Analysis of Track Irregularity Time-Frequency Characteristics Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition
-
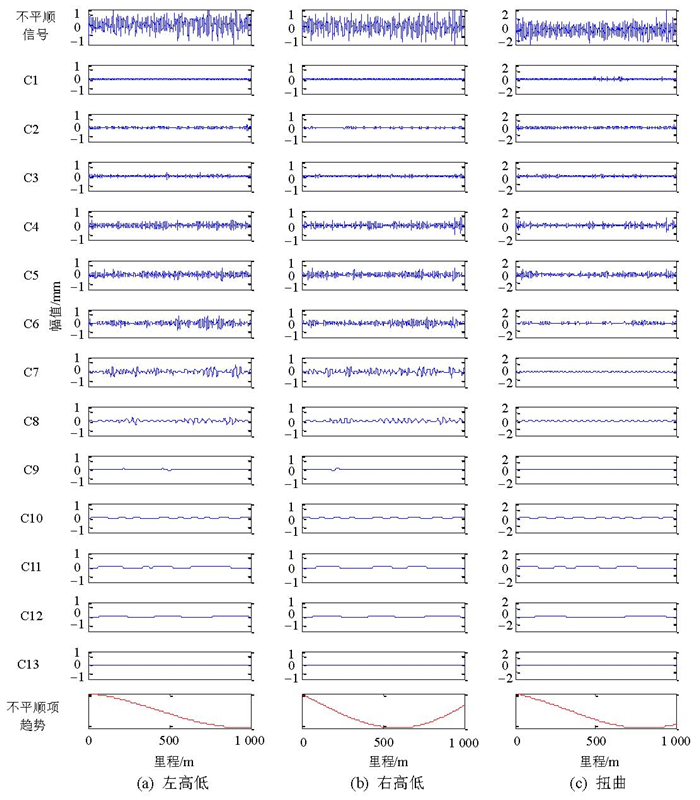
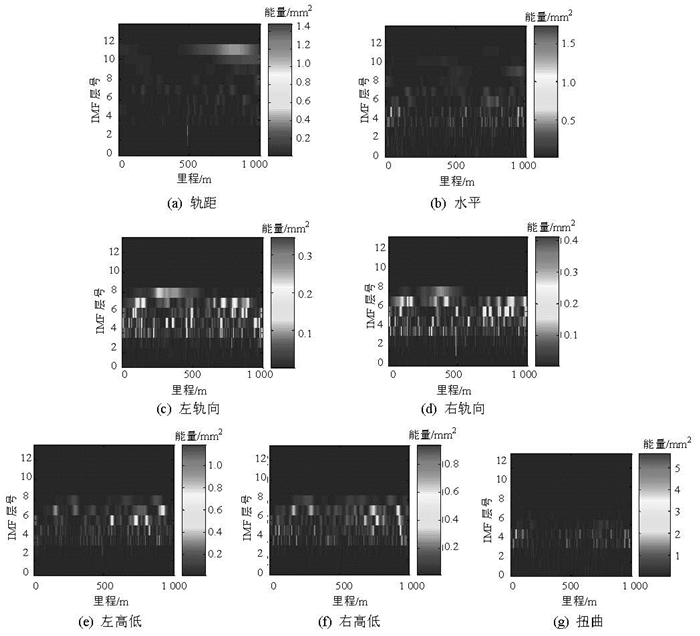
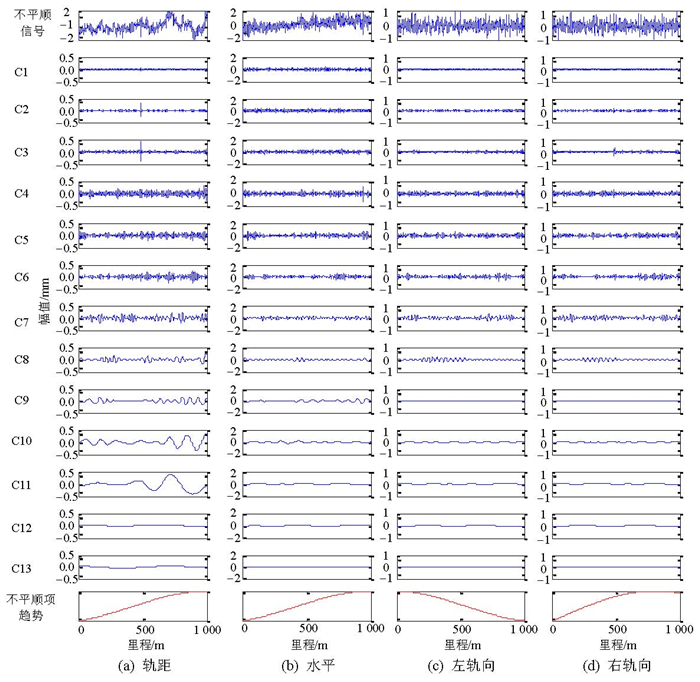
摘要: 高速铁路轨道不平顺测量值是由许多不同频率、不同幅值的单分量信号叠加而成的复杂随机过程.为分析轨道不平顺在空间域和频率域的分布特性,利用希尔伯特-黄变换方法提取轨道不平顺在时-频域的能量分布,为从幅值和波长两个方面综合评价轨道几何状态提供一种新的分析方法.首先,利用多元经验模态分解基于数据驱动的滤波特性,将轨道不平顺数据同时分解为不同尺度下的幅值-频率调制的多元本征模态函数;然后,通过希尔伯特变换计算各尺度下本征模态函数的瞬时频率,分析各层本征模态函数的频率和能量分布特征.通过对轨道检查车的实测轨道不平顺数据解算与分析表明:轨道不平顺的频率分布呈现出近似二进滤波特性,并且每个尺度下的频率带宽较窄;多元经验模态分解尺度图能确定轨道不平顺在各尺度下的能量分布及对应的波长特征;样本轨道不平顺数据中,轨距和水平不平顺的能量主要分布在中长波波段,轨向和高低的能量主要集中在空间波长4~36 m范围;扭曲的能量分布在波长为4.9 m和7.6 m的两个尺度内.Abstract: The measurement of high-speed railway track irregularities is a complex stochastic process, in which many single-component signals of different frequencies and amplitudes are present. In order to analyse the distribution characteristics of track irregularities in the spatial and frequency domains, the Hilbert-Huang transform was used to extract the energy distribution of track irregularity in the time-frequency domain. Track irregularity data was first decomposed into amplitude-frequency modulated multivariate intrinsic mode functions (IMF) at different scales, based on the data-driven filtering characteristics of multivariate empirical mode decomposition (MEMD). The instantaneous frequency of multivariate IMFs at each scale was then calculated by means of a Hilbert transform, from which the frequency and energy distribution characteristics were analysed. The analysis of the track inspection car indicates that the frequency distribution of track irregularities exhibits a characteristic of quasi-dyadic filter banks and that the frequency bandwidth is narrow at each scale. The energy distribution of the track irregularity and corresponding wavelengths can be determined from MEMD-based scalograms at different scales. In the sample track irregularity data, the energy of the gauge and cross level is mainly distributed in the medium and long wavelength frequencies. The energy of the alignment and profile is concentrated in the wavelengths between 4 and 36 m, and the energy of the twist is distributed in two wavelengths of 4.9 m and 7.6 m.
-
表 1 轨道不平顺各层IMF的平均频率和相对标准差
Table 1. Average frequency and relative standard deviation of IMFs of track irregularity
IMF
层号轨距 水平 左轨向 右轨向 左高低 右高低 扭曲 平均频率/m-1 相对标准差 平均频率/m-1 相对标准差 平均频率/m-1 相对标准差 平均频率/m-1 相对标准差 平均频率/m-1 相对标准差 平均频率/m-1 相对标准差 平均频率/m-1 相对标准差 C1 1.295 0 0.48 1.472 7 0.29 1.418 6 0.44 1.381 1 0.47 1.417 4 0.42 1.409 4 0.42 1.460 1 0.29 C2 0.629 4 0.23 0.763 0 0.20 0.745 6 0.17 0.721 8 0.19 0.715 8 0.18 0.718 5 0.18 0.770 1 0.20 C3 0.367 6 0.17 0.431 9 0.20 0.423 6 0.19 0.398 8 0.20 0.429 3 0.21 0.424 0 0.18 0.468 0 0.13 C4 0.251 7 0.15 0.226 8 0.21 0.235 7 0.20 0.237 1 0.17 0.222 3 0.16 0.219 3 0.16 0.201 7 0.17 C5 0.129 7 0.19 0.127 1 0.19 0.128 9 0.16 0.128 4 0.18 0.132 3 0.16 0.138 3 0.16 0.131 8 0.18 C6 0.073 2 0.17 0.071 5 0.14 0.072 2 0.15 0.070 1 0.16 0.071 0 0.15 0.070 2 0.16 0.074 8 0.15 C7 0.041 5 0.20 0.042 2 0.19 0.040 7 0.15 0.043 4 0.15 0.042 0 0.20 0.040 8 0.21 0.046 1 0.18 C8 0.026 4 0.17 0.027 1 0.11 0.028 4 0.08 0.028 0 0.08 0.027 8 0.10 0.028 3 0.13 0.028 1 0.13 C9 0.016 9 0.11 0.012 4 0.17 0.017 1 0.15 0.017 2 0.14 0.015 1 0.13 0.014 8 0.15 0.013 3 0.19 C10 0.007 6 0.16 0.008 2 0.20 0.008 3 0.26 0.008 8 0.22 0.008 7 0.24 0.009 5 0.17 0.008 6 0.15 C11 0.003 5 0.15 0.003 6 0.12 0.004 5 0.31 0.003 9 0.31 0.004 0 0.13 0.004 4 0.17 0.004 1 0.26 C12 0.002 2 0.18 0.002 3 0.12 0.002 4 0.13 0.002 3 0.11 0.002 9 0.09 0.002 8 0.12 0.002 2 0.22 C13 0.001 3 0.08 0.001 3 0.14 0.001 6 0.11 0.001 3 0.09 0.001 3 0.07 0.001 2 0.11 0.001 3 0.04 表 2 轨道不平顺各层IMF能量所占比例
Table 2. Energy percentage of IMFs of track irregularity
% IMF层号 轨距 水平 左轨向 右轨向 左高低 右高低 扭曲 C1 0.1 3.6 0.8 0.7 0.4 0.2 4.8 C2 0.3 5.2 1.8 1.6 1.3 0.7 5.5 C3 1.1 6.7 4.1 3.7 2.7 2.3 7.2 C4 5.5 19.0 15.2 15.2 12.8 15.0 30.1 C5 5.4 17.4 18.7 19.0 17.4 17.9 34.0 C6 6.5 13.5 20.1 22.1 27.8 23.5 12.7 C7 8.1 10.7 24.4 27.9 25.4 27.4 4.2 C8 5.2 6.0 14.3 9.2 10.9 11.7 0.9 C9 6.1 8.6 0.5 0.5 0.8 0.9 0.5 C10 19.1 5.1 0.2 0.1 0.3 0.3 0.1 C11 40.9 2.9 0.0 0.0 0.1 0.1 0.0 C12 0.7 0.8 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 C13 0.9 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 -
罗林, 张格明, 吴旺青, 等.轮轨系统轨道平顺状态的控制[M].北京:中国铁道出版社, 2006:97-105. 陈宪麦, 王澜, 陶夏新, 等.基于小波分析理论的轨道不平顺分析[J].铁道工程学报, 2008, 25(1):57-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2008.01.012CHEN Xianmai, WANG Lan, TAO Xiaxin, et al. Analysis of track irregularity with wavelets analysis theory[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2008, 25(1):57-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2008.01.012 张洁, 陈春俊, 林建辉.基于小波变换的轨道不平顺信号分析[J].西南交通大学学报, 2004, 39(4):469-471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2004.04.012ZHANG Jie, CHEN Chunjun, LIN Jianhui. Track irregularity analysis based on wavelet transform[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2004, 39(4):469-471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2004.04.012 徐磊, 陈宪麦, 徐伟昌, 等.基于小波和Wigner-Ville分布的轨道不平顺特征识别[J].中南大学学报:自然科学版2013, 44(8):3344-3350. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=SciencePaper201404040000013222XU Lei, CHEN Xianmai, XU Weichang, et al. Explored of track irregularity's characteristic identification based on wavelet method and Wigner-Ville distribution[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2013, 44(8):3344-3350. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=SciencePaper201404040000013222 徐磊, 陈宪麦.基于小波和Wigner-Hough变换的轨道特征不平顺联合分析[J].铁道学报, 2014, 36(5):88-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.05.015XU Lei, CHEN Xianmai. Analysis on track characteristic irregularity based on wavelet and Wigner-Hough transform[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2014, 36(5):88-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.05.015 刘彩云, 郭爱煌, 崔炳胜.高速铁路轨道不平顺的时频特征分析[J].电子测量技术, 2009, 32(7):29-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2009.07.008LIU Caiyun, GUO Aihuang, CUI Bingsheng. Time-frequency characteristic analysis of track irregularity of high-speed railway[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2009, 32(7):29-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2009.07.008 HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A, 1998, 454:903-995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 REHMAN N, MANDIC D P. Multivariate empirical mode decomposition[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A, 2010, 466:1291-1302. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2009.0502 REHMAN N, MANDIC D P. Filter bank property of multivariate empirical mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(5):2421-2426. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2106779 HUANG N E, WU Z H, LONG S R, et al. On instantaneous frequency[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(2):177-229. doi: 10.1142/S1793536909000096 FLANDRIN P, RILLING G, GONCALVES P. Empirical mode decomposition as a filter bank[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(2):112-114. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2003.821662 HUANG Y X, SCHMITT F G. Time dependent intrinsic correlation analysis of temperature and dissolved oxygen time series using empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2014, 130(2):90-100. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924796313001450 HUANG Y X, SCHMITT F G, LU Z, et al. Analysis of daily river flow fluctuations using empirical mode decomposition and arbitrary order Hilbert spectral analysis[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2009, 373(1/2):103-111. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=262554a5a4bca92c7f49ea6c3f3a588a HUANG G, SU Y, KAREEM A, et al. Time-frequency analysis of nonstationary process based on multivariate empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 142(1):04015065. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c6d2f29f9d949c791379dd026860eea7 -





 下载:
下载: