|
吴吉春, 陆乐.地下水模拟不确定性分析[J].南京大学学报:自然科学, 2011, 47(3):227-234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1859981WU Jichun, LU Le. Uncertainty analysis for groundwater modeling[J]. Journal of Nanjing University:Natural Sciences, 2011, 47(3):227-234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1859981
|
|
陆乐, 吴吉春, 陈景雅.基于贝叶斯方法的水文地质参数识别[J].水文地质工程地质, 2008(5):58-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2008.05.014LU Le, WU Jichun, CHEN Jingya. Identification of hydrogeological parameters based on the Bayesian method[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2008(5):58-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2008.05.014
|
|
BEVEN K, BINLEY A. The future of distributed models-model calibration and uncertainty prediction[J]. Hydrological Processes, 1992, 6(3):279-98. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1085
|
|
BEVEN K, FREER J. Equifinality, data assimilation, and uncertainty estimation in mechanistic modelling of complex environmental systems using the GLUE methodology[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2001, 249(1):11-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=990d8ae736d1912750863bbda2673049
|
|
HASSAN A E, BEKHIT H M, CHAPMAN J B. Using Markov Chain Monte Carlo to quantify parameter uncertainty and its effect on predictions of a groundwater flow model[J]. Environmental Moddelling & Software, 2009, 24(6):749-63. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a3ba178c48b0d63b420a771a6e1d6fd2
|
|
ROJAS R, KAHUNDE S, PETERS L, et al. Application of a multimodel approach to account for conceptual model and scenario uncertainties in groundwater modelling[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2010, 394(3):416-35. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7b3427f235876bd3c2cda5424e4a8601
|
|
BLASONE R S, VRUGT J A, MADSEN H, et al. Generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation(GLUE) using adaptive Markov Chain Monte Carlo sampling[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2008, 31(4):630-48. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2007.12.003
|
|
KUCZERA G, PARENT E. Monte Carlo assessment of parameter uncertainty in conceptual catchment models:the metropolis algorithm[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1998, 211(1):69-85. doi: 10.1016-S0022-1694(98)00198-X/
|
|
ROJAS R, FEYEN L, BATCLAAN O, et al. On the value of conditioning data to reduce conceptual model uncertainty in groundwater modeling[J]. Water Resources Research, 2010, 46:W08520-1-W08520-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e1552687227b55f831858d44c13751d7
|
|
刑贞相, 芮孝芳, 崔海燕, 等.基于AM-MCMC算法的贝叶斯概率洪水预报模型[J].水利学报, 2007, 38(12):1500-1506. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2007.12.014XING Zhenxiang, RUI Xiaofang, CUI Haiyan, et al. Bayesian probabilistic flood forecasting model based on adaptive metropolis-MCMC algorithm[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 38(12):1500-1506. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2007.12.014
|
|
ROJAS R, FEYEN L, DASSARGUES A. Conceptual model uncertainty in groundwater modeling:Combining generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation and Bayesian model averaging[J]. Water Resources Research, 2008, 44:12418. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ027477747/
|
|
NEUMAN S P. Maximum likelihood Bayesian averaging of uncertain model predictions[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2003, 17(5):291-305. doi: 10.1007/s00477-003-0151-7
|
|
YE M, NEUMAN S P, MEYER P D. Maximum likelihood Bayesian averaging of spatial variability models in unsaturated fractured tuff[J]. Water Resources Research, 2004, 40:W05113-1-W05113-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4eb4da517a2a77101e0cbc15f40c48de
|
|
曾献奎, 王栋, 吴吉春.地下水流概念模型的不确定性分析[J].南京大学学报:自然科学, 2012, 48(6):746-752. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njdxxb201206008ZENG Xiankui, WANG Dong, WU Jichun. Uncertainty analysis of groundwater flow conceptual model[J]. Journal of Nanjing University:Natural Sciences, 2012, 48(6):746-753. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njdxxb201206008
|
|
NEUMAN S P. Maximum likelihood Bayesian averaging of alternative conceptual mathematical models[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2003, 17(5):291-305. doi: 10.1007/s00477-003-0151-7
|
|
REFSGAARD J C, SLUIJS J P V D, BROWN J, et al. A framework for dealing with uncertainty due to model structure error[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2006, 29:1586-1597. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.11.013
|
|
GILKS W R, RICHARDSON S, SPIEGELHALTER D J. Markov chain monte carlo in practice[M]. London:Chapman & Hall, 1996:112-119.
|
|
HAARIO H, SAKSMAN E, TAMMINEN J. An adaptive metropolis algorithm[J]. Bernoulli, 2001, 7(2):223-242. doi: 10.2307/3318737
|
|
HAARIO H, SAKSMAN E, TANMIINEN J. Componentwise adaptation for high dimensional MCMC[J]. Computational Statistics, 2005, 20(2):265-273. doi: 10.1007/BF02789703
|
|
GEHNAN A, CARLIN J B, STREN H.S, et al. Bayesian data analysis[M]. London:Chapmann and Hall, 1995:142-151.
|
|
BURNHAM K P, ANDERSON D R. Model selection and multi-model inference:a practical information-theoretic approach[M]. New York:Springer-Verlag, 2002:163-177.
|
|
POETER E P, ANDERSON D. Multi-model ranking and inference in groundwater modeling[J]. Ground Water, 2005, 43(4):597-605. doi: 10.1111/gwat.2005.43.issue-4
|
|
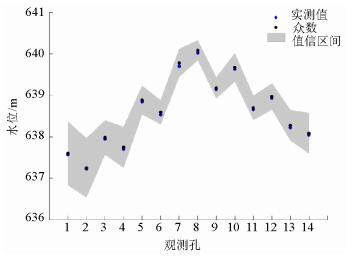
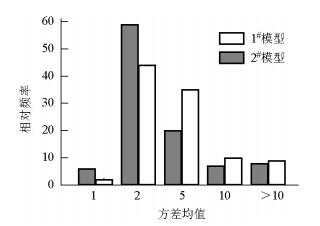
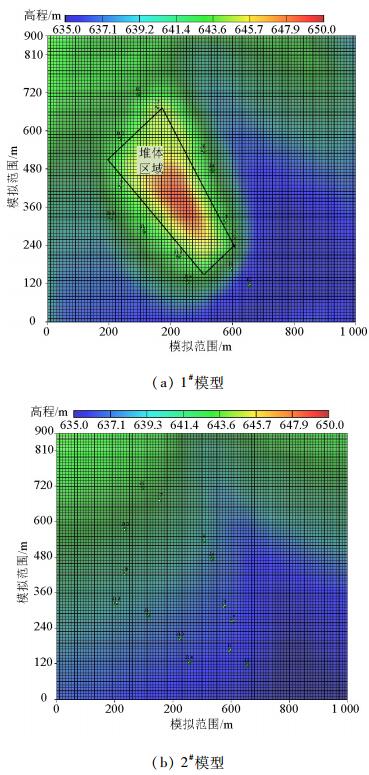
夏强.地下水不确定性问题的多模型分析方法及应用[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1011077537.htm
|
|
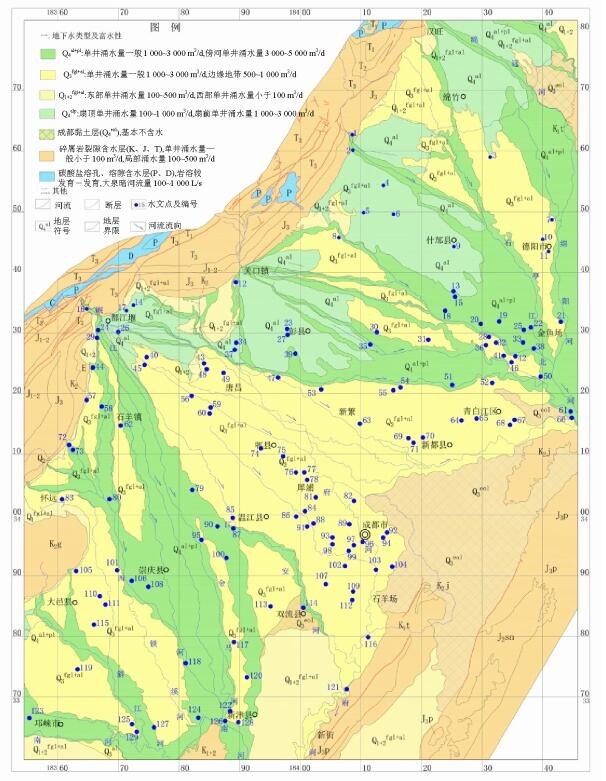
四川省地质局.成都幅水文地质报告[R].成都: 四川省地质局, 1977.
|
|
四川省地质局.都江堰幅水文地质报告[R].成都: 四川省地质局, 1977.
|
|
四川省地质矿产局.成都平原水文地质工程地质综合勘察评价报告[R].成都: 四川省地质矿产局, 1985.
|





 下载:
下载: