Stochastic Analysis of Effective Moment of Inertia of Cracked In-Service Reinforced Concrete Beams
-
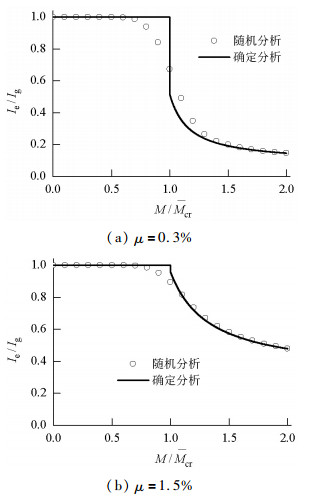
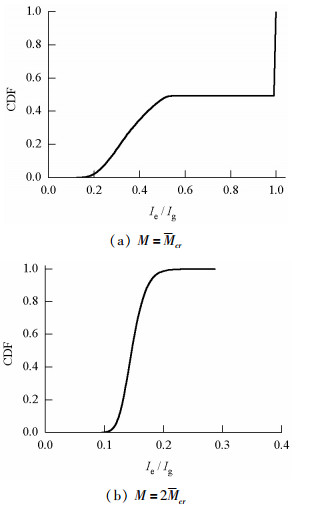
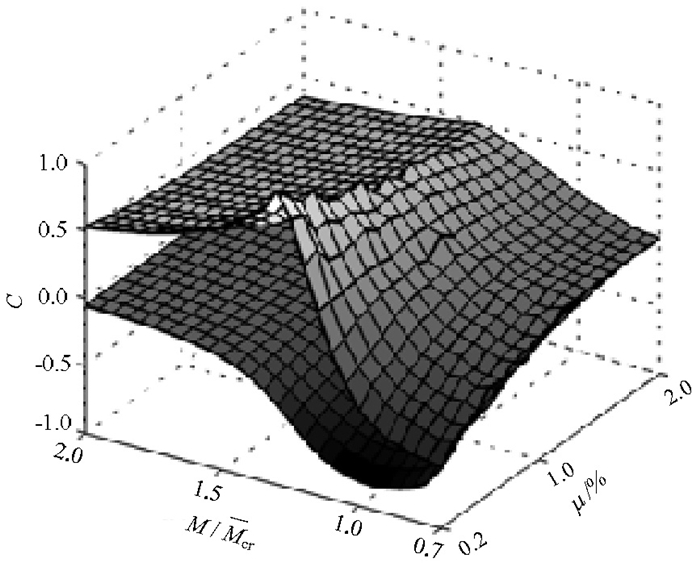
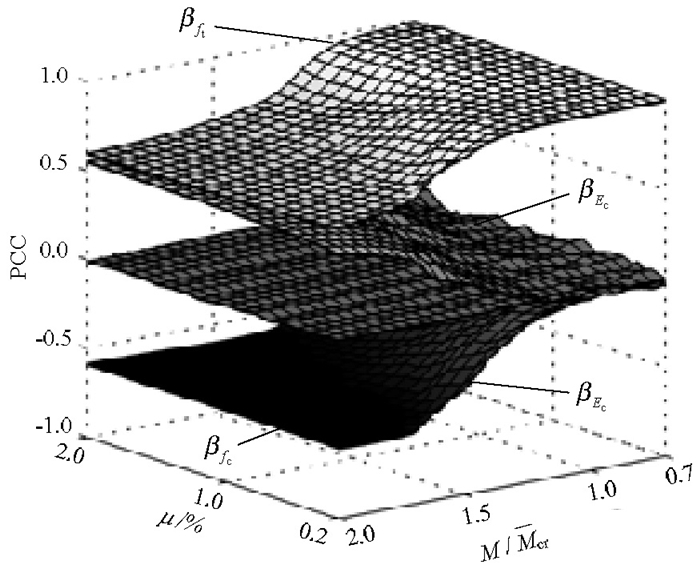
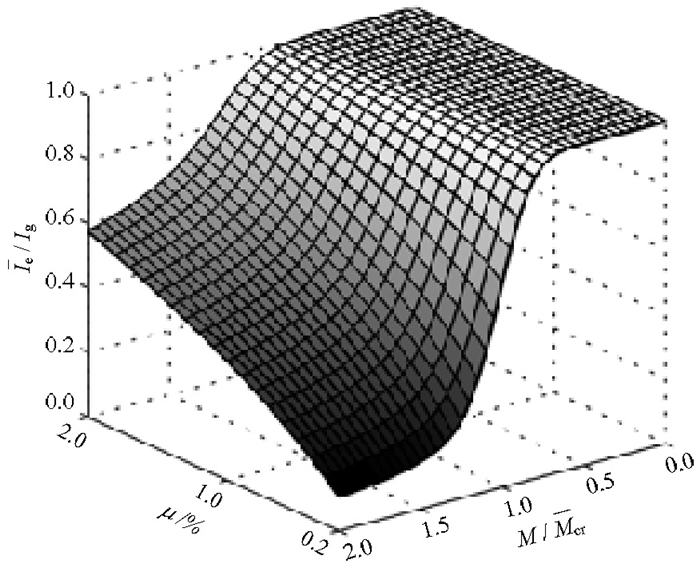
摘要: 由于混凝土材料的不确定性和非线性特性,开裂钢筋混凝土梁的有效惯性矩很难准确地预测,往往影响了对结构正常使用极限状态的准确估计.按我国规范,推导了在正常使用极限状态范围内,钢筋混凝土梁的有效惯性矩无量纲表达,并利用蒙特卡洛抽样进行了随机分析;对应不同的配筋率,研究了有效惯性矩随机分析和确定性分之间的差异及其产生的机理,利用偏相关系数表达各随机变量与有效惯性矩之间的敏感性.分析结果表明:由于混凝土的开裂非线性,采用模型参数的均值进行确定分析的结果与采用模型随机参数进行随机分析结果的均值不一致,这种不一致是由混凝土截面开裂发生的随机性与开裂前后刚度的差异共同引起;通过随机分析结果回归,给出了钢筋混凝土梁有效惯性矩的预测均值与95%保证率的预测范围列表;混凝土抗压强度对有效惯性矩几乎没有影响,而混凝土抗拉强度的敏感性最大.Abstract: For cracked reinforced concrete structures in working service life, calculation of the stiffness of the cracked reinforced concrete beam is important for the serviceability design of reinforced concrete structures. However, owing to the uncertainty and nonlinearity of concrete, it is difficult to precisely predict the effective moment of inertia of cracked concrete beams. In this study, the dimensionless equation for the effective moment of inertia recommended in specification GB50010-2010 for in-service reinforced concrete beams was derived, and a Monte Carlo method was employed to analyse its stochastic properties. The dimensionless effective moment of inertia was calculated using both a stochastic analysis with random variables and a deterministic analysis with mean values of the parameters. The results indicate that the mean values obtained with the stochastic analysis are not in agreement with those calculated with the deterministic analysis owing to the cracking nonlinearity of concrete. In addition, through regression of the stochastic analysis results, mean values of the effective moment of inertia are estimated at the 95% confidence interval. Finally, a sensitivity coefficient reflecting the correlation between each random variable and the effective moment of inertia was calculated using a partial correlation coefficient. The results demonstrate that the tensile strength of concrete is the most sensitive variable, while the compressive strength of concrete has nearly no effect on the effective moment of inertia.
-
随着我国高速铁路的迅猛发展,轮轨间动作用力不断增大,车轮多边形磨耗问题日益突出. 对2013年以前运营的数百个车轮进行了非圆化磨耗测试,统计结果显示,96%的车轮发生了偏心磨损,其次是低阶谐波磨损. 近些年来(主要指2014 年以后),高速列车车轮普遍出现了高阶多边形磨损,而车轮因多边形引起的轮轨冲击力达到车轮静载荷的1倍~3倍,轴箱加速度达到20g~40g[1]. 金学松等[1-3]通过长期的现场跟踪测试提出了我国最早发现的直线电机地铁车轮9边形磨耗的机理是轮对一阶弯曲振动所致,也正在通过测试给出多边形的一些机理解释. Morys[4]将车轮和制动盘视为三维旋转弹簧-阻尼单元连接的刚体,构建了车辆-轨道动力学模型,结合轮对长期磨耗模型研究了车轮多边形的发展规律发现,多边形磨耗的发展过程很大程度上取决于轨道特征和激励频率. Meywerk[5]建立单个轮对-轨道动力学模型,研究了轮对柔性和轨道弹性对车轮多边形磨耗的影响. Johansson等[6]基于滚动接触理论,建立三维车辆-轨道动力学模型,研究认为车轮多边形磨耗与车辆/轨道耦合系统的垂直共振有关. Wu等[7-8]研究认为同一转向架两轮对之间钢轨的3阶弯曲振动是导致车轮高阶多边形磨耗的主要因素,然而在运行中能否被激发还有待验证. Meinke等[9]提出高速轮对不同于普速轮对,其动力学是由陀螺力矩和惯性力矩决定的,研究了静、动不平衡对车轮多边形磨耗的影响. 胡晓依等[10]将车辆/轨道耦合动力学模型与Archard磨耗模型相结合,建立长期磨损迭代模型模拟运行时车轮多边形的整个发展历程. 宋志坤等[11]通过对比分析车轮粗糙度对车轮多边形的影响发现,提高镟修质量可以减缓多边形的增长速度.
上述研究主要是从现场跟踪或是车辆-轨道大系统动力学仿真入手,获得了一些可以解释车轮多边形现象的原因. 对于高速动车组车轮高阶多边形磨耗的成因,业界提出其受多重因素影响,很难给出统一的解释. 而现场目前不得不采用的方式是镟轮,这不仅缩短了车轮的使用寿命,也不符合低碳减排的国家要求. 所以研究车轮多边形磨耗形成和发展机理,明确其主要影响因素,是当前车轮多边形磨耗问题研究的重点. 为此,本文基于转子动力学理论建立轮轨动力学模型,结合磨耗模型研究多边形磨耗的发生和演化.
1. 车轮多边形磨耗发生与演化模型
1.1 轮对-轨道转子系统动力学模型
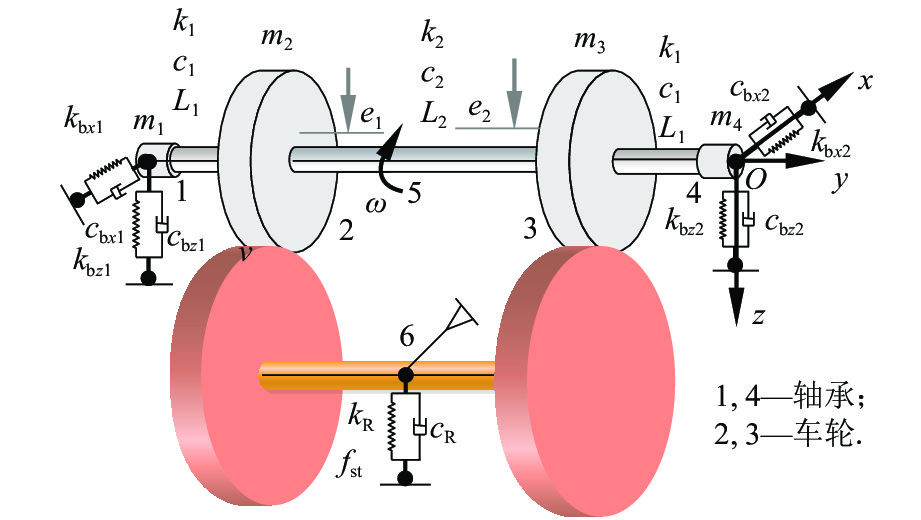
研究表明,轮对蠕滑是车轮多边形磨耗发生和发展的主要原因[12]. 轨道车辆结构庞大,自由度较多,其非线性因素复杂,通常根据研究需要对重点关注点精细建模,对于其他部分做适当简化. 因此,本文选取自由度较少的轮对轴箱装置为研究对象,如图1所示,将其简化为轮对-轨道转子系统,其中包括轴承、车轮、车轴及模拟轨道的两个大直径圆盘. 图1中:m1、m4分别为左、右轴箱质量;m2、m3分别为左、右车轮的质量;e1、e2分别为左右车轮的偏心量;kbx1、kbx2(kbz1、kbz2)分别为左、右轴承的纵向(垂向)刚度;cbx1、cbx2(cbz1、cbz2)分别为左、右轴承的纵向(垂向)的阻尼;k1、c1、L1分别为左、右轴段的刚度、阻尼和长度;k2、c2、L2分别为中间轴段的刚度、阻尼和长度; kR、cR、fst分别为扣件的刚度、阻尼和预压缩量; ω 为圆盘绕 O1自转的角速度.
为了分析转子的基本特征,假设:
1) 车轮为刚性圆盘;
2) 车轴为等直圆轴,具有一定的弯曲刚度和无限大的扭转刚度,两端相同的轴箱弹性支承;
3) 将簧上质量等效为轨道预压力,忽略轮轨接触斑处相对变形,假设轮轨一体支撑在扣件上.
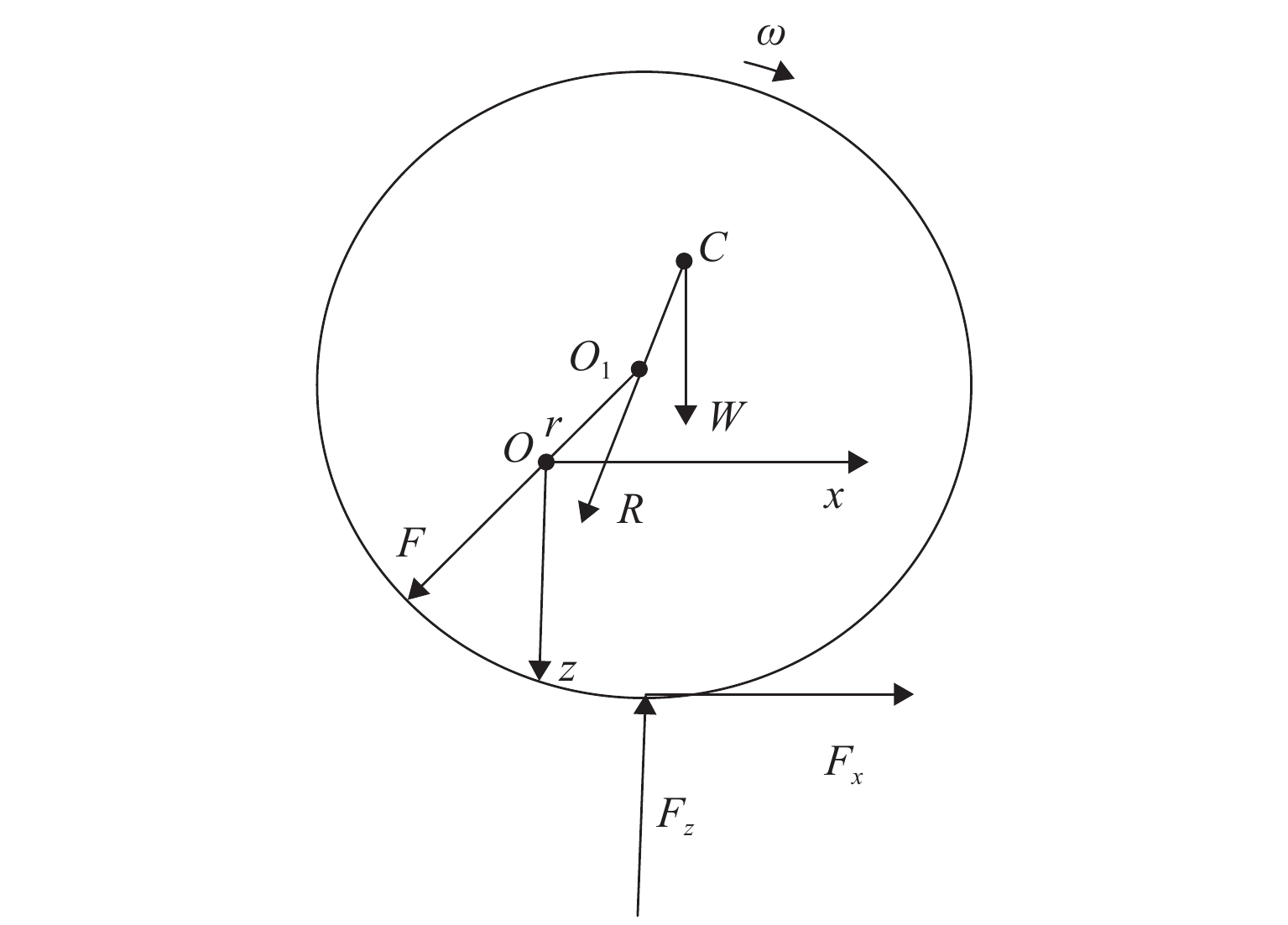
取O-xyz为固定坐标系,圆盘所在平面与弹性轴两端支承点连线的交点O为固定坐标系原点,y轴沿转子轴线,圆盘所在平面为xOz坐标参考平面. 圆盘瞬时位置和受力情况见图2,图中:O1为圆盘形心,C为圆盘质心,两者之间的距离O1C,即偏心量e;r为动挠度;F为轴的弹性恢复力;R为黏性阻尼力;W为重力;Fx和Fz分别为轮轨接触纵向蠕滑力和法向力. 选取(x(t),z(t))为圆盘形心O1广义坐标;t为时间.
1.2 轮轨滚动接触力模型
围绕轮轨滚动接触问题的求解,研究发展了许多理论模型,较著名的理论有Carter 理论、Kalker理论、沈氏理论等,其中Kalker 简化理论在铁路领域应用最广泛 [13]. 蠕滑力除了与蠕滑率有关以外还与接触区的形状、表面润滑状态、正压力的分布等有关. Kalker公式[14-15]为
{Fx=−GabC11γx,Fy=−GabC22γy−G(ab)3/2C23ξz, (1) 式中:Fy为横向蠕滑力;a、b分别为接触椭圆的长、短半轴长;G为剪切模量;C11、C22 、C23为蠕滑系数;γx、 γy、 ξz分别为纵向、横向和自旋蠕滑率.
根据接触椭圆偏心率及第一、二类完整椭圆积分可确定出接触斑长、短半轴长度[13]分别为
{a=mc(3π(δ1+δ2)2βFz)1/3,b=nc(3π(δ1+δ2)2βFz)1/3, (2) {mc=(2Epπ(1−e2c))1/3,nc=(2Ep√1−e2cπ)1/3,δi=1−υi2πEi,i=1,2,β=1/R11+1/R12+1/R21+1/R22, (3) 式中:Ep为第二类完整椭圆积分;ec为接触椭圆偏心率;υ1、υ2分别为接触体1、2的泊松比;E1、E2分别为接触体1、2的弹性模量;R11、R12和R21、R22分别为车轮和钢轨沿接触坐标系纵、横向的主曲率半径.
合成的蠕滑力Frr为
Frr=(F2x+F2y)12. (4) 修正蠕滑力Fr为
Fr={μFz[(FrrμFz)−13(FrrμFz)2+127(FrrμFz)3],Frr⩽3μFz,μFz,Frr>3μFz, (5) 式中:μ为摩擦系数;
${F_{\textit{z}}} = - {k_{\rm{R}}}({f_{{\rm{st}}}} + {\textit{z}})$ .1.3 轮对转子系统的动力学方程
参照多跨不平衡轴系的非线性动力学建模方法[16],结合拉格朗日方程建立轮对-轨道转子系统的动力学方程,如式(6).
{m1¨x1+c1˙x1+k1x1−k1x2=Fbx1,m1¨z1+c1˙z1+k1z1−k1z2=Fbz1−m1g,m2¨x2+c2˙x2−k1x1+(k1+k2)x2−k2x3=m2e1ω2cosωt+Fx1,m2¨z2+c2˙z2−k1z1+(k1+k2)z2−k2z3=m2e1ω2sinωt−m2g+Fz1,m3¨x3+c3˙x3−k2x2+(k1+k2)x3−k1x4=m3e2ω2cosωt+Fx2,m3¨z3+c3˙z3−k2z2+(k1+k2)z3−k1z4=m4e2ω2sinωt−m3g+Fz2,m4¨x4+c4˙x4+k1x4−k1x3=Fbx2,m4¨z4+c4˙z4+k1z4−k1z3=Fbz2−m4g. (6) 表示成矩阵形式为
M¨u+C˙u+Ku=Fb+Fe+Fr+Fg, (7) 式中:M、C、K、Fb、Fe、Fr和Fg分别为转子系统的质量矩阵、阻尼矩阵、刚度矩阵、轴承力向量、不平衡力向量、轮轨接触力向量和重力向量;
$ \ddot{{\boldsymbol{u}}}、\dot{{\boldsymbol{u}}}、{\boldsymbol{u}} $ 分别为模型中质点的加速度向量、速度向量和位移向量.车轴各轴段的刚度如式(8).
ki=12EaiIiL3i, (8) 式中:Eai为车轴材料的弹性模量;Ii为车轴截面惯性矩,如式(9),daoi和daii为第i轴段的车轴外径和内径;Li为轴段长度.
Ii=π64(d4aoi−d4aii). (9) 1.4 车轮圆周磨耗深度模型
在车轮多边形磨耗预测中,通常采用的材料磨耗模型有Archard 模型和磨耗功模型. 研究表明,两者对应的车轮多边形演变趋势基本相同,但后者所得结果与现场实测数据更为接近,且计算效率较高[17],因此本文采用磨耗功模型,如式(10).
Δm=KwWw, (10) 式中:Δm为磨耗质量;Kw为磨耗功系数;Ww为接触斑内的磨耗功.
假设车轮在磨耗过程中钢轨平顺,横向磨耗均匀,仅考虑周向失圆. 结合式(10)推导可得,车轮圆周磨耗深度Δr为
Δr=R(θ−2π)−R(θ)=ΔmρAw=KwWwρAw=KwFxswρbwsw=KwFxρbw, (11) 式中:R(θ−2
π)为车轮滚动圆前一次磨耗后的半径,θ为车轮滚动圆的圆周某处对应的角度;R(θ)为后一次磨耗后的半径;Aw为磨耗面积;ρ为材料密度;sw为轮轨相对滑动距离;bw为磨耗区的平均宽度. 由式(11)可见,车轮磨耗与纵向蠕滑力有关,当纵向蠕滑力按照一定的频率周期性变化时,导致磨耗深度周期性变化,多边形磨耗纵向蠕滑力最大时,将出现磨耗峰值,且在车轮纵向振动的一个周期内只出现一次. 设车轮纵向振动频率为fx ,则相邻两个磨耗峰值的时间间隔为1/ fx ,轮对转频为 f2,则车轮转动周期为1/ f2. 可得车轮转动一圈内出现的磨耗峰值数(阶次)n为
n=fxf2. (12) 轮对转频 f2与列车运行速度v的关系为
$ {f_{\text{2}}} = v/({\text{π}} D) $ ,其中,D为车轮名义直径. 代入式(12)可知,车轮纵向振动频率为fx=nvπD. (13) 2. 多边形磨耗仿真分析
选取某型高速动车组轮对参数:车轴内径为30 mm,车轴外径为190 mm,轴颈中心距为1956 mm,滚动圆间距为1493 mm,寿命周期内车轮直径Dw=920~830 mm,ρ=7850 kg/m3,E1=E2=2.06 × 1011 Pa,v1=v2=0.3,e=0.1 mm,kR=20 MN/m,(轴承刚度)kb= 1×1010 N/m,μ = 0.25,v=300 km/h.
2.1 车轮多边形磨耗特征
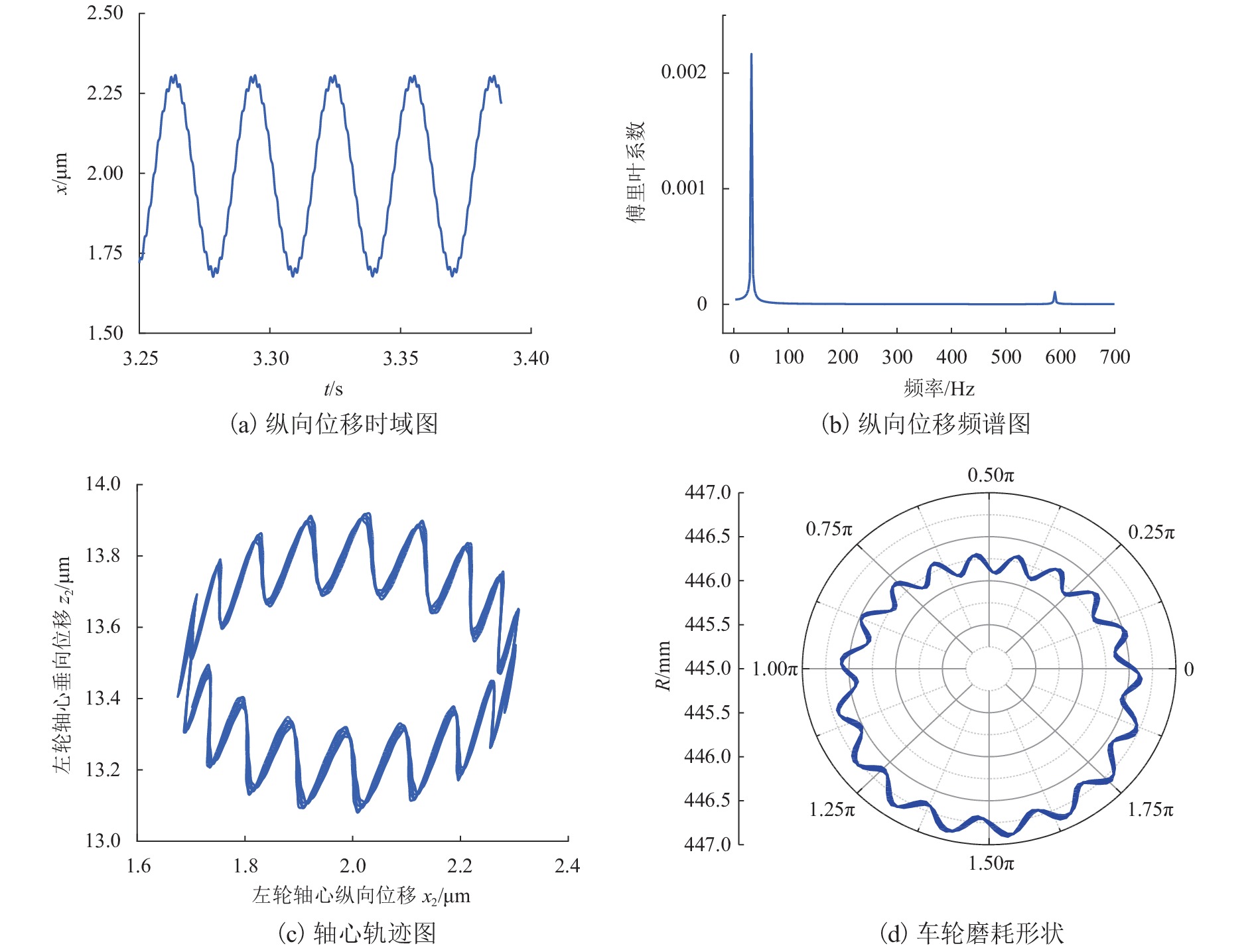
分析e=0.1 mm、v=300 km/h、Dw=920 mm时,左侧车轮的纵向振动位移时域图和频域图、轴心轨迹及车轮圆周磨耗图以表征车轮的振动特征和磨耗特征,如图3.
由图3(a)、(b)可见:纵向振动位移为含有两种频率成分的周期信号,其低频频率等于轮对转频,高频频率接近于600 Hz,频谱图可以有效表征轮对-轨道转子系统的振动特征. 由图3(c)、(d)可见:轴心轨迹呈波浪状椭圆,车轮圆周磨耗形状为偏心多阶多边形;车轮多边形磨耗与轮对纵向周期振动有关,车轮磨耗形状图可有效表征车轮多边形的磨耗特征.
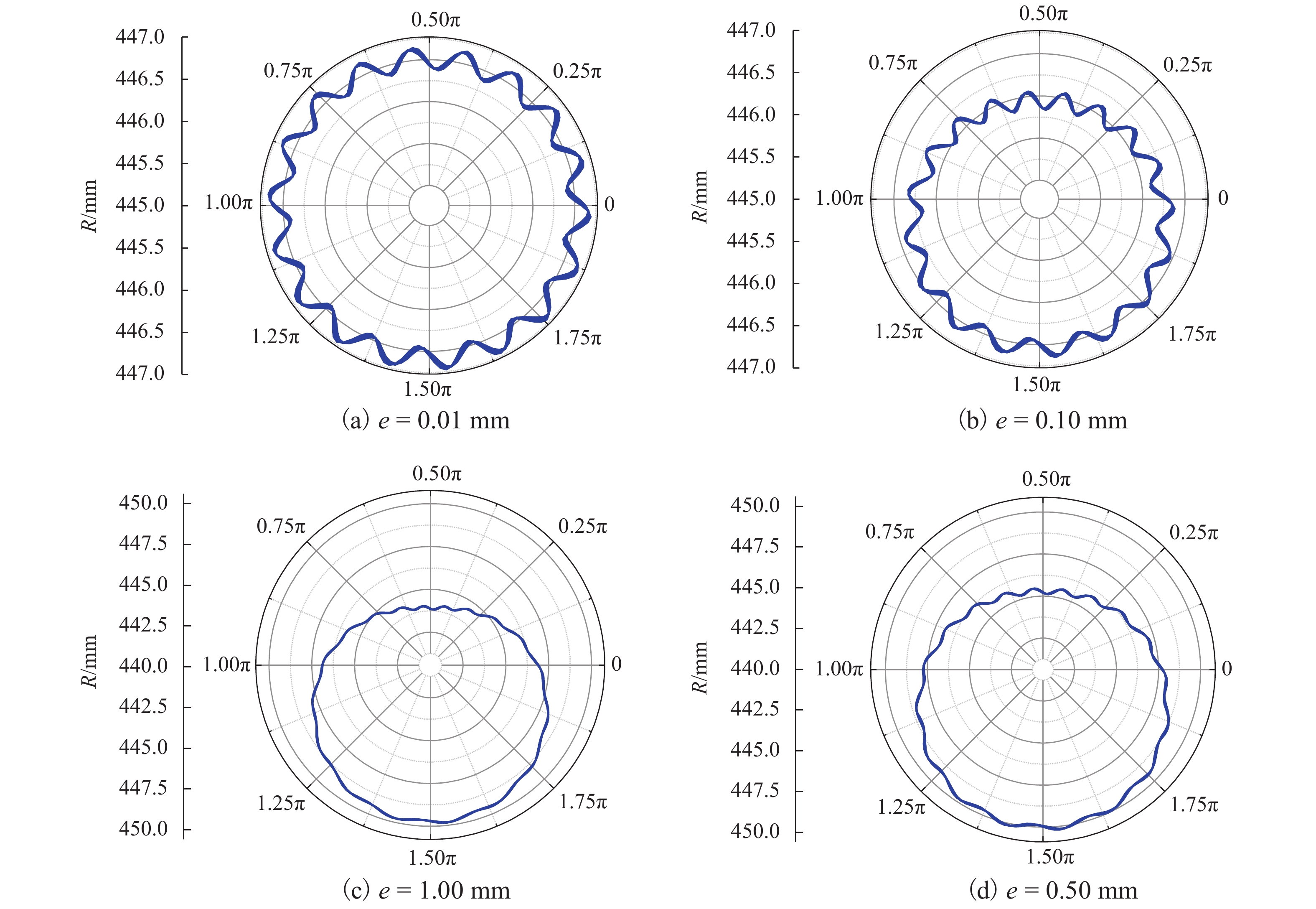
2.2 偏心量的影响
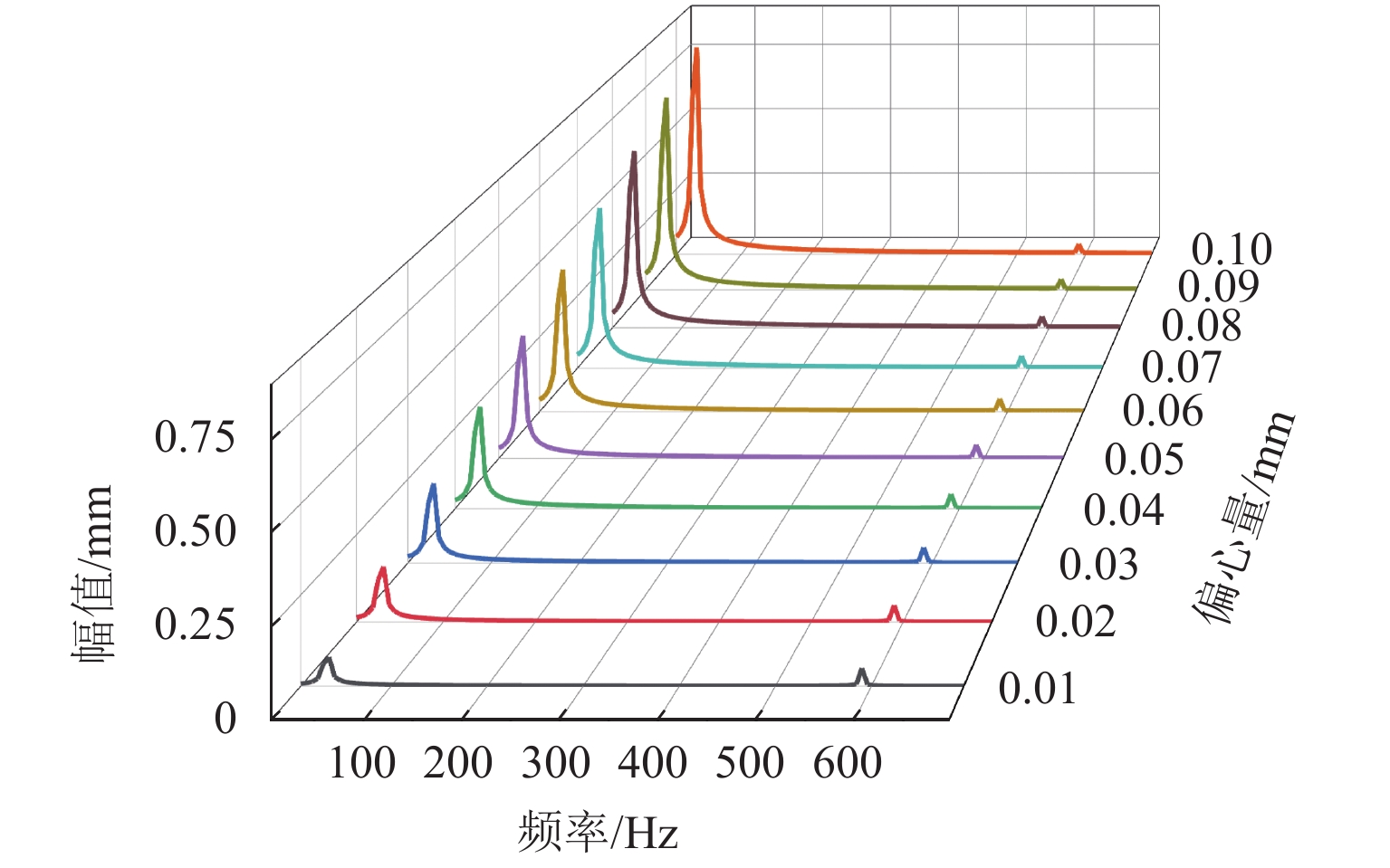
偏心量e在0.01~0.10 mm时对轮对-轨道转子系统振动特征的影响如图4. 图4(a)可见,不同偏心量下,振动位移包含两种频率成分:低频频率等于轮对转频,其幅值A随着偏心量的增大而增大,说明偏心量引起的惯性力增加,使得轮对振动幅值增大;高频频率均固定在580 Hz附近,说明高频频率与偏心量无关.
e=0.01,0.10,0.50,1.00 mm时,偏心量对车轮磨耗特征的影响如图5. 由图5可见:随着偏心量的增大,车轮出现了明显的椭圆化和高阶多边形磨耗现象,高阶多边形磨耗幅值略有减小,但阶次恒定. 此时的车轮磨耗为一阶叠加了多阶的多边形磨耗,且多阶多边形的阶次与偏心量的变化无关.
2.3 运行速度和车轮直径的影响
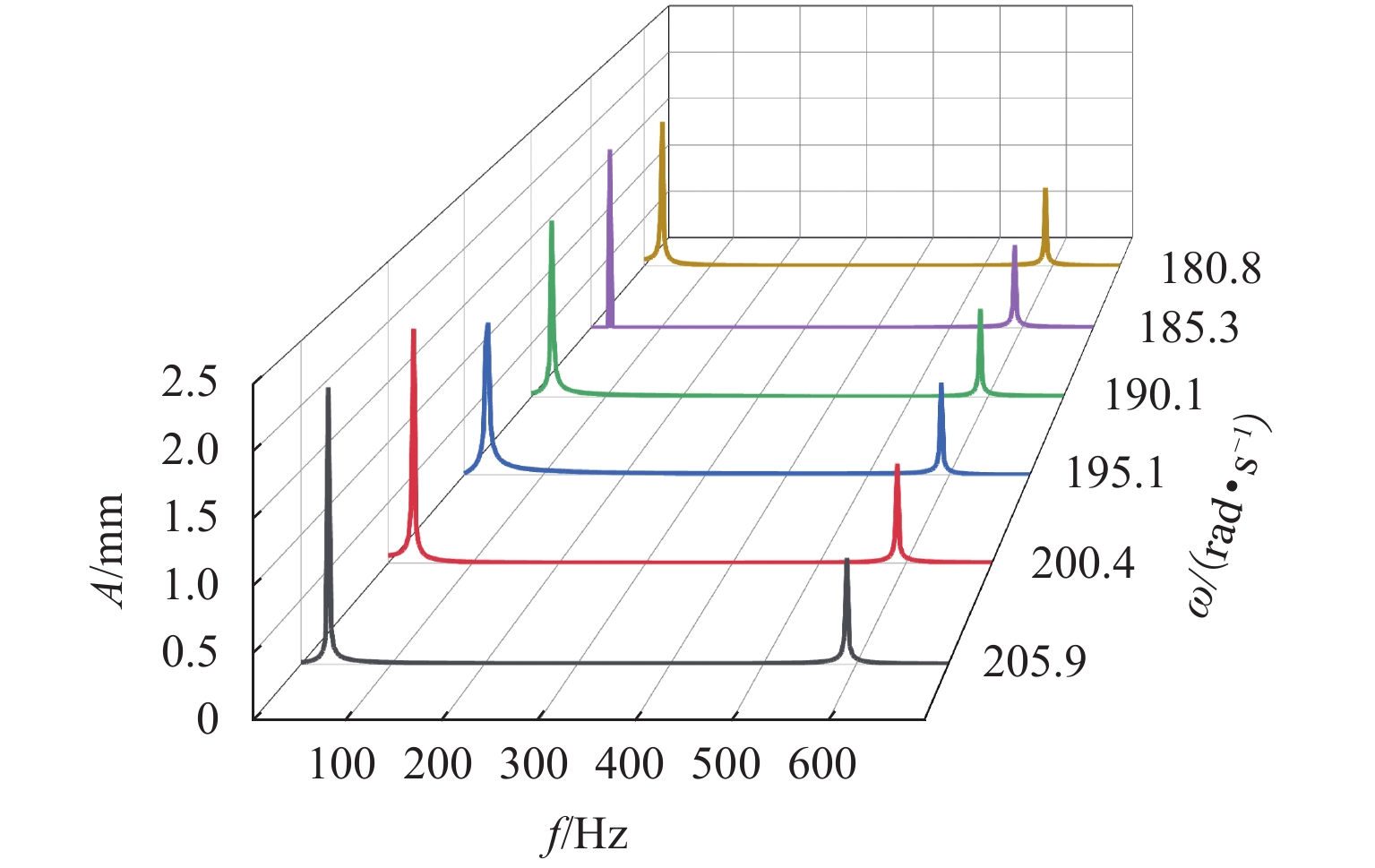
已有研究发现,车轮多边形磨耗的发生与演化取决于运行速度、车轮直径和轮轨固有振动[18]. 高铁为300 km/h恒速运行方式,由于目前动车组采用镟轮检修模式,车轮寿命期内的车轮直径在920~830 mm变化,对应取轮对角速度为180.8~205.9 rad/s,相当于轮对转频为25.2~58.0 Hz.
图6为不同角速度的频谱图,由图6可见,不同轮对角速度下,轮对振动位移也包含两种频率成分:低频频率随着转速的增大而增大,大小等于该转速对应的转频;高频频率仍然为一个固定频率,大小约为580 Hz.
为了进一步研究轮对转频对车轮多边形磨耗特征的影响,定义频率比N为固定频率f1和轮对转频f2之比. 取频率比N=18.0~20.5,绘制车轮圆周磨耗图,如图7. 由图7可见:当固定频率与轮对转频比为整数倍时,即N=18.0,19.0,20.0时,车轮圆周方向上发生并演化出了多边形,多边形阶数等于频率比,且车轮转速越高,多边形阶数越小;当固定频率与轮对转频比不为整数,即N=18.5,19.5,20.5时,未演化成带有明显阶次的车轮多边形,车轮磨耗为均匀磨耗. 可见,车轮多边形磨耗的演化呈现明显的“频率整分”特征.
车轮纵向振动存在一个固定频率,当该频率接近于车轮转频的整数倍时,车轮磨耗快速演化为阶数等于该整数倍的多边形.
2.4 现场跟踪实测验证
现场实测发现,列车运行速度为 300 km/h,在车轮轮径寿命周期从920~830 mm 变化过程中,存在3个车轮多边形磨耗高速发展时期,车轮直径为830、875 mm和915 mm,对应18阶、19阶和20阶车轮多边形磨耗,而在其他直径未发生明显阶次的多边形磨耗[19].
将现场实测数据代入式(12)和式(13),可计算出对应的轮对转频f2和纵向振动频率fx,见表1.
表 1 车轮多边形磨耗参数分析Table 1. Analysis of wheel polygonal wear parametersn D/mm ω/(rad·s−1) f2/Hz fx/Hz 20 915 182.1 29.0 580.1 19 875 190.5 30.3 576.3 18 830 200.8 32.0 575.6 由表1可见:v=300 km/h,车轮直径分别为830、875 mm和915 mm的3种情况均对应一个大小约为580 Hz的固定频率,该“固定频率”分别等于对应的轮对转频的整数倍,同时也分别发生了与相应整数倍相等的18阶、19阶和20阶车轮多边形磨耗;在车轮轮径寿命周期内,对应的轮对转频不能整除固定频率的车轮直径时,却未检测到明显的多边形磨耗. 综上,现场实测数据分析表明,车轮边形磨耗呈“频率固定和转频整分”特征,此磨耗特征与本文建立的轮对-轨道转子动力学系统车轮多边形演化模型所得结论一致.
3. 固定频率的来源与影响
为了探究上述研究中的固定频率来源,利用本文建立的轮对转子动力学模型进行模态分析,并与建立的轮轨接触实体有限元模型模态分析结果进行对比验证. 进而研究车轴直径等系统参数对固定频率的影响,并确定各参数的灵敏度.
3.1 集中质量模型模态分析
令系统主振动
$ u = \varphi {\text{sin}}(\omega t + \phi ) $ ,代入式(7)对应的系统${\boldsymbol{M}}\ddot {\boldsymbol{u}} + {\boldsymbol{Ku}} = {\boldsymbol{0}},\;{{\boldsymbol{u}} \in {{\boldsymbol{R}}_{8 \times 1}}}$ ,可得系统的特征方程为(K−ω2M)ϕ=0, (14) 式中:
${\boldsymbol{ \phi}} = {({\phi _1},{\phi _2},\cdots,{\phi _8})^{\text{T}}} $ ,为系统振动幅值列向量.由式(14)得
{ϕTiMϕj=0,ϕTiKϕj=0,i≠j,ϕTiMϕj=mpi,ϕTiKϕj=kpi,i=j, 式中:
${\boldsymbol{\phi}} _{i}$ 、${\boldsymbol{\phi}} _{j} $ 为系统第i、j阶模态的振幅向量;mpi、kpi为当i=j时系统的模态质量和模态刚度.利用Kronecker符号:
{ϕTiMϕj=δijmpi,ϕTiKϕj=δijkpi, (15) 式中:i=j时
${\delta _{{{ij}}}}=1 $ ,${i \ne j} $ 时$ {\delta _{{{ij}}}}=0$ .由
$ {{\boldsymbol{\phi }}_{i}^{\text{T}}}{{K}}{{\boldsymbol{\phi}} _{i}} = {\omega _i}^2{{\boldsymbol{\phi}} _{i}^{\text{T}}}{{M}}{{\boldsymbol{\phi}} _{i}} \Rightarrow {k_{{\rm{p}}i}} = {\omega _i}^2{m_{{\rm{p}}i}} $ ,得第i阶固有频率为ωi=√kpimpi. (16) 由式(7)可得
{m1¨x1+c1˙x1+(k1−kb)x1−k1x2=0,m1¨z1+c1˙z1+(k1−kb)z1−k1z2=0,m2¨x2+c2˙x2−k1x1+(k1+k2)x2−k2x3+μkRz2=0,m2¨z2+c2˙z2−k1z1+(k1+k2+kR)z2−k2z3=0,m3¨x3+c3˙x3−k2x2+(k1+k2)x3−k1x4+μkRz3=0,m3¨z3+c3˙z3−k2z2+(k1+k2+kR)z3−k1z4=0,m4¨x4+c4˙x4+(k1−kb)x4−k1x3=0,m4¨z4+c4˙z4+(k1−kb)z4−k1z3=0. (17) 式(17)结合特征方程式(14)可得:
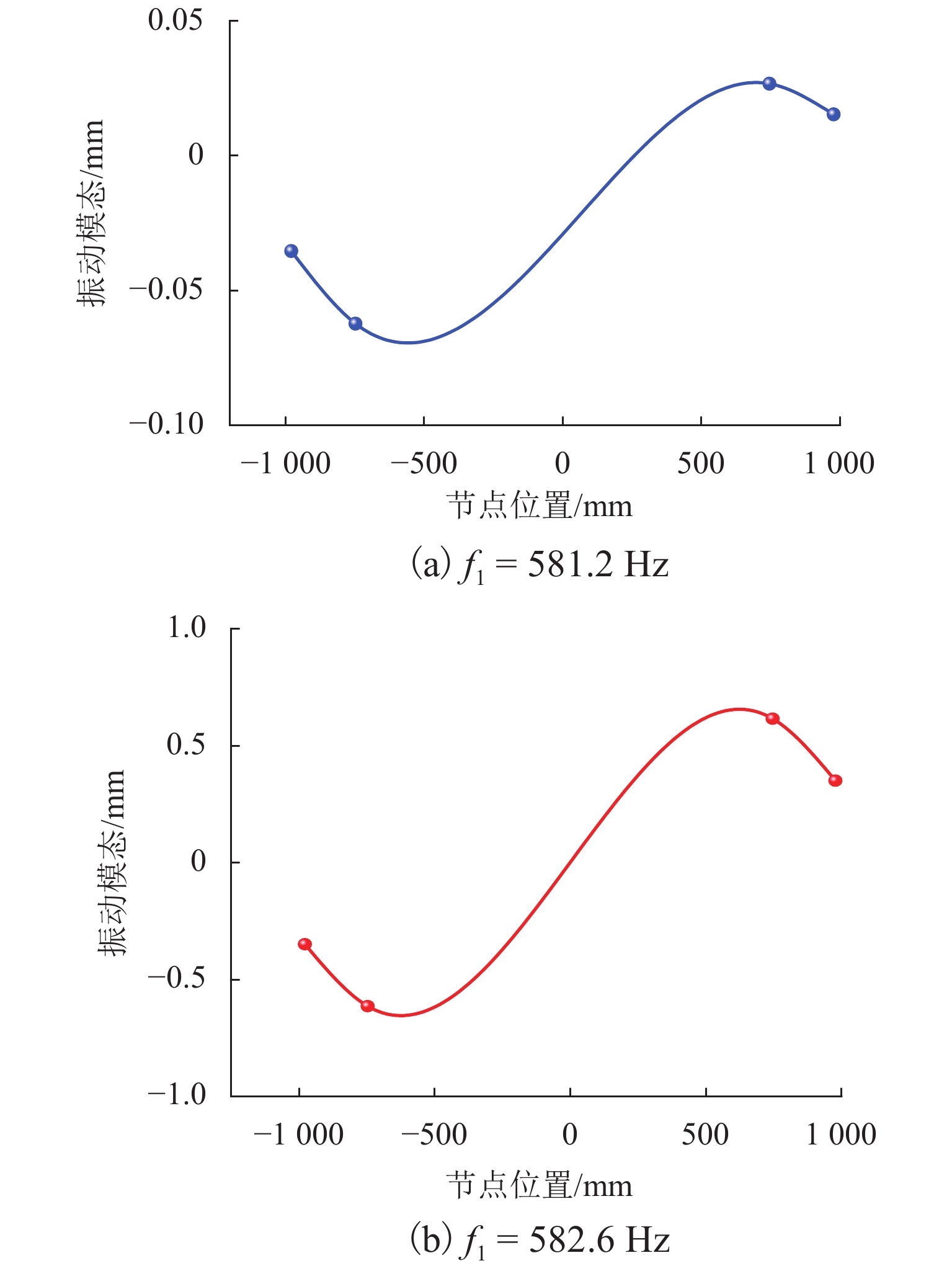
([k1−kb0−k1000000k1−kb0−k10000−k10k1+k2μkR−k20000−k10k1+k2+kR0−k20000−k20k1+k2μkR−k10000−k20k1+k2+kR0−k10000−k10k1−kb000000−k10k1−kb]−ω2[m10m100m2000m20000m300000m3000000m40000000m4])[ϕ1ϕ2ϕ3ϕ4ϕ5ϕ6ϕ7ϕ8]=0. (18) 将系统质量参数m1、m2、m3、m4和刚度参数k1、k2、kb、kR代入求解,获得了式(18)中的8阶模态,其中固定频率附近的各阶模态见图8. 由图8可见:固定频率等于2.1节中发现的580 Hz附近时,轮对转子系统的振动为二阶弯曲振动.
3.2 实体有限元模型模态分析
为了进一步研究固定频率与钢轨、轮对及耦合的关系,除上述轮对的尺寸参数外,取60 kg钢轨断面,钢轨长度6.0 m,轨枕距625 mm,扣件宽度170 mm,扣件垂向刚度20 MN/m,转向架固定轴距2.5 m,建立轮轨耦合实体有限元模型进行模态分析,研究转动效应对轮轨耦合系统固有频率的影响.
由表2可见:不考虑转动效应的刚轮柔轨、柔轮刚轨、柔轮柔轨,分别对应有1、4、5个固有频率接近“固定频率”580 Hz,而不同转速下轮轨耦合系统的固有频率均出现了5个接近固定频率的值. 说明转速和钢轨柔性对固定频率附近的固有频率影响不大,可以认为轮对对固定频率的贡献比钢轨大,虽然钢轨柔性对固定频率的贡献不大,但是将轮对和钢轨都考虑成柔性更符合实际情况. 所以在研究不同转速对轮轨耦合系统的固有频率影响时,将轮轨考虑成柔性.
表 2 轮轨耦合系统的固有频率Table 2. Natural frequency of rotor system of wheel setHz 不考虑转动效应 考虑转动效应 刚轮柔轨 柔轮刚轨 柔轮柔轨 柔轮柔轨 519.40 567.16 565.42 565.42 559.49 567.19 580.73 580.61 574.77 577.74 583.07 582.97 593.11 578.03 584.48 584.37 605.90 585.43 585.47 585.65 608.93 585.45 586.78 586.94 622.27 748.22 591.33 591.35 648.97 769.92 621.80 621.81 考虑转动效应下柔性轮对柔性钢轨的振动模态如图9所示,由图9可知:固定频率附近的柔性轮轨振动均对应轮对的2阶弯曲,而钢轨则分别呈现8阶横向弯曲、8阶横向弯扭耦合和8阶垂向弯曲;轮对的2阶弯曲振动是固定频率的主要来源,这一结论验证了式(18)中的集中质量模型的分析结果,也再次验证了本文所建立的轮对轨道转子动力学模型的可行性. 综上所述,出现580 Hz左右的“频率固定”现象的原因,主要由轮对的2阶弯曲所致,钢轨柔性对固定频率的影响不大.
3.3 扣件刚度对固定频率的影响
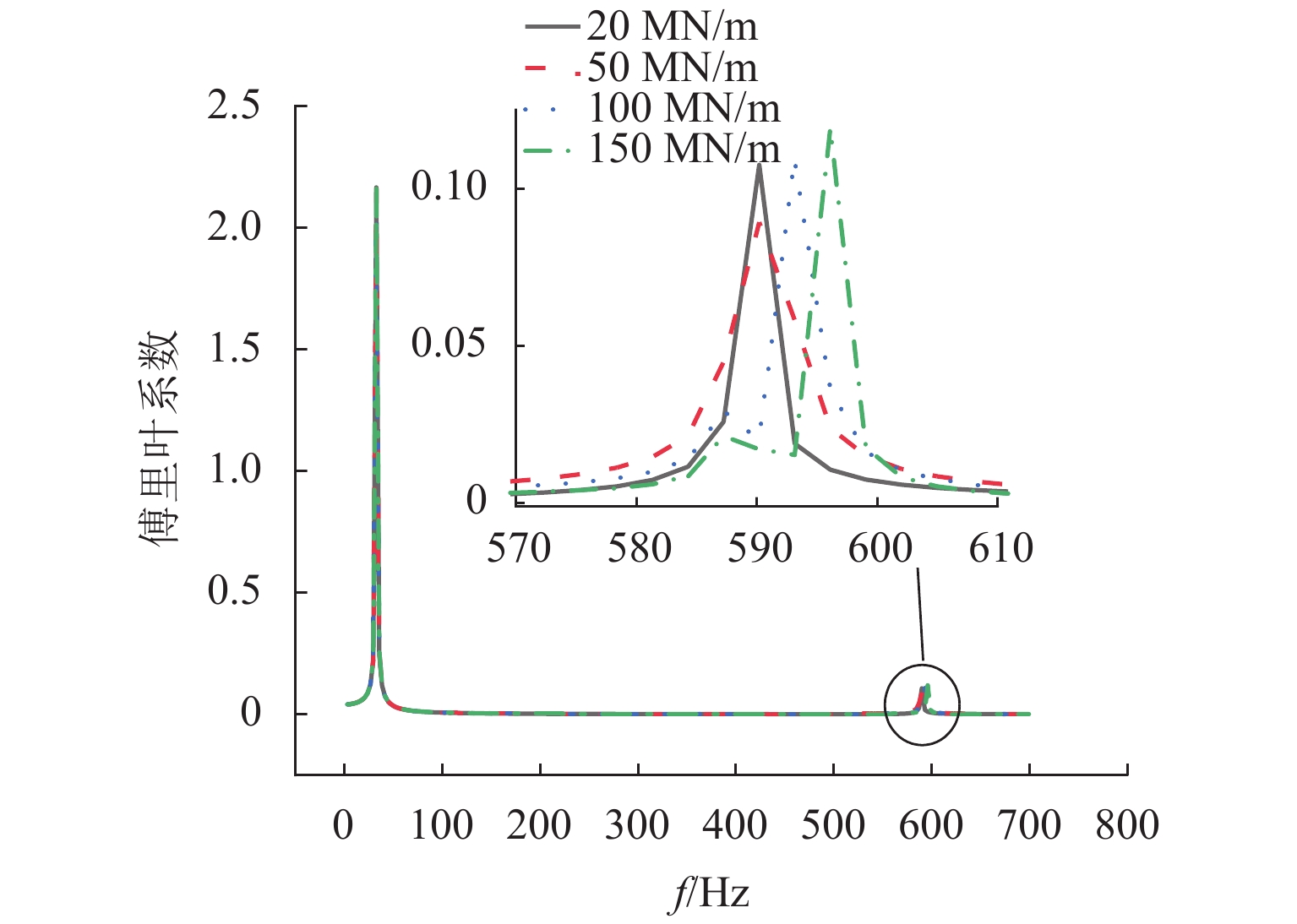
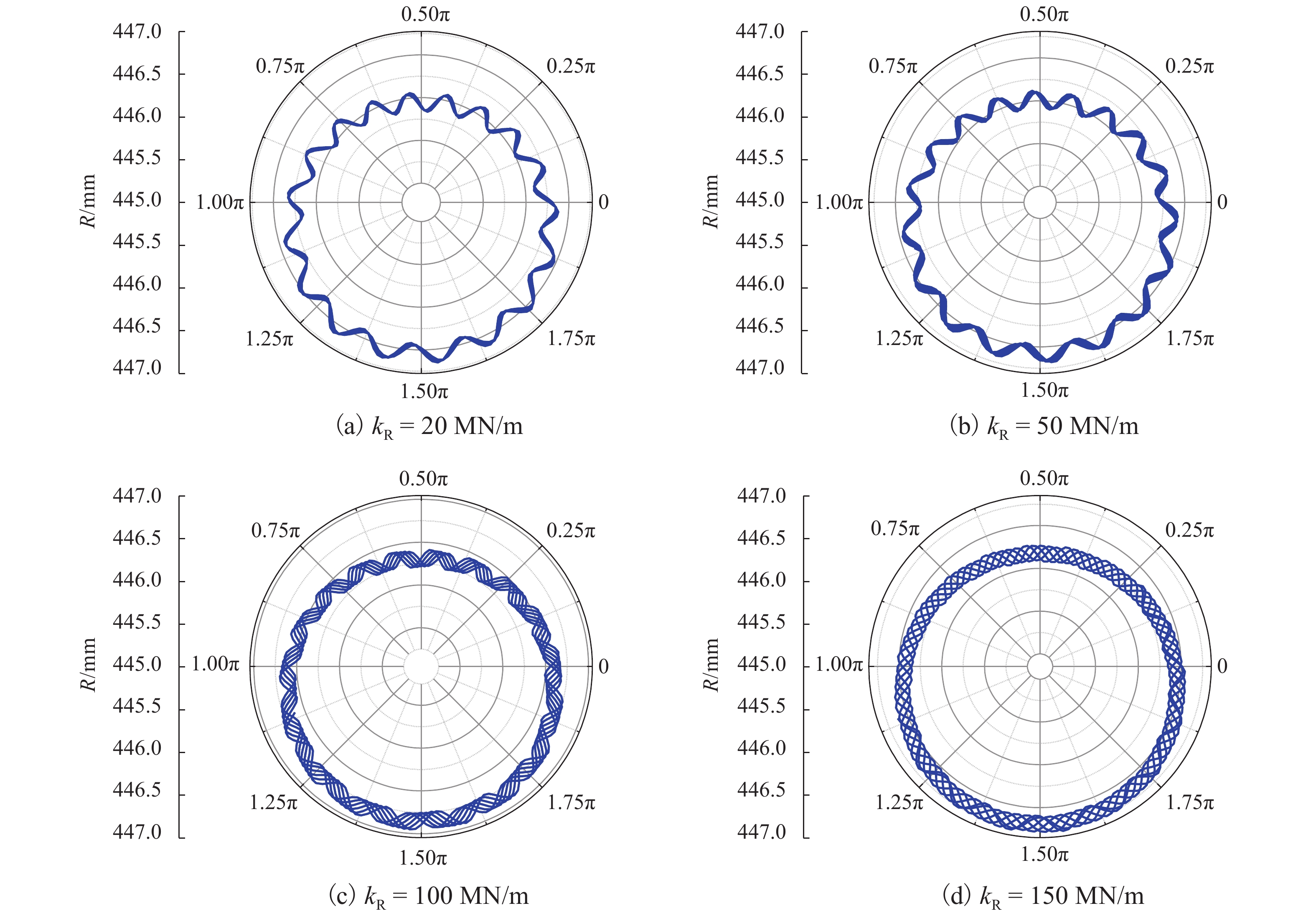
由式(8)、(18)可见,车轮多边形磨耗的固定频率主要与车轴直径、轮对质量、轴承刚度和扣件刚度有关. 分别研究扣件刚度为20、50、100、150 MN/m时,扣件刚度对固定频率的影响.
图10为同扣件刚度幅频图,由图10可见:随着扣件刚度的增加,固定频率及其对应的振动幅值均略有增大. 图11为不同扣件刚度的磨耗特征,由图11可见:随着扣件刚度的增大,由于固定频率的增大,与转频的比值逐渐远离整数倍,车轮磨耗形状由kR=20 MN/m的明显多阶多边形逐渐变为kR=150 MN/m均匀磨耗. 可见,增大扣件刚度对车轮多边形磨耗有一定的抑制作用.
3.4 车轴外径对固定频率的影响
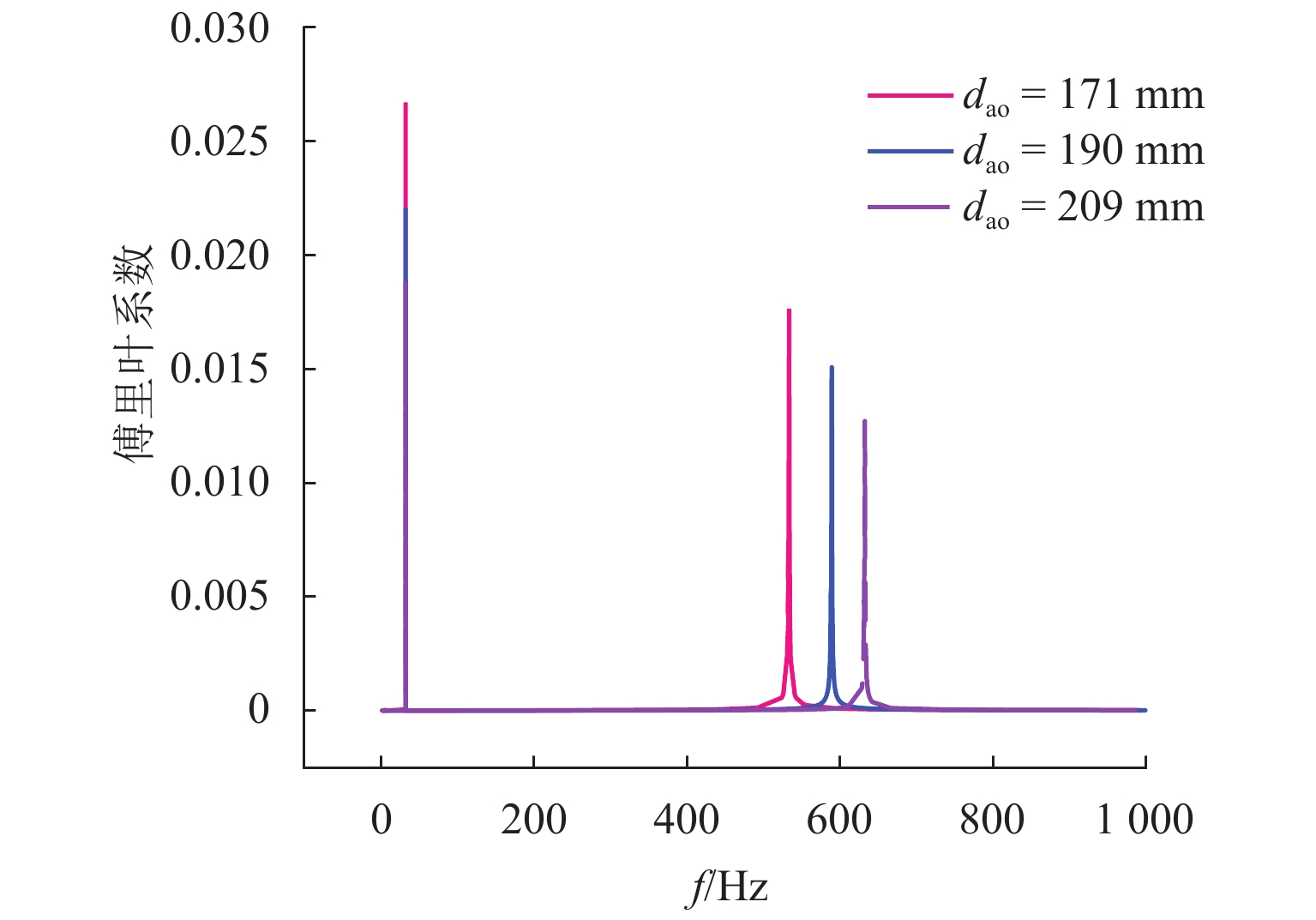
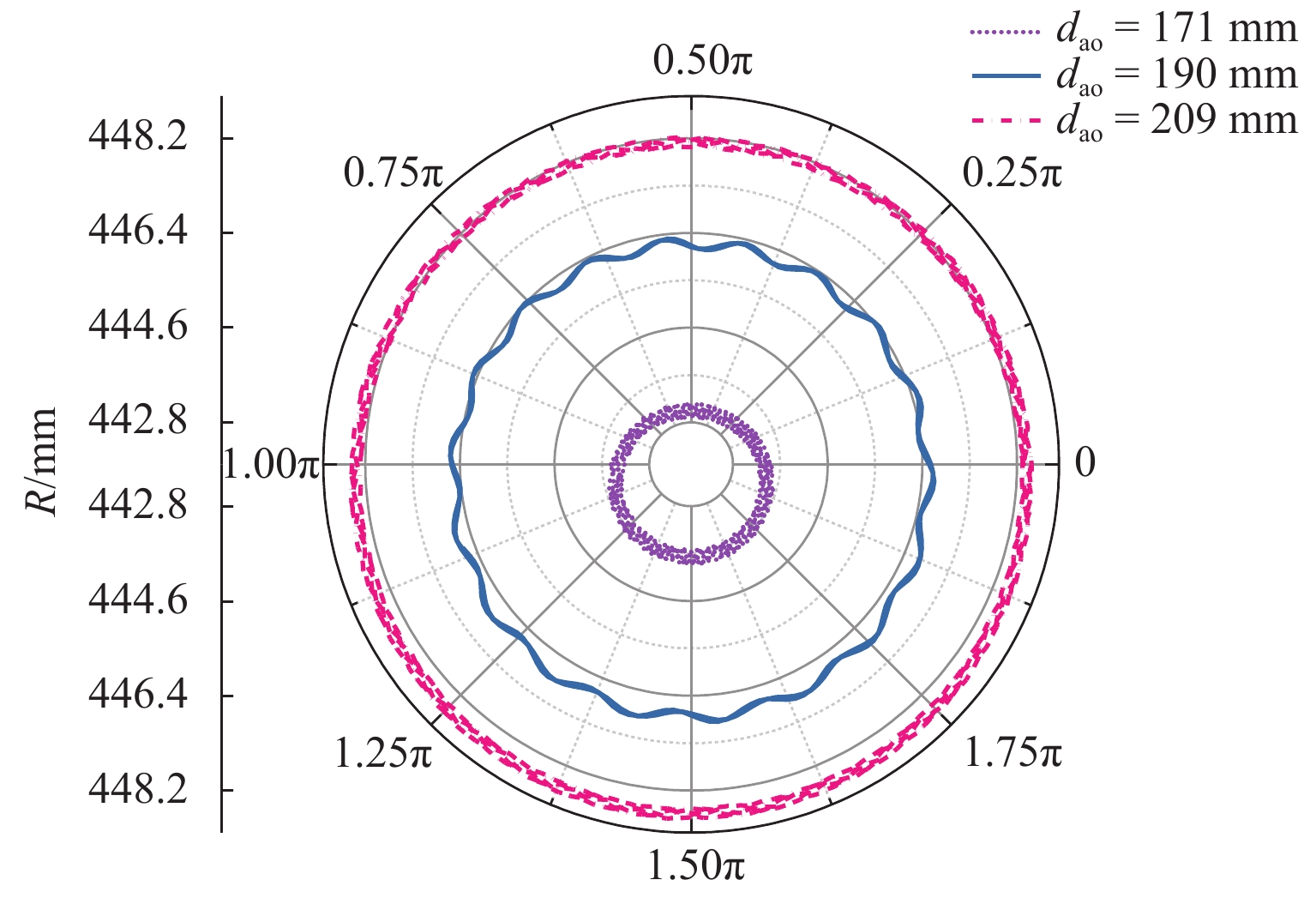
转速一定,取车轴外径分别为171、190 mm和209 mm,研究车轴外径对固定频率的影响.
图12为不同车轴直径(dao)的幅频图,由图12可见:随着车轴外径的增加,由于轮对刚度增加,固定频率增大,转频和固定频率的幅值均减小. 图13为不同车轴直径的磨耗特征,由图13可见:增大和减小车轴直径,均能因固定频率不再等于转频的整数倍而避免多阶多边形的发展;减小车轴外径会加速车轮的均匀磨耗. 可见,通过增大车轴外径可有效抑制车轮多边形.
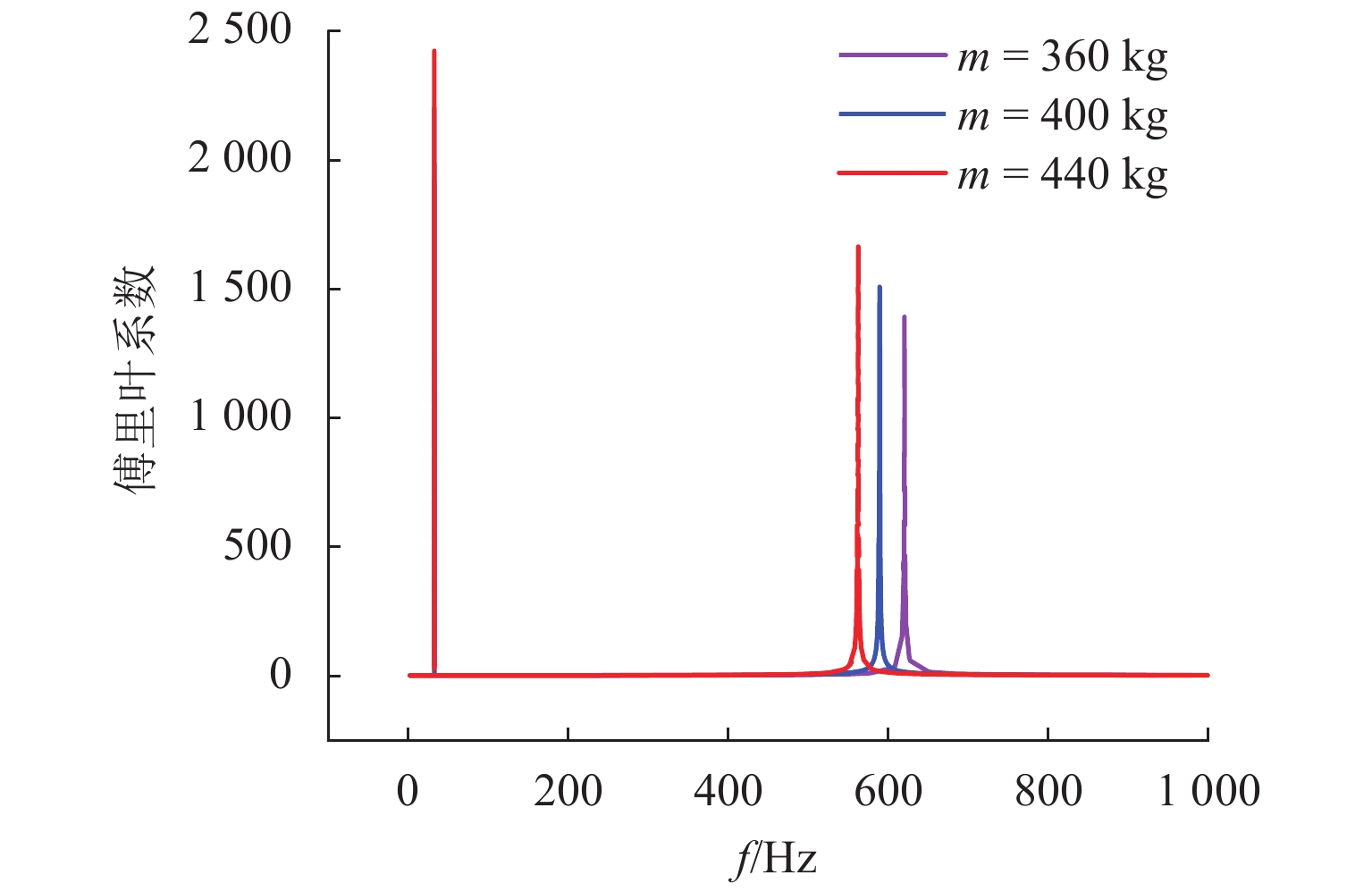
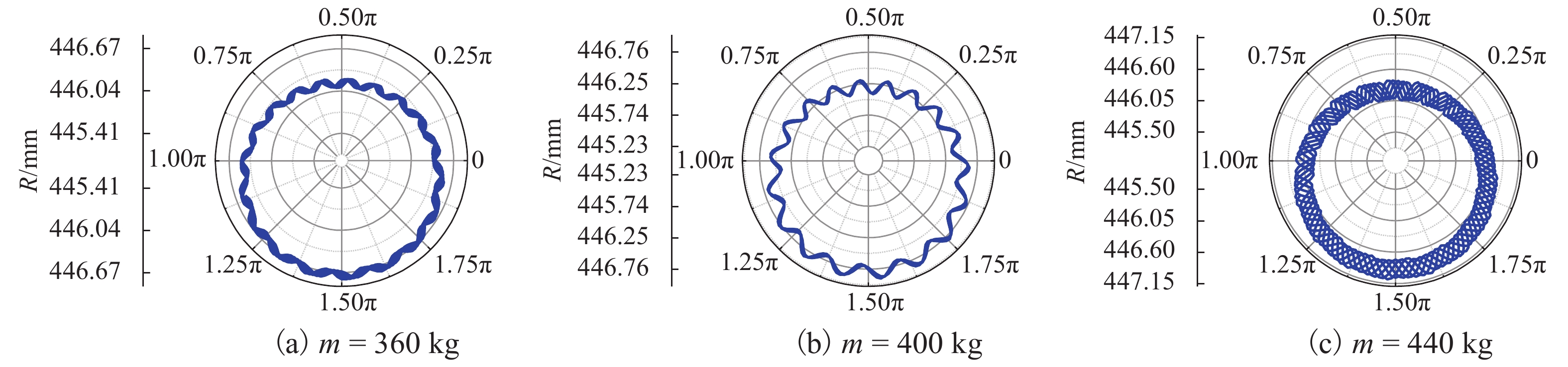
3.5 车轮质量对固定频率的影响
取车轮质量(m)分别为360、400 kg和440 kg,研究车轮质量对固定频率的影响. 由图14的振动特征可见:随着车轮质量的减小,固定频率增大,转频和固定频率的幅值均减小. 由图15的磨耗特征可见:增大和减小车轮质量,均能因固定频率不再等于转频的整数倍而避免多阶多边形的发展;增大车轮质量会加速车轮的均匀磨耗量. 因此,可以通过车轮轻量化抑制车轮多边形磨耗.
3.6 支承刚度对固定频率的影响
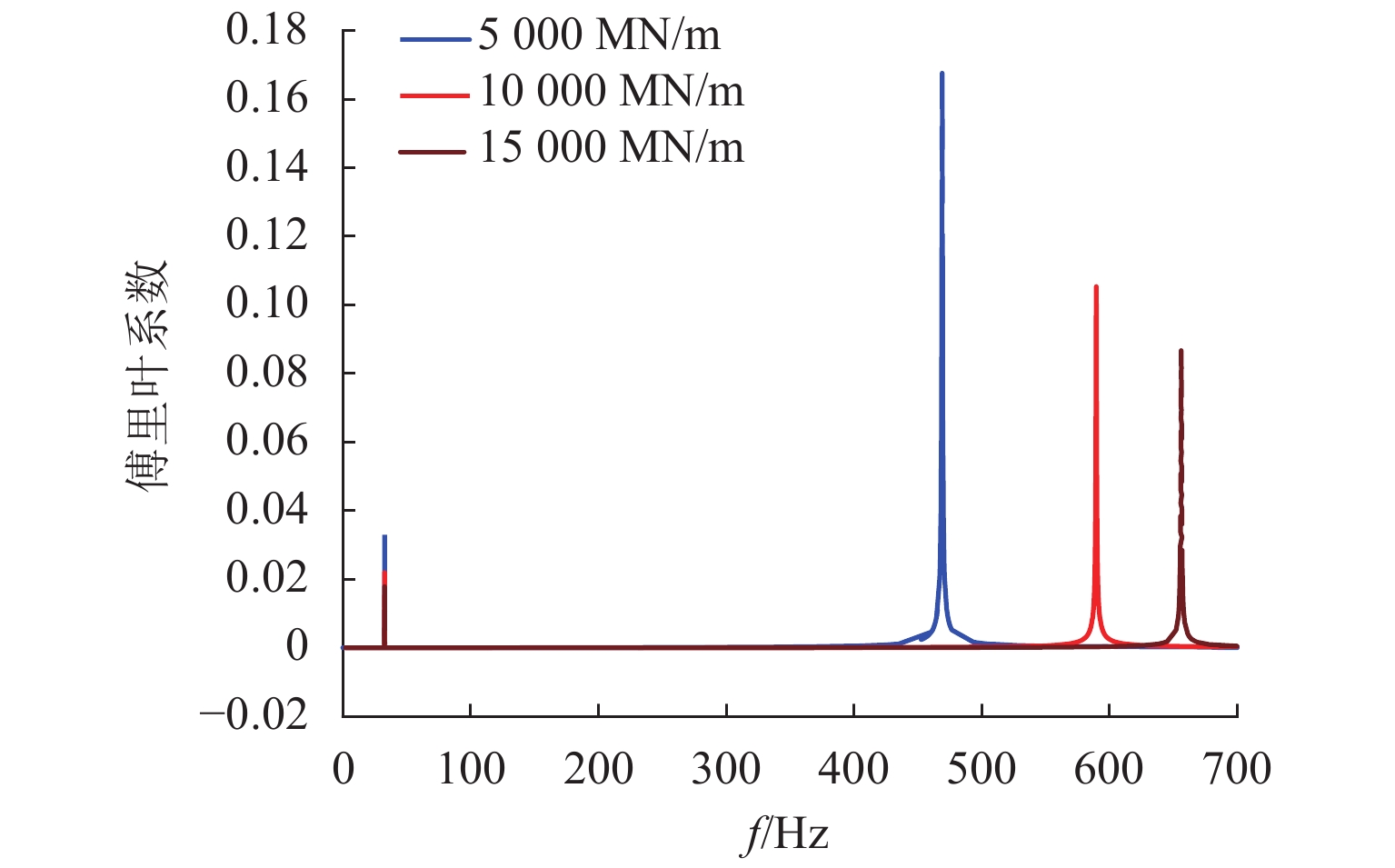
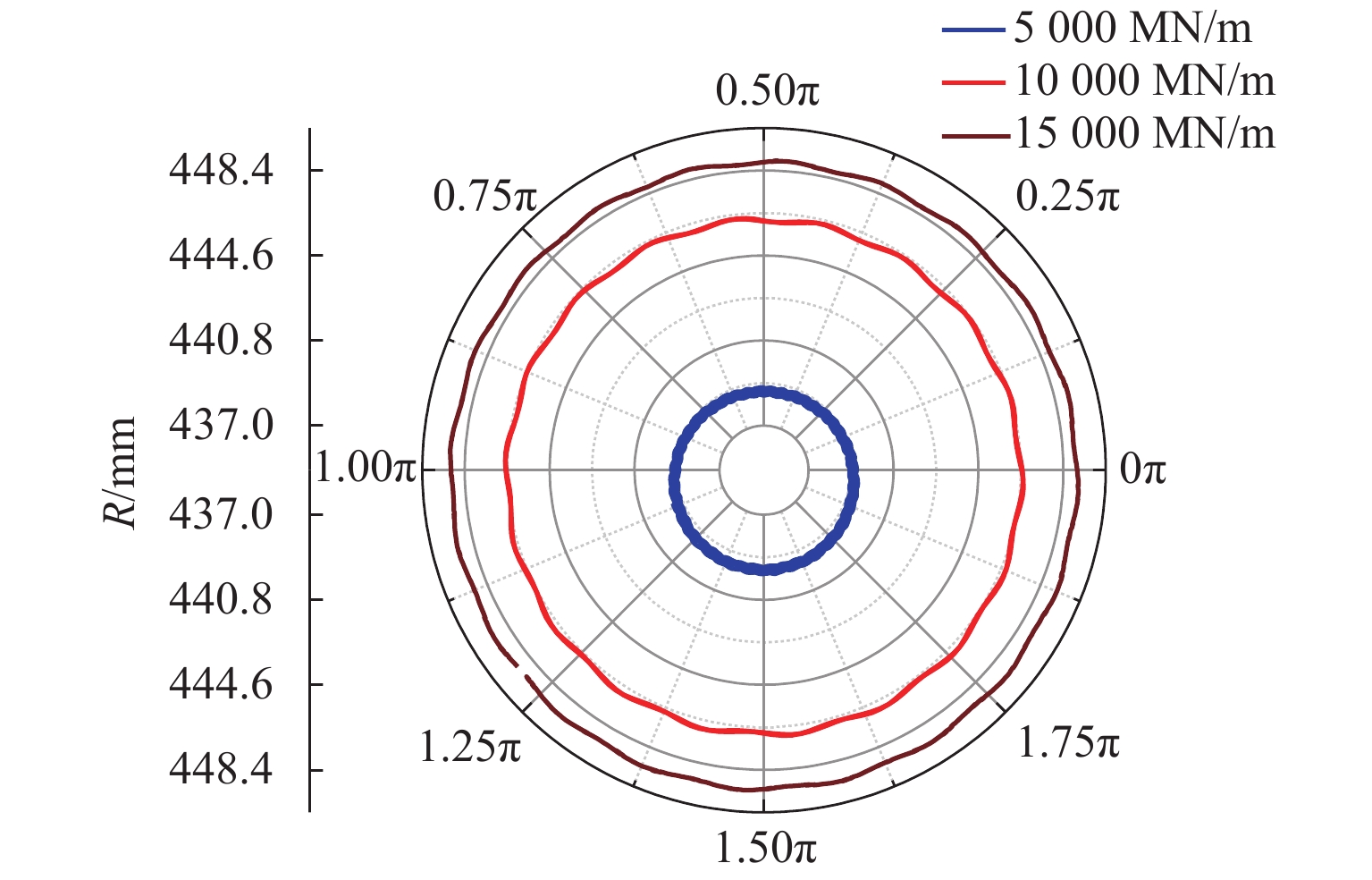
取支承刚度分别为5000、10000、15000 MN/m,研究支承刚度对固定频率的影响.
由图16中的振动特征可见:随着支承刚度的减小,固定频率减小,转频和固定频率的幅值均增大. 由图17中的磨耗特征可见:增大和减小支承刚度,均能因固定频率不再等于转频的整数倍而避免多阶多边形的发展;减小支承刚度会加速车轮的均匀磨耗量. 因此,可以通过增大支承刚度抑制车轮多边形磨耗.
3.7 灵敏度分析
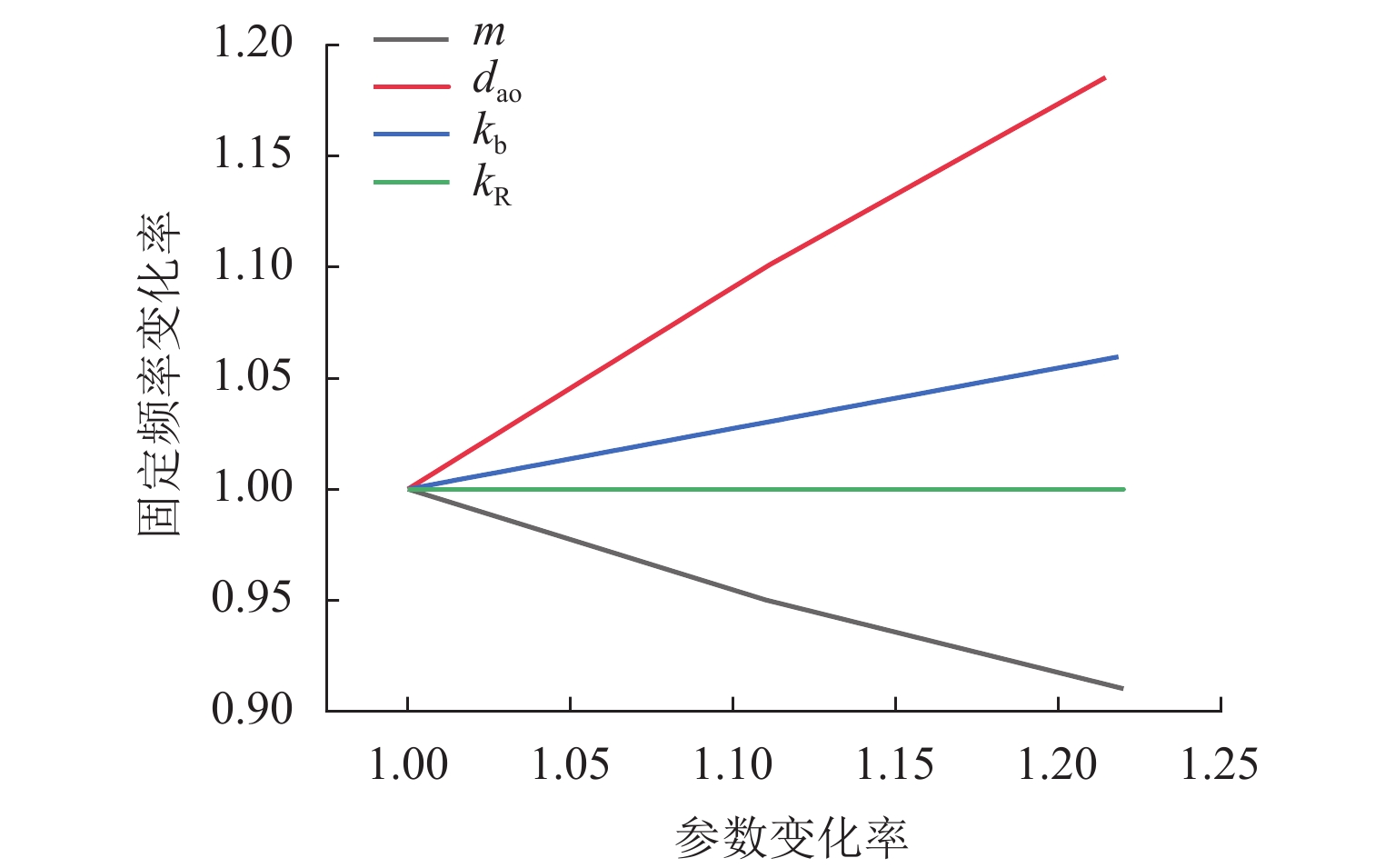
改变车轴外径等系统参数可一定程度抑制车轮多边形磨耗的演化,为了给现场抑制车轮多边形提供理论依据,分别研究各系统参数对固定频率的灵敏度.
由式(14)可得
$ K{\boldsymbol{\phi}} = {\omega ^2}M{\boldsymbol{\phi}} $ ,则设计变量α对固定频率的灵敏度为λ=∂ω2∂α=ϕT(∂K∂α−ω2∂M∂α)ϕ. (19) 设
$ \Delta K $ 、$ \Delta M $ 是由参数变化$ \Delta \alpha $ 而产生的刚度矩阵和质量矩阵的增量,则由式(19)可得固定频率灵敏度的摄动公式为λ=Δω2Δα=ϕT(ΔKΔα−ω2ΔMΔα)ϕ. (20) 图18为固定频率灵敏度分析结果,由图18可见:随着车轮质量的增大,固定频率灵敏度快速下降;随着车轴外径增加、支承刚度增大,固定频率灵敏度快速增大;随着扣件刚度增大,固定频率灵敏度几乎不变. 上述系统参数对固定频率的灵敏度从大到小的顺序依次为车轴外径>车轮质量>支承刚度>扣件刚度. 可见,轮对自身特性是车轮多边形磨耗的主要影响因素,而轨道特性的影响较小.
结合3.3节~3.6节的研究结果可见:通过调整系统参数改变固定频率的大小,使其避开被轮对转频整分,可避免车轮磨耗演化为车轮多边形. 具体参数调整可依据本文确定的灵敏度,也可以通过改变运行速度以改变轮对转频,来达到同样的目的.
4. 结 论
本文建立了车轮多边形磨耗发生和演化模型,表征了轮对-轨道转子动力学系统的振动特征和车轮多边形磨耗特征,揭示了车轮多边形发生和演化的规律. 主要结论如下:
1) 基于轮对-轨道转子动力学理论建立轮轨接触动力学模型,结合磨耗功模型研究多边形磨耗,并用现场跟踪实测数据验证了模型的可靠性.
2) 通过频谱分析和磨耗特征分析发现车轮多边形磨耗遵循“定频整分”的规律.
3) 通过模态分析发现固定频率与车轮转动激发的轮对2阶弯曲振动的固有频率一致,而钢轨的柔性对固定频率的贡献不大.
4) 通过破坏整分条件即可抑制多边形发展的思路,确定了改变固定频率的灵敏度顺序,为抑制车轮多边形磨耗提供了理论依据.
本文建立的高速车轮多边形磨耗模型中,未考虑动载荷及悬挂等的影响,而磨耗演化全过程预测研究也将是下一步进行的工作.
-
表 1 随机变量的随机特性
Table 1. Statistical properties of random variables
随机变量 均值 变异系数 分布形式 βfc=fc=βfcfcm 1 0.15 正态分布 βEc=Ec=βEc(fc/10)1/3 21 500 0.08 正态分布 βft=ft=βft(ft)2/3 0.3 0.15 正态分布 βEs=Es=βEsEsm 1 0.033 正态分布 表 2 公式(9)的拟合系数
Table 2. Fitting coefficients for Eq. (9)
系数 fcm/MPa 30 40 50 60 a0 -0.297 2 -0.060 0 -0.046 1 -0.043 3 a1 0.915 4 0.844 7 0.816 6 0.803 3 a2 1.383 0 0.864 9 0.810 9 0.788 5 a3 -0.345 8 -0.324 2 -0.309 5 -0.298 9 a4 -0.157 4 -0.110 9 -0.110 1 -0.120 5 a5 -1.272 0 -0.921 2 -0.879 2 -0.859 9 a6 0.048 8 0.045 1 0.042 4 -0.040 4 a7 0.063 5 0.061 4 0.060 1 0.060 5 a8 -0.018 4 -0.033 5 -0.034 1 -0.031 0 a9 0.330 4 0.254 6 0.245 3 0.240 8 表 3 Csup的拟合系数(0.7Mcr<M≤1.3Mcr)
Table 3. Fitting coefficients for Csup (0.7Mcr < M≤1.3Mcr)
系数 fcm/MPa 30 40 50 60 b0 3.459 3.768 3.565 4.160 b1 0.243 0.087 -0.065 -0.067 b2 -12.340 -13.000 -12.260 -14.060 b3 -0.891 -0.690 -0.628 -0.662 b4 3.150 3.143 3.275 3.339 b5 10.040 10.490 9.600 11.280 b6 0.057 -0.009 -0.009 -0.010 b7 0.550 0.563 0.519 0.577 b8 -2.697 -2.711 -2.717 -2.814 b9 -1.507 -1.552 -1.21 -1.681 表 4 Csup的拟合系数(1.3Mcr<M≤2Mcr)
Table 4. Fittingcoefficients for Csup(1.3Mcr < M≤2Mcr)
系数 fcm/MPa 30 40 50 60 b0 11.190 11.850 12.520 12.020 b1 -3.742 -3.418 -3.376 -3.522 b2 -15.160 -16.470 -17.590 -16.590 b3 0.814 0.775 0.792 0.968 b4 2.911 2.611 2.506 2.443 b5 7.419 8.251 8.925 8.348 b6 -0.100 -0.098 -0.094 -0.117 b7 -0.222 -0.209 -0.227 -0.276 b8 -0.647 -0.569 -0.523 -0.473 b9 -1.240 -1.413 -1.553 -1.448 表 5 Cinf的拟合系数(0.7Mcr<M≤1.3Mcr)
Table 5. Fittingcoefficients for Cinf (0.7Mcr < M≤1.3Mcr)
系数 fcm/MPa 30 40 50 60 b0 5.850 6.078 6.266 6.332 b1 0.390 0.456 0.329 0.387 b2 -17.960 -18.730 -19.170 -19.420 b3 -0.459 -0.445 -0.396 -0.396 b4 1.320 1.134 1.230 1.092 b5 14.870 15.640 15.980 16.240 b6 0.065 0.062 0.065 0.067 b7 0.117 0.118 0.068 0.064 b8 -0.909 0.820 -0.804 -0.730 b9 -3.715 -3.959 -4.058 -4.146 表 6 Cinf的拟合系数(1.3Mcr<M≤2Mcr)
Table 6. Fittingcoefficients for Cinf(1.3Mcr < M≤2Mcr)
系数 fcm/MPa 30 40 50 60 b0 -6.724 -6.985 -7.292 -7.615 b1 1.696 1.638 1.651 1.721 b2 9.641 10.080 10.580 11.080 b3 -0.151 -0.125 -0.127 -0.168 b4 -1.624 -1.609 -1.622 -1.657 b5 -4.673 -4.909 -5.180 -5.440 b6 0.003 0.003 0.002 0.013 b7 0.078 0.066 0.067 0.071 b8 0.389 0.395 0.398 0.406 b9 0.759 0.799 0.849 0.894 -
BISCHOFF P H. Reevaluation of deflection prediction for concrete beams reinforced with steel and fiber-reinforced polymer bars[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2005, 114(7):1499-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5eb4eb09b58e59dc22467eacd2b49d7e 徐腾飞, 白雪濛, 赵人达.加载过程中钢筋混凝土梁弯曲型变的随机性分析[J].西南交通大学学报, 2015, 50(4):630-634. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.04.009XU Tengfei, BAI Xuemeng, ZHAO Renda. Stochastic analysis of bending deflection for reinforced concrete beam in loading process[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(4):630-634. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.04.009 GILBERT R I. Tension stiffening in lightly reinforced concrete slabs[J]. Journal of the Structural Division ASCE, 2007, 133(6):899-903. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9ff00ac19894721356adbe553e227e57&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn 丁大钧.钢筋混凝土构件抗裂度、裂缝和刚度[M].南京:南京工学院出版社, 1986:17-26. 过镇海, 时旭东.钢筋混凝土原理和分析[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2007:257-267. 李志华, 苏小卒.钢筋混凝土受弯构件挠度计算方法综述分析[J].四川建筑科学研究, 2011, 37(2):30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1933.2011.02.008LI Zhihua, SU Xiaozu. Review of study on the methods for computing deflections of reinforced concrete flexural members[J]. Sichuan Building Science, 2011, 37(2):30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1933.2011.02.008 XU Tengfei, XIANG Tianyu, ZHAO Renda, et al. Stochastic analysis on flexural behavior of reinforced concrete beams based on piecewise response surface scheme[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2016, 59:211-222. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2015.10.004 GILBERT R I, WARNER R F. Tension stiffening in reinforced concrete slabs[J]. Journal of the Structural Division, 1978, 104(2):1885-2900. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=bad026accbc3a0e2904b30472290761e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn BALAKRISHAN S, MURRAY D W. Concrete constitutive model for NLFE analysis of structures[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1988, 114(7):1449-1466. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1988)114:7(1449) COLLINS M P, VECCHIO F J. The modified compression-field theory for reinforced concrete elements subjected to shear[J]. ACI Journal, 1986, 83(2):219-231. doi: 10.1021-nn1019972/ PARKHYA G K., MORLEY C T. Tension stiffening and moment-curvature relation for reinforced concrete elements[J]. ACI Journal, 1990, 87(5):597-605. https://www.concrete.org/publications/internationalconcreteabstractsportal/m/details/id/2680 FLOEGL H, MANG H A. Tension stiffening concept based on bond slip[J]. Journal of the Structural Division ASCE, 1982, 108(12):2681-2701. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5a80f08c13e009794a567315b83588d0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn CHOIL C K, CHEUNG S H. Tension stiffening model for planar reinforced concrete members[J]. Computers and Structures, 1996, 59(1):179-190. doi: 10.1016/0045-7949(95)00146-8 BRANSON D E. Instantaneous and time-dependent deflections of simple and continuous reinforced concrete beams[R]. Alabama: Alabama Highway Department, 1963. ACI Committee 318. ACI 318-05 building code requirements for structural concrete[S]. Washington D. C.: American Concrete Institute, 2005. BISCHOFF P H, ANDREW S. Effective moment of inertia for calculating defections of concrete moment containing steel reinforcement and fiber-Reinforced polymer reinforcement[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 2007, 104(1):68-5. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3c5770e47671fef7188c3c3e5b8f34d6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn 中华人民共和国住房与建设保障部. GB50010——2010混凝土结构设计规范[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2010. 姜磊, 姚继涛, 信任, 等.验研究钢筋混凝土薄板受拉刚化效应[J].混凝土, 2011(1):62-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hnt201101016JIANG Lei, YAO Jitao, XIN Ren, et al. Tension stiffening in reinforced concrete slabs and test research[J]. Concrete, 2011(1):62-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hnt201101016 JUNG J K, MAHMOUD M R T, HYUK-CHUN N, et al. Reliability analysis to resolve difficulty in choosing from alternative deflection models of RC beams[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 37:240-252. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.06.024 周婧, 陈秦, 王慧英.钢筋混凝土框架结构竖向不规则参数的概率评估[J].建筑结构学报, 2014, 35(3):39-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jzjgxb201403006ZHOU Jing, CHEN Qin, WANG Huiying. Probability evaluation of vertical regularity parameters for reinforced concrete frame structures[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2014, 35(3):39-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jzjgxb201403006 褚松涛, 曹少卫, 高夕良.成都东客站承轨层桥建合一结构设计施工综合技术[J].建筑施工, 2010, 32(6):520-524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1001.2010.06.016CHU Songtao, CAO Shaowei, GAO Xiliang. Comprehensive techonogy of structure design and construction for bridge and building combined rail bearing floor of cheng du east railway station[J]. Building Construction, 2010, 32(6):520-524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1001.2010.06.016 徐腾飞, 向天宇, 赵人达.偏心钢筋混凝土受压柱长期变形分析[J].西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(4):26-630. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xnjtdxxb201404010XU Tengfei, XIANG Tianyu, ZHAO Renda. Long-term random deflection of eccentrically load RC column[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4):26-630. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xnjtdxxb201404010 徐腾飞, 向天宇, 白雪濛, 等.基于分片响应面的钢筋混凝土梁变形随机模拟[J].工程力学, 2014, 31(11):170-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201411023.htmXU Tengfei, XIANG Tianyu, BAI Xuemeng, et al. Stochastic simulation of reinforced concrete beam with piecewise response surface[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(11):170-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201411023.htm XU Tengfei, CASTEL A, GILBERT R I, et al. Modeling the tensile steel reinforcement strain in RC-beams subjected to cycles of loading and unloading[J]. Engineering Structures, 2016, 126:92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.07.043 XU Tengfei, CASTEL A. Modeling the dynamic stiffness of cracked reinforced concrete beams under low-amplitude vibration loads[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2016, 368:135-147. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=365141718e2d5c6cd5d6c8882cb8c065 VAL D V, STEWART M G, MELCHERS R E. Effect of reinforcement corrosion reliability of highway bridges[J]. Engineering Structure, 1998, 20(97):1010-1019. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ad1fc36b75edcbc78ebdf06c9f3a7df9 YANG I H. Prediction of time-dependent effects in concrete structures using early measurement data[J]. Engineering Structures, 2007, 29:2701-2710. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2007.01.015 YANG I H.. Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of time-dependent effects in concrete structures[J]. Engineering Structures, 2007, 29:1366-1374. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2006.07.015 徐腾飞, 吴涤, 汪军, 等.预应力混凝土简支足尺试验梁变形随机分析[J].中国公路学报, 2015, 28(9):67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.09.009XU Tengfei, WU Di, WANG Jun, et al. Stochastic analysis of deflection of prestressed concrete simply supported full-scale test beam[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(9):67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.09.009 -






 下载:
下载:






















































 下载:
下载: