Influence of Reservoir Water Storage on Wind Characteristics over Bridge Site in Mountainous Area
-
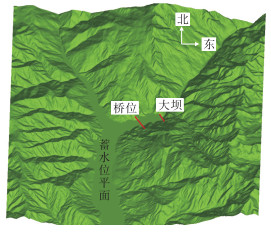
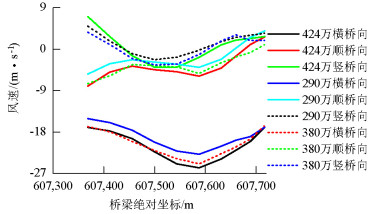
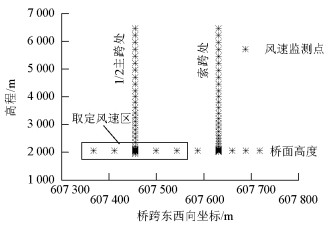
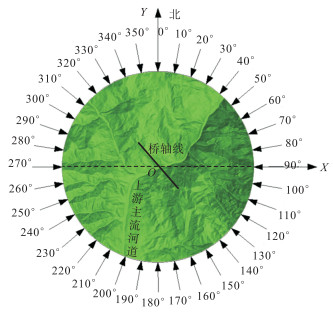
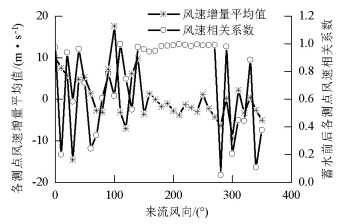
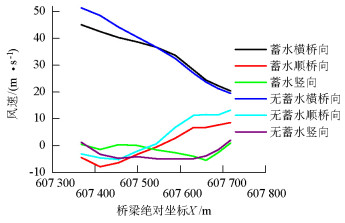
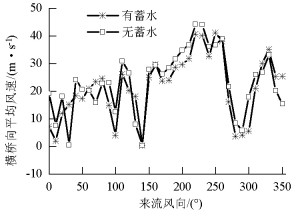
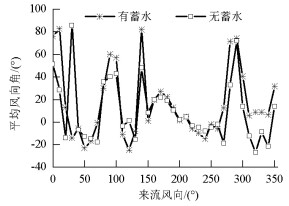
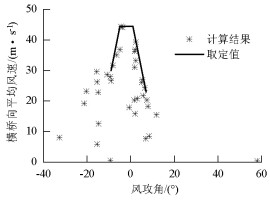
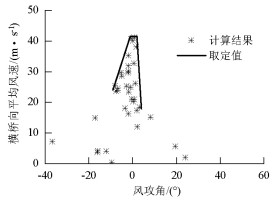
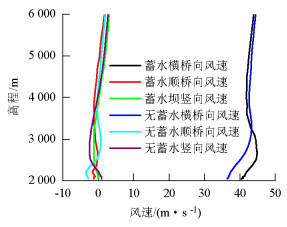
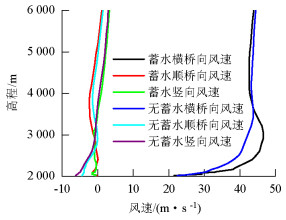
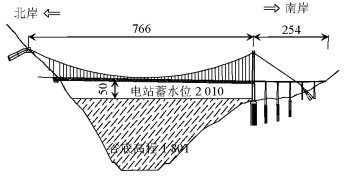
摘要: 为研究山区水电大坝蓄水后对库区桥位风场特性的影响,以某复杂深切峡谷大跨度悬索桥为工程背景,通过Gambit和ICEM分别构建了原始地形以及大坝蓄水后的地形数值模型,并应用软件FLUENT对两个模型进行了数值模拟,多工况对比分析了大坝蓄水对桥址区风速沿竖向和主梁跨向分布以及对主梁平均风速、风攻角和风向角的影响.研究结果表明:无蓄水时该桥址区风速有较明显的加速效应,风速放大系数高达1.14,但蓄水后明显降低;大坝蓄水后,大多数工况下主梁平均风速均有不同程度的降低,主梁的正攻角效应明显减弱,主梁平均风向角整体变化规律一致,风剖面形状在低海拔范围内有较大变化,而随着海拔增加二者逐渐趋于相同.Abstract: In this study, the influence of a hydropower dam built in a mountainous region on the wind characteristics of a bridge site in the reservoir area after storing water was examined.For this purpose, the example of a long-span suspension bridge over a deep-cutting gorge in a complicated mountainous area was considered.The numerical terrain model of the original site and that of the site after the reservoir was filled with water were built by Gambit and ICEM. Numerical simulations for the two models were performed by employing computational fluid dynamics commercial software FLUENT. Different cases were analysed to identify the influence of the reservoir water storage on the distribution of wind velocities along the vertical direction and along the bridge deck, and to identify the influence of water storage on the average velocity of the bridge deck, attack angle, and wind direction angle. The wind velocity at the bridge site clearly increases as compared to the velocity before the reservoir is filled with water, and the velocity amplification factor reaches up to 1.14. However, the velocity amplification factor decreases significantly after the reservoir was filled with water. The average velocity of the bridge deck in most cases decreased to different extents, and the effect of the positive attack angle decreased significantly after reservoir water storage.The variation in the average wind direction angle is consistent with that in the original model. The wind profile shapes exhibit considerable changes in a low altitude range after water storage, but they gradually tend to be the same as the altitude increases.The conclusions of this study provide a basis for the wind-resistant design of bridges.
-
表 1 工况风速放大系数(200°~260°)
Table 1. Wind velocity amplification coefficient (200°~260°)
来流工况 200° 210° 220° 230° 240° 250° 260° 无蓄水 0.90 0.95 1.14 1.13 0.93 0.95 1.01 蓄水 0.76 0.82 1.05 1.03 0.84 1.06 0.98 表 2 风速与风攻角包络值
Table 2. Envelop value of wind velocity and attack angles
主梁高度处平均风攻角/(°) 主梁横向平均风速/(m·s-1) 无蓄水 蓄水 无蓄水 蓄水 -9 -9 30.0 24.0 -5~1 -1~2 44.5 41.2 7 5 23.0 18.0 -
中交公路规划设计院. JTG/T D 60-01-2004公路桥梁抗风设计规范[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2004. 李永乐, 唐康, 蔡宪棠, 等.深切峡谷区大跨度桥梁的复合风速标准[J].西南交通大学学报, 2010, 45(2):167-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2010.02.001LI Yongle, TANG Kang, CAI Xiantang, et al.Integrated wind speed standard for long-span bridges over deep-cutting gorge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(2):167-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2010.02.001 李永乐, 张明金, 徐昕宇, 等.高海拔高温差深切峡谷桥址区日常大风成因[J].西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(6):935-941. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.06.001LI Yongle, ZHANG Mingjin, XU Xinyu, et al. Causesof daily strong wind on bridge site in deep gorge withm high altitude and high temperature difference[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(6):935-941. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.06.001 刘红年, 张宁, 吴涧, 等.水库对局地气候影响的数值模拟研究[J].云南大学学报, 2010, 32(2):171-176. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yndxxb201002010LIU Hongnian, ZHANG Ning, WU Jian, et al. Study of effects of reservoir on local climate using numerical simulation[J]. Journal of Yunnan University, 2010, 32(2):171-176. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yndxxb201002010 BITSUAMLAK G T, STATHOPOULOS T, BEDARD C, et al. Numerical evaluation of wind flow over complex terrain:review[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2004, 17(4):135-145. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0893-1321(2004)17:4(135) CHOCK G Y K, COCHRAN L. Modeling of topographic wind speed effects in Hawaii[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and industrial Aerodynamics, 2005, 93(8):623-638. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2005.06.002 KIM H G, PATEL V C, LEE C M. Numerical simulation of wind flow over hilly terrain[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and industrial Aerodynamics, 2000, 87(1):45-60. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(00)00014-3 BITSUAMLAK G T, STATHOPOULOS T, EACUTE C B. Numerical evaluation of wind flow over complex terrain:review[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2004, 17(4):135-145. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0893-1321(2004)17:4(135) MURAKAMI S. Current status and future trends in computational wind engineering[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1997, 67/68(1):3-34. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034605833010_0a7f.html XIAO Yiqing, LI Chao, LI Qiusheng, et al. Numerical simulation of wind speed distributions over complex terrains[C]//The 12th International Conference on Wind Engineering Caims. Australia: Australasian Wind Engineering Society, 2007: 1119-1126. 邓院昌, 刘沙, 余志, 等.实际地形风场CFD模拟中粗糙度的影响分析[J].太阳能学报, 2010, 31(12):1644-1648. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tynxb201012022DENG Yuanchang, LIU Sha, YU Zhi, et al. Effect of roughness on CFD wind field simulation over natural terrain[J]. ACTA Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2010, 31(12):1644-1648. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tynxb201012022 ABDI D S, BITSUAMLAK G T. Wind flow simulationson idealized and real complex terrain using various turbulence models[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 75(8):30-41. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0965997814000787 周志勇, 肖亮, 丁泉顺, 等.大范围区域复杂地形风场数值模拟研究[J].力学季刊, 2010, 31(1):101-107. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lxjk201001015ZHOU Zhiyong, XIAO Liang, DING Quanshun, et al. Numerical simulation study of wind environment for the flow around large region with complex terrain[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2010, 31(1):101-107. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lxjk201001015 李永乐, 蔡宪棠, 唐康, 等.深切峡谷桥址区风场空间分布特性的数值模拟研究[J].土木工程学报, 2011, 44(2):116-122. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201100107457LI Yongle, CAI Xiantang, TANG Kang, et al. Study of spatial distribution feature of wind fields over bridge site with a deep-cutting gorge using numerical simulation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2011, 44(2):116-122. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201100107457 李永乐, 遆子龙, 汪斌, 等.山区Y形河口附近桥址区地形风特性数值模拟研究[J].西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(2):341-348. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.013LI Yongle, TI Zilong, WANG Bin, et al. Numerical simulation of wind characteristics over bridge site near Y-shaped river junction in mountainous area[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2):341-348. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.013 -




 下载:
下载: