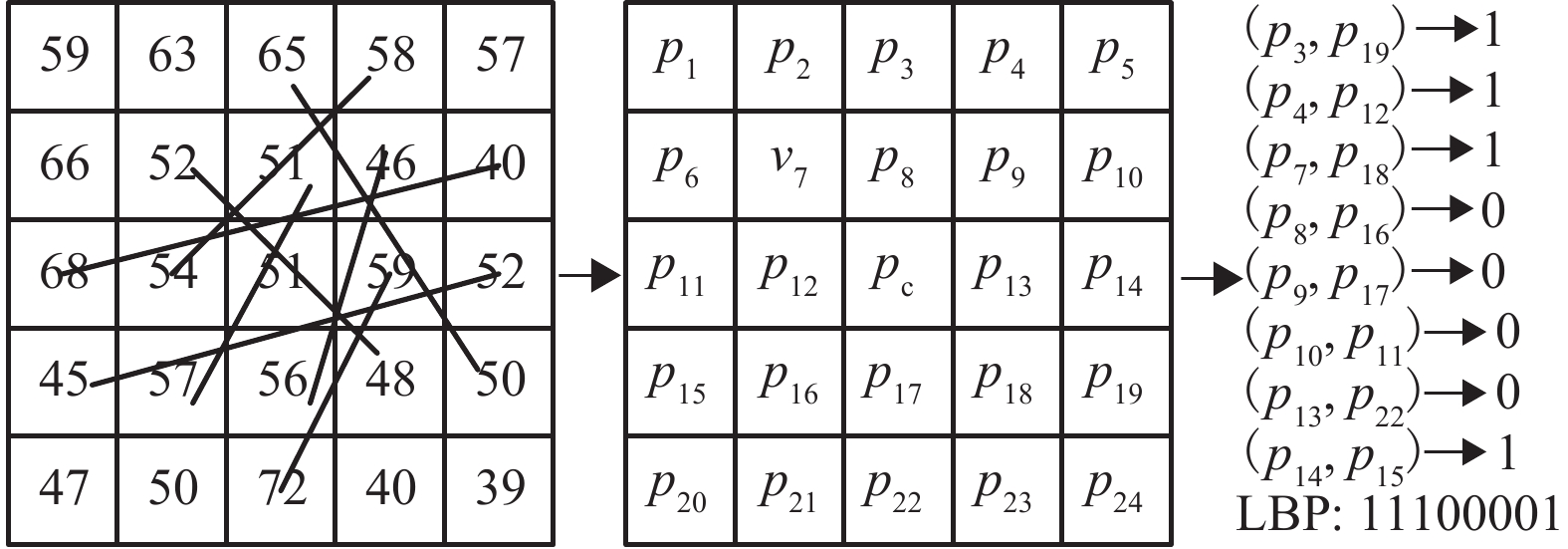
An Improved LBP Feature for Rail Fastener Identification
-
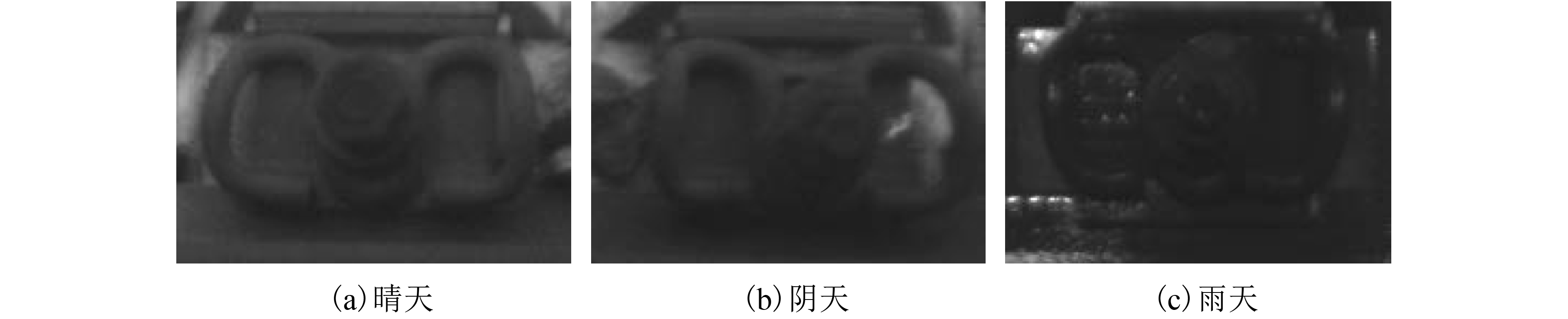
摘要: 为了提高铁路扣件基于视觉的自动化检测精度,提出了一种改进的LBP (local binary pattern)编码算法. 该方法为了避免基本LBP对噪声敏感问题,根据不同邻域的不同噪声强度,结合测量误差服从高斯分布的原则,计算邻域内像素均值和偏差;根据偏差大小,自动设置阈值,实现自适应噪声抑制. 为了避免基本LBP表达邻域差分关系不完整的缺陷,提出了利用邻域内随机采样的方式得到采样点对,通过比较随机点对的差分关系得到LBP编码. 对在晴天、阴天、雨天等不同天气条件下的铁路扣件图像上进行实验,并与原始以及其他改进LBP进行比较. 结果表明,本文的算法具有更高的检测准确率,晴天提高了3.32%,阴天提高了3.27%,雨天提高了4.10%,能够满足铁路扣件自动化检测的需要.Abstract: An improved LBP (local binary pattern) algorithm is proposed to raise the auto-detection accuracy on fasteners. The original LBP is sensitive to noise. To solve this problem, the pixel means value and deviation are calculated, according to the different noise in different neighborhood and the measuring error is following the Gaussian distribution. Then the threshold is set to realize adaptive noise suppression, according to the deviation values. The original LBP cannot completely express the neighboring difference relationship. To avoid this defect, the proposed method gets the sampled point pairs by random sampling in neighborhood. Then LBP coding is generated through comparing the difference relationship of random point pairs. Tests are carried on fasteners images on clear, cloudy and rainy days with original and other improved LBP algorithms. The comparing results show the proposed method owns more detection accuracy. The detection accuracies increase by 3.32%, 3.27% and 4.10% independently on clear, cloudy and rainy days, which shows the proposed method can meet auto-detection on railway fasteners.
-
Key words:
- LBP /
- anti-noise /
- fastener /
- image recognition /
- image detection
-
表 1 晴天扣件识别率
Table 1. Fastener recognition on clear day
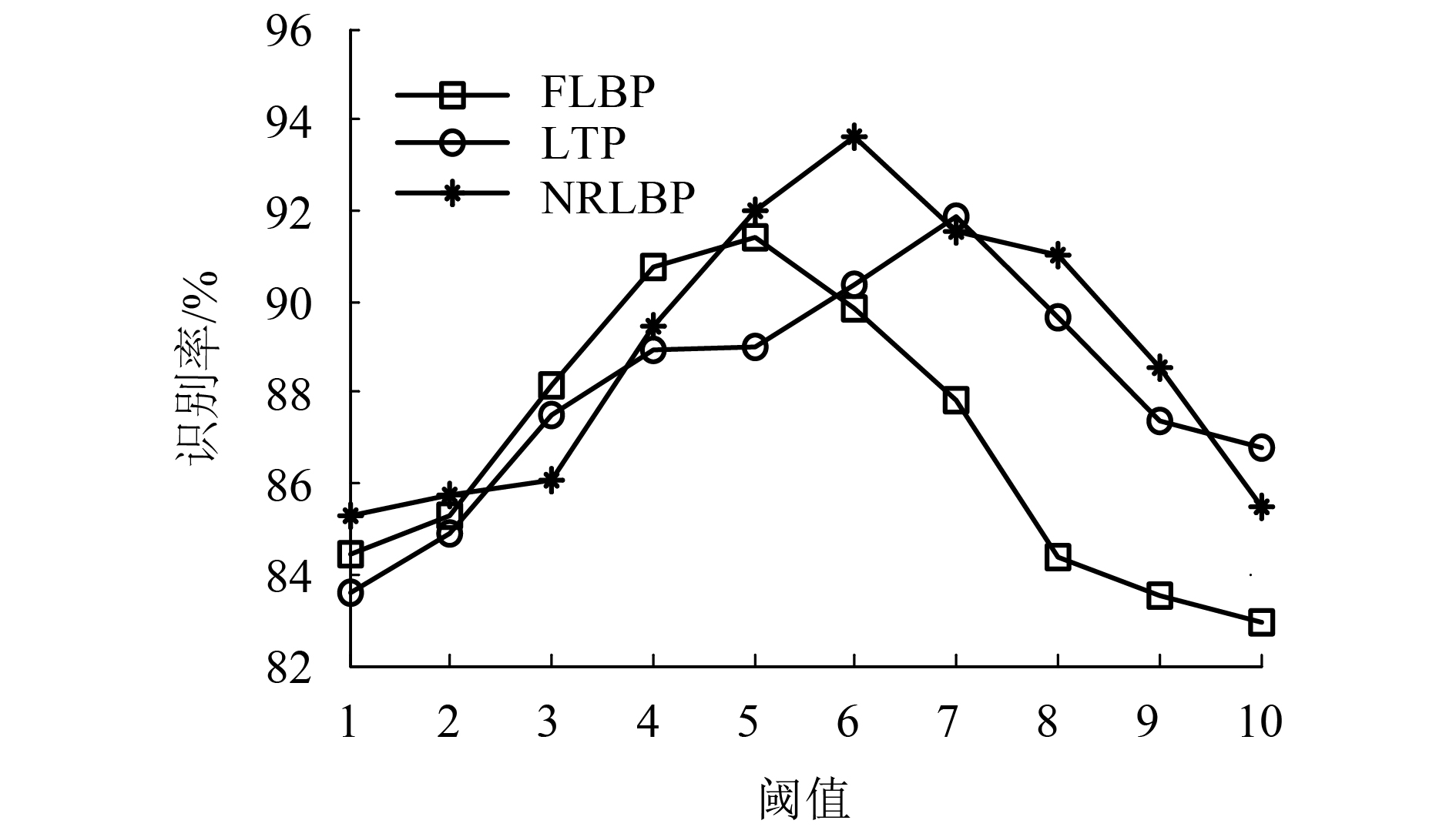
方法 识别率/% LBP 89.35 LBPU2 90.46 LTP 91.85 DLBP 90.89 FLBP 91.42 NRLBP 93.62 本文方法 96.94 表 3 雨天扣件识别率
Table 3. Fastener recognition on rainy day
方法 识别率/% LBP 75.16 LBPU2 77.32 LTP 80.52 DLBP 79.06 FLBP 79.45 NRLBP 81.23 本文方法 85.33 表 2 阴天扣件识别率
Table 2. Fastener recognition on cloudy day
方法 识别率/% LBP 85.76 LBPU2 86.59 LTP 88.03 DLBP 86.95 FLBP 88.72 NRLBP 89.57 本文方法 92.84 表 4 计算时间对比
Table 4. Computation time comparisons
方法 时间/s LBP 108.711 本文方法 157.408 -
SINGH M, SINGH S, JAISWAL J, et al. Autonomous rail track inspection using vision based system[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Homeland Security and Personal Safety. [S. l.]: Alexandria: IEEE, 2006: 56-59 MARINO F, DISTANTE A, MAZZEO P, et al. A real-time visual inspection system for railway maintenance: automatic hexagonal-headed bolts detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics,Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2007, 37(3): 418-428 YELLA S, DOUGHERTY M, GUPTA N. et al. Condition monitoring of wooden railway sleepers[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2009, 17(1): 38-55 许贵阳,史天运,任盛伟,等. 基于计算机视觉的车载轨道巡检系统研制[J]. 中国铁道科学,2013,34(1): 139-144XU Guiyang, SHI Tianyun, REN Shengwei, et al. Development of the on-board track inspection system based on computer vision[J]. China Railway Science, 2013, 34(1): 139-144 肖新标,金学松,温泽峰. 钢轨扣件失效对列车动态脱轨的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2006,6(1): 10-15XIAO Xinbiao, JIN Xuesong, WEN Zefeng. Influence of rail fastener failure on vehicle dynamic derail-ment[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2006, 6(1): 10-15 YANG Jinfeng, WEI Tao, LIU Manhua, et al. An efficient direction field-based method for the detection of fasteners on high-speed railways[J]. Sensors, 2011, 11(8): 7364-7381 XIA Yiqi, XIE Fengying, JIANG Zhiguo. Broken railway fastener detection based on adaboost algorithm[C]// International Conference on Opto-electronics and Image Processing. Beijing: IEEE, 2010: 313-316 刘甲甲,李柏林,罗建桥,等. 融合PHOG和MSLBP特征的铁路扣件检测算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(2): 256-263LIU Jiajia, LI Bailin, LUO Jianqiao. et al. Railway fastener detection algorithm integrating PHOG and MSLBP features[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(2): 256-263 REN J, JIANG X, YUAN J. LBP encoding schemes jointly utilizing the information of current bit and other LBP bits[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(12): 2373-2377 REN J, JIANG X, YUAN J. Noise-resistant local binary pattern with an embedded error-correction mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(10): 4049-4060 GUO Zhenhua, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG D. A completed modeling of local binary pattern operator for texture classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(6): 1657-1663 SONG Tiecheng, LI Hongliang, MENG Fanman, et al. Noise-robust texture description using local contrast patterns via global measures[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(1): 93-96 WANG Kai, BICHOT C, ZHU Chao, et al. Pixel to patch sampling structure and local neighboring intensity relationship patterns for texture classification[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(9): 853-856 LIAO S, LAW M W K, CHUNG A C S. Dominant local binary patterns for texture classification[J]. IEEE transactions on image processing, 2009, 18(5): 1107-1118 KWAK J T, XU S, WOOD B J. Efficient data mining for local binary pattern in texture image analysis[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(9): 4529-4539 SATPATHY A, JIANG X, ENG H L. LBP-based edge-texture features for object recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(5): 1953-1964 REN J, JIANG X, YUAN J. et al. Optimizing LBP structure for visual recognition using binary quadratic programming[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(11): 1346-1350 LI Wei, CHEN Chen, SU Hongjun, et al. Local binary patterns and extreme learning machine for hyperspectral imagery classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(7): 3681-3693 OJALA T, PIETIKAINEN M, MAENPAA T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(7): 971-987 TAN X, TRIGGS B. Enhanced local texture feature sets for face recognition under difficult lighting conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(6): 1635-1650 AHONEN T, PIETIKAINEN M. Soft histograms for local binary patterns[C]//Proceedings of the Finnish signal processing symposium. Finsic: [s. n.], 2007, 5(9): 1-4 WEINBERGER M J, RISSANEN J J, AERS R B. Applications of universal context modeling to lossless compression of gray-scale images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1996, 5(4): 575-586 -





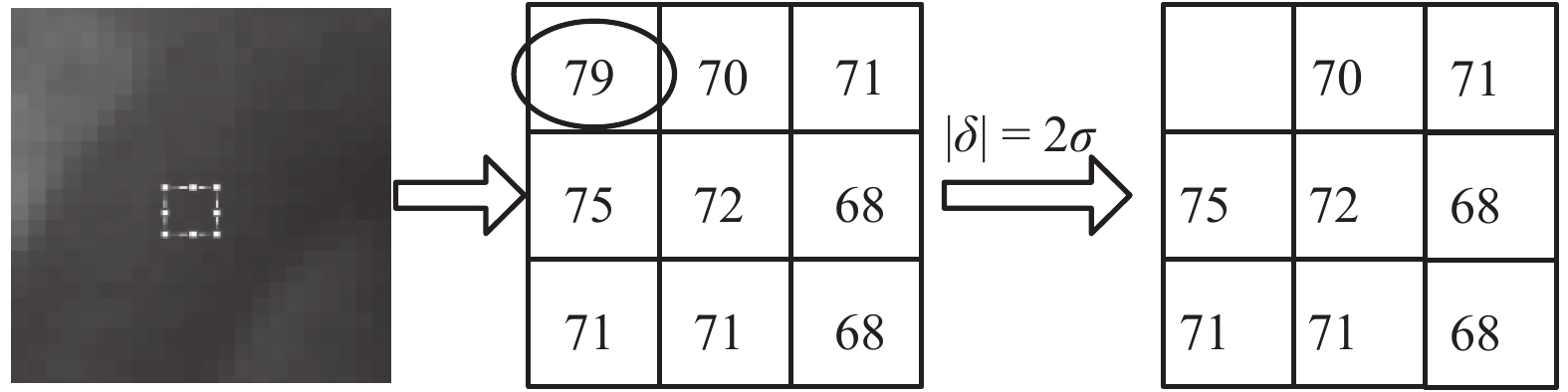
 下载:
下载: