Site Selection Method of Booster Substations by Integrating Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process with 3D Geographic Information System
-
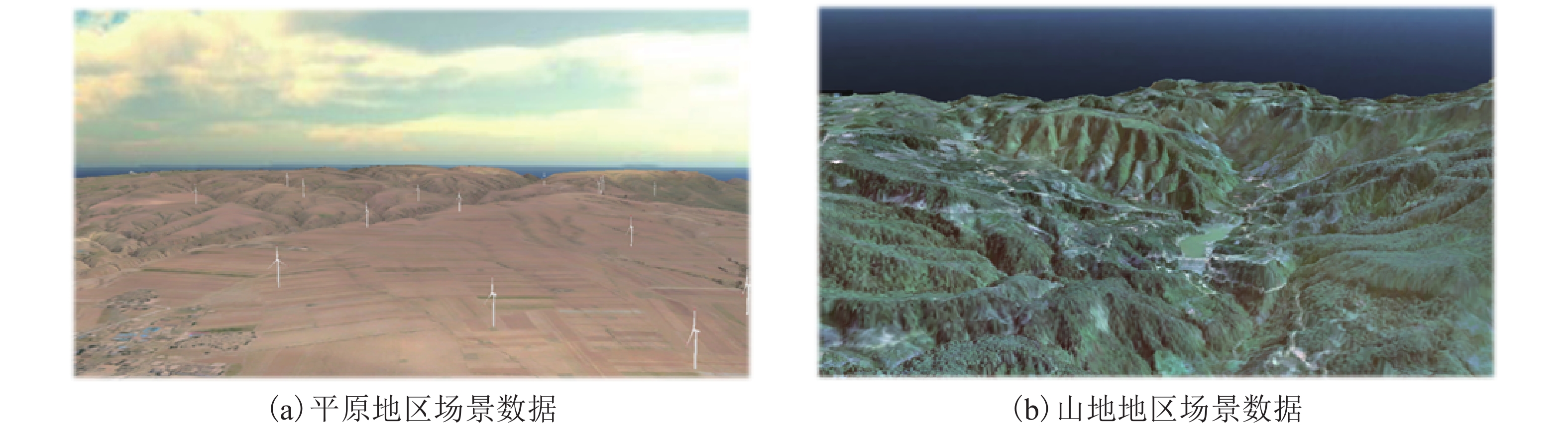
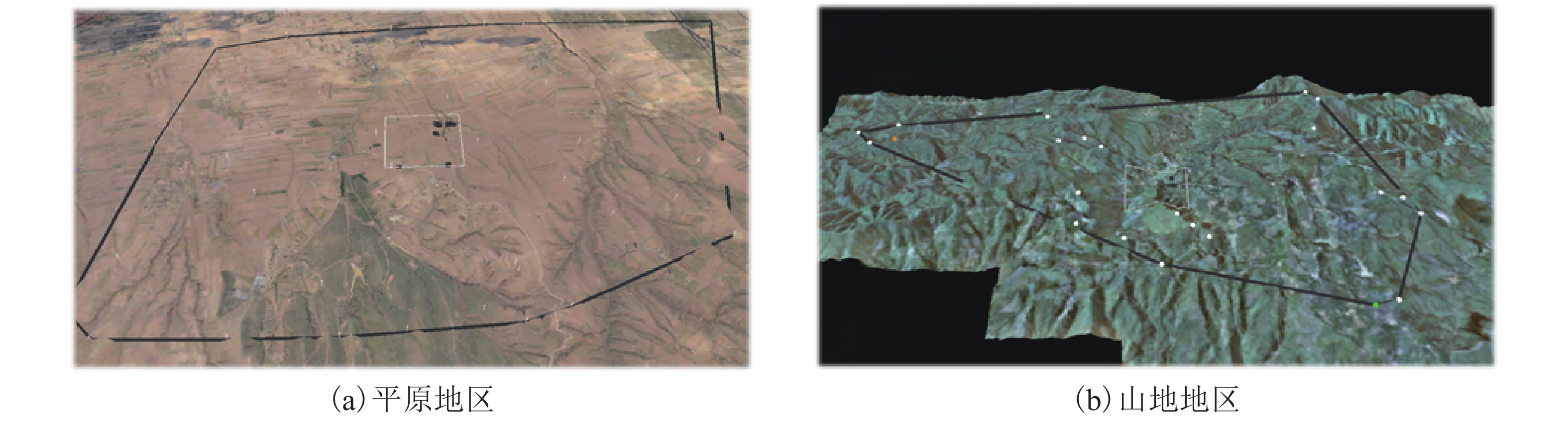
摘要: 为了克服传统风电场升压站选址方法的局限性,基于模糊层次分析选址综合评价方法,在三维GIS中对升压站的选址进行了可行性比对分析. 首先从施工成本、选址地形因子、灾害指标、临近资源及障碍区域五个类别的准则建立风电场升压站选址递阶层次结构;其次集成三维地理信息系统与模糊层次分析法构建一种新的选址评估模型;通过预设几何初选规则获取模型输入参数,最终解算模糊评价矩阵实现升压变电站自动选址. 通过对不同地形的已建成风电场升压变电站选址结果进行比对研究实验表明:以风机分布区域范围内的2 m分辨率的数字高程模型作为实验数据,系统解算时间均在10 min内. 平原最佳选址的站址评分为0.957 8优于已建成站址评分0.941 2;山地最佳选址的站址评分为0.743 5优于已建成站址0.706 8. 该方法有效地提升了选址的时间效率且具备较高的精准性及较好的适用性.Abstract: In order to overcome the limitations of the traditional selection method of booster substations on wind farms and realize an efficient and low-cost site selection of booster substations, feasibility analyses of candidate sites selected for booster substations are conducted in 3D geographic information system (GIS) based on fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. First, a hierarchical structure of the site selection of booster substations is defined from five aspects: construction cost, disaster index, location factor, obstacle area and adjacent resources. Then, a new siting evaluation model is established by integrating the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process with 3D GIS to realize the evaluation. The model input parameter are obtained by presetting the geometric primary selection rules, and finally the fuzzy evaluation matrix is solved to realize the automatic location selection of the boost substation. Comparing the experimental results of site selection of booster substations on wind farms built in different terrains shows that the calculation time is within 10 min using digital elevation model with 2 m resolution in the fan area. The optimal site score of plain is 0.957 8, which is better than that of the actual built site (0.941 2); the optimal site score of mountain is 0.743 5, which is also better than that of the actual built site (0.706 8). The results show that the method has high accuracy and universal applicability.
-
Key words:
- booster site selection /
- fuzzy analytic hierarchy process /
- GIS /
- onshore wind farms
-
表 1 风电场升压站选址评价指标体系
Table 1. System of site evaluation indexes for booster station
一级准则层(F层) 次级指标层(S层) 施工工程量成本准则(F1) 升压站填挖工程量(S1) 集电线路成本(S2) 进站道路工程量(S3) 灾害指标准则(F2) 百年一遇洪水水位(S4) 地震基本烈度(S5) 选址地质沉降(S6) 选址地形因子准则(F3) 局部皱褶度(S7) 局部凹凸性质(S8) 局部高差极值(S9) 障碍区域准则(F4) 农田用地范围(S10) 特殊用地范围(S11) 生活用地范围(S12) 极端地形区域范围(S13) 临近资源准则(F5) 送电距离(S14) 出线方向距离(S15) 水资源区域(S16) 表 2 0.1~0.9标度法及说明
Table 2. The 0.1 – 0.9 scale method and its specifications
标度值 定义 说明 0.5 同等权重 指标相比同等重要 0.6 权重稍高 该指标稍加重要于另一指标 0.7 权重较高 该指标明显重要于另一指标 0.8 权重特高 该指标较另一指标重要的多 0.9 权重极高 该指标较另一指标极端重要 0.1,0.2 反比较 若该指标 si 与指标 sj 对比得到
标度值 rij,0.3,0.4 则指标 sj 与指标 si 对比得到的
标度值 1 – rij表 3 实验粗选参数
Table 3. Parameters of rough site selection
项目 升压站规格 集电出电规划 区域性质 施工工程量 障碍区域 性质 50 m × 50 m 最短距离 筛除谷底地形 减少挖方规避填方 与障碍区域交集为空 表 4 备选站址次级指标评价矩阵因素
Table 4. Evaluation matrix of candidate sites
站址 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 S11 S12 S13 S14 S15 S16 A 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 0.5 1.0 0.7 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.7 0.7 0.7 B 0.6 0.7 0.5 1.0 0.9 0.9 0.5 0.0 0.6 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.3 0.4 C 0.4 0.5 0.5 1.0 0.9 1.0 0.6 1.0 0.7 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 D 1.0 0.6 0.5 0.0 0.9 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.9 0.8 E 0.8 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.9 1.0 0.5 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.9 1.0 1.0 表 5 评分值
Table 5. Score value
地形
种类站址 已有
站址A B C D E 平原 0.551 8 0.837 1 0.600 5 0.612 3 0.957 8 0.941 2 山地 0.625 4 0.743 8 0.743 5 0.711 1 0.693 9 0.706 8 -
游欣佩,马平. 基于模糊层次分析法的风电场优化选址方法研究[J]. 电力科学与工程,2012,28(12): 45-49.YOU Xinpei, MA Ping. Wind farm optimal location based on fuzzy analytic hierarchy process[J]. Electric Power Science & Engineering, 2012, 28(12): 45-49. 刘海燕,庞小平. 利用GIS和模糊层次分析法的南极考察站选址研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2015,40(2): 249-252.LIU Haiyan, PANG Xiaoping. Selection of antarctic research stations based on GIS and fuzzy AHP[J]. Geomatics & Information Science of Wuhan University, 2015, 40(2): 249-252. 王倩. 寒冷山区风电场升压站选址[J]. 科技创新导报,2017(35): 17-18. Helimax Energy Inc. Analysis of wind power potential in Ontario[R]. Ontario: Technical Report/OPA, 2005 SUSAN K. WILLIAMS, T AC, GRANT B, et al. Arizona wind energy assesment[R]. [S.L.]: Arizona Technical Report/Northern Arizona University, 2007 KLINE D, HEIMILLER D, COWLIN S. GIS method for developing wind supply curves[R]. Office of Scientific & Technical Information Technical Report, 2008 BEATA S S, JOACHIM V. GIS-based approach for the evaluation of wind energy potential:a case study for the Kujawsko-Pomorskie Voivodeship[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2011(15): 1696-1707. JASON R J. Multicriteria GIS modeling of wind and olar farms in Colorado[J]. Renewable Energy, 2010, 35(10): 2228-2234. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2010.03.014 ROB V H, VASILIS F. GIS-based wind farm site selection using spatial multi-criteria analysis (SMCA):evaluating the case for New York State[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2011, 15(7): 3332-3340. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2011.04.010 MARI R, BOTTAI L, BUSILLO C, et al. A GIS-based interactive web decision support system for planning wind farms in Tuscany (Italy)[J]. Renewable Energy, 2011, 36(2): 754-763. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2010.07.005 NAZLI Y A, ELCIN K, SEBNEM D. GIS-based environmental assessment of wind energy systems for spatial planning:a case study from western turkey[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2010, 14(1): 364-373. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2009.07.023 PILAR C, TOMÁS A. Wind farms:GIS-based visual impact assessment and visualization tools[J]. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 2013, 40(3): 229-237. doi: 10.1080/15230406.2013.809231 CAVAZZI S, DUTTON A G. An offshore wind energy geographic information system (OWE-GIS) for assessment of the UK’s offshore wind energy potential[J]. Renewable Energy, 2016, 87: 212-228. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2015.09.021 ADDISU D M, PECE V G. A web-based participatory GIS (PGIS) for offshore wind farm suitability within Lake Erie,Ohio[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 41: 162-177. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.08.030 刘学峰,王健. 试议陆上风电场升压站选址[J]. 中国勘察设计,2016(3): 92-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9607.2016.03.001 岑晋峰. 浅析风力发电场升压站站址选择[J]. 中国勘察设计,2013(1): 80-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9607.2013.01.004 乔兵. 风电场升压站选址应注意的问题[J]. 内蒙古石油化工,2009(10): 89-89. 卢华兴,刘学军,汤国安. 地形复杂度的多因子综合评价方法[J]. 山地学报,2012,30(5): 616-621.LU Huaxing, LIU Xuejun, TANG Guoan. Terrain complexity assessment based on multivariate analysis[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2012, 30(5): 616-621. 朱庆. 三维GIS及其在智慧城市中的应用[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2014,16(2): 151-157.ZHU Qing. Full three-dimensional GIS and its key roles in smart city[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2014, 16(2): 151-157. 朱庆. 3维GIS技术进展[J]. 地理信息世界,2011,9(2): 25-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2011.02.006ZHU Qing. Technical progress of three dimensional GIS[J]. Geomatics World, 2011, 9(2): 25-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2011.02.006 郭金玉,张忠彬,孙庆云. 层次分析法的研究与应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2008,47(1): 148-153.GUO Jinyu, ZHANG Zhongbin, SUN Qingyun, et al. Study and applications of analytic hierarchy process[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2008, 47(1): 148-153. CHAO K, DANG F, JIA Y. Application of AHP in the selection of our country wind farm’s location[C]//International Conference on Management and Service Science. Wuhan: IEEE, 2011: 1-4 ZHAO Z, HUANG W. Multi-objective decision-making on wind power projects based on AHP method[C]//International Conference on Computer Distributed Control & Intelligent Environmental Monitoring. Changsha: IEEE, 2011: 242-245 姬东朝,宋笔锋,喻天翔. 模糊层次分析法及其在设计方案选优中的应用[J]. 系统工程与电子技术,2006,28(11): 1692-1552. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2006.11.022JI Dongchao, SONG Bifeng, YU Tianxiang. FAHP and its application in the selection of design scheme[J]. Systems Engineering & Electronics, 2006, 28(11): 1692-1552. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2006.11.022 张吉军. 模糊层次分析法(FAHP)[J]. 模糊系统与数学,2000,14(2): 80-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7402.2000.02.016ZHANG Jijun. Fuzzy analytical hierarchy process[J]. Fuzzy Systems & Mathematics, 2000, 14(2): 80-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7402.2000.02.016 陶余会,刘家才,张吉军. 如何构造模糊层次分析法中模糊一致判断矩阵[J]. 四川师范学院学报,2002,23(3): 282-285. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5072.2002.03.017TAO Yuhui, LIU Jiacai, ZHANG Jijun. How to make fuzzy consistent judgement matrix of the fAHP[J]. Journal of Sichuan Teachers College, 2002, 23(3): 282-285. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5072.2002.03.017 中华人民共和国建设部. 岩土工程勘察规范: GB50021—2001[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2002 中国电力企业联合会. 风力发电场设计技术规范: DL/T5383—2007[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2007 中国电力企业联合会标准化中心. 变电站总布置设计技术规程: DL/T5056—2007[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2008 -





 下载:
下载: