Influence of Vent Location on Efficiency of Smoke Extraction in Tunnel Fire
-
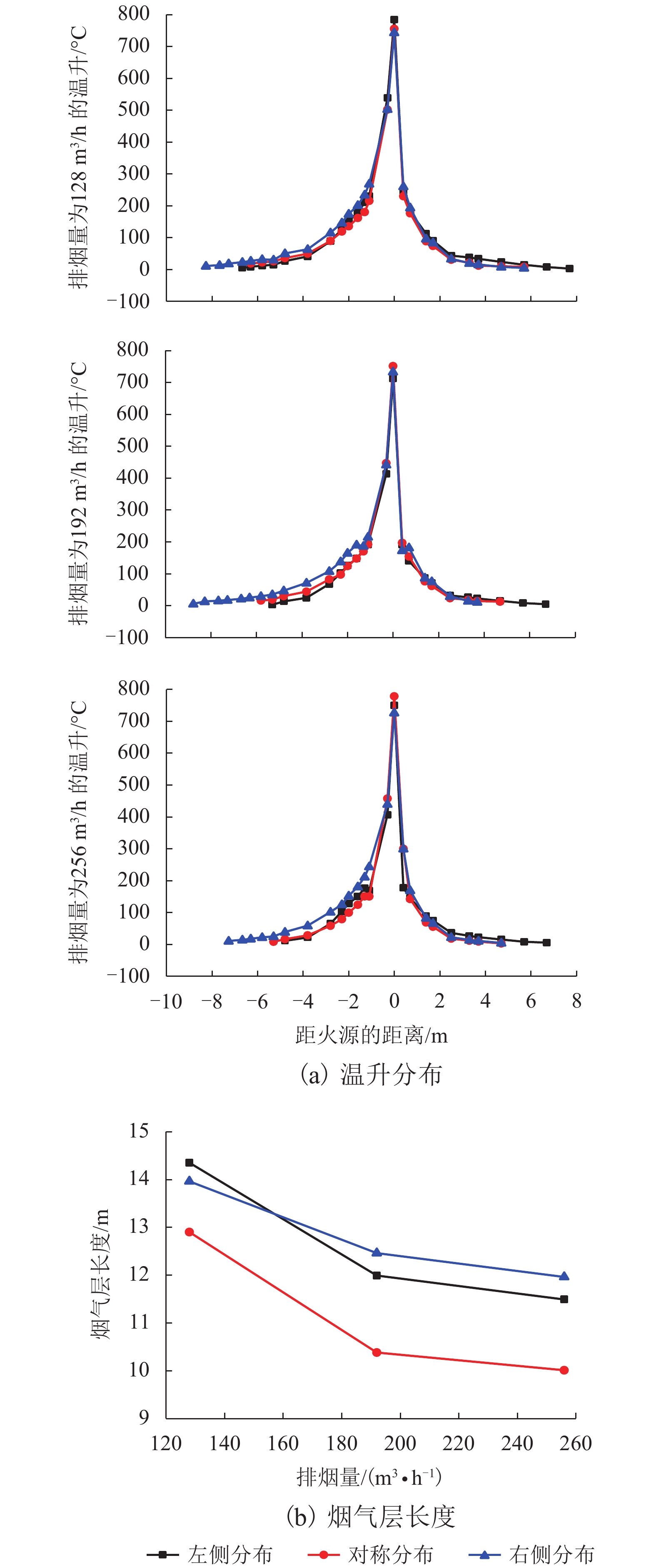
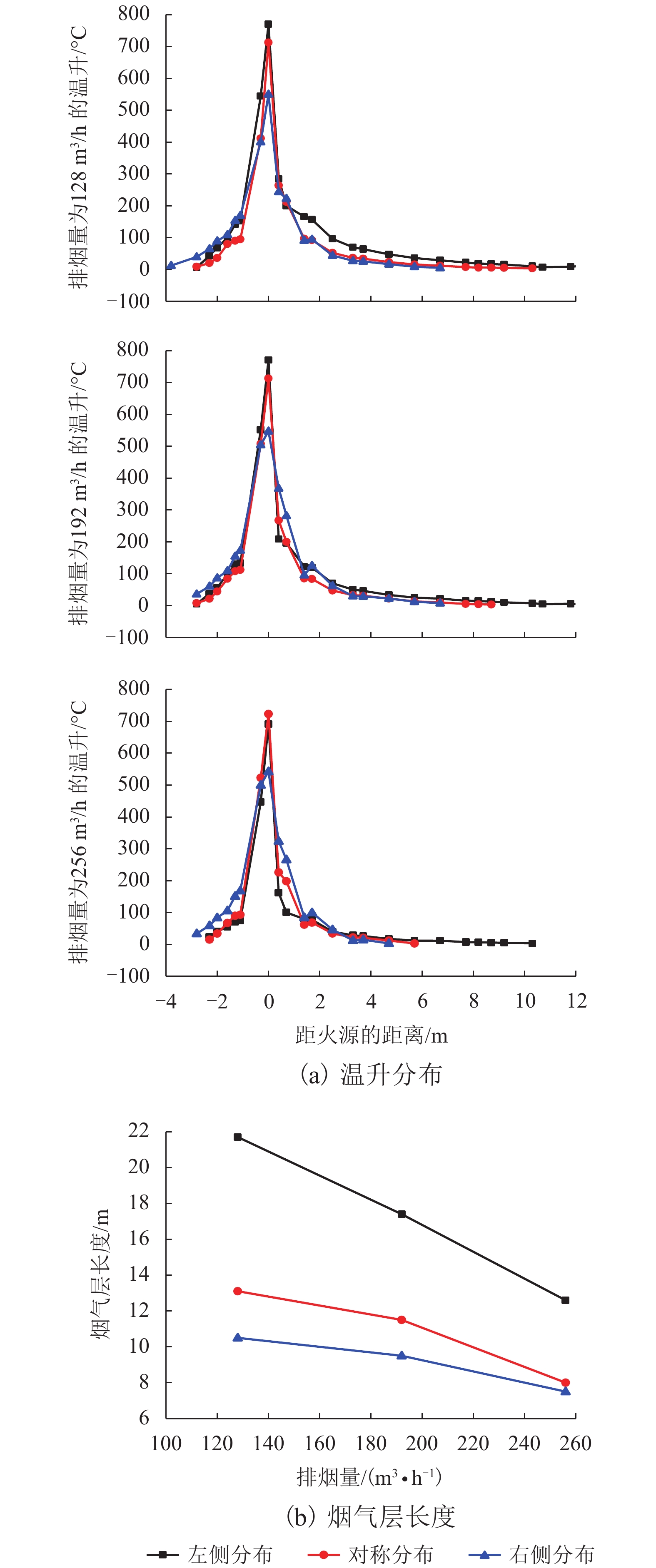
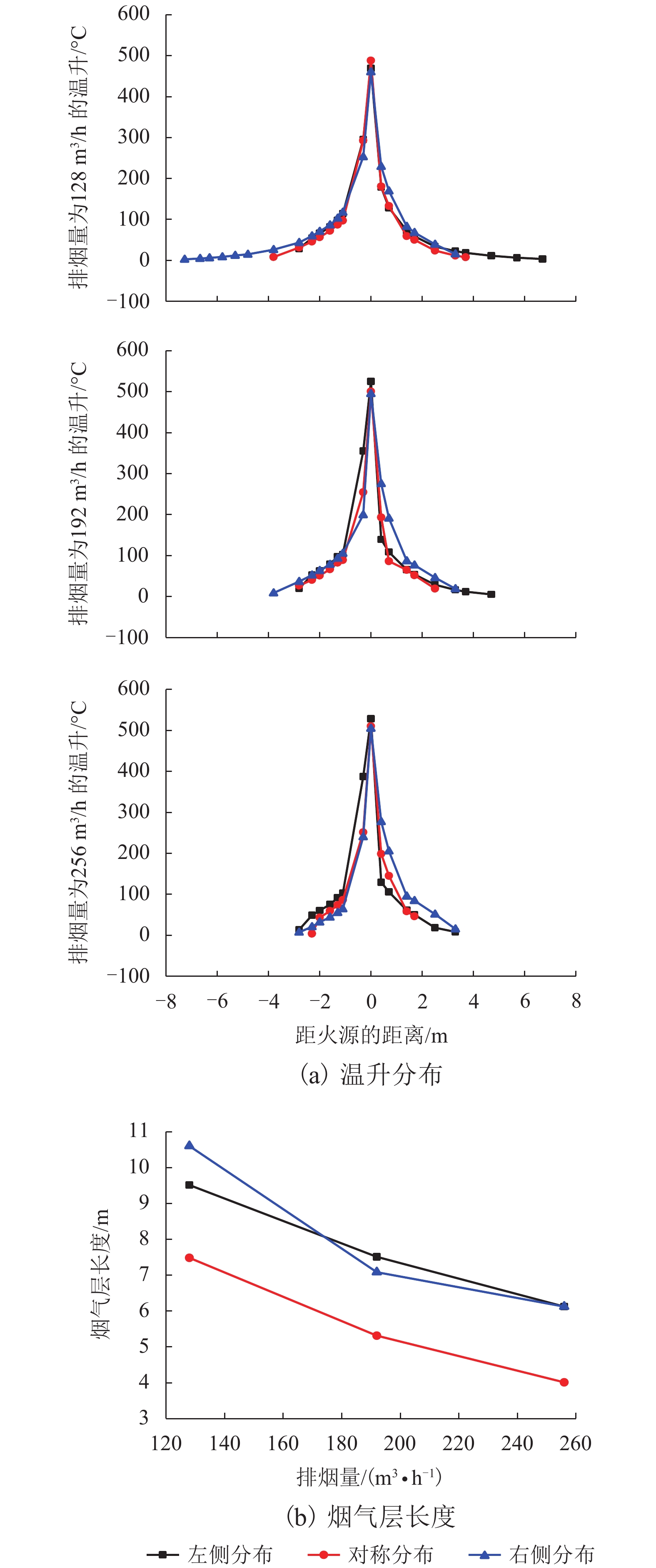
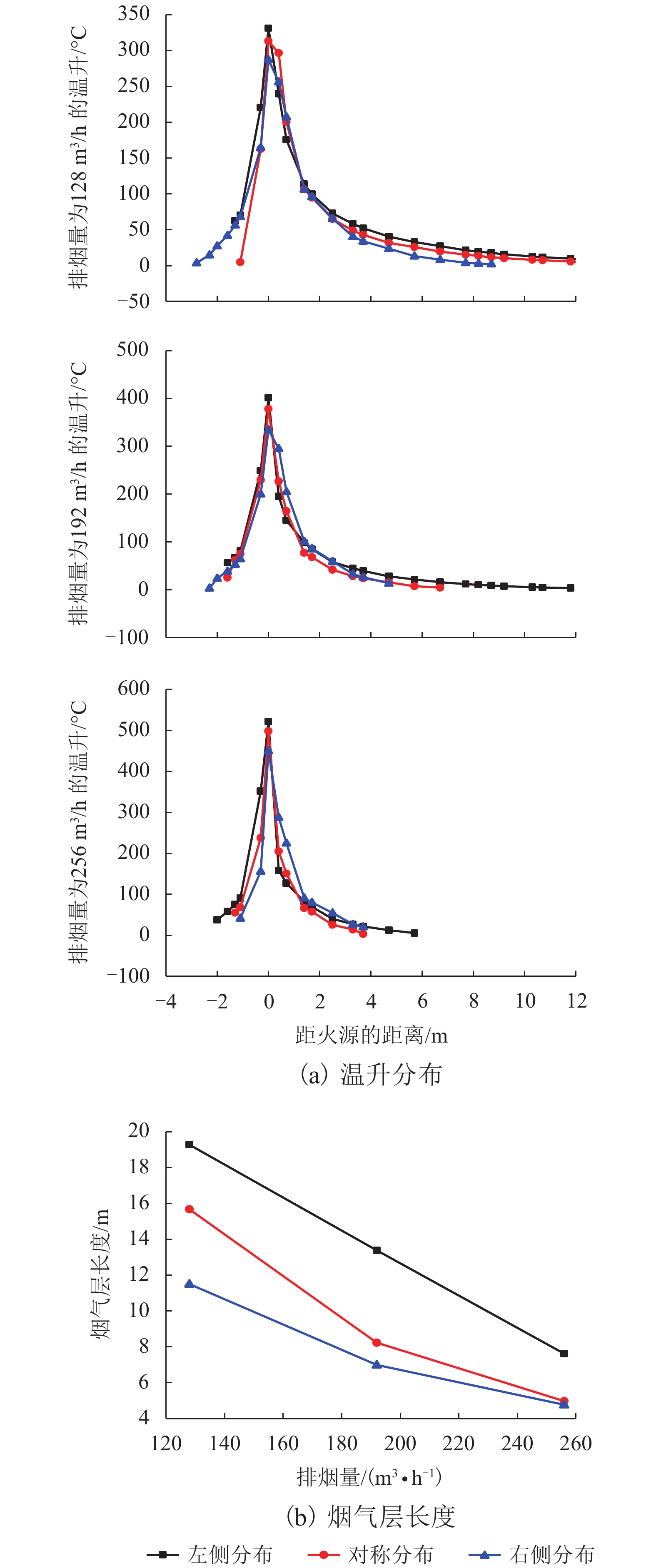
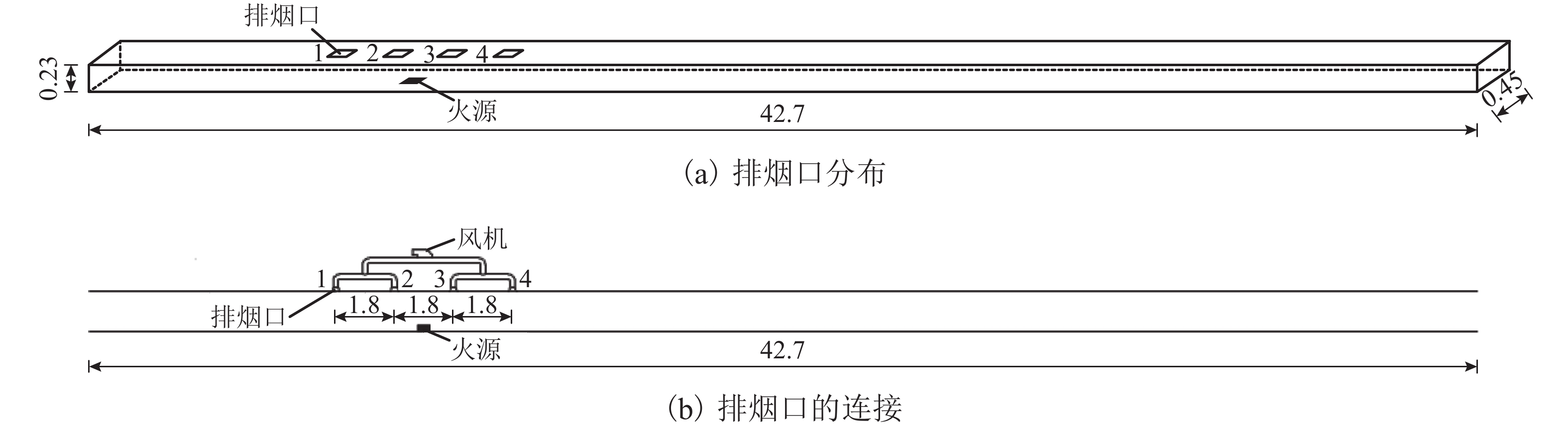
摘要: 为研究长大隧道其排烟口位置对半横向排烟效率的影响,本文以Memorial Tunnel 为原型建立1∶20隧道模型,其尺寸为 42.7 m × 0.45 m × 0.23 m,并采用坡度为水平和3.2%两种状态,以油池火(甲醇)作为火源,在模型隧道中进行了一系列的实验. 同时,采用火灾动力学模拟软件FDS 6.0.1对排烟口位于火源左侧、右侧和两侧对称分布3种工况进行数值模拟,对比数值模拟和实验结果,得出以下结论: (1)在水平隧道中,排烟口对称分布于火源两侧时,烟气层大致呈对称分布,排烟效率最高,相对于排烟口分布于火源左侧或右侧,其排烟效率能分别提高10.22%~13.58%和7.66%~16.84%;当两排烟口位于火源左侧或右侧时,烟气向排烟口所在位置相反方向蔓延距离增长,排烟效率不存在明显差异. (2)在倾斜隧道中,烟气在火源两侧呈不对称分布,向隧道高端蔓延距离较长;当排烟口仅火源左侧(低端)布置时排烟效率最低,而对称分布于火源两侧时的排烟效率有所提高,较排烟口仅左侧分布提高了33.9%~39.6%;排烟口仅分布于火源右侧(高端)时的排烟效率最高,与排烟口仅分布于火源左侧时相比,排烟效率提高了40.5%~51.6%. (3)倾斜隧道中排烟口位置对排烟效率的影响较水平隧道更为显著,且随着排烟量的增加,该影响程度逐渐减小.Abstract: To study the influence of smoke vent location on smoke extraction efficiency for semi-transversal smoke control system in long tunnel, a 1∶20 reduced-scale tunnel model was built on the basis of Memorial Tunnel. The model has a dimension of 42.7 m × 0.45 m × 0.23 m, with two gradients of 0% and 3.2%. A series of fire experiments were conducted in the tunnel model with the fire source of pool fire (methanol). Meanwhile, three different scenarios were simulated using Fire Dynamics Simulator (FDS 6.0.1), in which two smoke vents are located on the left side, the right side, or both sides of fire source. By comparing the numerical simulation and experimental results, the following conclusions are made: (1) In the horizontal tunnel (0% gradient), the smoke layer distributes symmetrically for the smoke vents symmetrically located on both sides of fire source. Smoke extraction efficiency in this scenario reaches the maximum, with increases of 10.22%–13.58% and 7.66%–16.84% in contrast to the other two cases with smoke vents on the left and right sides respectively. These two cases show no significant difference in smoke extraction efficiency although the length of smoke layer is prolonged; (2) In the tunnel with a gradient of 3.2%, smoke layer asymmetrically distributes on both sides of fire source and more smoke spreads to the uphill side. Smoke extraction efficiency is the lowest for smoke vents on the left side of fire source (downhill side), it increases by 33.9%–39.6% for vents symmetrically located on both sides of fire source, and reaches the maximum for vents on the right side of fire source (uphill side), increasing by 40.5%–51.6% compared with that with the vents on the left side; (3) The influence of smoke vent location on smoke extraction efficiency in the inclined tunnel is more significant than that in horizontal tunnel and the degree of influence reduces with the increase of smoke extraction volume.
-
Key words:
- tunnel fire /
- smoke vent location /
- efficiency of smoke extraction
-
表 1 实验工况
Table 1. Experimental conditions
实验编号 排烟量/(m3•h−1) 开启排烟口编号 排烟口位置 1 128 1、2 火源左侧 2 192 3 256 4 128 2、3 火源两侧 5 192 6 256 7 128 3、4 火源右侧 8 192 9 256 -
SANTOS-REYES J, BEARD A N. An analysis of the emergency response system of the 1996 Channel tunnel fire[J]. Tunnelling & Underground Space Technology, 2017, 65(1): 121-139. SHAFEE S, YOZGATLIGIL A. An experimental study on the burning rates of interacting fires in tunnels[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2018, 96(1): 115-123. JI Jie, TONG Qi, WANG Liangzhu, et al. Application of the EnKF method for real-time forecasting of smoke movement during tunnel fires[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2017, 115(1): 398-412. ZHANG Hongtao, GAO Mingxu. The application of support vector machine (SVM) regression method in tunnel fires[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2018, 211(1): 1004-1011. ZHONG Wei, FAN Chuangang, JI Jie, et al. Influence of longitudinal wind on natural ventilation with vertical shaft in a road tunnel fire[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 57(2): 671-678. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.10.063 ZHONG Wei, LÜ Jinjin, LI Zhaozhou, et al. A study of bifurcation flow of fire smoke in tunnel with longitudinal ventilation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 67(6): 829-835. HUANG Youbo, LI Yanfeng, DONG Bingyan, et al. Numerical investigation on the maximum ceiling temperature and longitudinal decay in a sealing tunnel fire[J]. Tunnelling & Underground Space Technology, 2017, 72(1): 120-130. HSU Wensheng, HUANG Yuhsiang, SHEN Tzusheng, et al. Analysis of the Hsuehshan tunnel fire in Taiwan[J]. Tunnelling & Underground Space Technology, 2017, 69(1): 108-115. 胡隆华. 隧道火灾烟气蔓延的热物理特性研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2006. JI Jie, FAN Chuangang, ZHONG Wei, et al. Experimental investigation on influence of different transverse fire locations on maximum smoke temperature under the tunnel ceiling[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(17): 4817-4826. JI Jie, GAO Zihe, FAN Chuangang, et al. Large eddy simulation of stack effect on natural smoke exhausting effect in urban road tunnel fires[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 66(6): 531-542. VAUQUELIN O, MGRET O. Smoke extraction experiments in case of fire in a tunnel[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2002, 37(5): 525-533. doi: 10.1016/S0379-7112(02)00014-0 LIN Peng, LO Siuming, LI Tao. Numerical study on the impact of gradient on semi-transverse smoke control system in tunnel[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2014, 44(3): 68-79. LIN Peng, ZHANG Yuchun, LI Tao, et al. A numerical study on the impact of vehicles’ blockage on the performance of semi-transversal smoke control system in tunnel fire[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 135(1): 247-259. CHEN Longfei, HU Longhua, TANG Wei, et al. Studies on buoyancy driven two-directional smoke flow layering length with combination of point extraction and longitudinal ventilation in tunnel fires[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2013, 59(7): 94-101. 陈建忠,曹正卯,张琦. 侧壁排烟模式下超宽断面沉管隧道火灾排烟效率研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2017,13(s1): 393-399.CHEN Jianzhong, CAO Zhengmao, ZHANG Qi. Study on the efficiency of smoke exhausting under lateral exhaust mode in extra-wide immersed tunnel fire[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2017, 13(s1): 393-399. CHOW W K, GAO Y, ZHAO J H, et al. A study on tilted tunnel fire under natural ventilation[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2016, 81: 44-57. doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2016.01.014 RIESS I, BETTELINI M, BRANDT R. Smoke extraction in tunnels with considerable slope[C]// Proceedings of the 4th International Conference Safety in Road and Rail Tunnels. Madrid: [s.n.], 2001: 503-512 TAJADURA R B, MORROS C S, MARIGORTA E B. Influence of the slope in the ventilation semi-transversal system of an urban tunnel[J]. Tunnelling & Underground Space Technology Incorporating Trenchless Technology Research, 2006, 21(1): 21-28. 范传刚. 隧道火灾发展特性及竖井自然排烟方法研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2015 HURLEY M J, GOTTUK D T, HALL J R, et al. SFPE Handbook of fire protection engineering[M]. New York: Springer, 2016: 3471-3472 -




 下载:
下载: