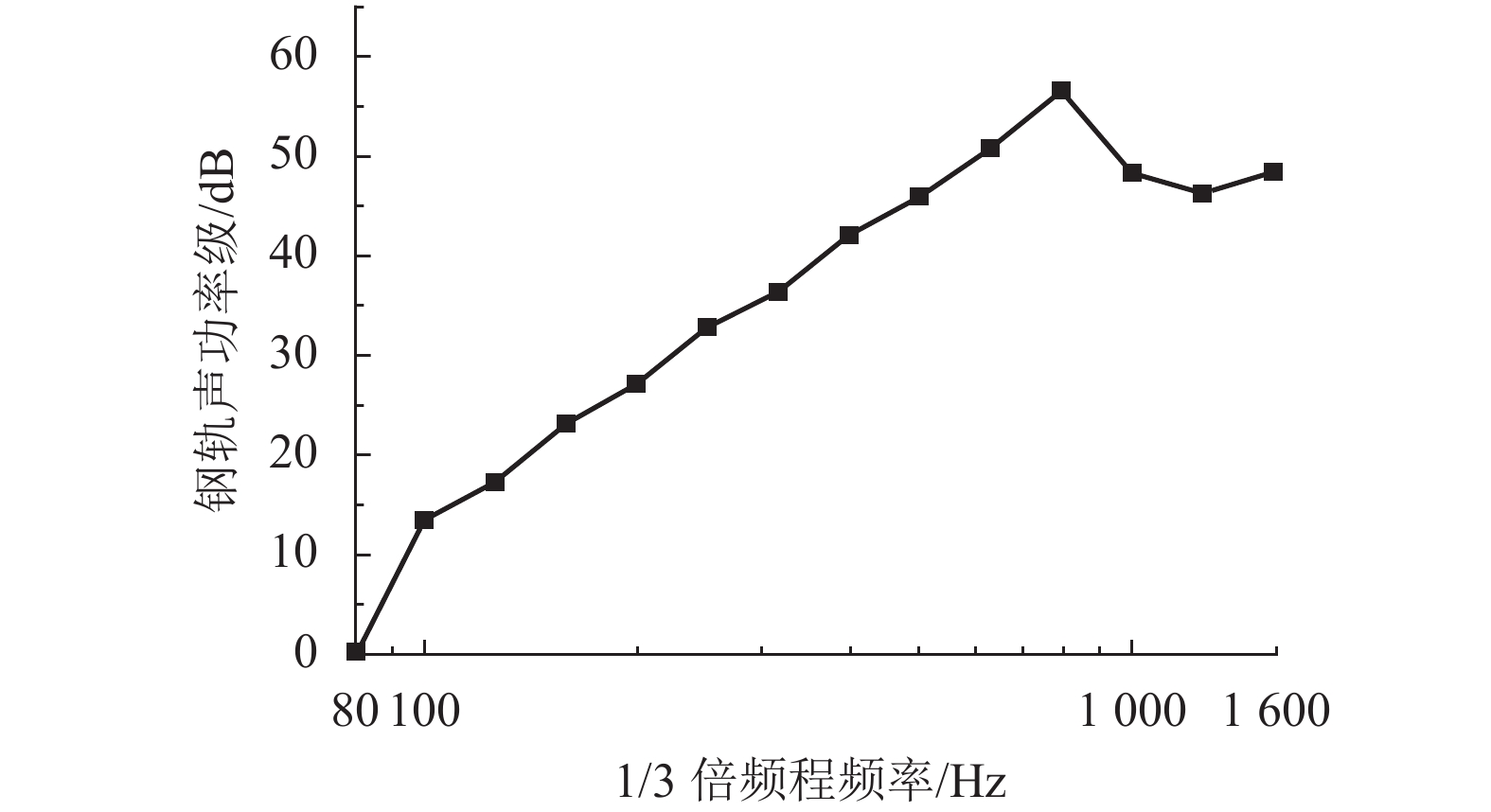
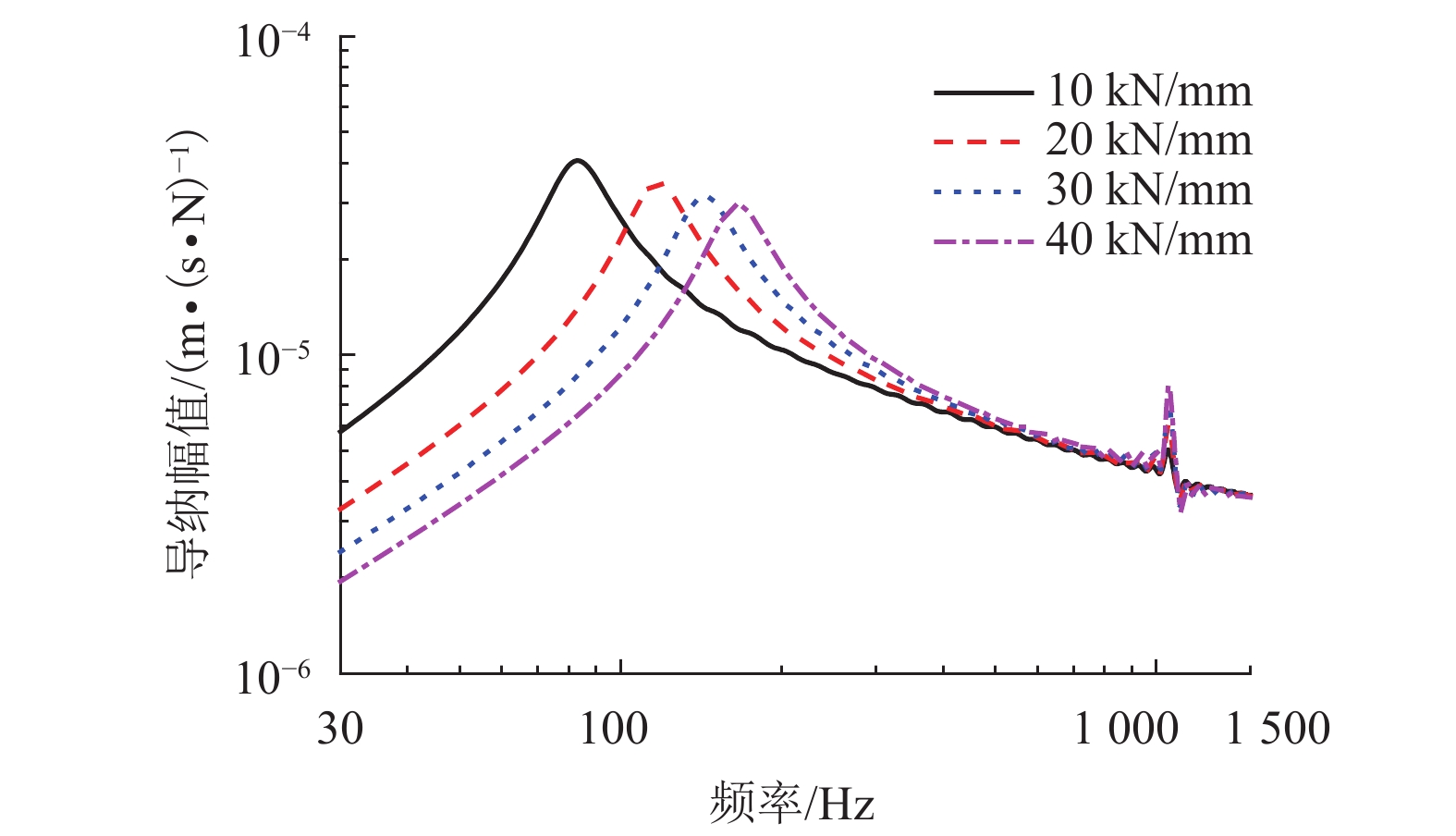
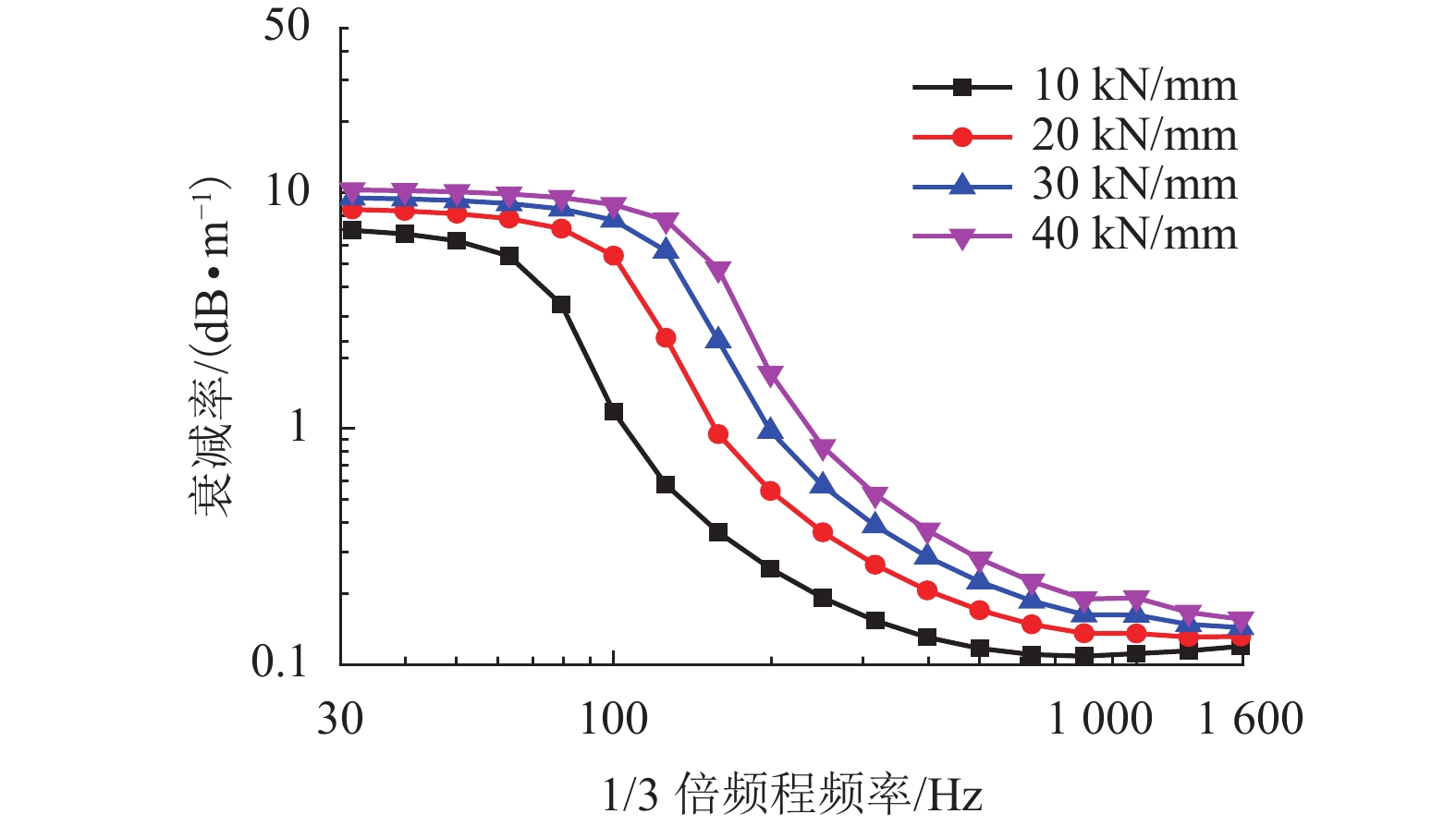
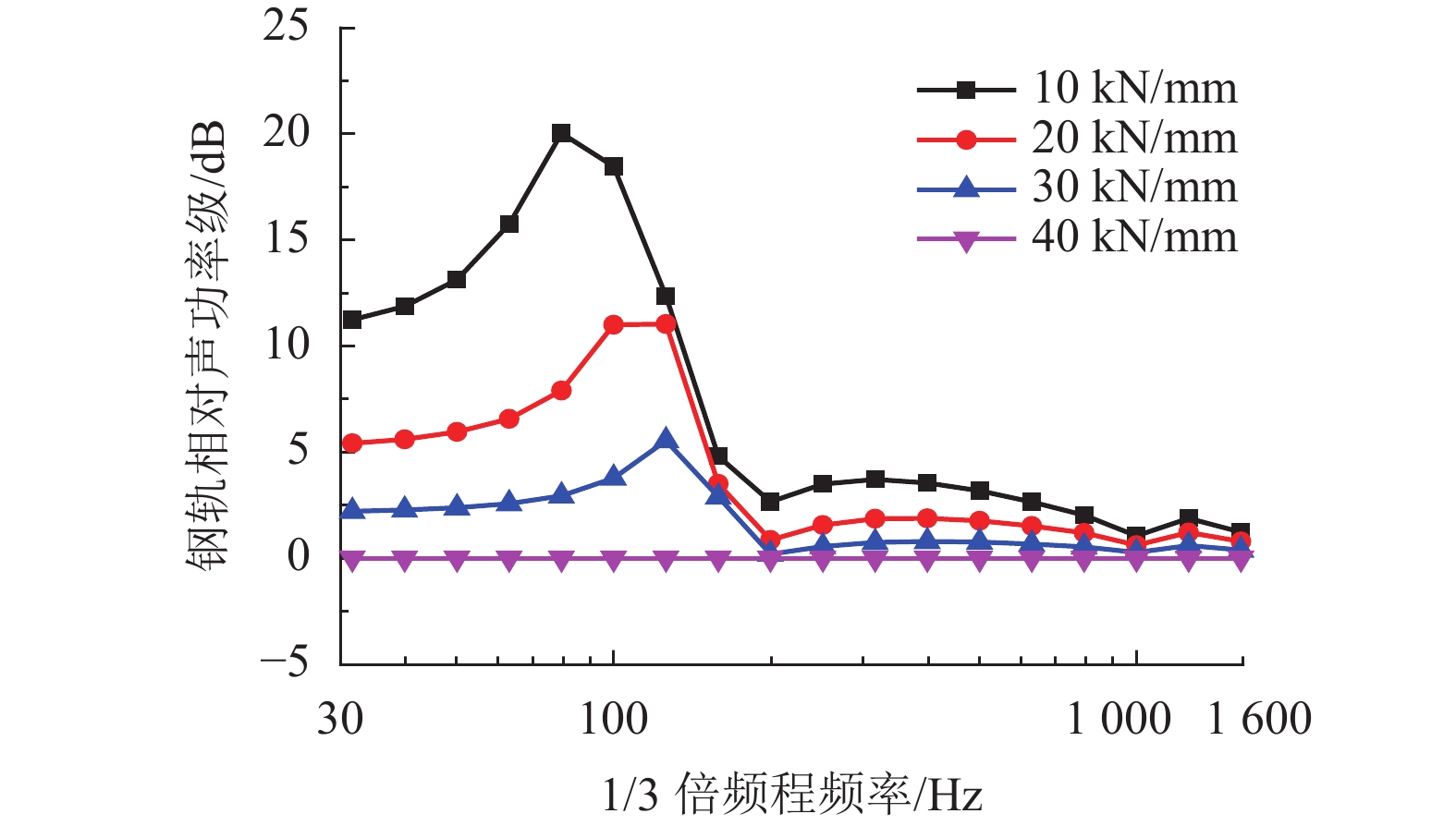
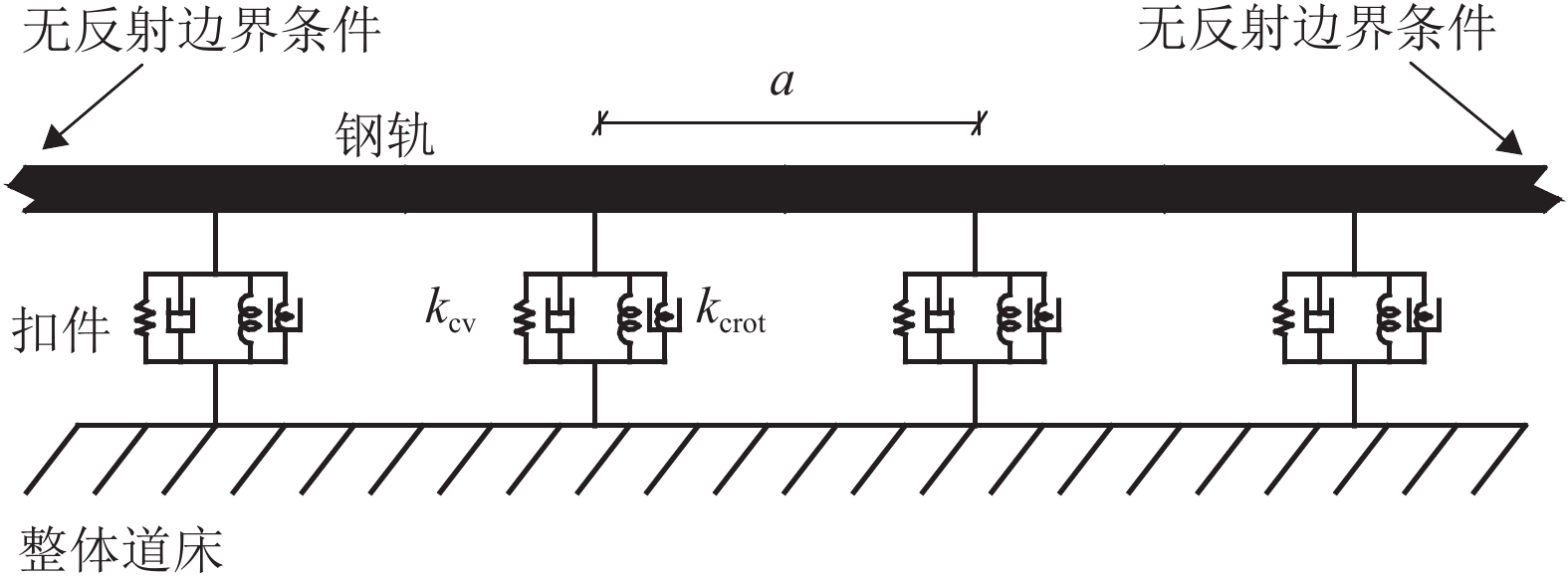
摘要: 为了研究整体道床轨道扣件刚度对钢轨垂向振动声功率特性的影响,建立了平面半轨道模型,利用谱元法计算了钢轨导纳,建立了轨道周期子结构模型,利用谱传递矩阵法计算了轨道衰减率;结合钢轨导纳和轨道衰减率计算结果,得到了单位简谐点激励作用下的钢轨声功率级,分析了扣件刚度对钢轨相对声功率级的影响. 研究结果表明:在单位简谐点激励作用下,中低频范围内的钢轨声功率级随着频率的增大而提高,在1/3倍频程中心频率800 Hz处,钢轨声功率级出现峰值;钢轨声功率级随着扣件刚度的减小而增大,但主要影响的频率范围为400 Hz以下;扣件刚度减小越多,钢轨声功率级增大越显著;扣件刚度的减小使得钢轨声功率级在钢轨弯曲共振频率处增加量最大,这是因为在该频率下钢轨导纳幅值增加量和轨道衰减率减少量均较大.Abstract: To study the effects of fastener stiffness of the monolithic bed track on vertical rail sound power characteristics, the plane half-track model was built and the spectral element method was utilised to obtain rail mobility. A periodic track-substructure model was also built, and the spectral transfer matrix method was utilised to obtain the track decay rate. Combining the results of both rail mobility and track decay rate, the power level of rail sound under unit harmonic point excitation was calculated, and the effects of fastener stiffness on the relative rail sound power level were investigated. The results show that the power level of rail sound increases with the increase in the frequency in the low-medium frequency range. The power level of rail sound has a peak at the centre frequency of 800 Hz in the one third octave band. With the decrease in fastener stiffness, the power level of rail sound increases, which is more obvious in frequency range under 400 Hz. The level is increased more significantly when the stiffness gets a larger decrease. The rail sound power level mostly increases at the rail bending resonance frequency because the rail mobility amplitude increases and the track decay rate decreases deeply.
-
Key words:
- stiffness /
- rail sound power /
- mobility /
- track decay rate /
- spectral element method /
- spectral transfer matrix method
-
表 1 计算参数
Table 1. Calculating parameters
部件 项目 符号 参数 钢轨 模型长度/m LH 25 弹性模量/GPa E 210 泊松比 υ 0.3 截面面积/m2 A 7.75×10-3 密度/(kg•m–3) ρ 7 850 剪切矫正因子 K 0.532 9 绕水平轴惯性矩/m4 I 3.22×10-5 扣件 垂向刚度/(kN•mm–1) kv 14 阻尼损耗因子 ηp 0.25 轨下垫板沿纵向的长度/m br 0.17 扣件间距/m a 0.625 表 2 有砟轨道计算参数
Table 2. Calculating parameters of ballast track
项目 符号 参数 钢轨剪切矫正因子 K 0.4 垫板垂向刚度/(kN•mm–1) kpv 180 垫板阻尼损耗因子 ηp 0.2 道砟垂向刚度/(kN•mm–1) kbv 60 道砟阻尼损耗因子 ηb 1 扣件间距/m a 0.6 轨枕质量/kg ms 150 -
李小珍,刘全民,张迅,等. 铁路高架车站车致振动实测与理论分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(4): 612-618LI Xiaozhen, LIU Quanmin, ZHANG Xun, et al. Measurement and theoretical analysis of vehicle-induced vibration on elevated railway station[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4): 612-618 李小珍,张志俊,冉汶民,等. 桥上列车高速运行引起的地面振动试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5): 815-823LI Xiaozhen, ZHANG Zhijun, RAN Wenmin, et al. Field test of ground vibration induced by high-speed train on elevated bridge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 815-823 王平,周昌盛,韦凯,等. 随机振动过程中轮轨系统内的能量研究[J]. 铁道工程学报,2015,32(5): 30-34WANG Ping, ZHOU Changsheng, WEI Kai, et al. The energy research on the wheel-rail system in the process of stochastic vibration[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2015, 32(5): 30-34 任海,肖友刚. 地铁车内噪声的成因及控制策略[J]. 铁道车辆,2009,47(4): 25-28REN Hai, XIAO Yougang. The cause and control strategy of vehicle interior noise[J]. Rolling Stock, 2009, 47(4): 25-28 王平,唐剑,杨鹏,等. GJ-III减振扣件轨道对轨道交通高架段环境噪声的影响分析[J]. 铁道标准设计,2017,61(3): 4-9WANG Ping, TANG Jian, YANG Peng, et al. Analysis of the influence of GJ-III fastener vibration damping track on environment noise of metro viaduct section[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2017, 61(3): 4-9 THOMPSON D. Railway noise and vibration: mechanisms, modelling and means of control[M]. Oxford: Elsevier Limited, 2008: 175-197 JONES C J C, THOMPSON D J, DIEHL R J. The use of decay rates to analyse the performance of railway track in rolling noise generation[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 293(3/4/5): 485-495 CEN. EN 15461: 2008+A1: 2010 Railway applications-noise emission-characterization of the dynamic properties of track selections for pass by noise measurements[S]. Brussels: CEN Management Centre, 2010 DOYLE J F. Wave propagation in structures: spectral analysis using fast discrete fourier transforms[M]. New York: Springer, 1997: 150-197 IGAWA H, KOMATSU K, SANO M. Wave propagation analysis of frame structures using the spectral element method[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 2004, 277(4): 1071-1081 LEE U. Spectral element method in structural dynamics[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2009: 355-369 THOMPSON D J. Wheel-rail noise generation, part III: rail vibration[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 1993, 161(3): 421-446 MAN A P D. A survey of dynamic railway track properties and their quality[D]. Delft: TU Delft, 2002 ESQUIVEL-SIRVENT R, COCOLETZI G H. Band structure for the propagation of elastic waves in superlattices[J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1994, 95(1): 86-90 RYUE J, THOMPSON D J, WHITE P R, et al. Decay rates of propagating waves in railway tracks at high frequencies[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2009, 320(4/5): 955-976 HECKL M A. Railway noise-can random sleeper spacings help?[J]. ActaAcustica united with Acustica, 1995, 81(6): 559-564 HECKL M A. Coupled waves on a periodically supported Timoshenko beam[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2002, 252(5): 849-882 -





 下载:
下载: