Indoor Geomagnetic Positioning Based on Joint Algorithm of Particle Filter
-
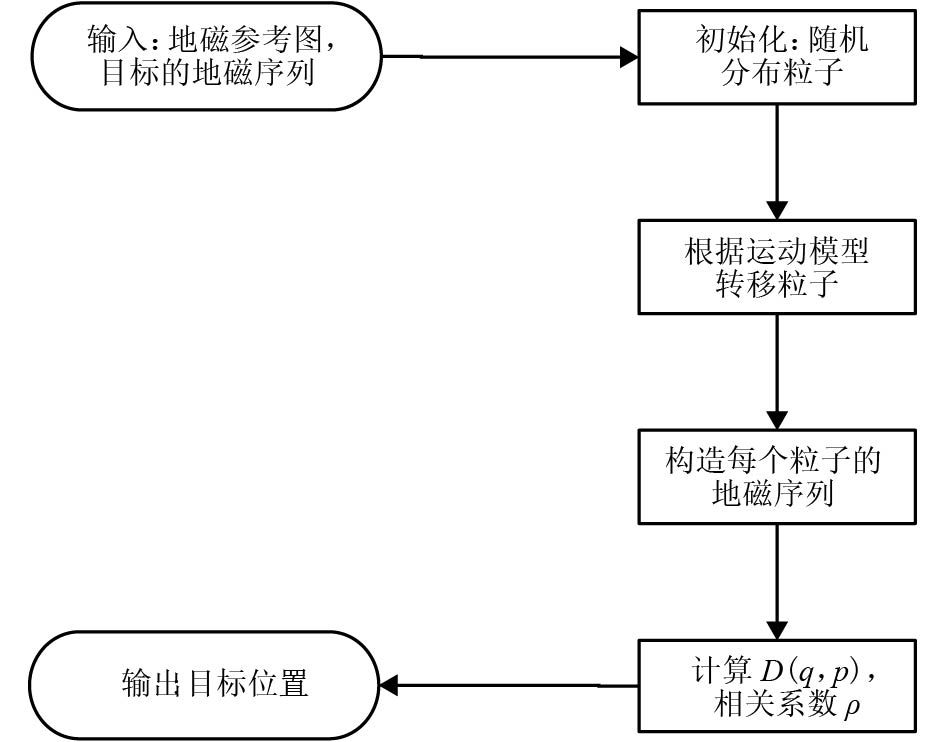
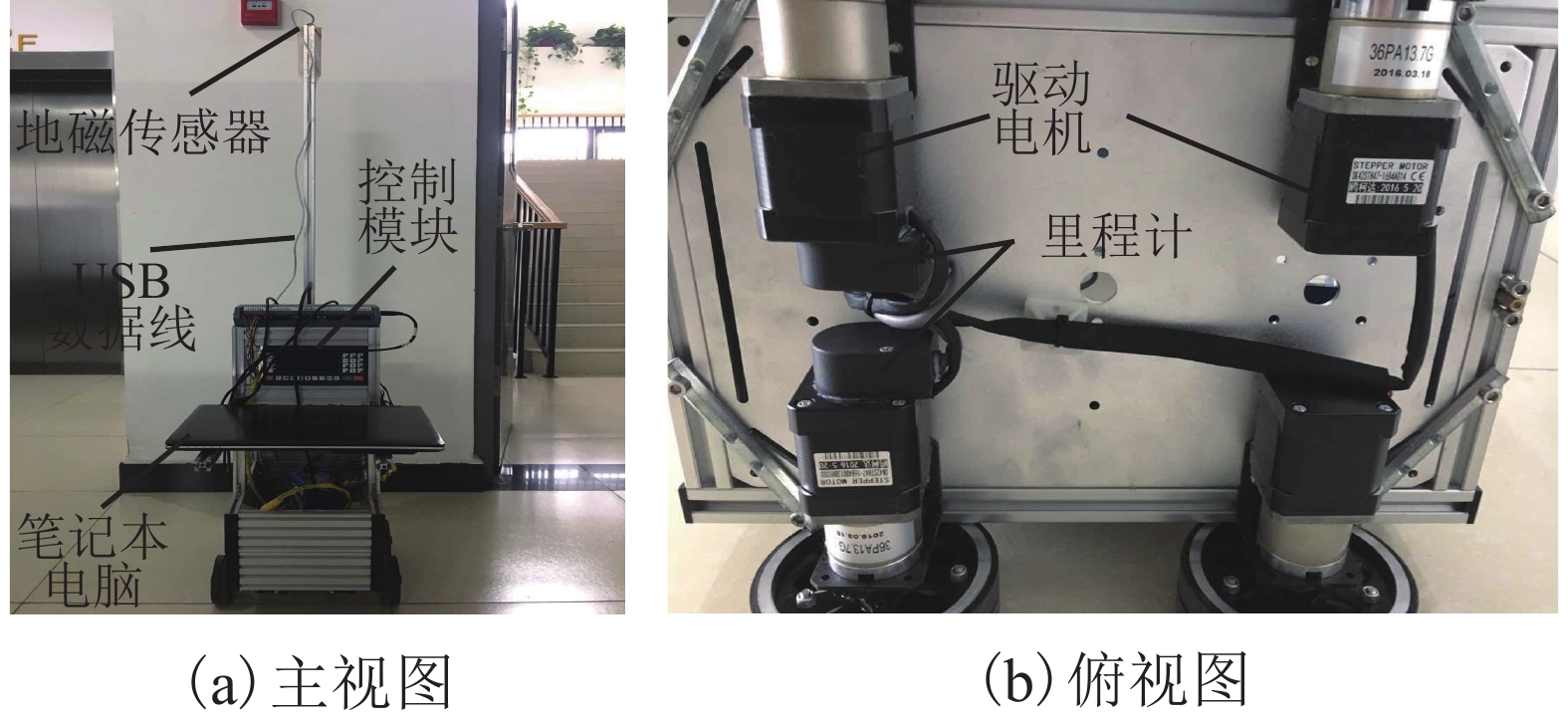
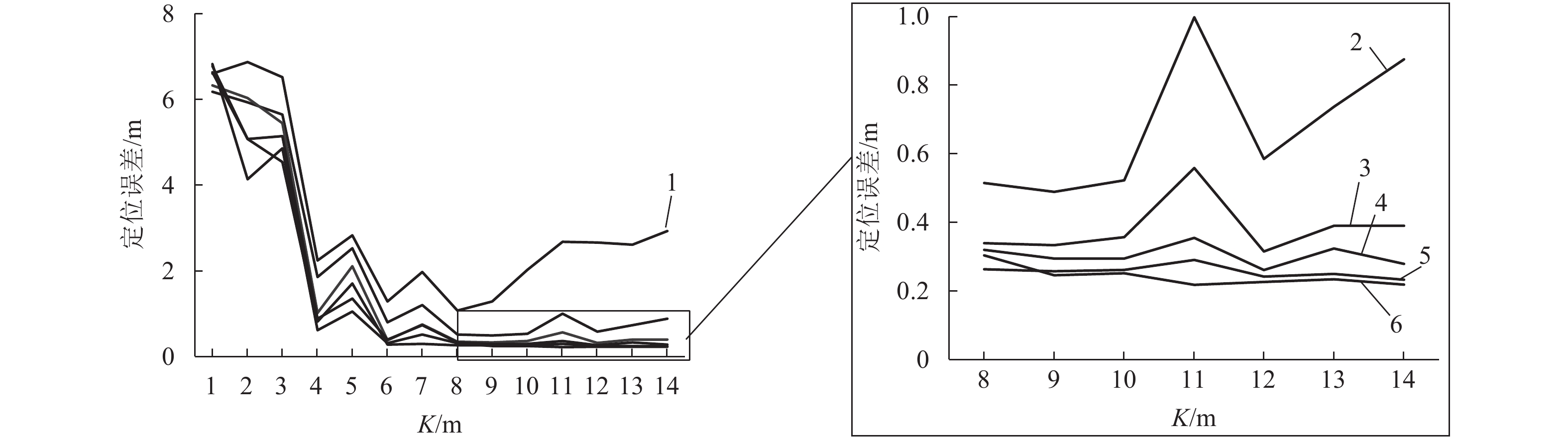
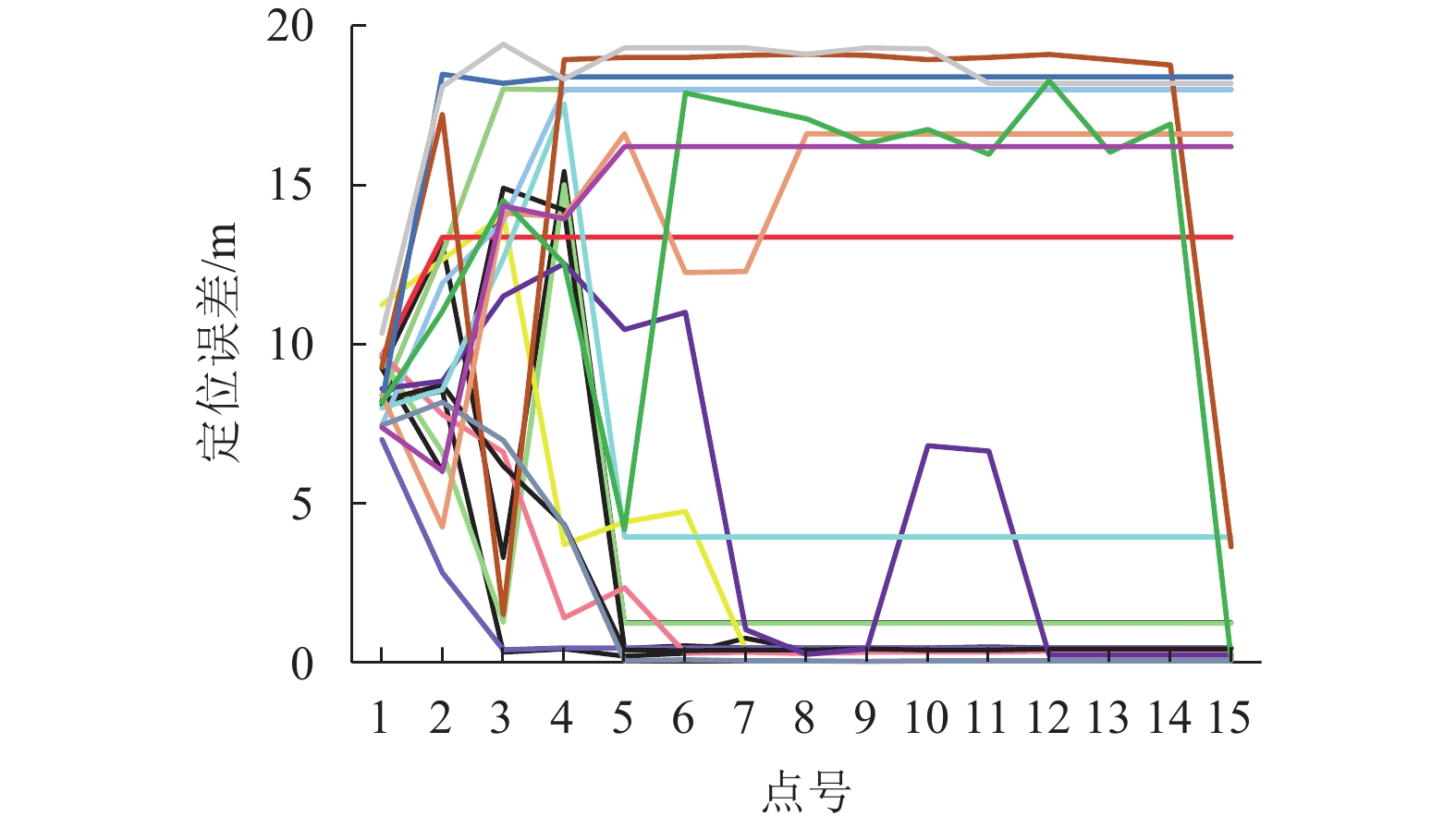
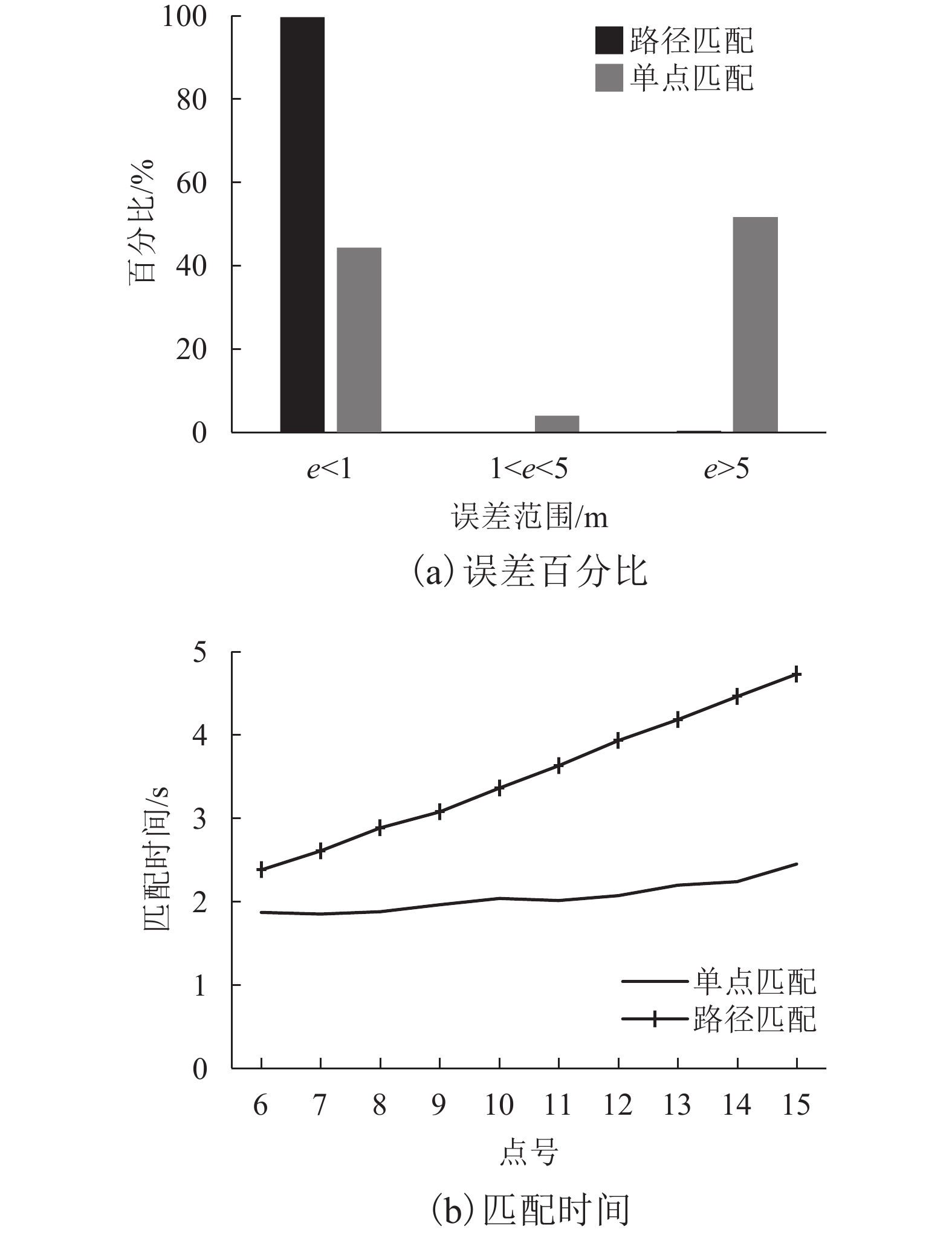
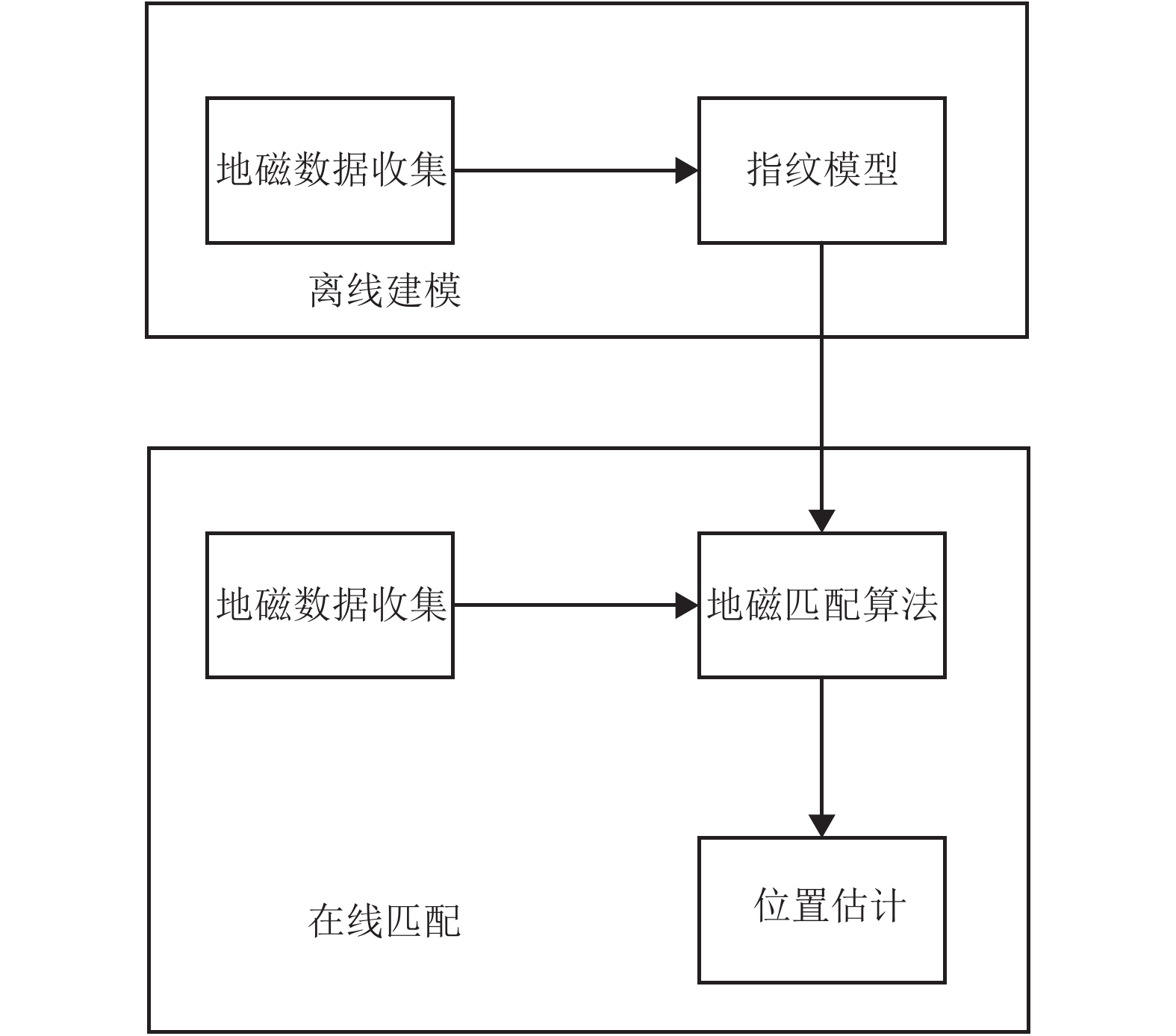
摘要: 室内地磁场受钢结构与其它铁磁材料的影响,造成磁场区域局部异常,使室内地磁场具有特异性. 受益于此种现象,室内地磁定位技术得以实现. 然而在大型建筑中地磁场的特异性会减弱,这导致定位结果出现模糊现象. 针对这一现象,文中提出了基于路径匹配的室内地磁定位技术,通过增加匹配特征数量来解决此问题. 使用基于动态时间规整(dynamic time warp,DTW)算法与粒子滤波(particle filter,PF)算法的新型联合算法,并以路径匹配的模式对目标进行追踪. 在匹配过程中又通过计算斯皮尔曼等级(Spearman)相关系数确定路径之间的相似度,使之作为辅助定位. 最后用装载了磁传感器的测量机器人进行实验验证,结果表明:路径匹配具有足够的地磁特征数量,能够解决特异性减弱情况下定位结果模糊现象,且定位精度优于1 m.Abstract: The indoor geomagnetic field is affected by the presence of a steel structure and other ferromagnetic materials, causing local anomalies in the magnetic field region and and a unique indoor magnetic field. Indoor geomagnetic positioning technology can be realized by exploiting this phenomenon. However, in large buildings, the specificity of the geomagnetic field is weakened, which leads to the distortion of positioning results. To overcome this problem, an indoor geomagnetic positioning technology based on path matching was proposed, which increases the number of matching features. A new joint algorithm was used combining the dynamic time warp algorithm with the particle filter algorithm, which can track the target in a path matching mode. In the matching process, the similarity between the paths was determined by calculating the Spearman correlation coefficient, to assist the positioning. Finally, experimental verification was performed using a measuring robot loaded with a magnetic sensor. The results show that the path matching exhibits a sufficient number of geomagnetic features, which can overcome the phenomenon of blurring the positioning results under the condition of weakening specificity, and the positioning accuracy is higher than 1 m.
-
Key words:
- particle filter /
- geomagnetic field /
- dynamic time warp /
- indoor positioning systems /
- target tracking
-
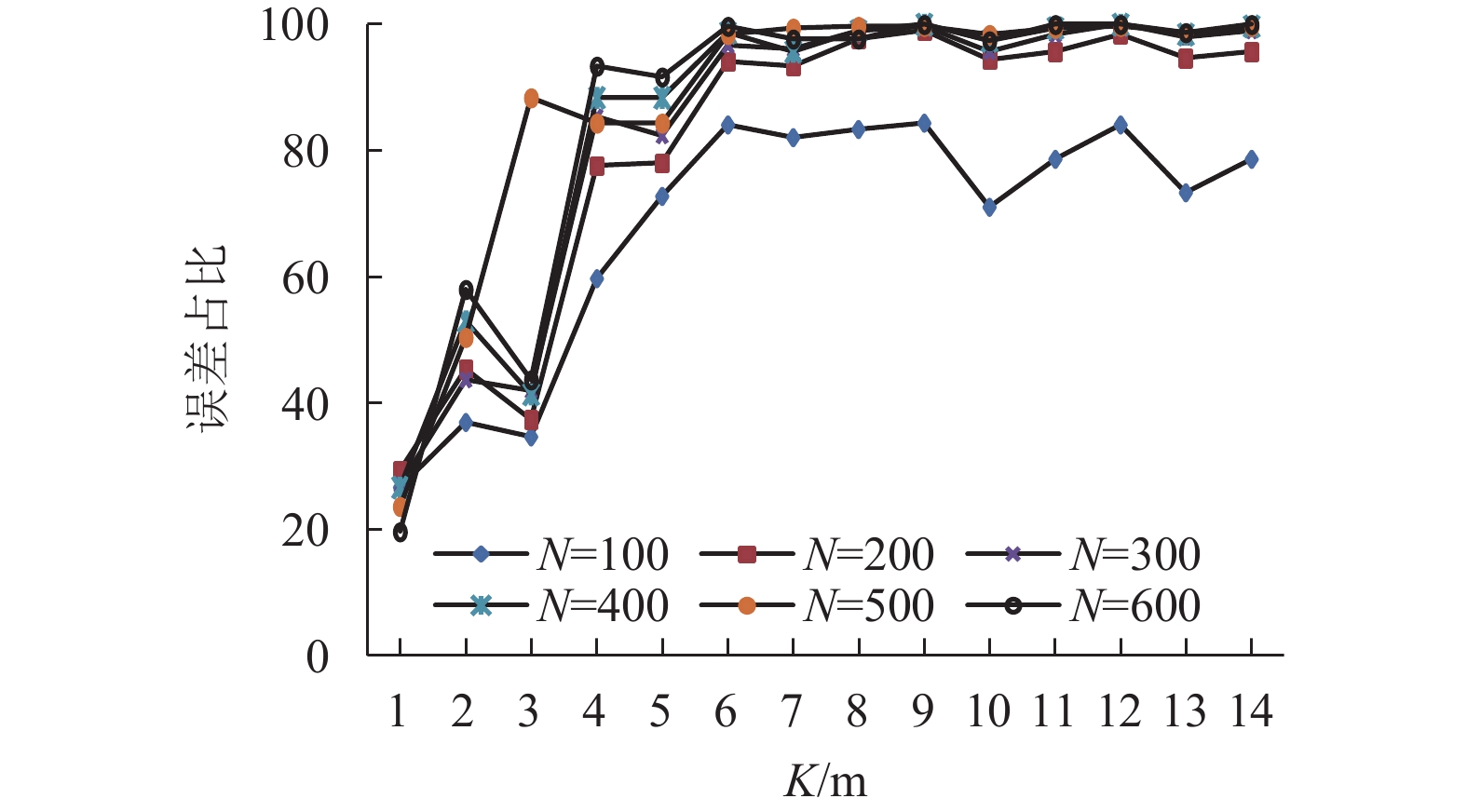
表 1 不同粒子数匹配时间
Table 1. Time required to match different particle counts
N 100 200 300 400 500 600 时间/s 1.92 2.96 3.84 4.73 5.72 6.71 -
VALVERDE T G, SOLA A G, HAGRAS H, et al. A fuzzy logic-based system for indoor localization using WiFi in ambient intelligent environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2013, 21(4): 702-718. LUOH L. ZigBee-based intelligent indoor positioning system soft computing[J]. Soft Comput., 2013, 18: 443-456. NI L M, LIU Yunhao, LAU Y C, et al. LANDMARC: indoor location sensing using active RFID[C]//Proceedings of the First IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, 2003, Fort Worth: [s.n.], 2003: 407-415 SKVORTZOV V Y, LEE H K, BANG S, et al. Application of electronic compass for mobile robot in an indoor environment[C]//IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2007: 2963-2970 LI B, GALLAGHER T, DEMPSTER A G, et al, How feasible is the use of magnetic field alone for indoor positioning?[C]//2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN). Sydney: [s.n.], 2012: 1-9 SUKSAKULCHAI S, THONGCHAI S, WILKES D M, et al. Mobile robot localization using an electronic compass for corridor environment[C/OL]//2000 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. Nashville: IEEE, 2000, 5: 3354-3359 SIIKSAKULCHAI S, THONGCHAI S, WILKES D M, et al. Mobile robot localization using an electronic compass for corridor environment[C/OL]//IEEE International Conference on Systems, 2000[2017-12-12]. http://www8.cs.umu.se/research/ifor/dl/LOCALIZATION-NAVIGATION/Mobile%20Robot%20Localization%20using%20an%20Electronic%20Compass%20for%20Corridor.pdf Kim S E, Kim Y, Yoon J, et al. Indoor positioning system using geomagnetic anomalies for smartphones[C/OL]//2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation. Sydney: University of New South Wales, 2012[2017-10-22]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6418947 FRASSL M, ANGERMANN M, LICHTENSTERN M, et al. Magnetic maps of indoor environments for precise localization of legged and non-legged locomotion[C]//IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2013: 913-920 PUTTA R, MISRA M, KAPOOR D. Smartphone based indoor tracking using magnetic and indoor maps[C]//2015 IEEE Tenth International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing. Singapore: IEEE, 2015: 7-9 LI B, GALLAGHER T, RIZOS C, et al. Using geomagnetic field for indoor positioning[J]. J. Appl. Geod., 2013, 7: 299-308. RIEHLE T H, ANDERSON S M, LICHTER P A, et al. Indoor waypoint navigation via magnetic anomalies[C]//2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Boston: IEEE, 2011: 5315-5318 黄鹤,赵焰,王春来,等. 地磁室内定位基准图数据采集系统设计[J]. 测绘通报,2017(2): 54-59.HUANG He, ZHAO Yan, WANG Chunlai, et al. Design of the acquisition system of indoor positioning reference map based on magnetic field data[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2017(2): 54-59. -




 下载:
下载: