Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Rail Vibration Acceleration under Train Load
-
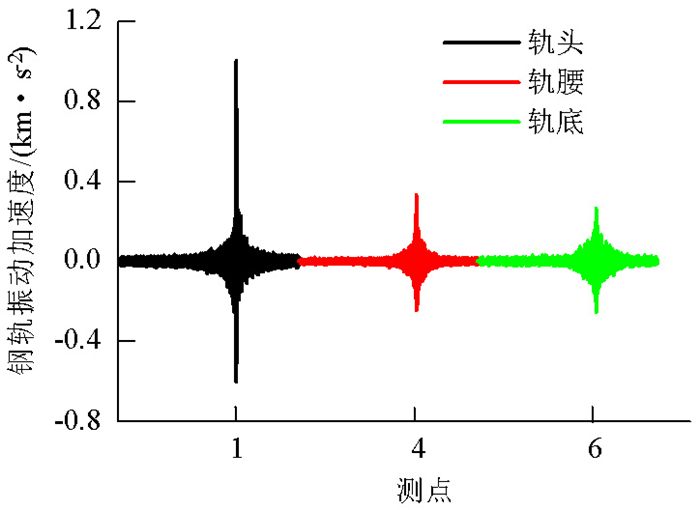
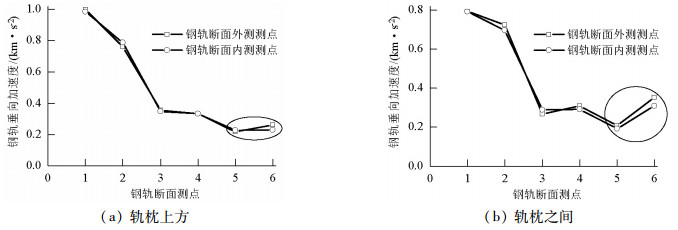
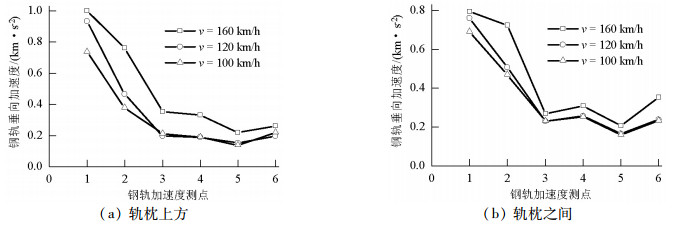
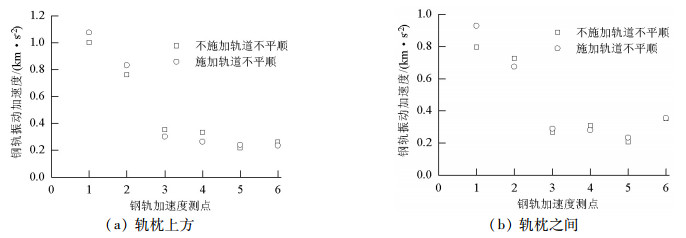
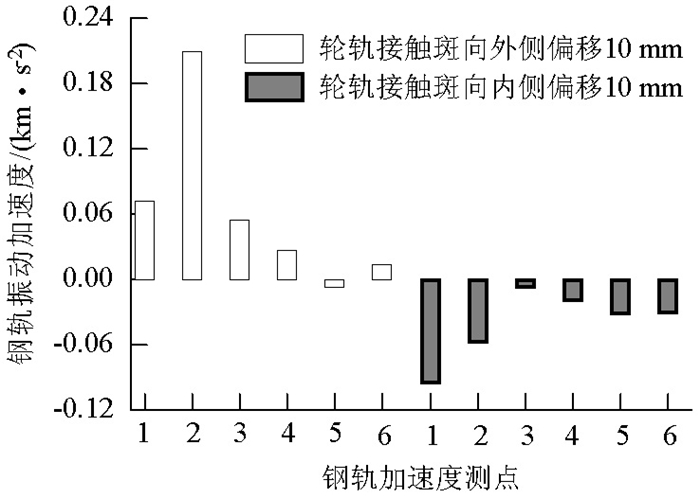
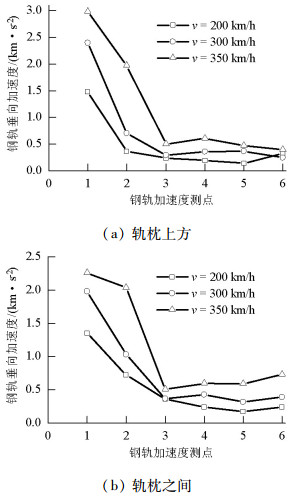
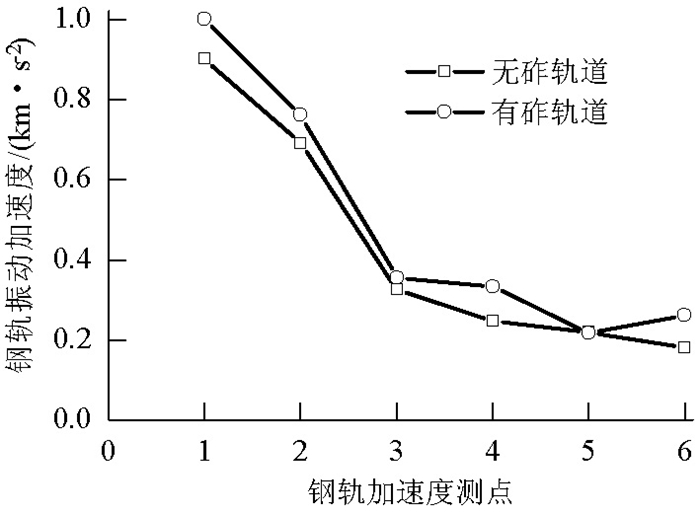
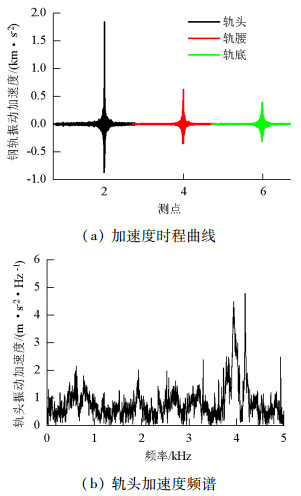
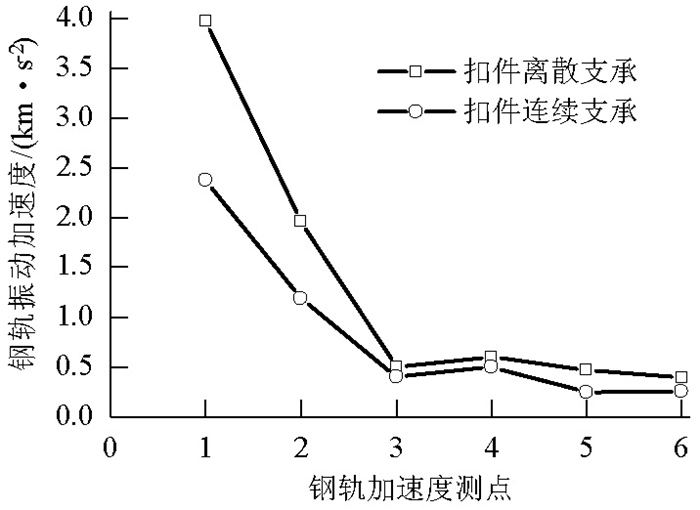
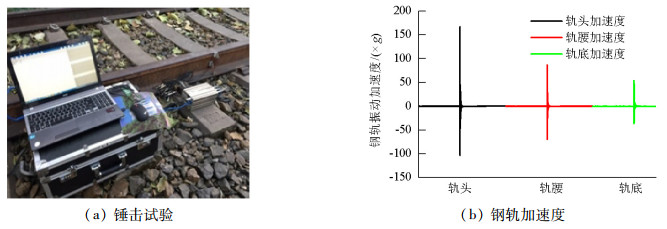
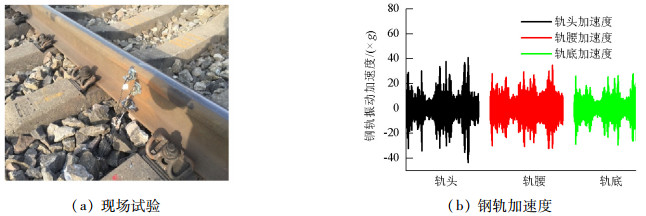
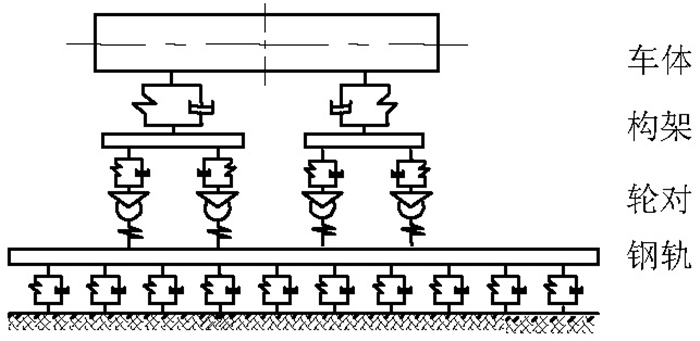
摘要: 为了探究列车通过时钢轨振动的基本参数和敏感区域,基于多体动力学软件GENSYS和有限元软件ABAQUS,分别建立车辆-轨道动力学模型和轨道-下部基础有限元模型.以动力学模型计算得到的轮轨力为激励,输入轨道-下部基础有限元模型,计算分析车速、轨道不平顺和钢轨支承方式等因素对钢轨加速度的影响.研究结果表明:钢轨加速度从轨头到轨底逐渐减小,轨枕上方轨头加速度明显大于轨枕之间.钢轨加速度对车速最为敏感,车速从200 km/h增加到350 km/h时,无砟轨道轨头加速度从1.476 km/s2增加到2.980 km/s2.连续支承式无砟轨道,钢轨加速度小于传统离散支承式无砟轨道.加速度传感器建议安装在轨头外侧,传感器的采集频率、量程应考虑列车速度、轨道不平顺等影响.Abstract: A vehicle-track dynamic model and track-substructure finite element model were established to study the basic parameters and sensitive areas of rail vibration, respectively, when a train passes. The models were developed based on the co-simulation of MBS software GENSYS and finite element software ABAQUS. The wheel-rail forces from the vehicle-track model were used as the excitation source in the track-substructure model, and the effects of train speed, track irregularity, and different types of track supports on rail acceleration were analyzed. The research results show that rail acceleration decays from the head to the foot of a rail, and the acceleration of the rail head above the sleepers is significantly greater than that between the sleepers. The acceleration of the rail head is sensitive to speed. For a ballastless track, as the traveling speed increases from 200 km/h to 350 km/h, the rail head acceleration increases from 1.476 km/s2 to 2.980 km/s2. The rail acceleration of a continuously supported ballastless track is less than that of the traditional, discrete supported ballastless track. The installation of acceleration sensors outside the rail head is recommended. The frequency and range selection of the sensor should be made taking into consideration the train speed, track irregularity, and other factors.
-
Key words:
- vehicle-track interaction /
- track dynamics /
- finite element model /
- rail acceleration /
- sensor
-
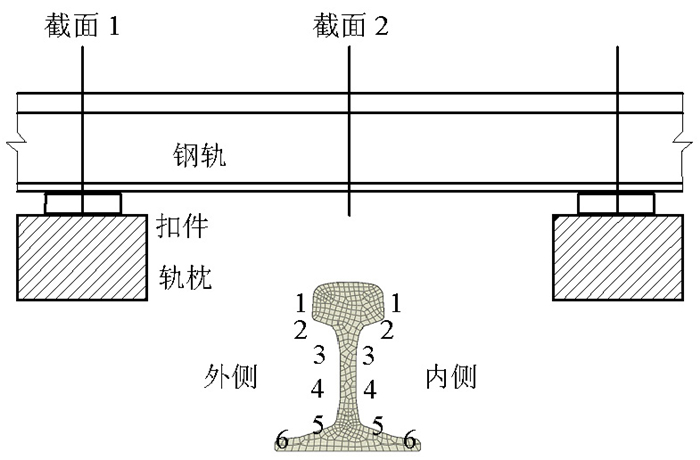
表 1 无砟轨道钢轨垂向加速度
Table 1. Vertical rail acceleration of slab track
m·s-2 外侧测点 测面1 测面2 1 2 980 2 260 2 1 968 2 034 3 500 510 4 604 600 5 470 592 6 397 729 -
COENRAAD E.现代铁路轨道[M]. 2版.王平, 陈嵘, 井国庆, 译.北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2014: 204-205. 李克飞, 刘维宁, 孙晓静, 等.北京地铁5号线高架线减振措施现场测试与分析[J].中国铁道科学, 2009, 30(4):25-29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2009.04.005LI Kefei, LIU Weining, SUN Xiaojing, et al. In-situ test and analysis on the vibration mitigation measures of the elevated line in Beijing Metro Line 5[J]. China Railway Science, 2009, 30(4):25-29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2009.04.005 马春生, 肖宏, 高亮.高速铁路弹性轨枕有砟轨道力学特性试验研究[J].土木工程学报, 2015, 48(增刊2):81-87. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-OGTY201507001201.htmMA Chunsheng, XIAO Hong, GAO Liang. Experimental study on mechanical characteristics of elastic sleeper ballast track on high-speed railways[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2015, 48(Sup. 2):81-87. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-OGTY201507001201.htm 翟婉明.车辆-轨道耦合动力学[M]. 3版.北京:科学出版社, 2007:95-132. BARKE D, CHIU W K. Structural health monitoring in the railway industry:a review[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2005, 4(1):81-93. doi: 10.1177/1475921705049764 刘鹏辉, 杨宜谦, 尹京.地铁隧道内不同轨道结构振动测试与分析[J].振动与冲击, 2014, 33(2):31-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2014.02.006LIU Penghui, YANG Yiqian, YIN Jing. Test and analysis on vibration of different track structures in tunnel[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(2):31-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2014.02.006 LEE M L, CHIU W K. Determination of railway vertical wheel impact magnitudes:Field trials[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2007, 6(1):49-65. doi: 10.1177/1475921707072063 REMINGTON P J. Wheel/rail rolling noise, Ⅱ:Validation of the theory[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1987, 81(6):1824-1832. doi: 10.1121/1.394747 刘林芽, 雷晓燕, 练松良.提速铁路过渡段的动力响应测试分析[J].铁道工程学报, 2005, 22(5):15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2005.05.004LIU Linya, LEI Xiaoyan, LIAN Songliang. Analysis of dynamic response by transition zone of speed-raise railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2005, 22(5):15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2005.05.004 ZHAI Wanming, HE Zhenxing, SONG Xiaolin. Prediction of high-speed train induced ground vibration based on train-track-ground system model[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2010, 9(4):545-554. doi: 10.1007/s11803-010-0036-y 郑国琛, 祁皑.福州地铁运行引起的环境振动加速度预测分析[J].工程力学, 2015, 32(增刊1):331-336, 341. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8419287ZHENG Guochen, QI Ai. Prediction on vibration acceleration of the environment induced by Fuzhou metro[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(Sup.1):331-336, 341. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8419287 翟婉明, 蔡成标, 王开云.高速列车-轨道-桥梁动态相互作用原理及模型[J].土木工程学报, 2005, 38(11):132-137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2005.11.024ZHAI Wanming, CAI Chengbiao, WANG Kaiyun. Mechanism and model of high-speed train-track-bridge dynamic interaction[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2005, 38(11):132-137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2005.11.024 PERSSONⅠ. Documentation of gensys[M]. Östersund: [s. n.], 2000: 1-18. 练松良, 刘扬, 杨文忠.沪宁线轨道不平顺谱的分析[J].同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2007, 35(10):1342-1346. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tjdxxb200710010LIAN Songliang, LIU Yang, YANG Wenzhong. Analysis of track irregularity spectrum of Shanghai-Nanjing railway[J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science, 2007, 35(10):1342-1346. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tjdxxb200710010 LIER S V. The vibro-acoustic modelling of slab track with embedded rails[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2000, 231(3):805-817. doi: 10.1006/jsvi.1999.2564 林红松, 颜华.有轨电车埋入式无砟轨道及关键部件型式研究[J].铁道工程学报, 2016, 33(6):60-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.06.013LIN Hongsong, YAN Hua. Type research on the embedded ballastless track structures and key components of modern tram way[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2016, 33(6):60-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.06.013 -





 下载:
下载: