Calculation Method of Trailing Edge Failure Surface of Retrogressive Landslide
-
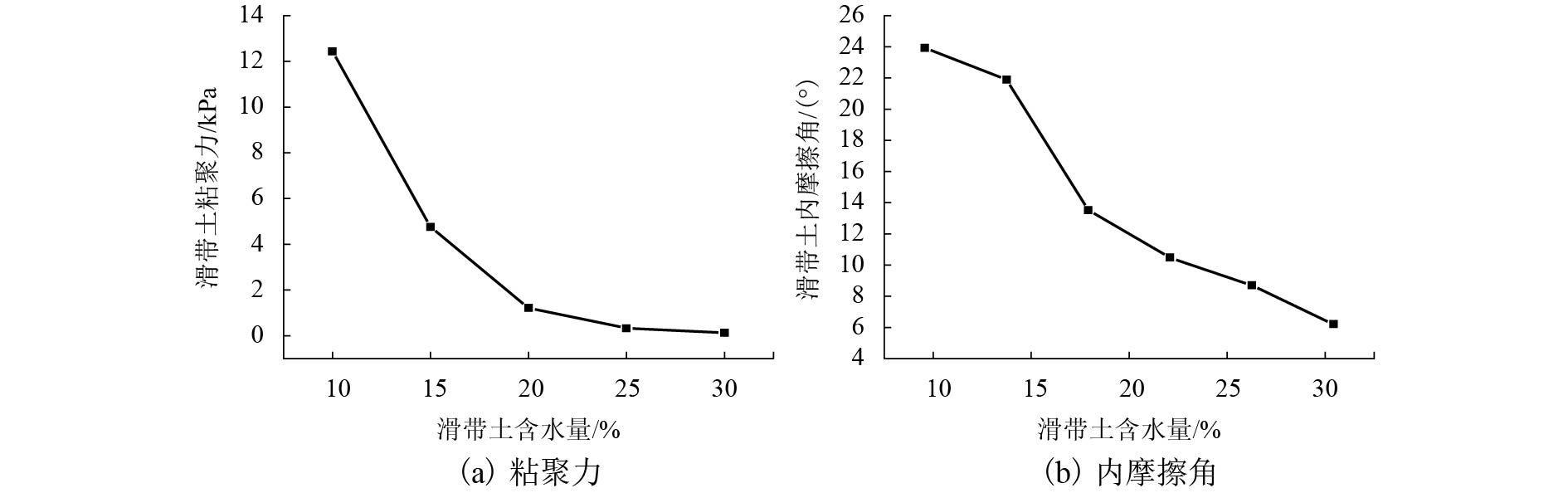
摘要: 斜坡发生牵引式滑动破坏,形成后缘拉裂面,后缘面形态对滑坡稳定性分析及推力计算具有重要影响,但其在滑坡体内部的空间特征难以确定. 为探索后缘破裂面的形成机理和计算理论,建立合理的数学力学模型,提出后缘破裂面倾角的计算方法,确定各级滑块的最危险破裂倾角,并将其所在破裂面作为条分型式,计算各级滑块的稳定系数,实现滑坡渐进破坏过程的稳定性分析;同时,开展室内模型试验进行验证,研发了新的模型试验装置,其主体由若干渗透盒组成,能够构成各种几何形状的分段式滑面;通过向不同分段的渗透盒注水,实现牵引式滑坡的逐级失稳过程,并测试各级滑块最终形态的后缘破裂面倾角. 结果表明:后缘破裂面倾角计算值与试验值具有较高的一致性,主要集中在70° 左右,相对误差介于2%~4%之间;滑坡体失稳形成的各级滑块稳定性不同,第一级滑块的稳定程度最差,越向坡体后侧稳定性越好. 可为牵引式滑坡的稳定性分析提供新的思路.Abstract: Slope failure is induced by retrogressive slide, forming a trailing edge tension crack surface. The shape of the trailing edge surface has an important influence on landslide stability analysis and thrust calculation. However, it is difficult to determine the spatial characteristics of the landslide. In order to explore the formation mechanism and calculation theory of the trailing edge fracture surface, a reasonable mathematical and mechanical model was established. The calculation method of the trailing edge fracture inclination angle was put forward, from which the most dangerous fracture inclination angle of each level slider was found. Finally, the fracture surface was used as a stripe type to calculate the stability coefficient of each level slider and carry out the stability analysis of the landslide progressive failure process. Simultaneously, an indoor model test was conducted for verification. A new model test device was developed as well. Its main body was composed of a number of permeable boxes, thereby forming sectional sliding surfaces of various geometric shapes. By injecting water into different permeable boxes, step-by-step instability process of retrogressive landslide was realized. Then the trailing edge inclination of the final form of the sliders at each stage was measured. The results show that the calculated value of the inclination of the trailing edge is in good agreement with the test value. It is mainly concentrated at about 70°, with a relative error between 2% and 4%. The stability of the sliders is different at each level. Thus, the stability of the first stage is the worst, whereas the stability of the backside of the landslide body is better. These research results can provide a new procedure for conducting the stability analysis of retrogressive landslide.
-
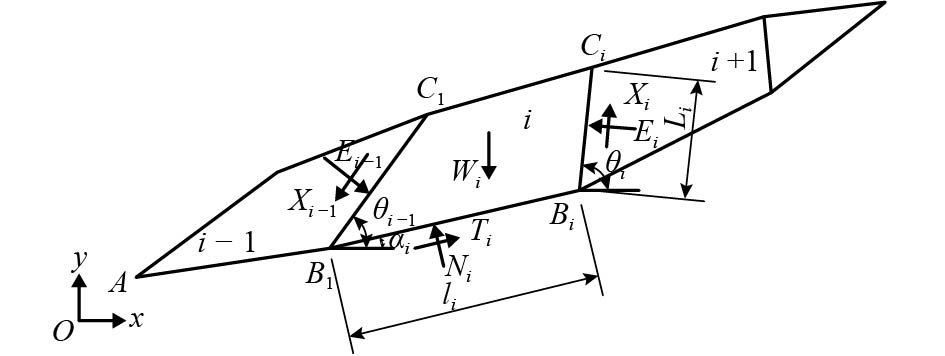
表 1 滑块1:后缘面破裂倾角计算结果
Table 1. Block 1: results of the fracture angle of the trailing edge
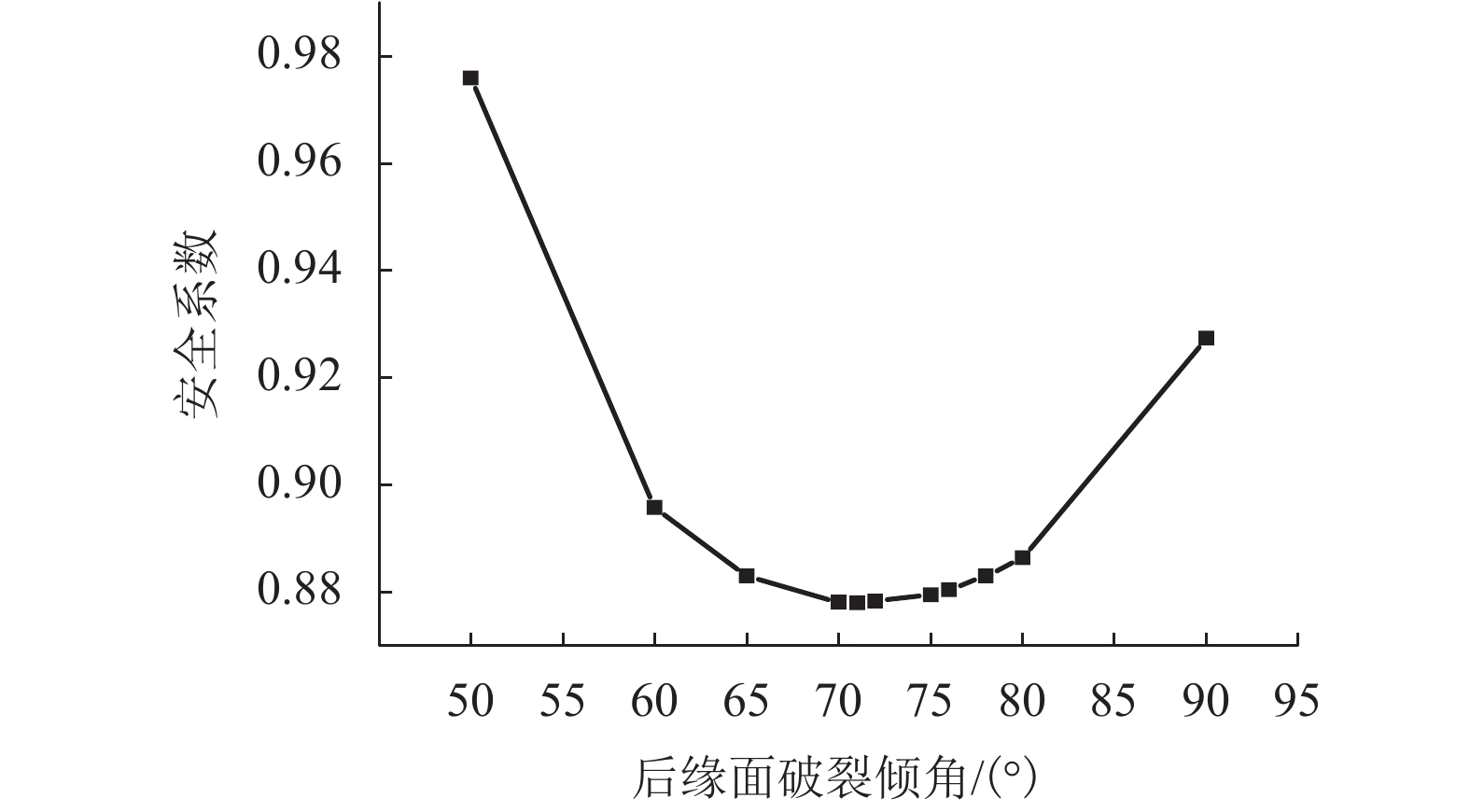
θ1/(°) Aera/m2 $l_{{B_1}{C_1}}$/m F1 30 0.189 8 0.955 6 2.475 0 40 0.131 2 0.630 8 1.226 3 50 0.114 2 0.494 0 0.975 9 60 0.086 3 0.416 3 0.895 7 65 0.079 3 0.390 2 0.882 9 70 0.073 2 0.355 1 0.878 0 71 0.072 2 0.349 6 0.877 9 72 0.071 1 0.344 9 0.878 3 75 0.068 2 0.328 4 0.879 4 76 0.067 2 0.323 8 0.880 4 78 0.065 5 0.315 3 0.882 9 80 0.063 7 0.307 6 0.886 3 90 0.056 2 0.283 4 0.923 7 100 0.051 2 0.247 7 0.936 1 110 0.045 4 0.230 9 0.973 6 表 2 滑块2:后缘面破裂倾角计算结果
Table 2. Block 2: results of the fracture angle of the trailing edge
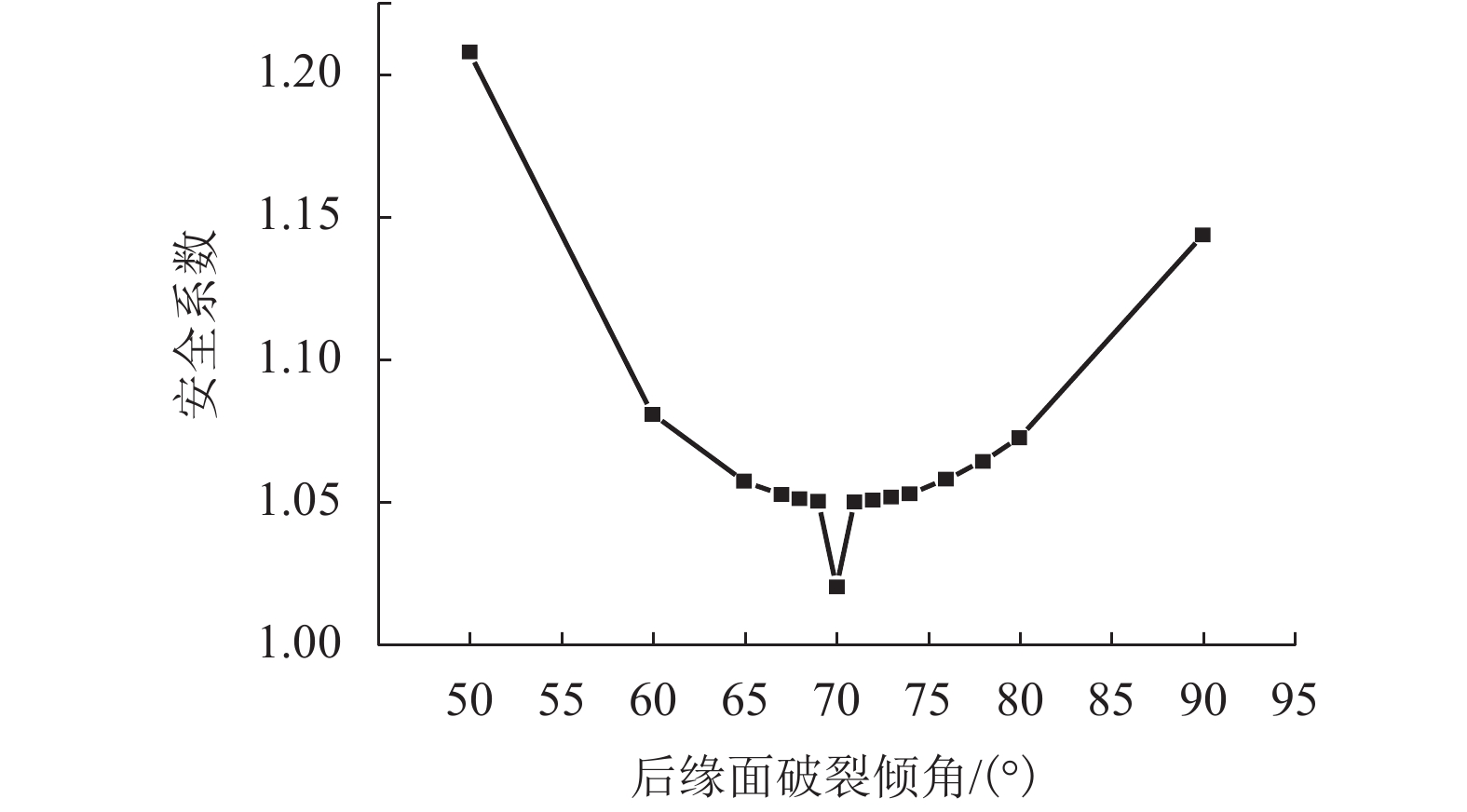
θ2/(°) Area/m2 $l_{{B_2}{C_2}}$/m F2 36 0.152 0 0.684 5 1.895 1 40 0.137 7 0.600 0 1.554 6 50 0.112 2 0.466 2 1.208 2 60 0.097 6 0.391 0 1.081 0 65 0.091 4 0.365 7 1.057 5 67 0.089 1 0.357 2 1.053 0 68 0.088 0 0.353 2 1.051 5 69 0.086 9 0.349 4 1.050 7 70 0.085 8 0.345 9 1.050 6 71 0.084 8 0.342 4 1.050 4 72 0.083 8 0.339 2 1.051 0 73 0.082 8 0.336 1 1.052 0 74 0.081 9 0.333 2 1.053 2 76 0.079 9 0.327 8 1.058 3 78 0.078 1 0.323 1 1.064 6 80 0.076 3 0.318 7 1.072 8 90 0.067 9 0.304 0 1.144 0 100 0.059 9 0.299 3 1.281 4 110 0.052 1 0.303 9 1.536 0 120 0.043 9 0.306 7 1.906 7 122 0.041 8 0.308 7 2.018 4 表 3 滑块3:后缘面破裂倾角计算结果
Table 3. Block 3: results of the fracture angle of the trailing edge
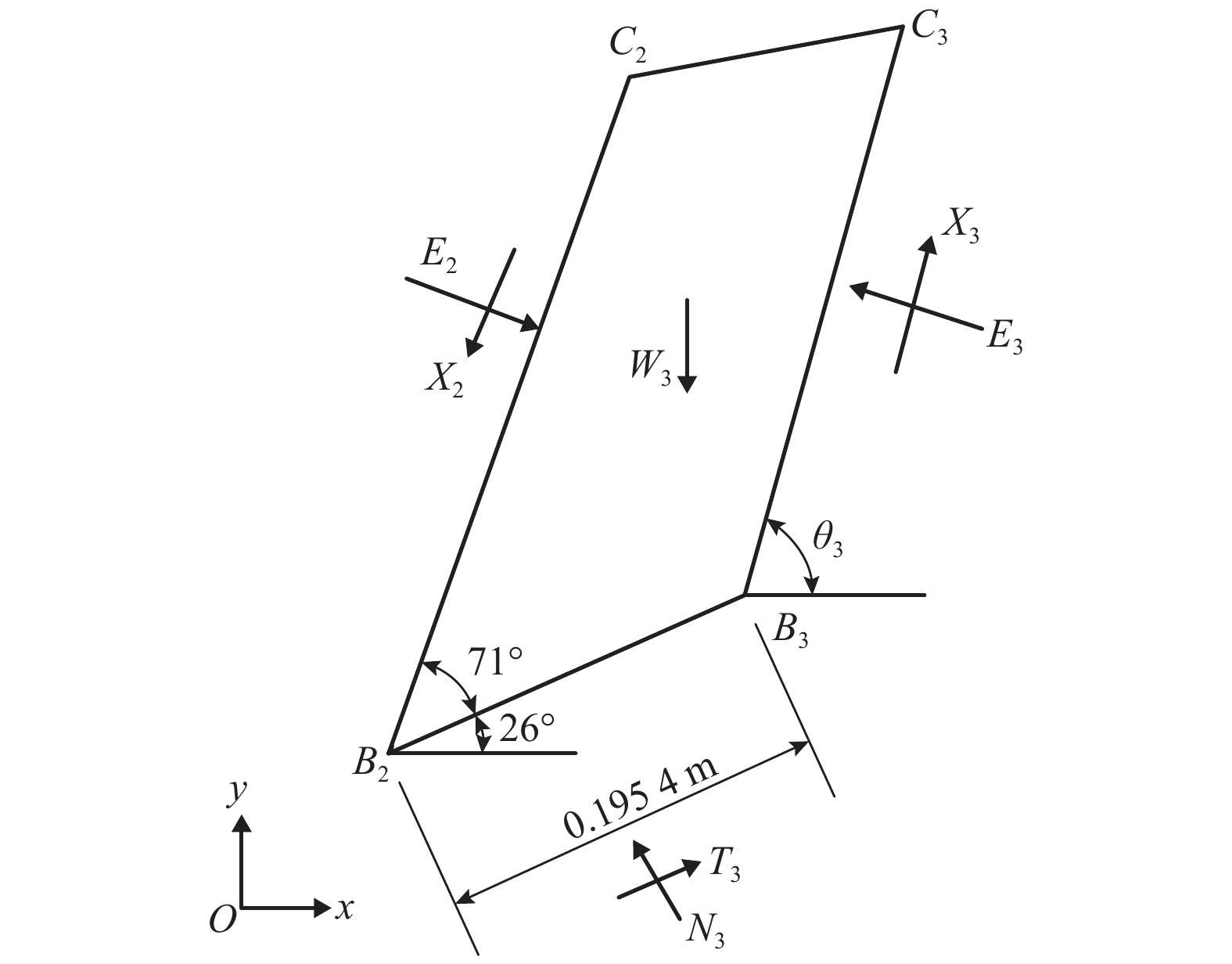
θ3/(°) Area/m2 $l_{{B_3}{C_3}}$/m F3 39 0.085 7 0.493 1 1.524 7 50 0.061 0 0.375 1 1.373 5 60 0.050 7 0.316 4 1.275 9 61 0.049 9 0.312 0 1.269 8 62 0.049 0 0.307 8 1.267 7 63 0.048 2 0.303 8 1.264 3 64 0.047 4 0.300 0 1.262 1 65 0.046 6 0.296 4 1.261 0 66 0.045 9 0.293 0 1.258 3 67 0.045 2 0.289 7 1.256 6 68 0.044 4 0.286 6 1.258 8 69 0.043 7 0.283 7 1.259 2 70 0.043 0 0.280 9 1.260 5 80 0.036 7 0.260 6 1.300 5 90 0.031 1 0.248 4 1.388 6 100 0.025 8 0.245 3 1.542 4 105 0.023 6 0.245 9 1.627 8 表 4 后缘面破裂倾角统计表
Table 4. Inclinations of the trailing edge
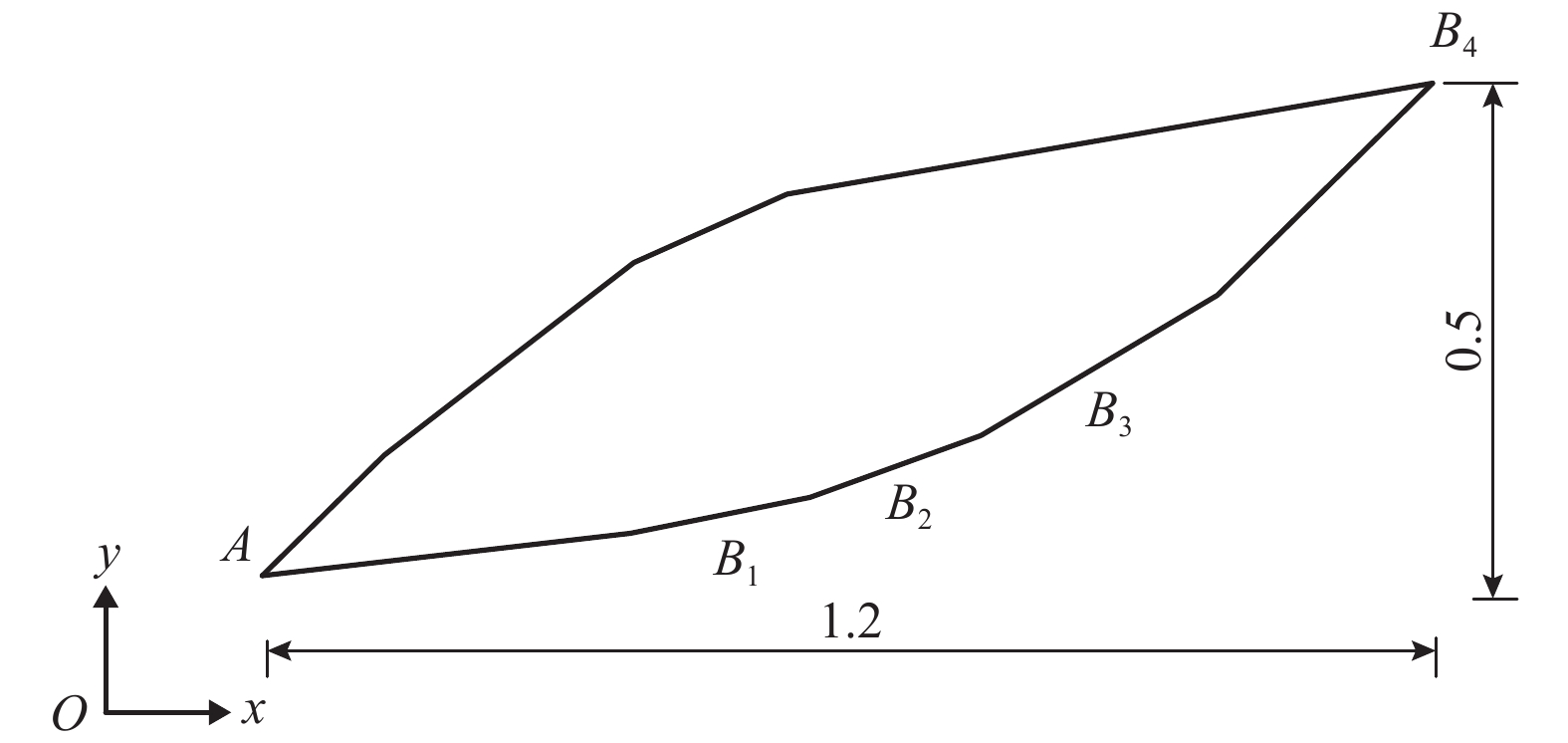
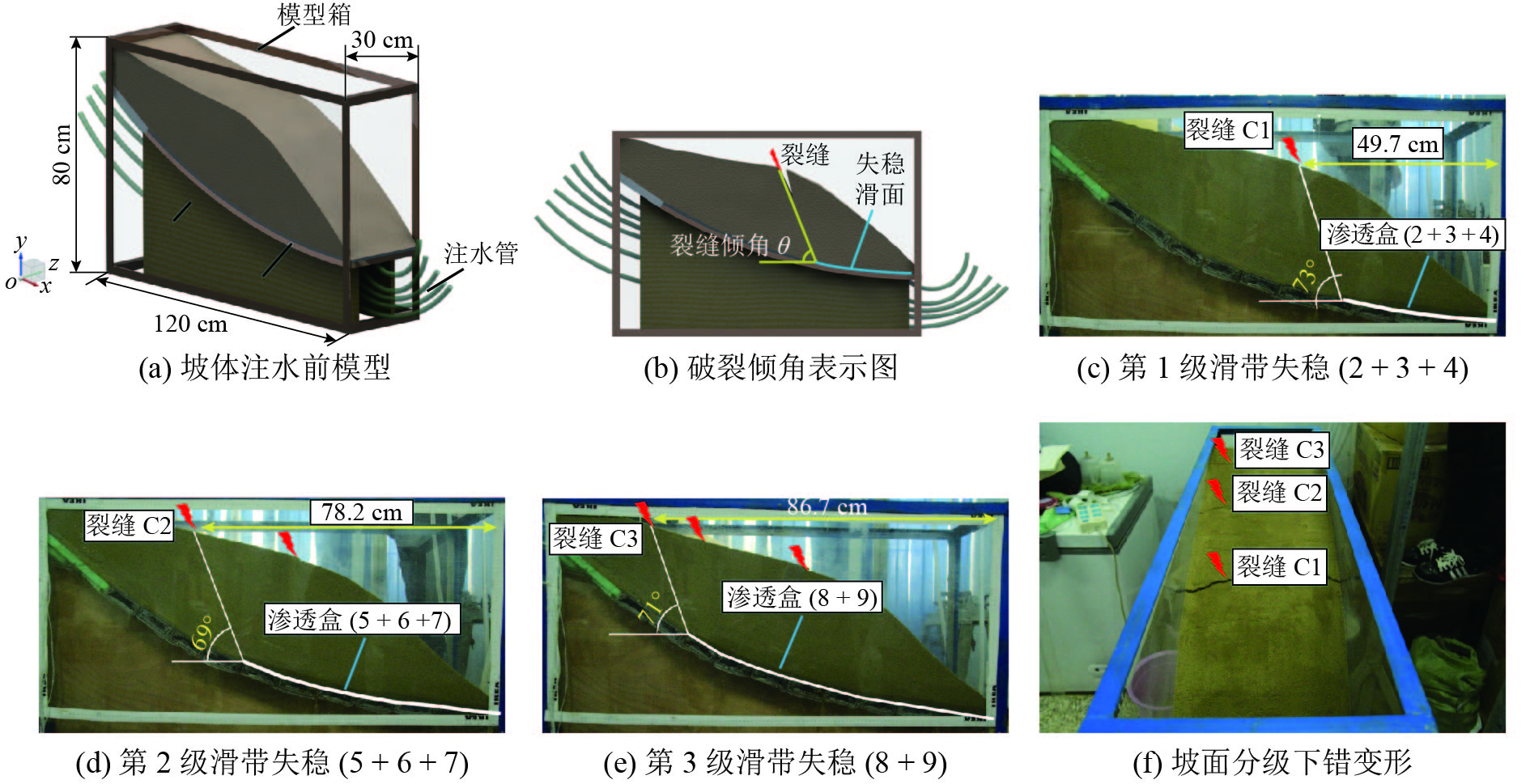
对象 工况1 工况2 工况3 渗透盒 2 + 3 + 4 5 + 6 + 7 8 + 9 破裂角/(°) 73 69 71 注:模型试验的第1级滑带长度(渗透盒2 + 3 + 4)即对应 图4中的AB1段;第2级滑带长度 (渗透盒5 + 6 + 7) 对 应B1B2段;第3级滑带长度 (渗透盒8 + 9) 对应B2B3段. (比例1 : 1) -
MARKO K, HANG T, PEETER T, et al. Analysis of a retrogressive landslide in glaciolacustrine varved clay[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 116: 109-116. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.07.012 张俊文,邹烨,李玉琳. 大型多层次堆积体破坏模式及其稳定性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(12): 2479-2489.ZHANG Junwen, ZOU Ye, LI Yulin. Faliure mechanism and stability analysis of big multi-layer deposit[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(12): 2479-2489. 周跃峰,龚壁卫,胡波,等. 牵引式滑坡演化模式研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(10): 1855-1862. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201410013ZHOU Yuefeng, GONG Biwei, HU Bo, et al. Evolution mode of retrogressive landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(10): 1855-1862. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201410013 王恭先, 王应先, 马惠民. 滑坡防治100例[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2008: 54-58 谭福林, 胡新丽, 张玉明, 等. 牵引式滑坡推力计算方法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(增刊2): 532-538TAN Fulin, HU Xinli, ZHANG Yuming, et al. Study of calculation method of retrogressive landslide thrust[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(S2): 532-538 张俊瑞. 某典型牵引式滑坡形成机制分析及稳定性评价[J]. 土工基础,2010,24(2): 45-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3152.2010.02.015ZHANG Junrui. Fourmation mechanism and stability analysis of a typical retrogressive landslide[J]. Soil Engineering and Foundation, 2010, 24(2): 45-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3152.2010.02.015 宋东日,任伟中,沈波,等. 牵引式滑坡的破坏机制及其加固措施探讨——以某高速公路牵引式滑坡为例[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(12): 3587-3593.SONG Dongri, REN Weizhong, SHEN Bo, et al. Discussion on failure mechanism of retrogressive landslide and its reinforcement measures:taking a certain expressway retrogressive landslide for example[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(12): 3587-3593. 曹弼,陈征宙,王树州,等. 不平衡推力法在牵引式滑坡中的优化计算—局部安全系数法[J]. 中国水运,2013,13(12): 132-136. 袁从华,童志怡,卢海峰. 牵引式滑坡特征及主被动加固比较分析[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(10): 2853-2858. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.10.049YUAN Conghua, TONG Zhiyi, LU Haifeng. Analysis of characteristics of retrogressive landslide and comparison between active and passive reinforcements[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(10): 2853-2858. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.10.049 ZHU D Y, LEE C F. Generalised framework of limit equilibrium methods and numerical procedure for slope stability analysis[J]. Geotechnique, 2003, 53(4): 377-395. doi: 10.1680/geot.2003.53.4.377 殷宗泽. 土工原理[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2007: 302-344 陈祖煜. 土质边坡稳定性分析——原理、方法、程序[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2003: 23-65 彭振斌,李俊,彭文祥. 基于Bishop条分法的边坡可靠度应用研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2010,41(2): 668-672.PENG Zhenbin, LI Jun, PENG Wenxiang. Application analysis of slope reliability based on Bishop analytical method[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2010, 41(2): 668-672. 刘子振,言志信. 边坡稳定计算斜条分法机理分析[J]. 岩土工程技术,2006,20(5): 217-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2006.05.001LIU Zizhen, YAN Zhixin. Mechanism analysis based on sub-section method of slices for slope stability calculation[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2006, 20(5): 217-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2006.05.001 CHEN C F, YANG Y. The parallel slice method for analysis of soil nailing based on genetic algorithm[C]//GeoShanghai International Conference 2006. [S.l.]: Geotechnical Special Publication,2006: 188-194 董育烦,张发明,郭炳跃,等. 土坡等圆心角斜条分稳定性分析法[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(9): 2595-2598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.09.052DONG Yufan, ZHANG Faming, GUO Bingyue, et al. Analytical method of soil slope stability based on gradient slice and equal central angle[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(9): 2595-2598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.09.052 董育烦,孟永旭,王永明. 土坡等圆心角斜条分法与经典条分法的比较[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2009,37(6): 697-701.DONG Yufan, MENG Yongxu, WANG Yongming. Comparison of D slice method and classical slice methods for soil slopes[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2009, 37(6): 697-701. 邓东平,李亮. 水平条分法下边坡稳定性分析与计算方法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(10): 3179-3188.DENG Dongping, LI Liang. Analysis of slope stability and research of calculation method under horizontal slice method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(10): 3179-3188. 熊将,王涛,盛谦. 库区边坡稳定性计算的改进Sarma法[J]. 岩土力学,2006,27(2): 323-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.02.032XIONG Jiang, WANG Tao, SHENG Qian. Improved sarma method for computing slope stability in reservoir region[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(2): 323-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.02.032 REGMI R K, JUNG K, NAKAGAWA H, et al. Study on mechanism of retrogressive slope failure using artificial rainfall[J]. Catena, 2014, 112: 27-41. 李龙起,罗书学,王运超,等. 不同降雨条件下顺层边坡力学响应模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(4): 755-762.LI Longqi, LUO Shuxue, WANG Yunchao, et al. Model tests for mechanical response of bedding rock slope under different rainfall conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(4): 755-762. 杨旭,周翠英,刘镇,等. 华南典型巨厚层红层软岩边坡降雨失稳的模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(3): 549-557.YANG Xu, ZHOU Cuiying, LIU Zhen, et al. Model tests for mechanism of typical soft rock slopes of red beds under rainfall in South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(3): 549-557. 李卓,何勇军,盛金保,等. 降雨与库水位共同作用下近坝库岸边坡滑坡模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(3): 52-59.LI Zhuo, HE Yongjun, SHEN Jinbao, et al. Landslide model for slope of reservoir bank under combined effects of rainfall and reservoir water level[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(3): 52-59. -





 下载:
下载: