Simplified Method for Analysing Pile-Supported Embankment Settlements over Soft Soil
-
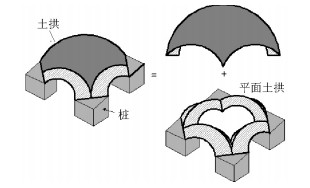
摘要: 针对路堤荷载作用下桩土复合地基的沉降计算,传统方法主要是把沉降分为加固区沉降和非加固区沉降两部分来考虑,存在着计算假设与实际不符、部分参数取值依赖于经验和无法较好考虑成层场地非均质性等缺点.基于此,通过引入均匀系数来考虑地基表面荷载分布的不均匀性,改进了正方形和三角形布桩条件下Hewlett & Randolph土拱模型,在此基础上,考虑桩土相互作用提出了一种桩土复合地基沉降的简化分析方法.该方法首先根据土拱模型和Vesic球孔扩张法分别计算桩顶、地基表面荷载和桩端力;然后采用可以考虑多土层的非均质地基土情况修正Mindlin解求得桩端力、地基表面荷载和桩侧摩阻力在地基内任意点引起的附加应力;其次通过分层总和法计算附加应力引起的沉降;最后将各分项沉降进行组合即可得到桩顶和地基表面沉降.将该计算方法结果与现场实测和数值分析结果进行对比,研究结果发现:简化分析方法的计算精度基本保持在5.0%~14.4%,计算精度能够满足工程需求.
-
关键词:
- 软土 /
- 桩承式路堤 /
- 沉降 /
- 土拱 /
- 修正Mindlin解
Abstract: A method for the settlement of pile-supported embankments over soft soil with due consideration of soil arching and pile-soil interactions is proposed. Traditionally, settlements comprising composite foundations and built under embankments are usually divided into two parts-reinforced and un-reinforced. However, when calculating the settlements, some assumptions which are somewhat disaccordance with the truth are made. In addition, some parameters employed in some traditional methods are uncertain and the nonuniformity of layered site is hardly to be considered. Therefore the access to a more accurate analytical results is restricted.Based on the arching model proposed by Hewlett and Randolph, a uniform coefficient has herein been incorporated to allow for evaluation of non-uniform vertical stresses acting on the soft ground. This, in turn, serves to deduce solutions for the arching effect in square and triangular pile configurations. In the method proposed, the load acting on the pile head and the resulting subsoil reaction could be evaluated through analysis of the soil-arching effect. The load at the pile tip can be calculated by employing the spherical cavity expansion theory. Subsequently, additional stresses induced by the load at the pile tip, subsoil reaction, and skin friction acting on the pile could be obtained through use of revised Mindlin's solution by considering the ground to be comprised of multi-layered soil. Settlement results, obtained by accounting for additional stresses, could then be calculated using the layer-wise summation method. Settlements of the pile head and ground surface could, thus, be evaluated by superimposing different partial settlements. The proposed method serves to analyse pile-head as well as ground-surface settlements and offers the advantage that the parameters employed in the analysis could be conveniently adopted and that the deduction procedure is concise. Comparison of results obtained using the proposed method with observed data and numerical results demonstrates that the proposed method is capable of accurately estimating the settlement of piles as well as ground surface of pile-supported embankments with only a slight deviation that varies from 5.0% to 14.4%, which is an acceptable value by engineering standards.-
Key words:
- soft soil /
- pile-supported embankment /
- settlement /
- soil arching /
- the revised Mindlin's solution
-
表 1 土体物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechnical parameters of soil
土层 厚度/m γ/(kN·m-3) 含水率w Cc/(1+e0) 塑限Ip 有效摩擦角φr 有效粘聚力cr 黏性填土 1.5 19.6 31 0.10 22 30 4 黏土 1.0 14.1 60 0.20 — 30 4 砂质黏土 6.0~8.0 20.8 31 0.07 12 26 13 街旅砾石 1.5 20.0 — 0.05 — 34 0 表 2 路堤填土、致密砾石和桩的参数
Table 2. Parametes of soil and pile
土层 γ
/(kN·m-3)φ c 杨氏模量/MPa ν 路堤填土 18.5 30 10 20 0.3 垫层砾石 20.0 26 60 70 0.3 桩 24.0 — 18 000 20 000 0.2 表 3 不同计算方法得到的桩和土沉降
Table 3. Calculated and observed settlement of pile and soil
mm 不同方法 本文理论计算 现场实测结果 数值分析结果 桩顶 7.6 8 9.9 桩间土 92.4 105 67.0 表 4 模型的几何参数和材料物理力学参数
Table 4. Material properties used in the numerical modeling and the proposed analytical solution
参数 路堤 软土 硬土 桩 桩帽 高度/m 4 — — — — 内摩擦角/(°) 30 9 22 — — 粘聚力/kPa 0 15 30 — — 杨氏模量/GPa 0.03 — — 35.00 35.00 压缩模量/MPa — 2.2 15.0 — — 泊松比 0.25 0.35 0.35 0.15 0.15 填土重度/(kN·m-3) 20.0 17.5 18.0 — — 桩间距/m — — — 2.5 1.0 直径/m — — — 0.40 1.13 表 5 不同计算方法得到的沉降
Table 5. The settlement by theoretical methods and numerical anaysis
mm 位置 工况 本文理论 数值分析 Chen模型 桩顶 1 131.0 148.0 141.0 2 16.3 12.0 21.0 桩间土 1 152.0 168.0 165.0 2 37.4 32.0 43.0 -
MAGAN J P. Methods to reduce the settlement of embankments on soft clay:a review[J]. Vertical & Horizontal Deformations of Foundatio Embankments, 2015, 1(40):77-91. https://cedb.asce.org/CEDBsearch/record.jsp?dockey=0088841 LIU H L, NG C W W, FEI K. Performance of a geogrid-reinforced and pile-supported highway embankment over soft clay case study[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2007, 133(12):1483-1493. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:12(1483) 陈云敏, 贾宁, 陈仁朋.桩承式路堤土拱效应分析[J].中国公路学报, 2004, 17(4):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2004.04.001CHEN Yunmin, JIA Ning, CHEN Renpeng. Soil arch analysis of pile-supported embankments[J]. Chinese Journal of Highway and Transport, 2004, 17(4):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2004.04.001 LU W H, MIAO L C. A simplified 2-D evaluation method of the arcing effect for geosynthetic-reinforced and pile-supported embankments[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2015, 65(65):97-103. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0266352X14002195 ABUSHARAR S W, ZHENG J J, CHEN B G, et al. A simplified method for analysis of a piled embankment reinforced with geosynthetics[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2009, 27(1):39-52. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2008.05.002 EEKELEN S J M V, BEZUIJEN A, TOL A F V. Validation of analytical models for the design of basal reinforced piled embankments[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2015, 43(1):56-81. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2014.10.002 ZHANG C L, JIANG G L, LIU X F, et al. Arching in geogrid-reinforced pile-supported embankments over silty clay of medium compressibility:field data and analytical solution[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2016, 77:11-25. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.03.007 CHEN R P, CHEN Y M, HAN J, et al. A theoretical solution for pile-supported embankments on soft soils under one-dimensional compression[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Engineering, 2008, 45(6):611-623. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=239fd43fd2047558d2b37ff3e6fd86cd HAN J, OZTOPRAK S, PARSON R L, et al. Numerical analysis of foundation columns to support widening of embankments[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2007, 34(6):435-448. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2007.01.006 SHAHIRA H, PAK A. Estimating liquefaction-induced settlement of shallow foundation by numerical approach[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2010, 37(3):267-279. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2009.10.001 中国建筑科学研究院. JGJ79-2012中华人民共和国行业标准建筑地基处理技术规范[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. 龚晓南.复合地基理论及工程应用[M].北京:中国建筑工业出版社, 2002:150-151. 池跃君, 宋二祥, 陈肇元.刚性桩复合地基沉降计算方法的探讨及应用[J].土木工程学报, 2003, 36(11):19-23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2003.11.004CHI Yuejun, SONG Erxiang, CHEN Zhaoyuan. An simplified method for settlement of rigid-pile composite foundation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2003, 36(11):19-23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2003.11.004 闫宝杰, 宋修广, 岳越群.粉喷桩复合地基附加应力的Boussinesq-Mindlin联合解法[J].岩土力学, 2007, 28(6):1255-1258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.06.037YAN Baojie, SONG Xiuguang, YUE Yuequn. Boussinesq-Mindlin united solution method for DJMP composite foundation additional stress[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(6):1255-1258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.06.037 陈永辉, 王新泉, 刘汉龙, 等. Y型桩桩侧摩阻力产生附加应力的分析计算[J].岩土力学, 2008, 29(11):2905-2911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.11.004CHEN Yonghui, WANG Xinquan, LIU Hanlong, et al. Analysis and calculation of additional stress due to skin friction of Y-shaped vibro-pile[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(11):2905-2911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.11.004 HELWETT W J, RANDOLPH M F. Analysis of piled embankment[J]. Ground Engineering, 1988, 21(3):12-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201509016 LOW B K, TANG S K, CHOA V. Arching in piled embankments[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1994, 120(11):1917-1938. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1994)120:11(1917) YASUFUKU N, HYDE A F. Pile end-bearing capacity in crushable sands[J]. Geotechnique, 1995, 45(4):663-676. doi: 10.1680/geot.1995.45.4.663 VESIC A S. Bearing capacity of deep foundations in sand[J]. Highway Research Record, 1963, 10(39):112-153. https://trid.trb.org/view.aspx?id=126654 刘俊飞.铁路CFG复合地基沉降控制机理与计算方法研究[D].成都: 西南交通大学, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10613-1011233264.htm MINDLIN R D. Force at a point in the interior of a semiinfinite solid[J]. Physics, 1936, 7(5):195-202. doi: 10.1063/1.1745385 张乾青.软土地基桩基受力性状和沉降特性试验与理论研究[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 2012. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KJYQ201320225.htm VESIC A S. Design of pile foundation[M]. Washington:National Cooperative Highway Research Program Synthesis of Practice, 1977:31-32. ZHUANG Y, WANG K Y, LIU H L. A simplified model to analyze the reinforced pile embankments[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2014, 42(2):154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2014.01.002 BRIANCON L, SIMON B. Performance of pile-supported embankment over soft soil full-scale experiment[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2011, 138(4):551-561. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=78359dcf70955a1ead0458790558c261 ROWE R K, LIU K W. Three-dimensional finite element modelling of a full-sacle geosynthetic-reinforced, piled-supported embankment[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 52(12):2041-2054. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2014-0506 -





 下载:
下载: