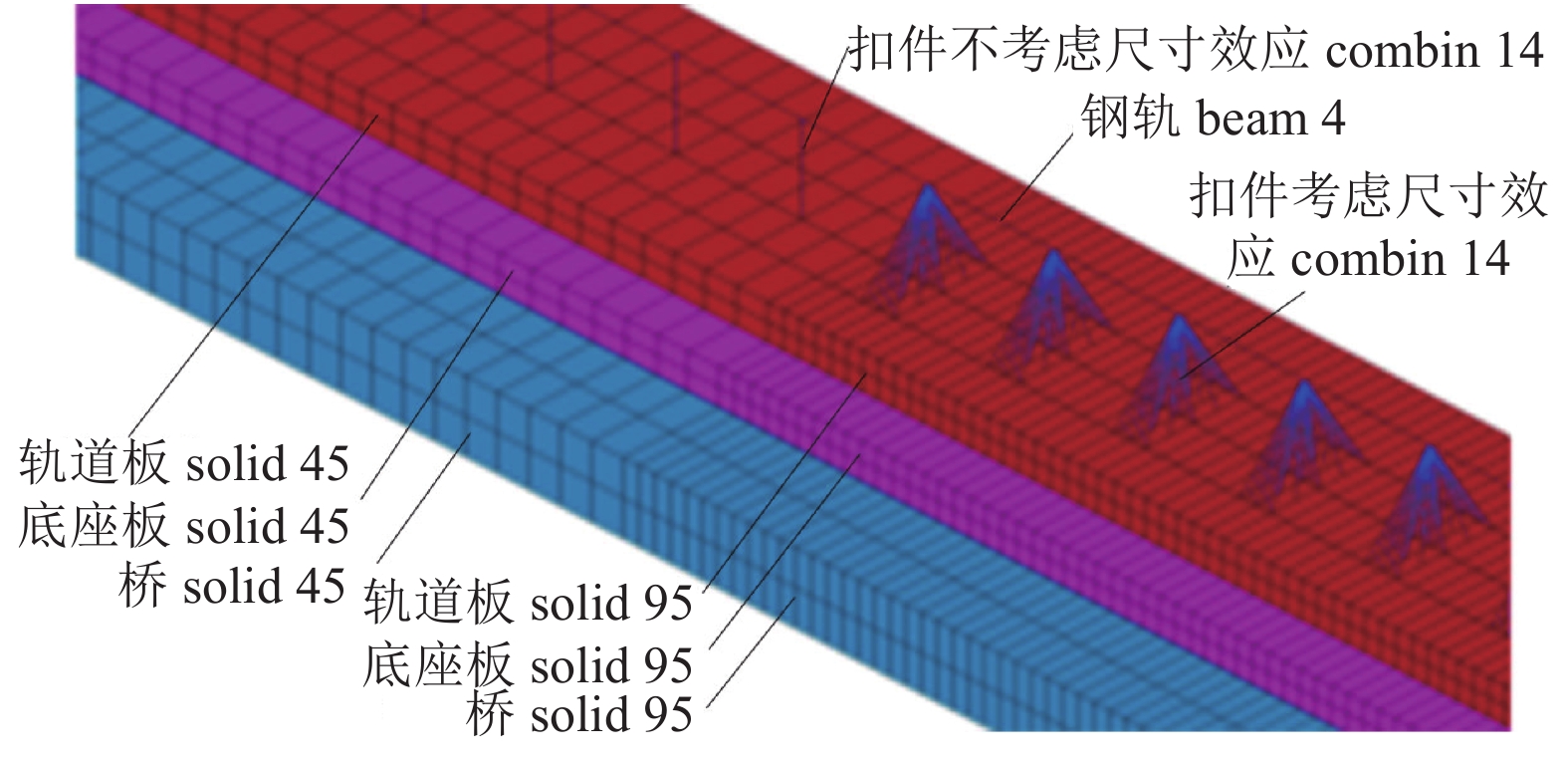
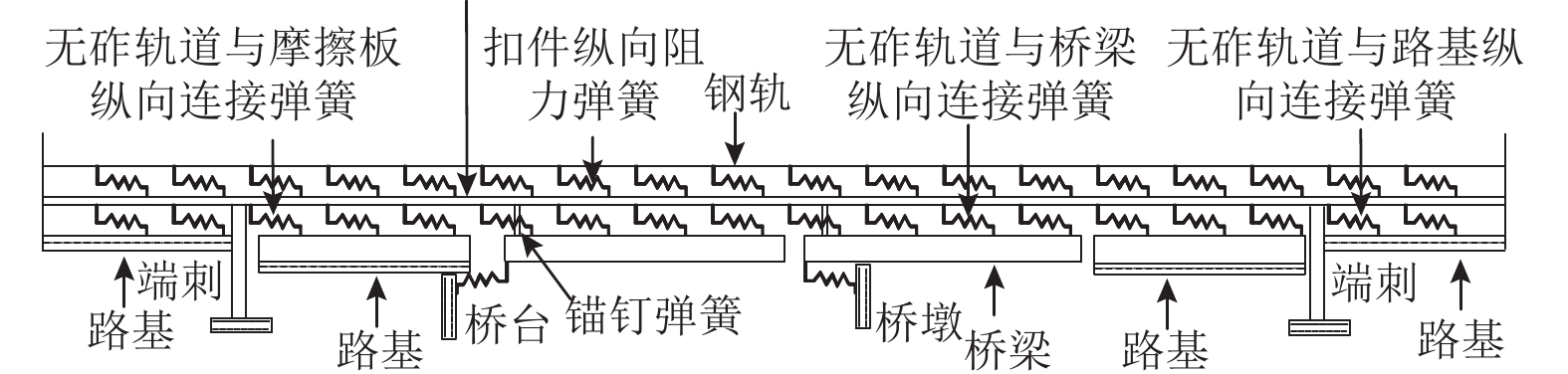
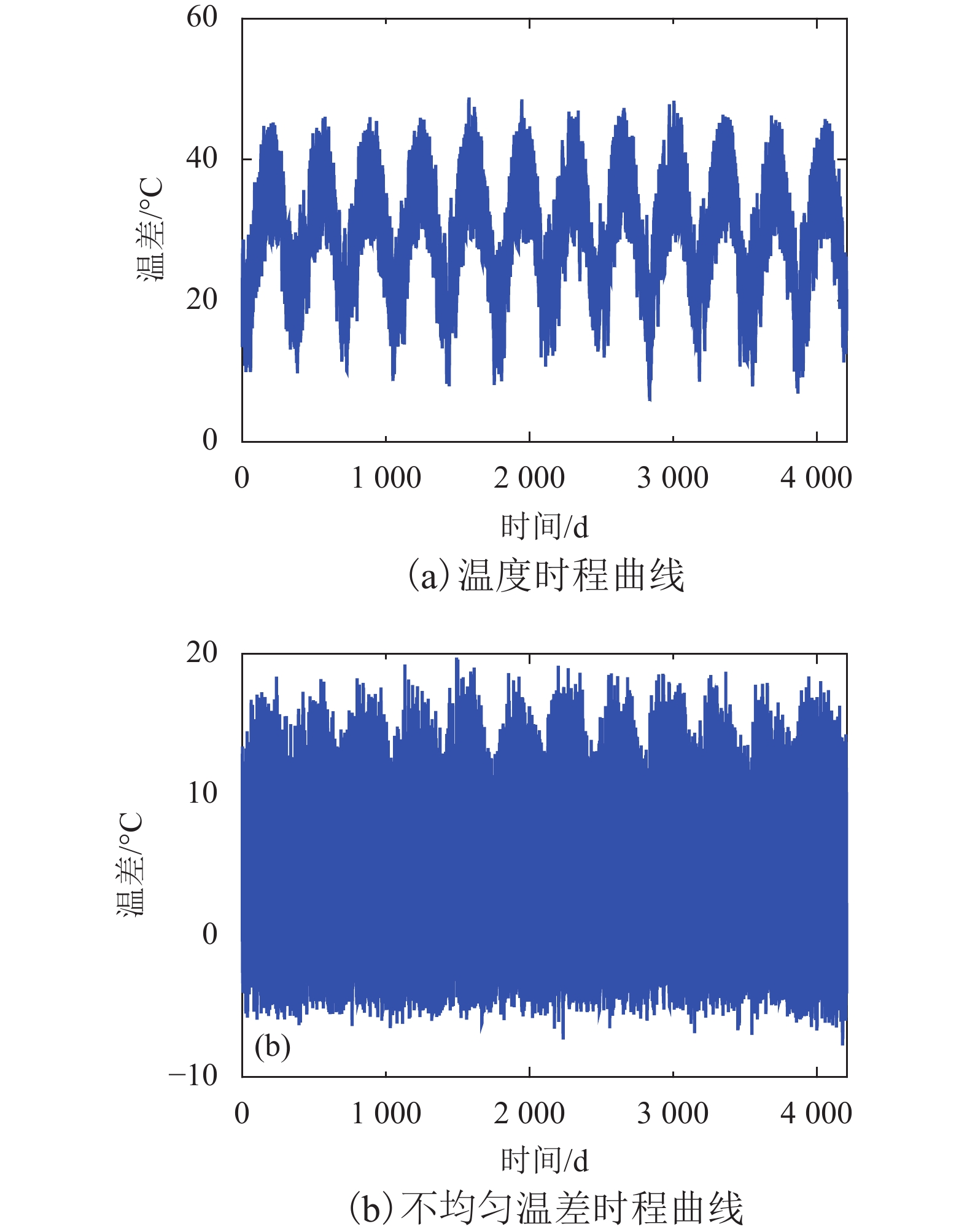
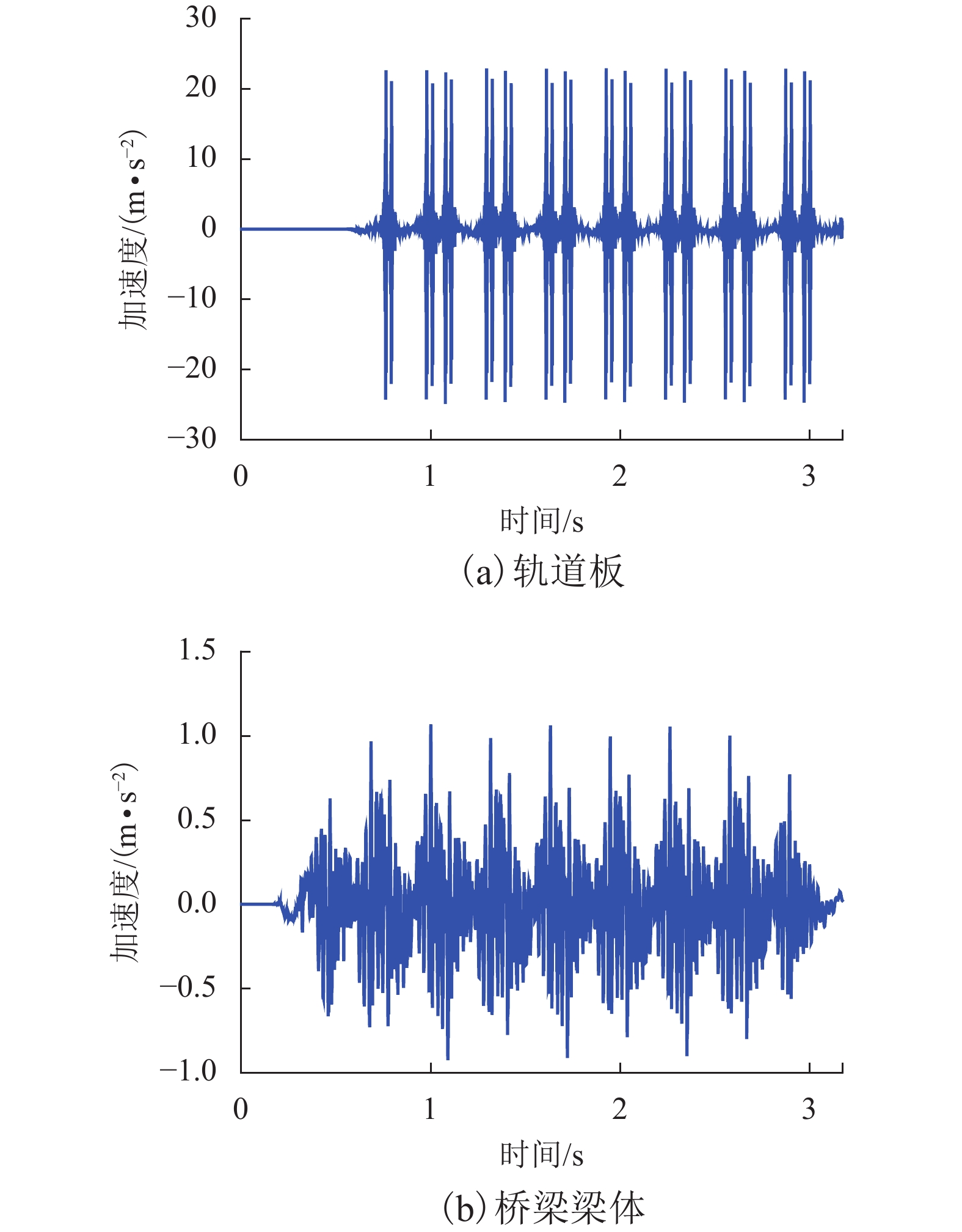
Theoretical Study on Fatigue Stress Spectrum of Longitudinal Connected Slab Track on Bridge
-
摘要: 为获得服役期间桥上纵连板式无砟轨道疲劳应力谱计算理论,考虑无砟轨道钢筋与混凝土的相互作用、无砟轨道混凝土的开裂与闭合效应、无砟轨道荷载的共同作用和时变特性,分别建立和验证了桥上纵连板式无砟轨道温度场计算模型、多尺度高速列车-纵连板式无砟轨道-桥梁三维有限元耦合动力学模型、纵连板式无砟轨道-桥梁-桥梁墩台纵向相互作用模型,并在此基础上,提出了桥上纵连板式无砟轨道疲劳应力谱计算理论.研究结果表明:利用提出的疲劳应力谱计算理论可得到服役期间桥上纵连板式无砟轨道各部件钢筋与混凝土应力时程曲线及疲劳应力谱;考虑多种荷载工况,能深入探讨桥上纵连板式无砟轨道疲劳破坏机理和影响规律;计算理论可为丰富和完善我国无砟轨道设计理论提供重要依据.Abstract: To obtain the fatigue stress spectrum, the calculation theory is proposed for longitudinally connected slab tracks on a bridge during service life. The temperature field calculation model of longitudinally connected slab tracks, the multi-scale high speed train-longitudinal connected slab track-bridge three-dimensional finite element coupling dynamic model, and the longitudinal connected slab track-bridge-piers and abutments longitudinal interaction model, which considers the interaction between steel bars and concrete in ballastless tracks, the crack and closure effects of concrete in the ballastless track, as well as the combined effects and time-varying characteristics of loads of the ballastless track, were established and verified. On the basis of these verifications, the calculation theory of the fatigue stress spectrum of longitudinally connected slab tracks on a bridge was proposed. The following conclusions were obtained: firstly, the stress time history and fatigue stress spectrum of steel bars and concrete in a ballastless track during service life can be obtained using the proposed calculation theory; secondly, the calculation theory can consider various loads and investigate the fatigue failure mechanism and its influence on depth; and lastly, the calculation theory can provide an important basis for enriching and perfecting the design theory of ballastless tracks in China.
-
表 1 纵向力计算结果对比表
Table 1. Comparison table of longitudinal force
比较项目 本文 工况1~3[21] 相差百分比/% 钢轨最大纵向力/kN 320.23 311.35 2.85 无砟轨道板最大纵向力/kN 251.72 253.00 -0.51 1号墩台纵向力/kN 279.23 272.00 2.66 7号墩纵向力/kN 471.49 473.00 -0.32 -
徐庆元,张旭久. 高速铁路博格纵连板桥上无砟轨道纵向力学特性[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版,2009,40(2): 526-532XU Qingyuan, ZHANG Xujiu. Longitudinal forces characteristic of Bogl longitudinal connected ballastless track on high-speed railway bridge[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2009, 40(2): 526-532 钟阳龙,高亮,侯博文. 不同植筋方案纵连板轨道砂浆层抗剪性能分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(1): 38-45ZHONG Yanglong, GAO Liang, HOU Bowen. Inrerlaminar shear performance of mortar layer in longitudinally connected ballastless track with different arrangement schemes of embedded steel bars[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(1): 38-45 戴公连,温学桧,苏海霆. 寒冷季节桥上无砟轨道横竖向温度梯度研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报:自然科学版,2015,43(7): 1-5DAI Gonglian, WEN Xuehui, SU Haiting. Study on horizontal and vertical temperature gradient of ballastless track on bridge in cold season[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2015, 43(7): 1-5 刘钰,赵国堂. CRTSⅡ型板式无砟轨道结构层间早期离缝研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2013,34(4): 1-7LIU Yu, ZHAO Guotang. Analysis of early gap between layers of CRTSⅡ slab ballastless track structure[J]. China Railway Science, 2013, 34(4): 1-7 林红松,刘学毅,杨荣山. 大跨桥上纵连板式轨道受压稳定性[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2008,43(5): 673-678LIN Hongsong, LIU Xueyi, YANG Rongshan. Compressive stability of continuous-slab-track on long-span bridge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2008, 43(5): 673-678 李坤. 高墩大跨连续刚构桥在温度作用下的轨道高低不平顺及对列车的动力影响[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2010 LUO W J, LEI X Y. Analysis of dynamic behavior for ballastless track-bridge with a hybrid method[J]. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing, 2014, 20(4): 487-500 滕东宇. 桥上纵连板式无砟轨道底座板耐久性研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2009 李斌. 组合荷载下桥上纵连板式无砟轨道疲劳应力谱及疲劳寿命预测研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2013 董乐义,罗俊,程礼. 雨流计数法及其在程序中的具体实现[J]. 航空计测技术,2004,24(3): 38-40DONG Leyi, LUO Jun, CHENG Li. Rain flow count method and its realization in programming[J]. Aviation Metrology & Measurement Technology, 2004, 24(3): 38-40 宋洋,刘志刚,汪宏睿,等. 随机风场下高速铁路接触线风振疲劳分析[J]. 铁道学报,2015,37(7): 20-26SONG Yang, LIU Zhigang, WANG Hongrui, et al. Analysis on influence of stochastic wind field on wind vibration fatigue of high-speed railway catenary[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2015, 37(7): 20-26 SCHINDLER A K, RUIZ J M, RASMUSSEN R O, et al. Concrete pavement temperature prediction and case studies with the FHWA HIPERPAV models[J]. Cement & Concrete Composites, 2004, 26(5): 463-471 中华人名共和国住房和城乡建设部. GB 50010—2010 混凝土结构设计规范[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2010 严作人. 层状路面体系的温度场分析[J]. 同济大学学报,1984,12(3): 76-85YAN Zuoren. Analysis of the temperature field in layered pavement system[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 1984, 12(3): 76-85 韩子东. 道路结构温度场研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2001 翟婉明. 车辆-轨道耦合动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 19-32 XU Qingyuan, OU Xi, AU F T K, et al. Effects of track irregularities on environmental vibration caused by underground railway[J]. European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids, 2016(59): 280-293 徐庆元,李斌,周小林. 高速列车作用下路基上板式无砟轨道动力系数[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版,2011,42(9): 2831-2836XU Qingyuan, LI Bin, ZHOU Xiaolin. Dynamic coefficient of slab track system on subgrade under high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2011, 42(9): 2831-2836 国家铁路局. TB 10621—2014 高速铁路设计规范[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2014 张卫华. 高速转向架技术的创新研究[J]. 中国工程科学,2009,11(10): 8-18ZHANG Weihua. Innovation study on the high-speed bogie technology[J]. Engineering Sciences, 2009, 11(10): 8-18 德国博格公司. 京津城际高速铁路博格纵连板桥上无砟轨道第8号技术报告[R]. 天津: 德国博格公司京津城际高速铁路设计部门, 2006 -





 下载:
下载: