Effect of Thread Wear on Anti-Loosening Ability of Threaded Fastener under Vibration
-
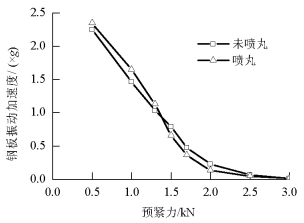
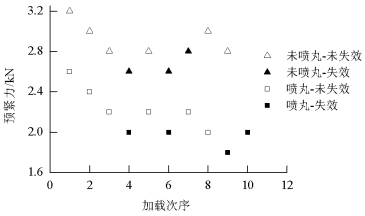
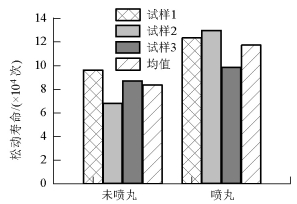
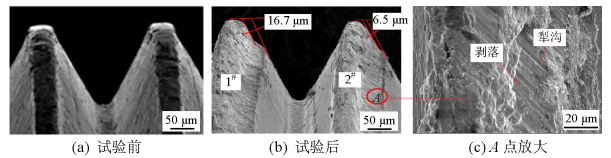
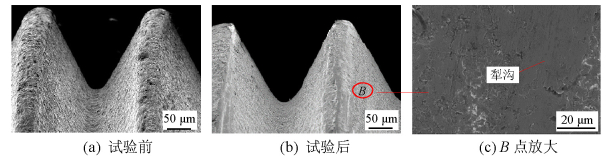
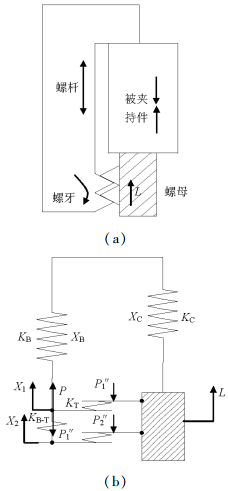
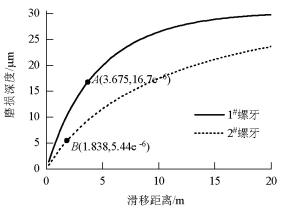
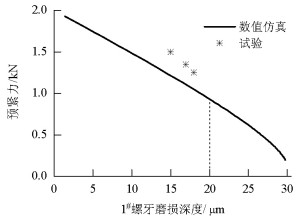
摘要: 为改善振动条件下螺纹紧固件抵抗松动能力,在紧固件横向振动试验装置上,测试了微粒子喷丸未处理及处理镀锌紧固件的抗松动能力,使用扫描电镜观察测量了试验前、后螺纹面磨损形貌和尺寸,建立了考虑螺纹面磨损深度的紧固件刚度模型,利用该模型计算分析了磨损深度改变对预紧力的影响.结果表明:未喷丸紧固件预紧力耐久极限为2.8 kN,喷丸紧固件为2.0 kN,未喷丸紧固件抗松动能力低于喷丸紧固件,未喷丸紧固件螺纹面发生严重磨损,喷丸紧固件螺纹面磨损轻微;螺纹面磨损深度随着滑移距离的增加而增加,紧固件预紧力随着螺纹面磨损深度的增加先呈线性降低,随后降低速度逐渐加快.螺纹面磨损降低了紧固件抵抗松动的能力.Abstract: In order to improve the anti-loosening ability of threaded fasteners under vibration, the anti-loosening abilities of the electro-zinc-plated fastener (EZP) and the electro-zinc-plated fastener treated by fine particle peening (FPP-EZP) were evaluated using a fastener transverse vibration apparatus. The surface damage and worn dimensions of the thread before and after testing were observed and measured using scanning electron microscopy. Then, a fastener stiffness model considering thread wear depth was used for numerical simulation of the effect of the wear depth on the threaded fastener preload. The test results show that the preload endurance limits of the EZP and FPP-EZP are respectively 2.8 kN and 2.0 kN, this suggests that the anti-loosening ability of the EZP is lower than that of the FPP-EZP. The observation results show severe damage on the thread surface for EZP, but no distinct damage on the FPP-EZP threads. The numerical simulation shows that the thread wear depth increases with the increase of the relative sliding distance between threads. Furthermore, the preload initially decreases nearly linearly with the increase in thread depth, and then rapidly. The thread wear can reduce the anti-loosening ability of threaded fasteners.
-
Key words:
- threaded fastener /
- wear /
- loosening /
- fine particle peening /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 试验紧固件材料力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of the test fastener material
名称 维氏硬度HV0.2 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 内部 表面 EZP 187.8 186.4 245 410 FPP-EZP 180.1 240.1 245 410 表 2 喷丸处理工艺参数
Table 2. Treatment parameters of fine particle peening
丸粒材质 筛号 喷射压强/MPa 喷射距离/cm 覆盖率/% 高速工具钢 300# 0.6 10 200 -
JUNKER G H. Criteria for self loosening of fasteners under vibration[J]. Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology, 1972, 44(10):14-16. doi: 10.1108/eb034949 PAI N G, HESS D P. Experimental study of loosening of threaded fasteners due to dynamic shear loads[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 2002, 253:585-602. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f0741b07704dd0e3cce99b9e5924c9b7 YAMAMOTO A, KASEI S, KUBO T. Investigations on the self-loosening of threaded fasteners under transverse vibration[J]. Journal of the Japan Society of Precision Engineering, 1977, 43:1069-1074. doi: 10.2493/jjspe1933.43.1069 JIANG Y, ZHANG M, PARK T W, et al. An experimental investigation on self-loosening of bolted joints[J] Journal of Mechanical Design, 2004, 126(5):925-931. doi: 10.1115/1.1767814 ARCHARD J F. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1953, 24:981-988. doi: 10.1063/1.1721448 ARCHARD J F. Single contacts and multiple encounters[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1961, 32:1420-1425. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=34ffadbe4772b54f63d4acaa1dba4888&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Sakai. Investigations of bolt loosening mechanisms[J]. Bulletin of the JSME 21, 1978(159):1391-1394. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3578b89142d5bc30838b357d76ddf49b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn 侯世远, 廖日东.螺纹连接松动过程的研究现状与发展趋势[J].强度与环境, 2014, 41(2):39-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3919.2014.02.007HOU Shiyuan, LIAO Ridong. Research progress on self-loosening of threaded fasteners[J]. Structure & Environment Engineering, 2014, 41(2):39-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3919.2014.02.007 于泽通, 刘建华, 张朝前, 等.轴向交变载荷作用下螺栓联接结构的松动试验研究[J].摩擦学学报, 2015, 35(6):732-736. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mcxxb201506012YU Zetong, LIU Jianhua, ZHANG Chaoqian, et al. An experimental study on self-loosening of bolted joints under axial vibration[J]. Tribology, 2015, 35(6):732-736. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mcxxb201506012 KIKUCHI S, SASAGO A, KOMOTORI J. Effect of simultaneous surface modification process on wear resistance of martensitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(20):6156-6160. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2009.04.024 BLANCHET T A. Coupled evolution of load distribution and wear on grease-lubricated lead screw threads[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2006, 49(4):502-512. doi: 10.1080/10402000600846060 CROCCOLO D, AGOSTINIS M D, VINCENZI N. Failure analysis of bolted joints:Effect of friction coefficients in torque-preloading relationship[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2011, 18(1):364-373. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2010.09.015 陈维金.德国与我国机车车辆用螺栓技术的对比分析[J].铁道技术监督, 2011, 39(4):2-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9178.2011.04.002CHEN Weijin. Comparative analysis of the bolt technology using locomotive of China and Germany[J]. Railway Quality Control, 2011, 39(4):2-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9178.2011.04.002 CHEN J J, SHIH Y S. A study of the helical effect on the thread connection by three dimensional finite element analysis[J]. Nuclear Engineering & Design, 1999, 191(2):109-116. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f1da7bf7486f1c3524962ec8e283acb6 -





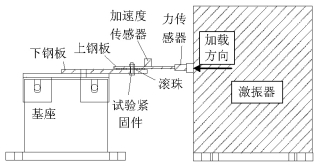
 下载:
下载: