Field Comparative Experiments of Pipe Pile Composite Foundation with Different Cushion Layers
-
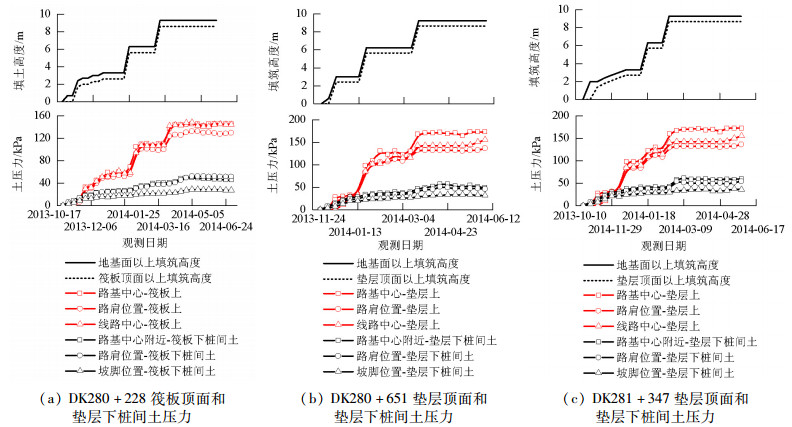
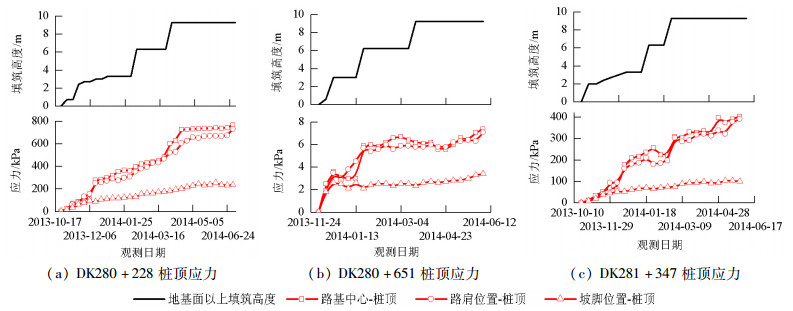
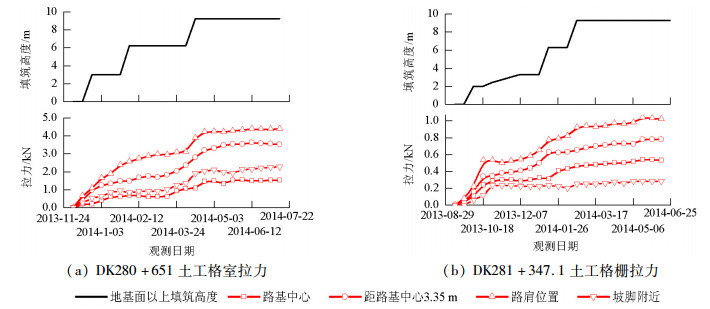
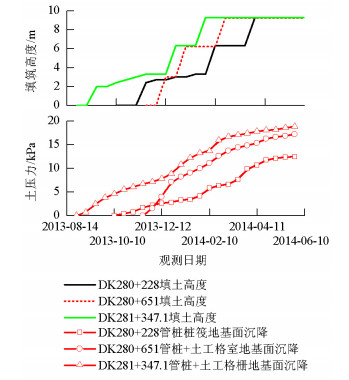
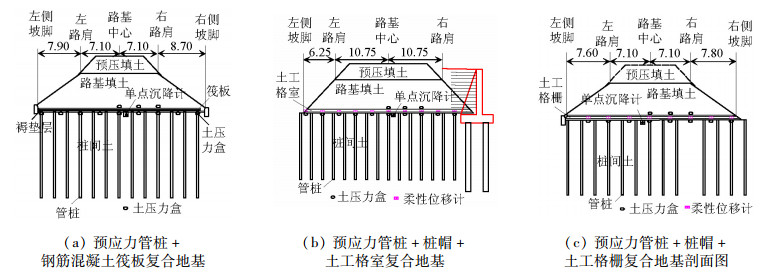
摘要: 为比较管桩+钢筋混凝土板复合地基、管桩+桩帽+土工格室复合地基、管桩+桩帽+土工格栅复合地基的受力和沉降控制效果,开展了3种复合地基处理深厚软土路基的现场试验,分析研究了不同垫层条件下管桩复合地基受力和变形规律,结果表明:路堤荷载作用下,桩顶和桩间土应力由路基中心向路肩、坡脚处逐渐减少,土工格栅垫层时桩土应力比为2.47~5.42,土工格室垫层加固桩土应力比为2.30~6.25;钢筋混凝土板垫层时桩土应力比为8.05~14.81;随着路基填土荷载的增大,土工格栅、土工格室拉力逐渐增大,路肩位置拉力最大,相同荷载作用下土工格室所受拉力大于土工格栅;3种复合地基加固措施中管桩+钢筋混凝土板对路基沉降的加固效果最好,稳定后地基面沉降分别为土工格栅和土工格室桩网复合地基地基面沉降的68.46%和72.56%.Abstract: In order to compare the stress and evaluate the ability to control deep soft soil settlement of three kinds of composite foundations, field experiments were carried out. Each pipe pile composite had a different cushion layer; a reinforced concrete slab, a geocell, and a geogrid, respectively. For the geocell and geogrid composites, a pile cap was added.Both the stress response, and the settlement, of the pipe pile composite foundations, under different cushion layers, were analyzed. The results show that the stress of both the pile's top surface and the soil between the piles was gradually reduced, from the subgrade center to the shoulder. The pile-soil stress ratios were 2.47-5.42, 2.30-6.25, 8.05-14.81 for the geogrid-reinforced cushion layer, the geocell-reinforced cushion layer, and the reinforced concrete slab cushion layer, respectively. As the load of the subgrade filling increased, the tensile strength of both the geogrid and the geocell gradually increased, and maximum tension occurred at the shoulder. The tensile strength of the geocell was greater than that of the geogrid, under the same load. The composite foundation of a pipe pile, plus a reinforced concrete slab is the best for controlling the settlement of the subgrade filling, and the settlement of the ground surface contributes 68.46% and 72.56% of entire settlement of the pipe pile-pile cap-geogrid and the pipe pile-pile cap-geocell composite foundations, respectively.
-
Key words:
- geocell /
- geogrid /
- pipe pile composite foundation /
- settlement /
- pile-soil stress ratio
-
表 1 管桩区填土完毕桩土应力
Table 1. Pile-soil stress ratios at the pipe pile area, after soil filling
分析对象 桩板 土工格栅 土工格室 路基中心 路肩 坡脚 路基中心 路肩 坡脚 路基中心 路肩 坡脚 桩顶土压力/kPa 604.3 520.5 178.0 233.1 198.2 73.0 288.6 238.6 67.2 桩间土土压力/kPa 40.8 38.6 22.1 43.0 39.0 29.5 46.2 41.3 29.2 桩土应力比 14.81 13.48 8.05 5.42 5.08 2.47 6.25 5.78 2.30 表 2 土工格栅、土工格室拉力
Table 2. The tension of the geocell and geogrid
加筋材料 尺寸 设计抗拉强度
/(kN·m-1)拉力/kN 路基中心 距路基中心3.3m 路肩处 靠近坡脚处 土工格栅 2.5 cm×2.5 cm 250 0.461 0.922 0.653 0.250 土工格室 40 cm×40 cm×5 cm 200 1.080 2.800 3.870 1.910 -
连峰, 龚晓南.桩-网复合地基加固机理现场试验研究[J].中国铁道科学, 2008, 29(3):7-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2008.03.002LIAN Feng, GONG Xiaonan. Field test study on the improvement mechanism of pile-net composite foundation[J]. China Railway Science, 2008, 29(3):7-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2008.03.002 邵国霞, 苏谦, 陈尚勇, 等.柔性荷载作用下桩筏加固地基变形特性试验研究[J].西南交通大学学报, 2017, 52(1):30-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.005SHAO Guoxia, SU Qian, CHEN Shangyong, et al. Experimental research on deformation characteristics of piled raft foundation under flexible load[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(1):30-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.005 李善珍, 马学宁, 时瑞国.高速铁路桩(帽)网和桩筏复合地基模型试验研究[J].铁道科学与工程学报, 2016, 13(4):600-605. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2016.04.002LI Shanzhen, MAXuening, SHI Ruiguo. Experimental study on CFG pile-(cap-)-net and pile-raft composite foundations of high speed railway[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2016, 13(4):600-605. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2016.04.002 苏谦, 李安洪, 罗照新, 等.桩顶加筋灰土垫层理论分析与工程设计探讨[J].岩土力学, 2008, 29(10):2687-2696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.10.018SU Qian, LI Anhong, LUO Zhaoxin, et al. Theoretical analysis of reinforced lime soil cushion above pile and its engineering design[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(10):2687-2696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.10.018 陈宏伟, 徐林荣.桩-筏(网)复合地基桩土应力比现场测试研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(6):63-69. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1718408CHEN Hongwei, XU Linrong. Field experiment of pile-soil stress ratio of pile-raft (net) composite foundation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(6):63-69. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1718408 雷正敏.复合地基桩网结构的加固机理及其设计方法探讨[J].铁道建筑技术, 2013(10):56-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2013.10.019LEI Zhengmin. Reinforcement mechanism and design method of pile-net composite foundation[J]. Railway Construction Technology, 2013(10):56-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2013.10.019 陈仁朋, 陈金苗, 汪焱卫, 等.桩网结构路基应力传递特性及累积沉降规律[J].土木工程学报, 2015, 48(增刊2):241-245. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90342X/2015S2/84777167504849538350485252.htmlCHEN Renpeng, CHEN Jinmiao, WANG Yanwei, et al. Stress transmission and cumulative settlement characteristics of geogrid reinforced pile supported embankment[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2015, 48(Sup.2):241-245. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90342X/2015S2/84777167504849538350485252.html 罗强.土工合成材料加筋砂垫层减小软土地基沉降试验研究[J].岩土工程学报, 2003, 25(6):710-714. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2003.06.014LUO Qiang. Application of geosynthetics-reinforced sand blanket to settlement reduction of soft ground[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2003, 25(6):710-714. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2003.06.014 苏谦.土工格栅、格室加筋砂垫层大模型试验及抗变形能力分析[J].西南交通大学学报, 2001, 36(2):176-180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2001.02.016SU Qian. Geogridand geocell-reinforced sand blanket:model test and the ability to reduce deformation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2001, 36(2):176-180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2001.02.016 陈昌富, 米汪, 赵湘龙.考虑高路堤土拱效应层状地基中带帽刚性桩复合地基的承载特性[J].中国公路学报, 2016, 29(7):1-9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.07.001CHEN Changfu, MI Wang, ZHAO Xianglong. Bearing characteristic of composite foundation reinforced by rigid pile with cap in layered ground considering soil arching effect of high embankment[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(7):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.07.001 曹新文.桩网复合地基土工格栅加筋效应的试验研究[J].岩土力学与工程学报, 2006, 125(1):3162-3167. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2006z1088CAO Xinwen. Experimental study on reinforcement effect of geogrid on composite foundation with dry jet mixing piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 125(1):3162-3167. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2006z1088 丁铭绩.京津客运专线路基桩板复合地基沉降特性研究[D].北京: 北京交通大学, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10004-2009126375.htm 赵明华, 龙军, 张玲, 等.不同型式复合地基试验对比分析[J].岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(4):611-618. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20132013051500051484ZHAO Minghua, LONG Jun, ZHANG Ling, et al. Comparative analysis of model tests on different types of composite foundations[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(4):611-618. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20132013051500051484 荆志东, 郭永春.新型桩板结构对高速铁路软基沉降控制作用离心试验[J].岩土力学, 2010, 31(8):2565-2574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.08.036JING Zhidong, GUO Yongchun. Centrifuge test of new pile-plate structure embankment settlement of soft soil of high-speed railway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(8):2565-2574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.08.036 赵伟, 杨果林.路堤下桩-网复合地基桩土应力现场试验研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 2009(3):95-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.03.020ZHAO Wei, YANG Guolin. Field experimental study on pile-soil stress ratio of pile-net composite foundation under embankment[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2009(3):95-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.03.020 -





 下载:
下载: