Corrosion Rate of Non-Galvanized High-Strength Steel Wires under Different Temperature and Humidity Conditions
-
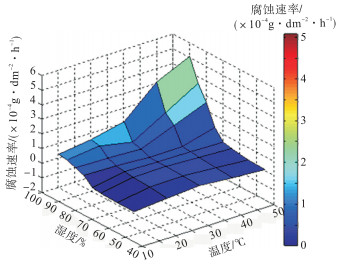
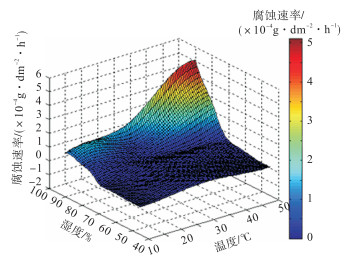
摘要: 为了预测主缆钢丝在服役过程中的腐蚀发展,计算了主缆钢丝在不同温度和湿度环境条件下的腐蚀速率,将主缆腐蚀环境的温度和湿度划分为5个等级,采用正交试验方法将其进行正交组合,控制恒温恒湿试验箱实验温度和湿度,利用微型极化电阻腐蚀传感器测量未镀锌高强钢丝的腐蚀速率,获得了温度、湿度与腐蚀速率的关系和耦合效应.试验结果表明:可将环境湿度70%、温度10℃以下区域归为钢丝弱腐蚀区;湿度75%以下、温度20~50℃区域归为钢丝低腐蚀区;湿度75%以上、温度10~50℃区域归为钢丝强腐蚀区.Abstract: This study helps to calculate the corrosion of steel wires of the main cable under different temperature and humidity conditions. The temperature and humidity conditions of the corrosive environment in which the main cable was placed were divided into five levels. Orthogonal experimental was conducted in this study. The corrosion rate of non-galvanized steel wires was measured by micro-polarization resistance corrosion sensors. The temperature and humidity conditions were controlled by a constant chamber. The experimental results provided the primary and secondary relation among temperature, humidity and corrosion rate. The results also provided the regression equation of the corrosion rate of non-galvanized steel wire under varying temperature and humidity conditions through regression fitting. On the basis of the corrosion rate results, corrosion areas were classified into three areas, weak corrosion area for humidity of 70% and temperature below 10℃. Low corrosion area for humidity below 75% and temperature of 20-50℃. Strong corrosion area for humidity of 75% or more and temperature of 10-50℃.
-
表 1 正交试验各因素取值设计表
Table 1. Values of each factor of orthogonal experiment design table
取值等级 温度/℃ 相对湿度/% 1 10 40~50 2 20 50~60 3 30 70 4 40 80 5 50 90 表 2 湿度因素取值设计表
Table 2. Values of humidity factor design table
取值等级 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 相对湿度/% 40~50 50~60 65 70 75 80 85 90 表 3 不同温度湿度组合条件下钢丝腐蚀速率值
Table 3. Corrosion rate values of steel wires for various temperature and humidity conditions
×10-4g/(dm2·h) 温度/℃ 湿度/% 40~50 50~60 65 70 75 80 85 90 10 0.017 6 0.021 3 0.089 1 0.164 0 0.701 0 0.930 0 1.153 0 1.201 0 20 0.229 0 0.447 0 0.453 0 0.567 0 0.645 0 0.875 0 1.372 0 1.523 0 30 0.434 0 0.469 0 0.499 0 0.518 0 0.525 0 0.787 0 0.948 0 2.068 0 40 0.262 0 0.318 0 0.435 0 0.499 0 0.533 0 1.676 0 2.283 0 4.038 0 50 0.117 0 0.152 0 0.351 0 0.477 0 1.172 0 2.561 0 3.592 0 5.082 0 表 4 温度、湿度与腐蚀速率的2k因子
Table 4. Temperature, humidity and corrosion rate of 2k factor table
因素取值 因素组合 重复试验 腐蚀速率/(×10-4g·dm-2·h-1) 标记符号 A B 1 2 3 总和 均值 - - A低B低 0.017 4 0.017 1 0.017 2 0.051 7 0.017 2 (1) + - A高B低 0.114 0 0.118 0 0.117 0 0.349 0 0.116 0 a - + A低B高 1.356 0 1.171 0 1.077 0 3.604 0 1.201 0 b + + A高B高 5.203 0 5.209 0 5.001 0 22.205 0 5.138 0 ab 表 5 正交试验结果极差分析
Table 5. Range analysis table of orthogonal test results
组均值 k A因素 B因素 k1 0.855 0.212 k2 1.222 0.281 k3 1.249 0.365 k4 2.009 0.445 k5 2.701 0.715 k6 - 1.366 k7 - 1.869 k8 - 2.782 R 1.845 2.570 表 6 正交试验结果方差分析计算
Table 6. Variance analysis table of orthogonal test results
因素 A B 计算式[15] K1 2.334 1.059 6 $ K=25∑i=1xi=25.4420P=125K2=25.8910W=25∑i=1x2i=63.7760$ K2 3.641 1.407 3 K3 4.276 2.225 0 K4 6.793 6.829 0 K5 8.389 13.921 0 Q 30.715 49.696 0 S 4.823 23.805 0 表 7 方差分析显著性计算
Table 7. Significant calculation table of variance analysis
方差来源 变差平方和 自由度 均方 F比 F统计量 显著性 A 4.823 4 1.206 2.086 F0.05(4, 24)=5.77 不显著 B 23.805 4 5.951 10.295 F0.05(4, 24)=5.77 显著 e 9.257 16 0.578 — — — 总和 37.885 24 — — — — 表 8 拟合回归统计结果
Table 8. Table of fitting regression statistics
拟合式 复相关系数 复测定系数 标准差 Q 1 0.952 0.906 0.039 0.016 2 0.937 0.878 0.031 0.009 -
孙跃, 胡津.金属腐蚀与控制[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2003:1-9. BETTI R, YANEV B. Corrosion monitoring research of new york city bridges[R]. Washington D. C.: Transportation Research Board, 2013. https://trid.trb.org/view/1286050 National Cooperative Highway Research Program. NCHRP-Report[R]. New York: [s.n.], 2004. 陈小雨, 沈锐利, 张培炎.悬索桥主缆的内部检测[J].世界桥梁, 2013, 41(1):86-90. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gwql201301019CHEN Xiaoyu, SHEN Ruili, ZHANG Peiyan. Internal inspection of suspension bridge main cable[J]. World Bridges, 2013, 41(1):86-90. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gwql201301019 SUZUMURA K, NAKAMURA S I. Environmental factors affecting corrosion of galvanized steel wires[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2004, 16:1-7. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2004)16:1(1) 黎学明, 陈大华.模拟酸雨溶液中温度对桥梁索缆镀锌钢丝腐蚀行为影响[J].腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2010, 22(1):14-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CAS201303040000304935LI Xueming, CHEN Dahua. Effect of temperature on corrosion behavior of galvanized steel bridge wires in simulated acid rain[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2010, 22(1):14-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CAS201303040000304935 杨文静, 黎学明, 周建庭.大跨度桥梁缆索模拟酸雨加速腐蚀行为研究[J].腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2011, 23(1):65-68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FSFJ201101018.htmYANG Wenjing, LI Xueming, ZHOU Jianting. Research of accelerated corrosion behavior of long-span bridge cable simulated acid rain[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2011, 23(1):65-68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FSFJ201101018.htm BETTI R, MARCONI G, KHAZEM D, et al. Experimental analysis of a nondestructive corrosion monitoring system for main cables of suspension bridges[J].Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2013, 18(7):653-662. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000399 缪长青, 尉廷华.大跨桥梁缆索钢丝腐蚀速率的研究[J].西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(3):513-518. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.03.022MIAO Changing, WEI Tinghua. Corrosion rate test of cable wires of large span bridge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(3):513-518. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.03.022 CHEN Xiaoyu, TANG Maolin. Influence analysis of the corrosion factors effect on the corrosion rate of steel wires of main cable of suspension bridge[C]//IABSE Conference. Guangzhou: [s.n.], 2016: 155-163. https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/iabse/report/2016/00000106/00000011/art00008 施彦彦.典型金属材料大气腐蚀的模拟电化学研究[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 2008. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1378979 俞明德, 沈锐利, 唐茂林, 等.西堠门大桥主缆横断面温度场研究[J].建筑科学与工程学报, 2010, 27(3):53-58. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbjzgcxyxb201003010YU Mingde, SHEN Ruili, TANG Maolin, et al. Research on temperature field of main cable section of xihoumen bridge[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 2010, 27(3):53-58. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbjzgcxyxb201003010 杨宁.大跨度悬索桥的主缆除湿防护系统[D].上海: 同济大学, 2006. DOUGLAS W B, RICHARD J. Linear polarization resistance sensor using the structure as a working electrode[C]//European Conference of The Prognostics and Health Management Society. Santa Clara: [s.n.], 2014: 1-7. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.655.3670 何为, 薛卫东.优化试验设计方法与数据分析[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2012:29-284. -





 下载:
下载: