Two-Dimensional Coupled Flutter Method Based on Genetic Hybrid Algorithm
-
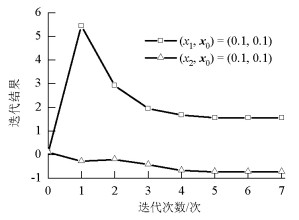
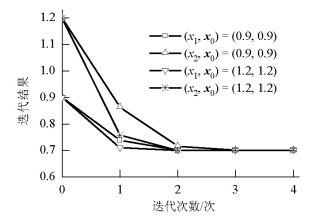
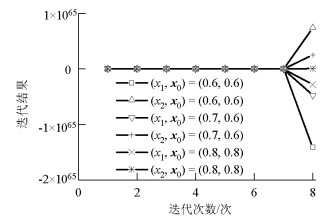
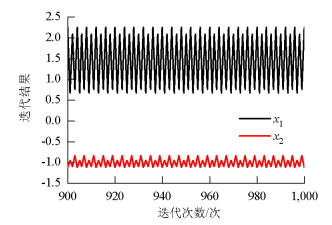
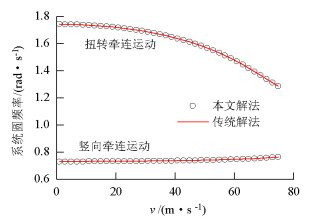
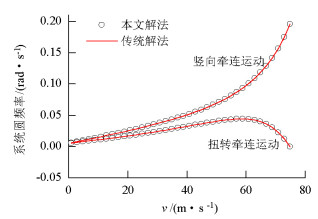
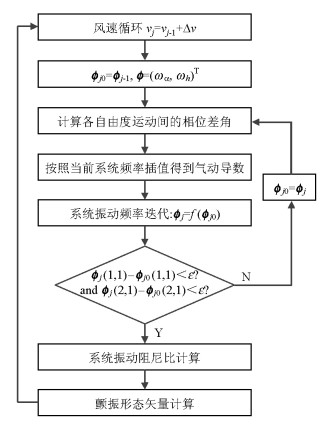
摘要: 对于传统的二维二自由度耦合颤振分步分析解法,创新性地将颤振分析转变为关于求解系统振动频率的非线性方程组问题.基于数值分析理论,引入如拟牛顿法等超线性收敛的数值迭代解法,研究了该类方法在数值迭代时的局部收敛性、初始值依赖性等问题.为规避上述风险发生在颤振分析中,将具有全局搜索优势的遗传算法应用于二维二自由度耦合颤振分析,结合最优算法L-M算法进行局部收敛修正,提出了基于遗传混合算法的分析方法.算例分析结果表明:在各个检测风速节点处,两种方法下的系统振动圆频率和系统牵连阻尼比计算误差都低于0.1‰,结果几乎一致;所建立的新分析方法思路清晰,求得颤振临界风速与传统方法完全一致,说明新的计算流程可行且计算结果准确;与传统方法相比,基于遗传混合算法的颤振方法每步求解过程无需初值的自选取,具有无条件收敛的优点.Abstract: Based on the traditional systematic analysis method of 2d2DOF (two dimensional two degree of freedom), flutter analysis was transformed into a solution to the nonlinear equations of system vibration frequency, innovatively. Several numerical iterative methods for superlinear convergence, such as the quasi-Newton method, were introduced on the basis of numerical analysis theory. Then, the local convergence and initial value dependency of these methods in numerical iteration were studied. To avoid the above-mentioned risks in the flutter analysis, the genetic hybrid algorithm, which has advantages in global searching, was combined with the optimal algorithm "L-M" for local convergence correction, and introduced into the 2d2DOF flutter analysis; a new analysis method was subsequently proposed. The sample numerical analysis showed that in each detected wind node, the calculation errors of the system vibration circle frequency and the system-implicated damping ratio under the two methods were lower than 0.1 per thousand, and the results were almost the same. Thus, the new method is effective, and the corresponding calculation result of the critical wind velocity is consistent with the traditional method; this shows that the new calculation procedure is feasible and the calculation results are accurate. Compared with the traditional method, the proposed method has the advantages of unconditional convergence, wherein initial values do not require artificial selection in each step of the solving process.
-
表 1 桥梁断面颤振分析结果对比
Table 1. Comparison results of the bridge flutter analysis
分析方法 颤振风速/(m·s-1) 颤振频率 传统不动点迭代法 74.9 1.288 1 本文遗传混合算法 74.9 1.288 1 -
SCANLAN R H, TOMKO J J. Airfoil and bridge deck flutter derivatives[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1971, 97(6):1717-1737. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JAKO200421349898472 HUSTON D R. Flutter derivatives from 14 generic deck sections[C]//Proc. of ASCE Structure Congress. Orlando: ASCE, 1987: 281-292. 陈政清, 于向东.大跨桥梁颤振自激力的强迫振动法研究[J].土木工程学报, 2002, 35(5):34-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2002.05.008CHEN Zhenqing, YU Xiangdong. A new method for measuring flutter self-excited forces of long-span bridges[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2002, 35(5):34-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2002.05.008 李志国, 王骑, 伍波, 等.不同攻角下扁平箱梁颤振机理研究[J/OL].西南交通大学学报, 优先出版. (2017-09-27)[2017-10-28].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20170927.2111.034.html. WILDE K, FUJINO Y, MASUKAWA J. Time domain modeling of brige deck flutter[J]. Structural Engineering Earthquake Engineering, 1996, 13(2):93-104. XIANG H, ZHANG R. On mechanism of flutter and unified flutter theory of bridges[M]//Wind Engineering Into the 21st Century. Rotterdam: [s.n.], 1999: 1069-1074. MATSUMOTO M, HAMASAKI H, YOSHIZUMI F. On flutter stability of decks for super long-span bridge[J]. Structural Engineering EarthquakeEngneering, 1997, 14:185-200. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=J-STAGE_547358 MATSUMOTO M. Flutter instability and recent development in stabilization of structures[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aecodynamics, 2007, 95(9/10/11):888-907. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6bfb4e4734a5ef44013433a56011ecb0 杨詠昕.大跨度桥梁二维颤振机理及其应用研究[D].上海: 同济大学, 2002. 杨詠昕, 葛耀君, 项海帆.大跨度桥梁典型断面颤振机理[J].同济大学学报, 2006, 34(4):455-460. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.04.006YANG Yongxin, GE Yaojun, XIANG Haifan. Flutter mechanism of representative sections for long-span bridges[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2006, 34(4):455-460. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.04.006 丁泉顺, 朱乐东.桥梁主梁断面气动耦合颤振分析与颤振机理研究[J].土木工程学报, 2007, 40(3):69-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2007.03.012DING Quanshun, ZHU Ledong. Aerodynamically coupling flutter analysis and flutter mechanism for bridge deck sections[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2007, 40(3):69-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2007.03.012 邵亚会, 葛耀君, 柯世堂.超大跨度悬索桥二维颤振频域直接分析方法[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2011, 43(8):119-123. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201102820863SHAO Yahui, GE Yaojun, KE Shitang. Straight forward method for two-dimensional flutter analysis of super-long-span suspension bridge in frequency domain[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology University, 2011, 43(8):119-123. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201102820863 罗亚中, 袁端才, 唐国金.求解非线性方程组的混合遗传算法[J].计算力学学报, 2005, 22(1):109-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2005.01.022LUO Yazhong, YUAN Duancai, TANG Guojin. Hybrid genetic algorithm for solving systems of nonlinear equations[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2005, 22(1):109-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2005.01.022 张鸿燕, 耿征. Levenberg-Marquard算法的一种新解释[J].计算机工程与应用, 2009, 45(19):5-9. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2009.19.002ZHANG Hongyan, GENG Zheng. Novel interpretation for Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2009, 45(19):5-9. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2009.19.002 项海帆, 葛耀君, 朱乐东, 等.现代桥梁抗风理论与实践[M].北京:人民交通出版社, 2005:206-216. 葛耀君.大跨度悬索桥抗风[M].北京:人民交通出版社, 2011:259-269. 朱小飞.迭代法解非线性方程组[D].合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2014. 晁玉翠.求解非线性方程组的修正牛顿法[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2007. 屈颖爽.基于拟牛顿法和遗传算法求解非线性方程组的混合算法[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2005. 陈政清.桥梁风工程[M].北京:人民交通出版社, 2005:67-73. -





 下载:
下载: