Man-Machine Functional Dimension Design of Riding Equipment in Subway Passenger Compartments
-
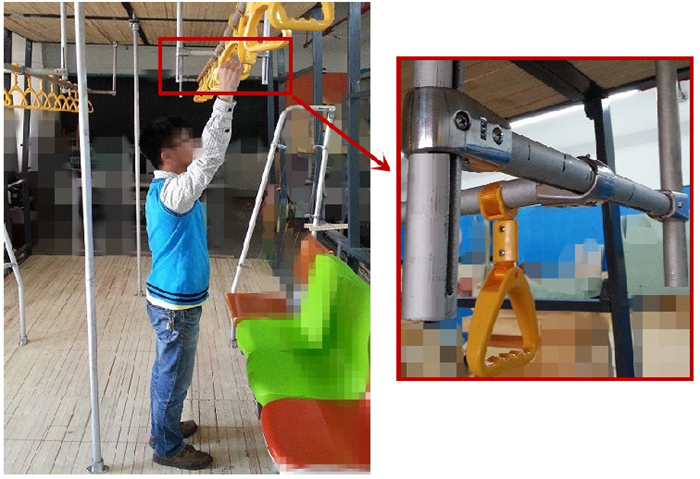
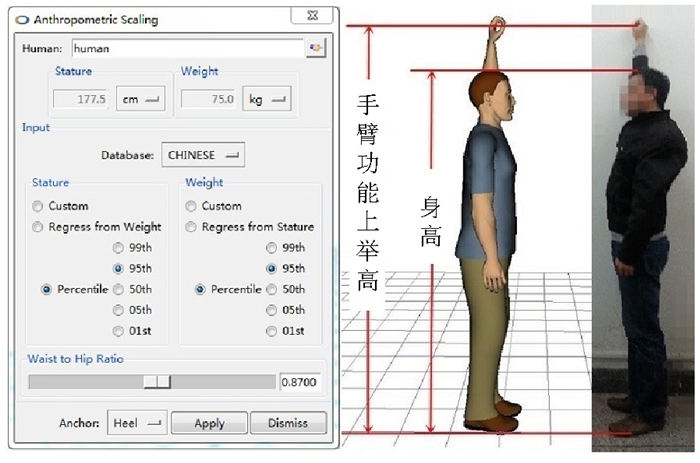
摘要: 为探讨乘客身材特征对地铁客室中乘坐设备功能尺寸设计的影响,运用人机工程学以人为中心的实验和相关分析法展开研究.围绕人的生理结构、心理尺度和乘坐设备的功能属性等因素,结合压力分布实验、虚拟仿真技术和主观评价分析,对人与地铁座椅和扶手之间的功能尺寸配置关系进行了测试与分析.研究结果表明:座椅腰靠纵向外凸圆弧的曲率半径为186 mm、座垫横向内凹圆弧的曲率半径为785 mm时更贴近人体坐姿的生理曲度和满足乘坐的舒适性要求;扶手的吊环高度设置在1 710 mm、横杆高度设置在1 860 mm时能够分别保障不同身材的乘客的使用需求,并能满足适用性、安全性和通行性之间的平衡.Abstract: A human-centred experiment and ergonomic correlation-analysis approach was adopted to investigate the impact of passenger body size on the functional dimension design of riding equipment in subway passenger compartments. Subsequently, the relationship between the functional dimension configuration among passengers, subway seats, and handrails was tested and analysed based on human physiological structure, psychological endurance, and functional properties of riding equipment. This was achieved by combining a pressure distribution experiment with virtual simulation technology and subsequent subjective evaluation and analysis. Results demonstrate that when the curvature radius of the backrest outer convex arc measures 186 mm while that of the cushion inner concave arc measures 785 mm, seat surface closely matches the physiological curvature of the body-sitting posture, thereby meeting the requirements of riding comfort. Also, when the height of handrail rings and that of cross rods are set as 1 710 mm and 1 860 mm, respectively, handrail height meets usage requirements of passengers having different bodies sizes as well as that of balance between applicability, safety, and accessibility.
-
Key words:
- subway passenger compartment /
- ergonomics /
- pressure distribution /
- virtual simulation
-
表 1 座椅基本指标的相关设置参数对比
Table 1. Comparison of relevant setting parameters concerning basic seat index
座椅指标 标准1 标准2 标准3 地铁座椅 座高/mm 400~460 380~450 440~540 440 座深/mm ≥350 ≥360 400~500 450 座宽/mm ≥380 ≥420 ≥440 430 靠背倾角/(°) 95~105 — 80~135 100 座垫倾角/(°) 3~7 — 3~7 6 表 2 地铁座椅曲面测试的实验数据
Table 2. Data concerning subway seat surface test
曲面指标 体压指标 主观
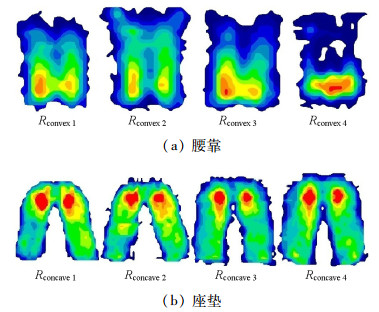
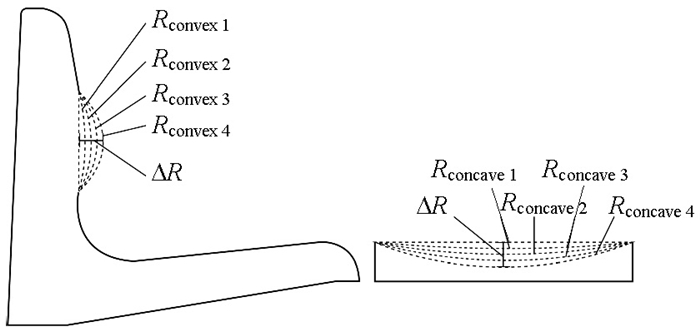
评分Pv/kPa Gm/(kPa·cm-2) Gv/(kPa·cm-2) A/cm2 Rconvex 1 1.16(0.11) 4.43(0.66) 0.54(0.07) 460(59) 3.1(0.66) Rconvex 2 0.95(0.10) 4.47(0.75) 0.49(0.07) 505(76) 3.9(0.69) Rconvex 3 1.13(0.06) 4.96(0.86) 0.52(0.10) 481(80) 2.7(0.65) Rconvex 4 1.41(0.09) 5.14(0.71) 0.57(0.09) 400(84) 1.6(0.62) Rconcave 1 3.69(0.47) 6.28(2.22) 0.73(0.08) 1 054(90) 3.0(0.74) Rconcave 2 3.57(0.43) 5.38(0.92) 0.70(0.06) 1 078(103) 3.8(0.83) Rconcave 3 3.55(0.50) 4.92(1.18) 0.69(0.08) 1 150(123) 4.1(0.74) Rconcave 4 3.58(0.54) 6.65(0.93) 0.75(0.06) 1 190(140) 3.6(0.72) 表 3 扶手测试高度的取值说明
Table 3. Value description for handrail height test
扶手 高度/mm 取值说明 吊
环1 510 P5女性身高修正值 1 610 P50女性与P5男性身高修正值 1 680 P95女性身高修正值 1 710
P50男性身高修正值和P1
女性手功能高修正值1 760 P5女性手功能高修正值 横
杆1 810 P95男性身高修正值 1 860 P99男性身高与P5男性和P50
女性手功能高修正值1 990 P95女性手功能高修正值 2 020 P50男性手功能高修正值 2 160 P95男性手功能高修正值 表 4 扶手高度测试的实验数据
Table 4. Data concerning handrail height test
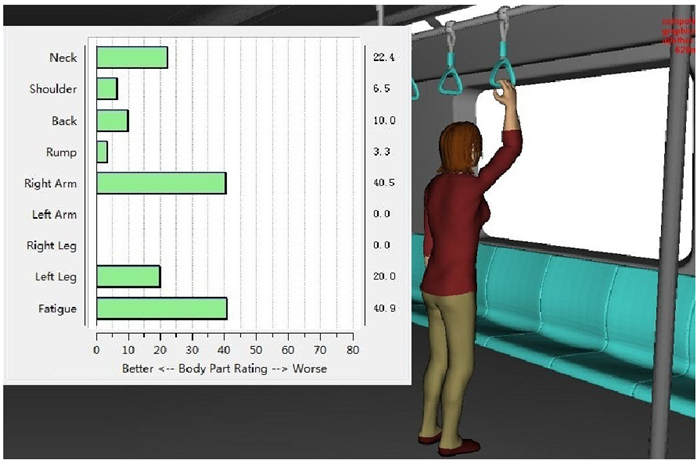
高度/mm 手臂夹角/(°) 手臂疲劳 整体疲劳 主观评价 1 510 57.0(14.2) 0.5(1.3) 36.9(1.7) 3.17(0.59) 1 610 75.2(23.1) 8.9(10.6) 35.5(5.2) 3.20(0.48) 1 680 90.5(26.6) 17.7(18.2) 35.4(3.2) 3.23(0.63) 1 710 105.1(42.2) 28.2(22.0) 35.9(7.1) 3.30(0.70) 1 760 118.9(42.8) 34.7(22.3) 38.1(11.8) 3.00(0.98) 1 810 132.2(43.9) 40.7(23.1) 40.5(14.6) 2.53(1.17) 1 860 144.3(45.7) 46.1(21.9) 45.1(12.2) 2.10(1.03) 1 990 152.0(35.9) 49.4(17.4) 47.2(9.2) 1.67(0.80) 2 020 167.6(30.4) 57.0(14.4) 51.3(8.0) 1.47(0.73) 2 160 180(0) 63.2(1.9) 54.6(0.1) 1.10(0.31) -
张庆贺, 朱合华, 庄荣.地铁与轻轨[M].北京:人民交通出版社, 2006:1-3. 赵江洪.人机工程学[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2006:7-9. SUZUKI H, SHIROTO H, NAKAGAWA C, et al. Development and utilization of ride comfort simulator[J]. Quarterly Report of Railway Technical Research Institute, 2006, 47(4):205-210. https://trid.trb.org/view/797612 王立国.地铁车辆内装设计关键技术研究[D].大连: 大连交通大学, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10150-2010047219.htm 魏伟.人机工程学原理在地铁与轻轨设计中的应用[D].武汉: 湖北美术学院, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10523-1012023998.htm BERKOVICH A, LU A, LEVINE B, et al. Observed customer seating and standing behavior and seat preferences on board subway cars in New York City[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2013, 2353(1):33-46. doi: 10.3141/2353-04 董石羽.中外地铁列车内空间设计比较研究探议[J].装饰, 2008, 178(2):125-127. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhuangshi200802043DONG Shiyu. A comparative study of chinese and foreign inner space design of subway train[J]. Art & Design, 2008, 178(2):125-127. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhuangshi200802043 蒋天容.基于乘坐体验的地铁车厢内部装饰设计研究[D].成都: 西南交通大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10613-1013250058.htm 常娜.地铁车厢内部环境设计与创新探析[J].艺术百家, 2013, 131(2):236-237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9104.2013.02.046CHANG Na. Design and innovation of interior environment of subway carriage[J]. Hundred Schools in Arts, 2013, 131(2):236-237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9104.2013.02.046 SUDA Y, MATSUOKA S, OGAWA T. A quantitative evaluation method of seat arrangement for commuter railway vehicles from the viewpoint of comfort and accessibility[J]. Japan Society of Mechanical Engineering International Journal, 1998, 41(4):929-937. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1998JSMEC..41..929S PARK S J, MIN S N, LEE H, et al. Express train seat discomfort evaluation using body pressure and anthropometric data[J]. Journal of the Ergonomics Society of Korea, 2014, 33(3):215-227. doi: 10.5143/JESK.2014.33.3.215 孙丽萍, 王立国.地铁车辆内装设计人机工程学分析[J].大连交通大学学报, 2010, 31(2):15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9590.2010.02.004SUN Liping, WANG Liguo. Ergonomics analysis of metro car interior decoration design[J]. Journal of Dalian Jiaotong University, 2010, 31(2):15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9590.2010.02.004 罗小燕.基于乘客感知需求的地铁座椅设计研究[D].成都: 西南交通大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10613-1014258381.htm KOBAYASHI T. Sexual differences in posture-related human behavior on subway trains, and their biological function[J]. Journal of Ethology, 1994, 12(2):121-130. doi: 10.1007/BF02350057 SARRAF T A, MARIGOLD D S, ROBINOVITCH S N. Maintaining standing balance by handrail grasping[J]. Gait & Posture, 2014, 39(1):258-264. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a9f15db36ecb1e78c61be1f5562d659c 北京市规划委员会. GB 50157-2013地铁设计规范[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2013. 全国汽车标准化技术委员会. QCT 633-2009客车座椅[S].北京: 中国计划出版社, 2010. 中华人民共和国铁道部. TB/T 3263-2011动车组乘客座椅[S].北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2011. 中华人民共和国铁道部. TB/T 3264-2011动车司机座椅[S].北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2011. 中国公路车辆机械总公司. GB 13094-2007客车结构安全要求[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007. 国家技术监督局. GB 10000-88中国成年人人体尺寸[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 1989. 国家技术监督局. GB/T12985-91在产品设计中应用人体尺寸百分位数的通则[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 1992. 徐明, 夏群生.体压分布的指标[J].中国机械工程, 1997, 8(1):65-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.1997.01.022XU Ming, XIA Qunsheng. The parameters of body pressure distribution on seat[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 1997, 8(1):65-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.1997.01.022 国家技术监督局. GB/T13547-92工作空间人体尺寸[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 1993. PORTER M J, GYI D E. Exploring the optimum posture for driver comfort[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 1998, 19(3):255-266. doi: 10.1504/IJVD.1998.062075 -





 下载:
下载: