Numerical Simulation of Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flow at Various Inlet Positions in Bubble Column at Low Gas Velocity
-
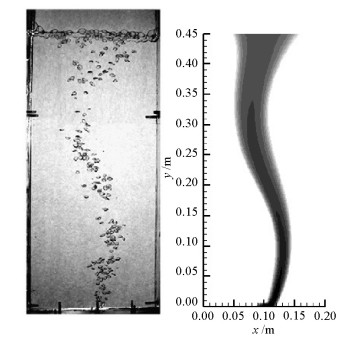
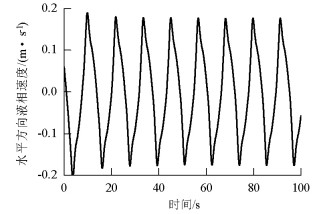
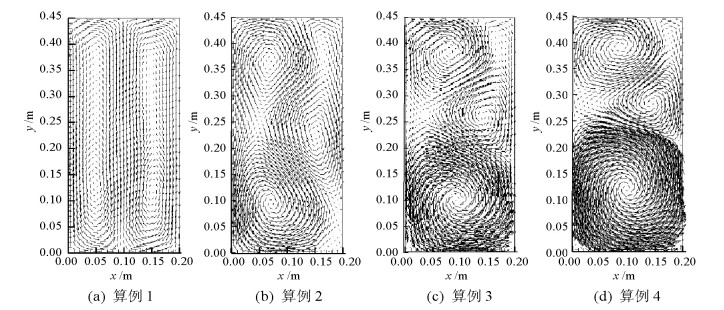
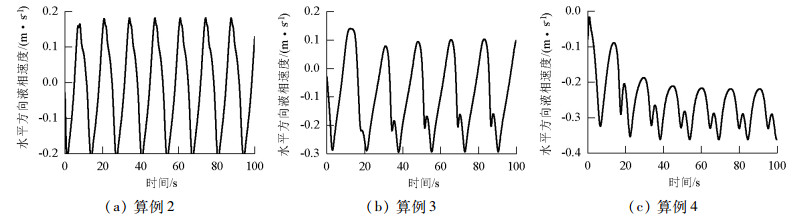
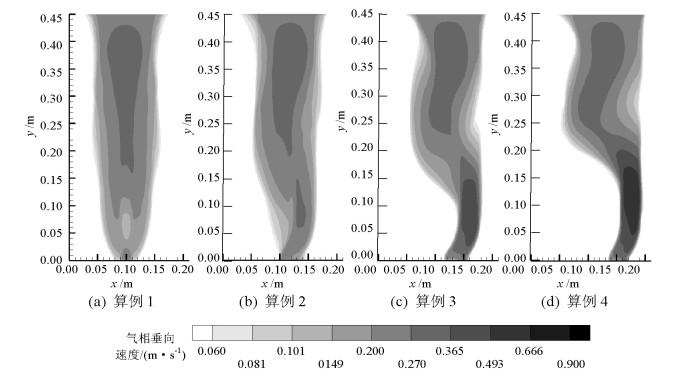
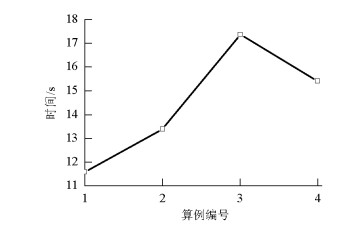
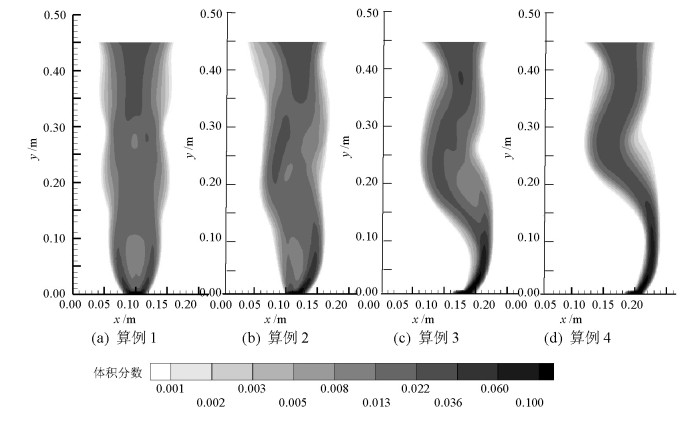
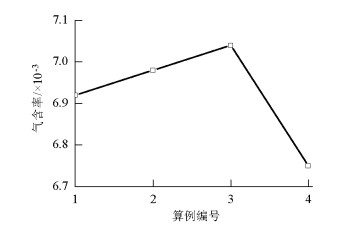
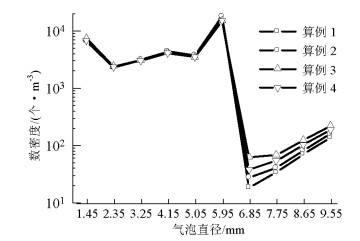
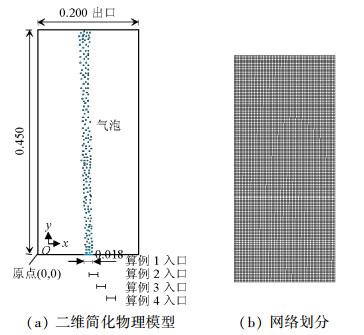
摘要: 为了研究不同入口下塔式曝气池气液两相流动规律,采用欧拉双流体模型耦合群体平衡模型(PBM,population balance model),在对计算域网格及气相分布与实验验证的基础上,研究了四种距离曝气池底部中心不同位置处的入口对曝气池内气液两相流动的影响,探讨了气含率、气泡数密度、液相水平速度等流体动力学性质,以期为塔式曝气池设计提供指导和依据.研究结果表明:欧拉双流体模型耦合PBM的模拟结果优于单一气泡尺寸的欧拉双流体模型;曝气池内气含率、气相分布、旋涡强度、液相水平速度均受入口位置影响;当入口位置逐渐远离曝气池中心时,气相分布逐渐呈之字形,旋涡强度增大,气含率及气泡羽流周期则先增大后减小;入口位置对气泡数密度无明显影响,气泡数密度在气泡直径5.95 mm下分布最多.Abstract: In order to examine the law of the gas-liquid two-phase flow at various inlet positions of a bubble column, an Euler-Euler two-fluid model coupled with the population balance model (PBM) was used to simulate the effects of four inlets at various positions in the middle of the bubble column bottom on gas-liquid two-phase flow in the bubble column. We verified the mesh of the computational domain and gas hold-up distribution by comparing with experimental data. This study also investigated dynamic behaviours of gas hold-up, bubble number density, liquid horizontal velocity, etc., which provide instructions and basis for the design of the bubble column. The simulated results using an Euler-Euler two-fluid model with PBM were found to be consistent with the experimental results and better than those calculated using an Euler-Euler two-fluid model with single bubble diameter. Furthermore, the dynamic behaviours of gas hold-up, liquid horizontal velocity, distribution of gas hold-up, and vortex strength were all affected by the inlet position. When the inlet was farther from the middle of the bottom of the bubble column, the gas hold-up had an S-shaped distribution and the vortex strength increased; the gas hold-up and bubble plume oscillation period initially increased and then decreased. The bubble number density was not significantly affected by the inlet positions in the bubble column. Moreover, the group with the bubble diameters of 5.95 mm had the largest bubble number density.
-
表 1 气泡直径分组
Table 1. Bubble size group discretization
组号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 尺寸/mm 1.45 2.35 3.25 4.15 5.05 5.95 6.85 7.75 8.65 9.55 表 2 网格及计算参数验证
Table 2. Verification of mesh and calculated parameters
网格单元数量 时间步/s 最大迭代步 气含率 5 763 0.010 0 30 0.006 70 7 353 0.010 0 30 0.006 64 10 050 0.010 0 30 0.006 92 14 400 0.010 0 30 0.006 83 22 725 0.010 0 30 0.006 64 10 050 0.002 5 30 0.006 92 10 050 0.005 0 30 0.006 92 10 050 0.020 0 30 0.006 95 10 050 0.010 0 10 0.006 93 注:实验气含率为0.006 90. -
李孟, 李向阳, 王宏智, 等.鼓泡塔气液两相流不同曳力模型的数值模拟[J].过程工程学报, 2015, 15(2):181-189. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgyj201502001LI Meng, LI Xiangyang, WANG Hongzhi, et al. Numerical simulation of gas-liquid two-phase flow in a bubble column with various drag models[J]. Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2015, 15(2):181-189. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgyj201502001 金丹.塔式曝气池内气液两相流动数值模拟及参数影响的研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2006. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10213-2007033726.htm 魏文礼, 赵小军, 刘玉玲.气泡浮力羽流动力特性三维数值模拟研究[J].西北农林科技大学学报自然科学版, 2014, 42(5):229-234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbnydxxb201405035WEI Wenli, ZHAO Xiaojun, LIU Yulin. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of dynamic characteristics of air bubble buoyancy plume[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University:Nat. Sci. Ed., 2014, 42(5):229-234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbnydxxb201405035 ALI B A, KUMAR C S, PUSHPAVANAM S. Analysis of liquid circulation in a rectangular tank with a gas source at a corner[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 144(3):442-452. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.07.009 肖柏青, 张法星, 戎贵文.气泡尺寸对曝气池内气液两相流数值模拟的影响[J].中国环境科学, 2012, 32(11):2006-2010. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.11.012XIAO Baiqing, ZHANG Faxing, RONG Guiwen. Influence of the bubble size on numerical simulation of the gas-liquid flow in aeration tanks[J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32(11):2006-2010. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.11.012 LEHR F, MILLIES M, MEWES D. Bubble-size distributions and flow fields in bubble columns[J]. AIChE Journal, 2002, 48(11):2426-2443. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1547-5905 邢楚填.鼓泡床反应器实验研究及CFD-PBM耦合模型数值模拟[D].北京: 清华大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10003-1015003690.htm WANG T, WANG J. Numerical simulations of gas-liquid mass transfer in bubble columns with a CFD-PBM coupled model[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(24):7107-7118. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2007.08.033 GUPTA A, ROY S. Euler-Euler simulation of bubbly flow in a rectangular bubble column:experimental validation with radioactive particle tracking[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 225(1/2/3/4/5/6):818-836. http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201500096707 徐琰, 董海峰, 田肖, 等.鼓泡塔中离子液体-空气两相流的CFD-PBM耦合模拟[J].化工学报, 2011, 62(10):2699-2706. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2011.10.004XU Yan, DONG Haifeng, TIAN Xiao, et al. CFD-PBM coupled simulation of ionic liquid-air two-phase flow in bubble column[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 62(10):2699-2706. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2011.10.004 LI G, YANG X, DAI G. CFD simulation of effects of the configuration of gas distributors on gas-liquid flow and mixing in a bubble column[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(24):5104-5116. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2009.08.016 DÍAZ M E, IRANZO A, CUADRA D, et al. Numerical simulation of the gas-liquid flow in a laboratory scale bubble column:Influence of bubble size distribution and non-drag forces[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 139(2):363-379. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2007.08.015 CLIFT R, GRACE J R, WEBER M E. Bubbles, drops, and particles[M]. London:Academic Press, 1978:97-146. LIANG X F, PAN H, SU Y H, et al. CFD-PBM approach with modified drag model for the gas-liquid flow in a bubble column[J]. Chemical Engineering Research & Design, 2016, 112:88-102. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1c58c6d3a71a3e6743d212a66d355eff LABORDE-BOUTET C, LARACHI F, DROMARD N, et al. CFD simulation of bubble column flows:investigations on turbulence models in RANS approach[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(21):4399-4413. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2009.07.009 HAGESAETHER L, JAKOBSEN H A, SVENDSEN H F. A model for turbulent binary breakup of dispersed fluid particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2002, 57(16):3251-3267. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2509(02)00197-5 HAGESAETHER L, JAKOBSEN H A, KAI H, et al. A coalescence and breakup module for implementation in CFD-codes[J]. Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, 2000, 8(0):367-372. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC027047405 LUO H, SVENDSEN H F. Theoretical model for drop and bubble breakup in turbulent dispersions[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1996, 66(5):766-776. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=98bf560591c7434318c40dbb975292a8 LUO H. Coalescence, breakup and liquid circulation in bubble column reactors[D]. Trondheim: Norwegian Institute of Technology, 1993. 罗玮.曝气池中气液两相流PIV实验研究及数值模拟[D].西安: 西安理工大学, 2006. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10700-2006047161.htm 肖浩飞.曝气池内气液两相流CFD数值模拟[D].上海: 东华大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10255-2010060817.htm 徐礼嘉, 陈彩霞, 夏梓洪, 等.鼓泡塔内气泡羽流周期性摆动的数值模拟[J].化学工程, 2012, 40(9):48-51. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hxgc201209011XU Lijia, CHEN Caixia, XIA Zihong, et al. Numerical simulation of bubble plume periodic oscillation in bubble column[J]. Chemical Engineering, 2012, 40(9):48-51. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hxgc201209011 BUWA V V, RANADE V V. Dynamics of gas-liquid flow in a rectangular bubble column:experiments and single/multi-group CFD simulations[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2002, 57(22/23):4715-4736. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009250902002749 肖柏青, 张法星, 刘春艳, 等.曝气池内气泡羽流附壁效应的试验研究[J].水力发电学报, 2012, 31(4):104-107. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slfdxb201204020XIAO Baiqing, ZHANG Faxing, LIU Chunyan, et al. Coanda effect of bubble plume in aeration tanks[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2012, 31(4):104-107. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slfdxb201204020 -





 下载:
下载: