Numerical Study of Horizontal Wave Load on Composite Pile Foundation in Marine Environment
-
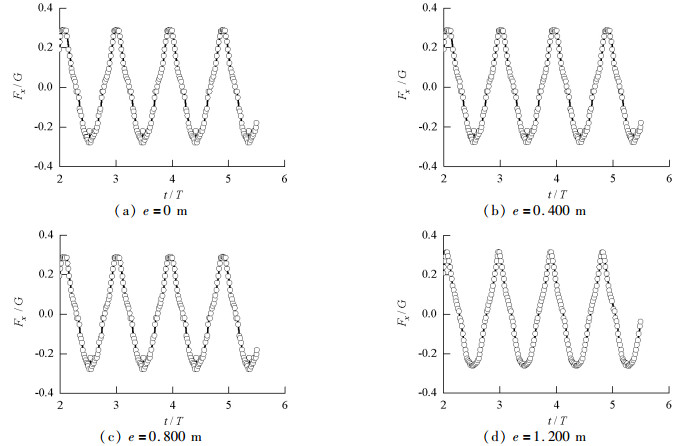
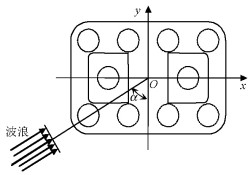
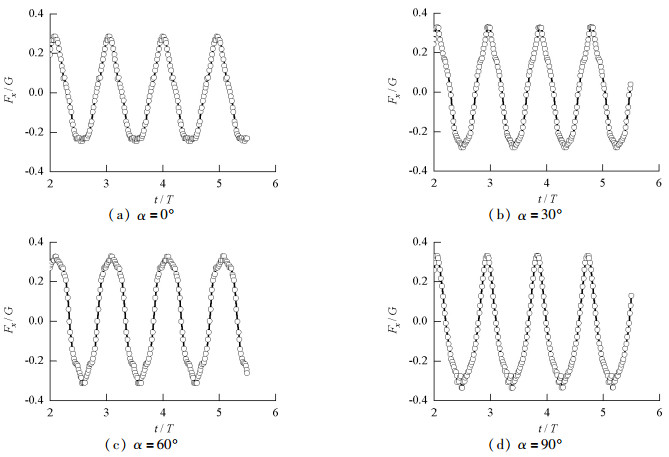
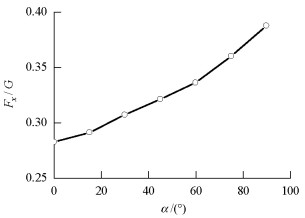
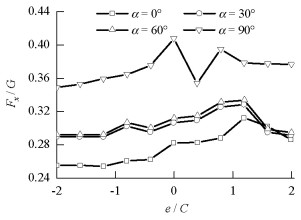
摘要: 为研究承台淹没深度及波浪入射角对桩-承台复合基础水平方向波浪荷载的影响,以平潭海峡公铁两用大桥某复合基础为研究对象,通过求解RANS方程(Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equation)和k-ε湍流模型,借助FLOW-3D软件建立了波浪与复合基础相互作用的三维数值模型.研究了承台淹没深度及波浪入射角对复合基础水平方向波浪荷载的影响,并给出了不同波浪入射角下复合基础水平方向波浪荷载幅值随承台淹没深度的变化曲线.研究结果表明:承台位于波峰与波谷之间时,复合基础所受波浪荷载较大,承台淹没深度为1倍承台高度时波浪荷载达到峰值;当波浪入射角定义为承台长轴线与波浪传播方向之间夹角时,复合基础所受波浪荷载随着波浪入射角增大,当波浪入射角达到90°时,波浪荷载最大,其值约为波浪入射角为0°时的1.4倍左右.Abstract: To investigate the effects of pile cap submerged depth and wave obliquity on wave load on a composite pile foundation, a three-dimensional numerical model for wave-structure interaction around the Pingtan Strait railway bridge foundation was established. This model was based on the CFD code FLOW-3D, in which the Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equation and k-ε turbulence model are used for wave simulations. After validating by analytical solutions and previous laboratory experiments, the model was used to study the effects of pile cap submerged depth and wave obliquity on wave load on the composite foundation. The numerical results indicate that the pile cap submerged depth can significantly affect the wave load on the composite pile foundation, and the wave load on the pile foundation is maximum when the submerged depth is approximately 1 times the pile cap thickness. In addition, the horizontal wave load on the composite foundation increases with the increment of wave incidence angle when the incidence wave angle is defined as the angle between the long axis of the cap and the wave propagation direction. When the wave incidence angle is 90°, the wave load on the foundation is approximately 1.4 times that with a wave incidence angle of 0°.
-
Key words:
- RANS /
- pile cap submerged depth /
- wave obliquity /
- composite foundation /
- wave
-
表 1 沿x轴网格尺寸分布
Table 1. Distribution of cell size in direction of the x-axis
x/m 0~100 100~200 200~300 网格尺寸/m 0.5 0.1 0.5 表 2 波浪模型验证过程中参数取值
Table 2. Parameters used in first validation
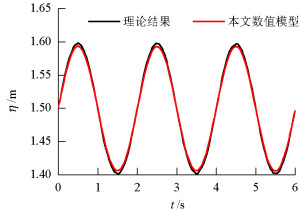
名称 取值 波高/m 0.100 波浪周期/s 2.00 水深/m 1.500 表 3 波浪-圆柱相互作用验证过程中参数取值
Table 3. Parameters used in validation process of wave-column interaction
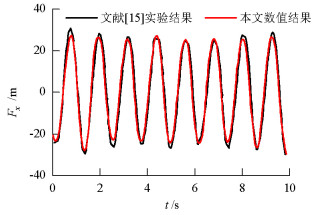
名称 取值 波高/m 0.07 波浪周期/s 1.22 水深/m 0.505 圆柱直径/m 0.25 表 4 数值案例所取参数
Table 4. Parameters used in numerical examples
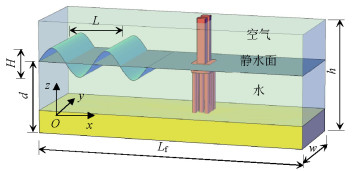
名称 取值 波高/m 2.000 波浪周期/s 10.00 水深/m 20.000 波浪入射角(承台长轴线与波浪传播方向夹角)/(°) 0 承台淹没深度(静水面处z坐标与承台底面z坐标之差)/m 0.500 -
张彦, 李国平.海洋环境对桥梁下部结构的影响[J].海岸工程, 2006, 25(1):35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2006.01.006ZHANG Yan, LI Guoping. Influence of marine environment on bridge understructure[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2006, 25(1):35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2006.01.006 党慧慧.跨海大桥下部结构地震效应分析[D].武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10497-2010036721.htm 瞿振华.跨海大桥下部结构设计与施工技术研究[D].上海: 同济大学, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10247-2007050131.htm 胡琦忠, 金伟良, 史方华, 等.大型跨海桥梁基础结构正常使用极限状态的可靠度分析[J].中国公路学报, 2008, 21(1):53-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2008.01.010HU Qizhong, JIN Weiliang, SHI Fanghua, et al. Reliability analysis of foundation structures of long-span-bridges on serviceability limit states[J]. China Journal of Highwat and Transport, 2008, 21(1):53-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2008.01.010 黄信.地震激励下水-桥墩动力相互作用分析[D].天津: 天津大学, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10056-2009072084.htm 杨万理, 李乔.深水桥梁墩-水耦合作用计算模式对比研究[J].世界桥梁, 2012, 40(2):46-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gwql201202012YANG Wanli, LI Qiao. Comparative study of pier-water interaction calculation model of deep water bridge[J]. World Bridge, 2012, 40(2):46-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gwql201202012 胡勇, 雷丽萍, 杨进先.跨海桥梁基础波浪(流)力计算问题探讨[J].水道港口, 2012, 33(2):101-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2012.02.002HU Yong, LEI Liping, YANG Jinxian. Study of wave force on foundation of sea-crossing bridges[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2012, 33(2):101-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2012.02.002 Morison J R. The force exerted by surface waves in piles[J]. Petrolem Transaction AIME, 1950, 189:149-157. http://www.tandfonline.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=cit0019&dbid=16&doi=10.1080%2F17445302.2018.1443377&key=10.2118%2F950149-G MACCAMY R C, FUCHS R A. Wave forces on piles:a diffraction theory[J]. US Army Corps of Engineering, Beach Erosion Board, 1954, 69:75-86. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnjtdxxb201802007 李世森, 张伟, 秦崇仁.大直径圆筒结构上波浪力的数值模拟与实验研究[J].中国港湾建设, 2003(2):11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2003.02.004LI Shisen, ZHANG Wei, QIN Chongren. Numerical simulation and experimental study of wave force on large diameter cylindrical structure[J]. China Harbour Engineering, 2003(2):11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2003.02.004 祝兵, 宋随弟, 谭长建.三维波浪作用下大直径圆柱绕流的数值模拟[J].西南交通大学学报, 2012, 47(2):224-229. http://manu19.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_xnjd/CN/abstract/abstract11576.shtmlZHU Bing, SONG Suidi, TAN Changjian. Numerical simulation for diffraction around large-diameter circular cylinder subjected to three-dimension wave[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2012, 47(2):224-229. http://manu19.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_xnjd/CN/abstract/abstract11576.shtml 谭长建, 祝兵.三维波浪-流-串行桩柱相互作用的数值分析[J].应用力学学报, 2010, 27(4):680-686. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yylxxb201004009TAN Changjian, ZHU Bing. Numerical study of three-dimensional wave-current interaction with cylinders[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2010, 27(4):680-686. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yylxxb201004009 YANG C, ERTEKIN R C. Numerical simulation of nonlinear wave diffraction by a vertical cylinder[J]. Journal of Offshore Mechanical and Arctic Engineering, 1992, 114:36-44. doi: 10.1115/1.2919950 蒋昌波, 刘晓建, 姚宇, 等.孤立波作用下破碎区单圆柱附近流动特性数值研究[J].水动力学研究与进:A辑, 2016, 31(4):472-479. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdlxyjyjz201604011JIANG Changbo, LIU Xiaojian, YAO Yu, et al. Numerical study of the flow characteristics around a single pile in the surf zone under solitary waves[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2016, 31(4):472-479. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdlxyjyjz201604011 ZANG J, TAYLOR P H, MORGAN G, et al. Steep wave and breaking wave impact on offshore wind turbine foundations-ringing re-visited[C]//The 25th International Workshop on Water Waves and Floating Bodies. Harbin: [s.n.], 2014: 1-4. 期刊类型引用(7)
1. 宋远红,邓星桥,江源渊,王进戈. 关键参数对滚子包络内啮合蜗杆传动接触与润滑性能的影响. 机械传动. 2019(03): 17-21 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 张敬孜,王进戈,杨捷,周亮,彭瑞. 变齿厚内齿轮平面包络外转子鼓形蜗杆传动装置设计. 工程科学与技术. 2019(03): 205-211 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 宋远红,邓星桥,江源渊. 蜗轮偏转角对圆柱滚子包络内啮合蜗杆啮合性能的影响. 机械传动. 2018(03): 18-22 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 柳在鑫,李金宽,朱焱,廖鸿辉. 倾斜式双滚子包络环面蜗杆传动加工及性能测试. 机械传动. 2018(08): 116-120 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 胡登洲,王进戈,杨捷,安铃芝,杨婷. 平面二次包络内蜗轮齿面成型方法. 工具技术. 2017(07): 75-78 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 邓星桥,王凯,江源渊,冯志鹏,张攀. 圆柱滚子包络蜗杆传动不同啮合方式的性能分析. 西华大学学报(自然科学版). 2017(03): 30-35 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 尤玉晶,吉卫喜,宋丽娟,谢健,王煜. 自动扶梯用ZC1型蜗杆传动副啮合区面积分析. 机械设计与研究. 2016(06): 36-40 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-





 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术
