Numerical Study on Wave-Induced Oscillatory Liquefaction in Anisotropic Seabed
-
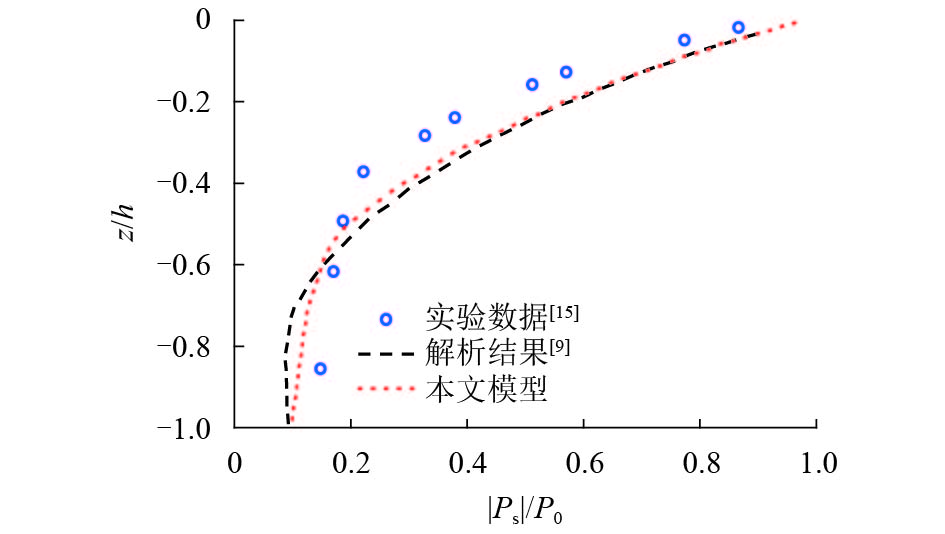
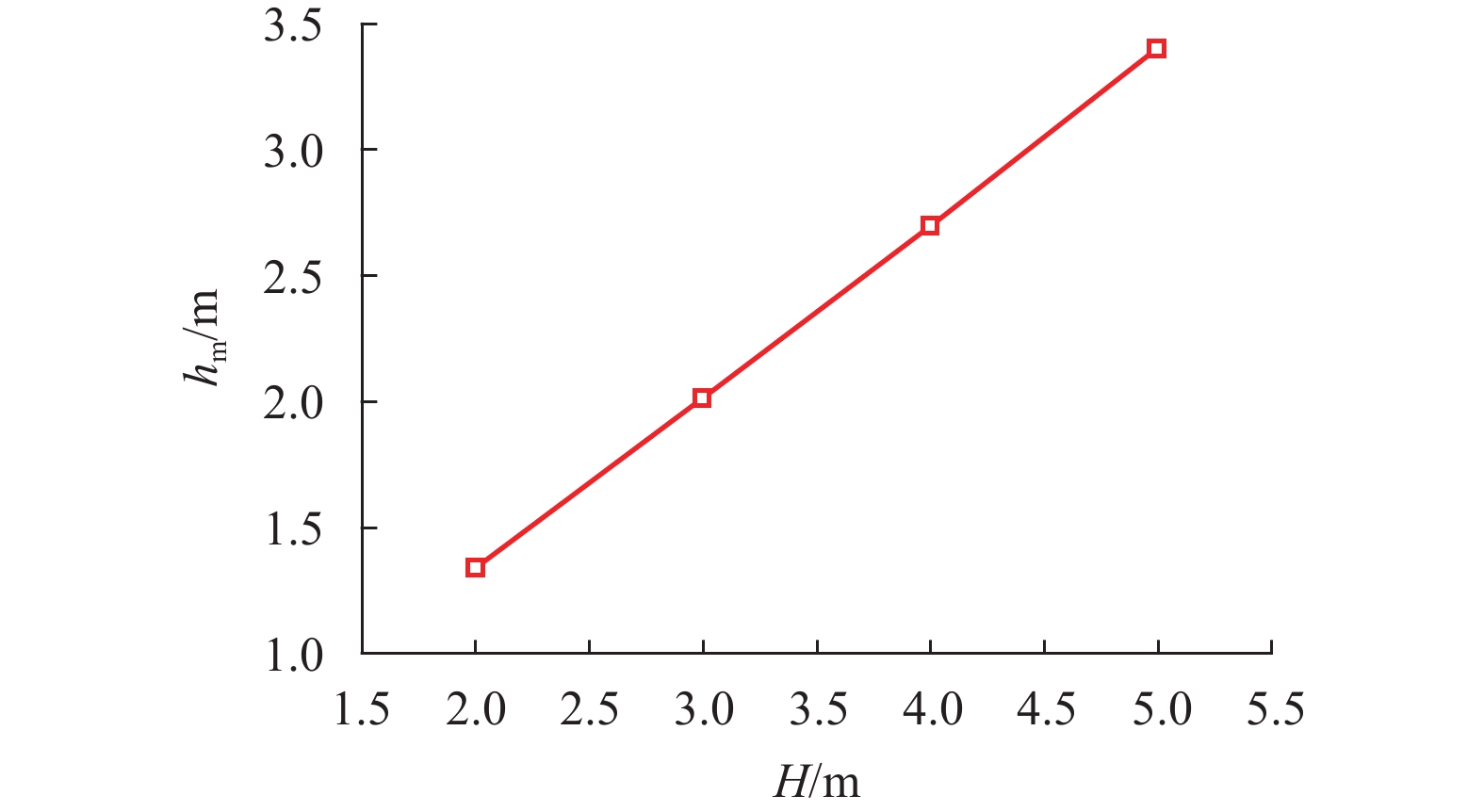
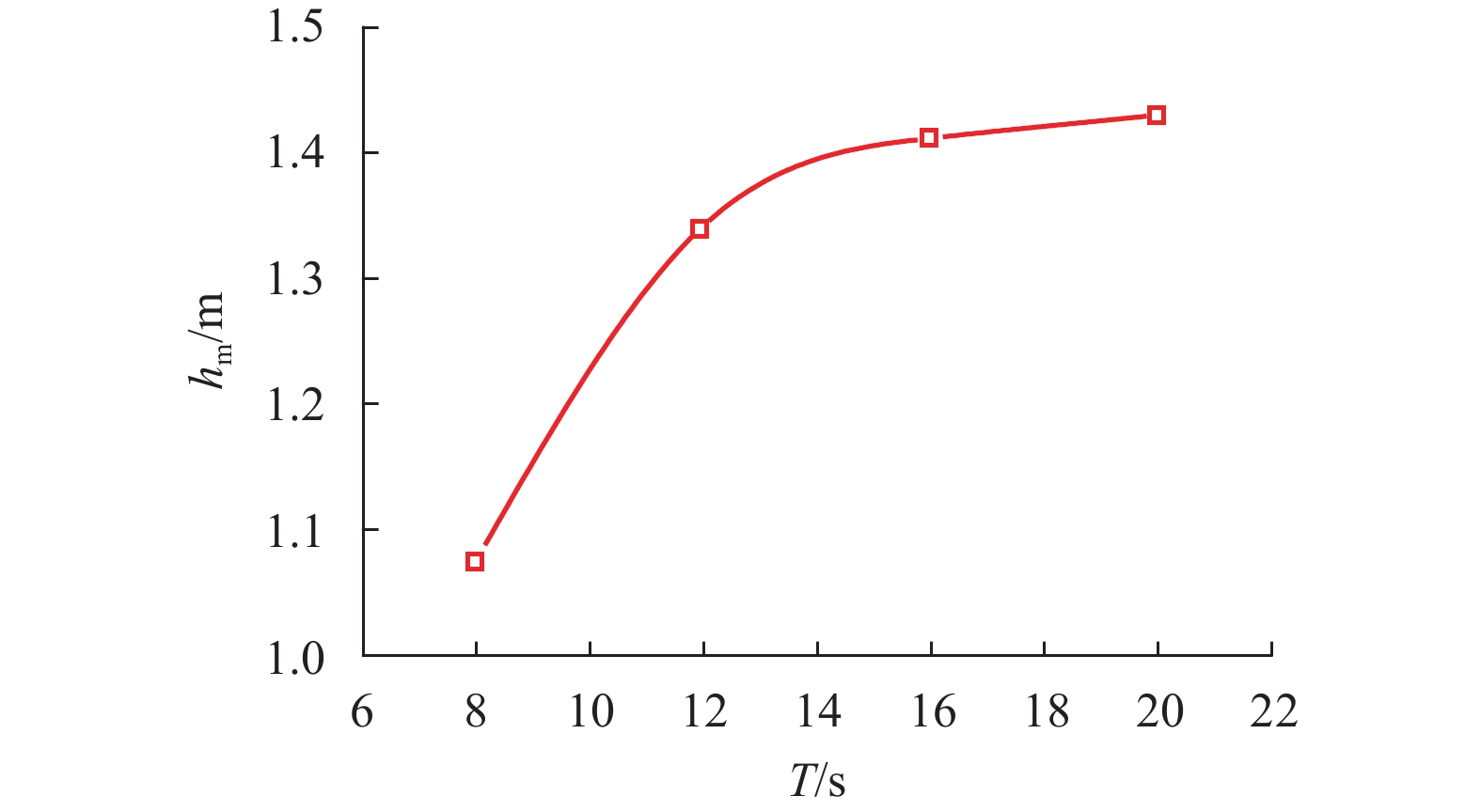
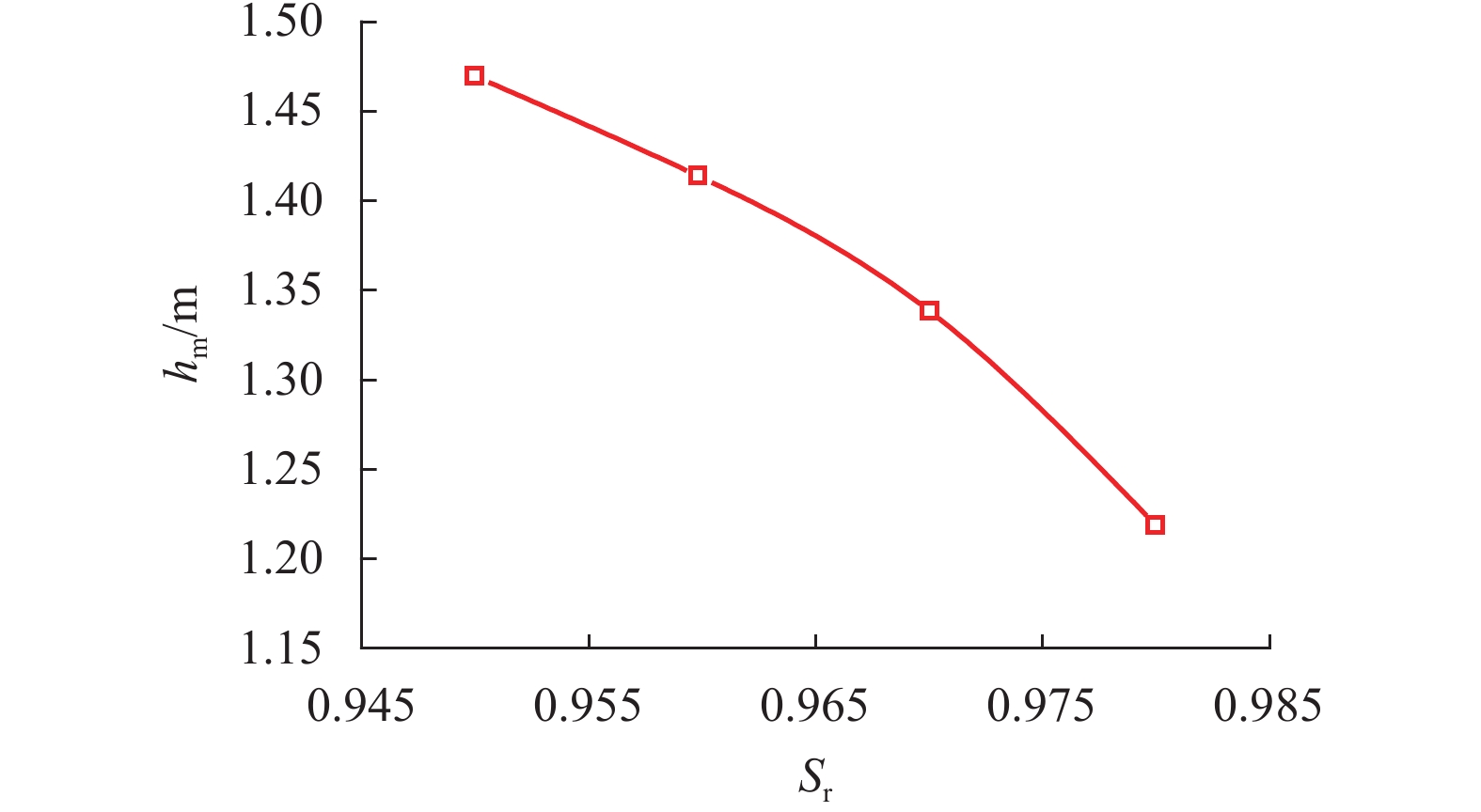
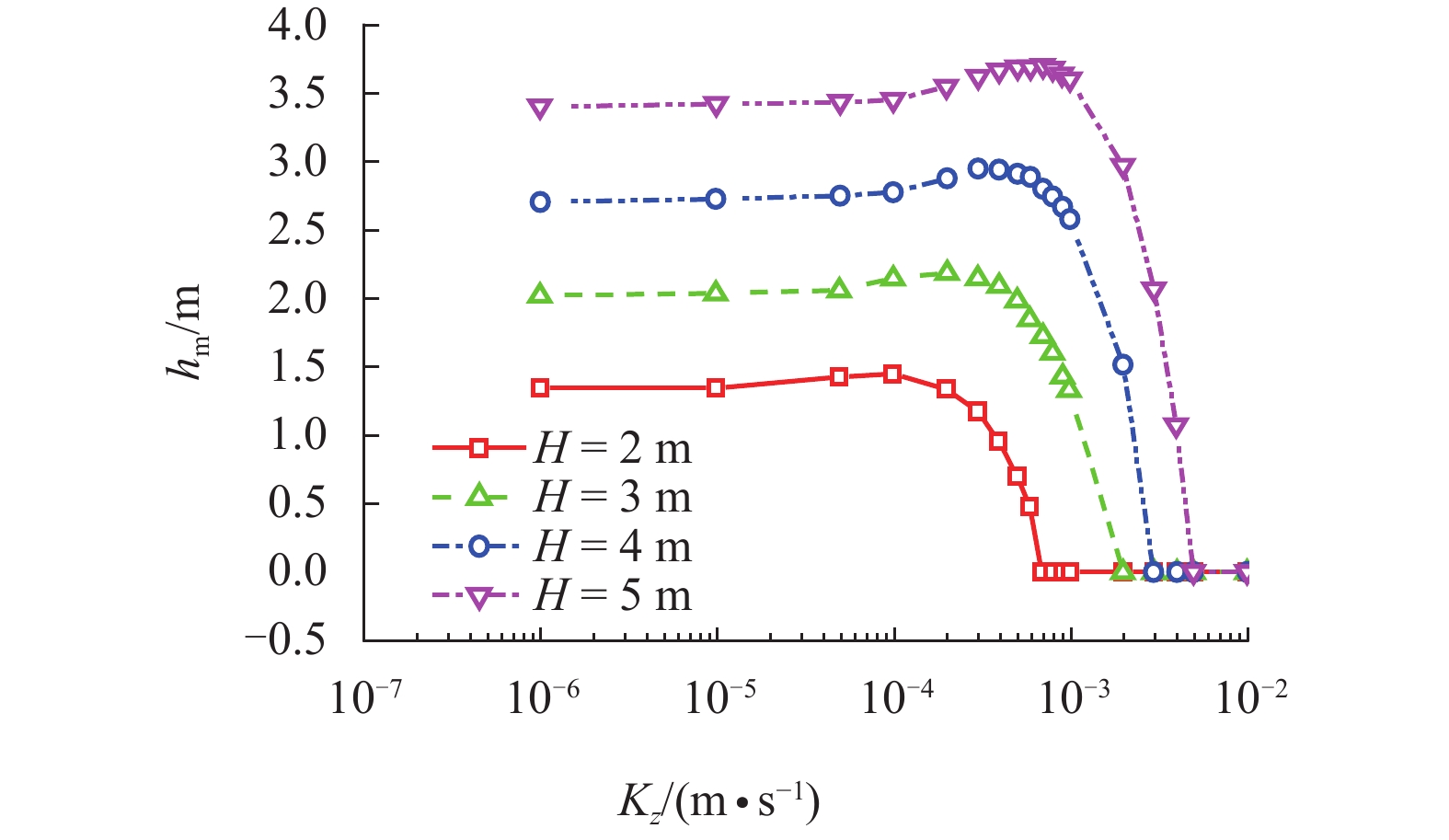
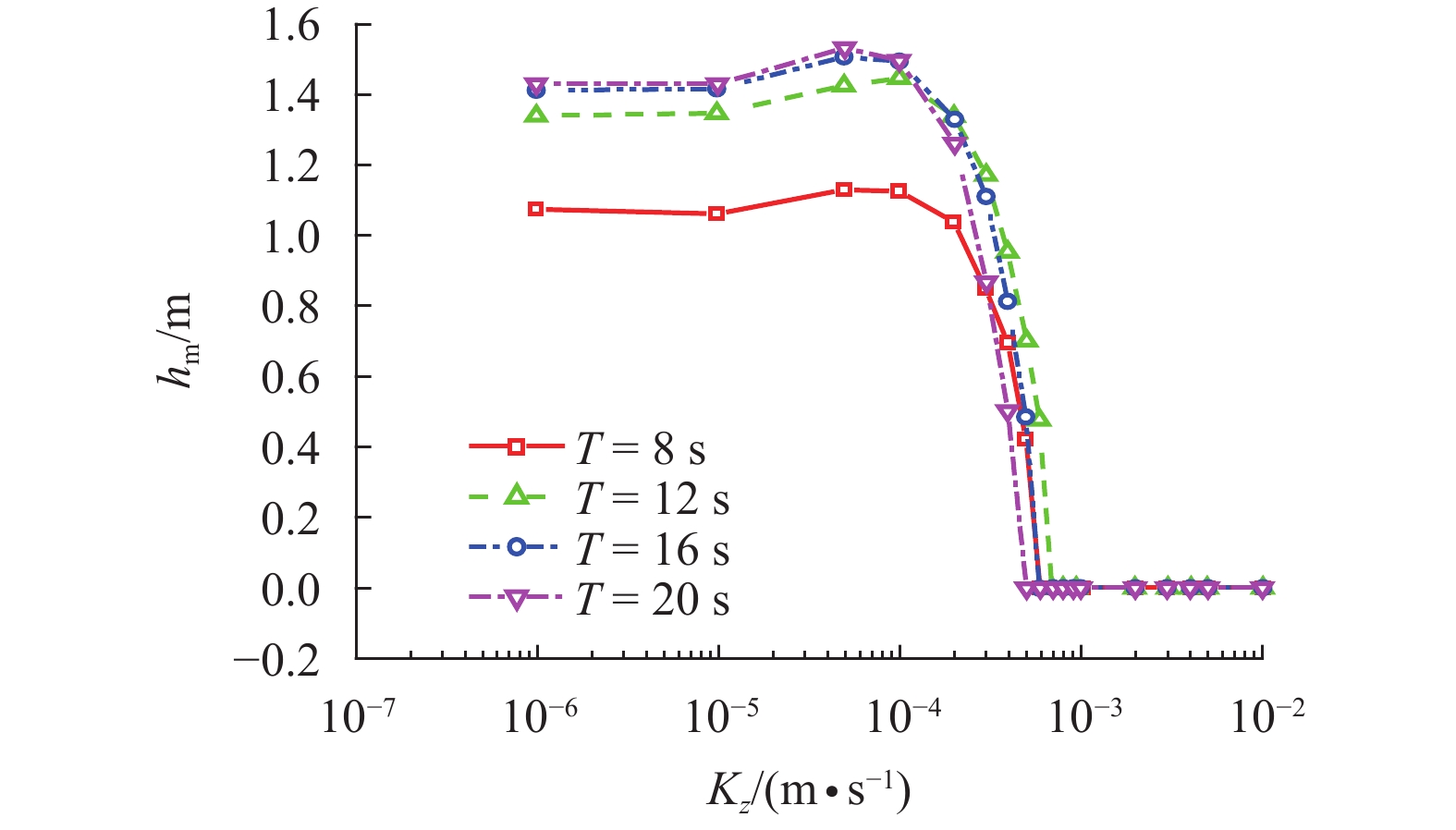
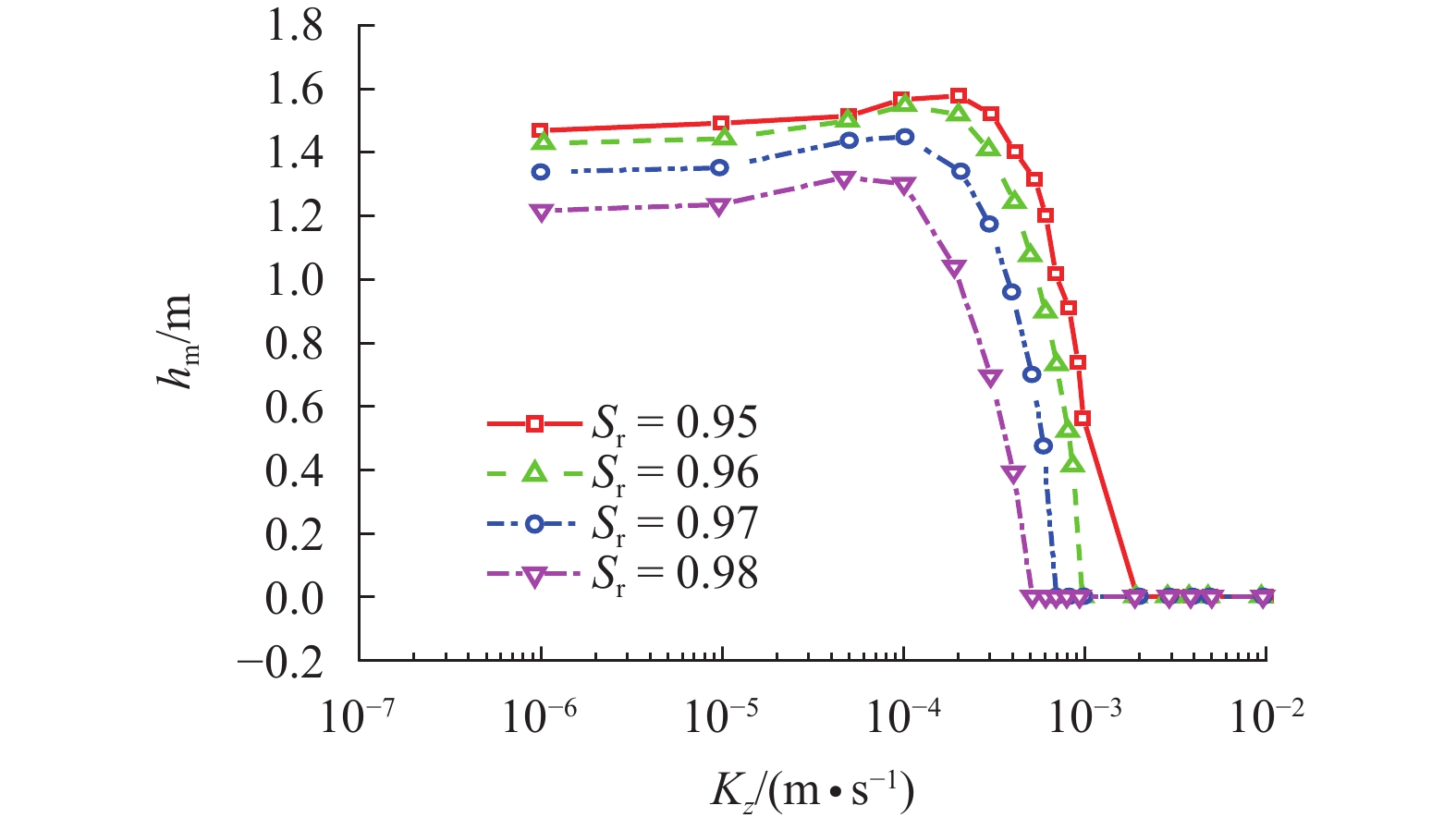
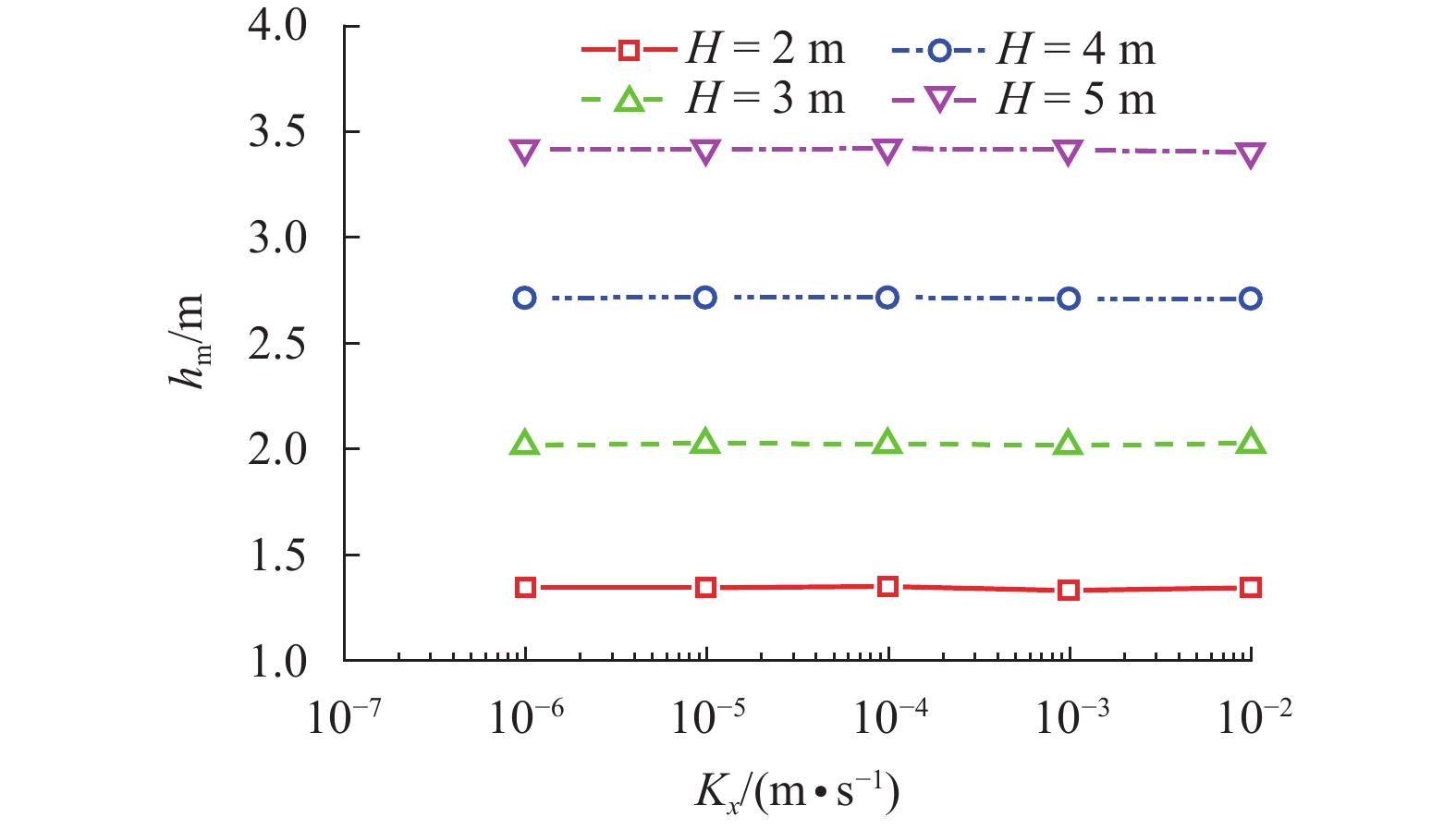
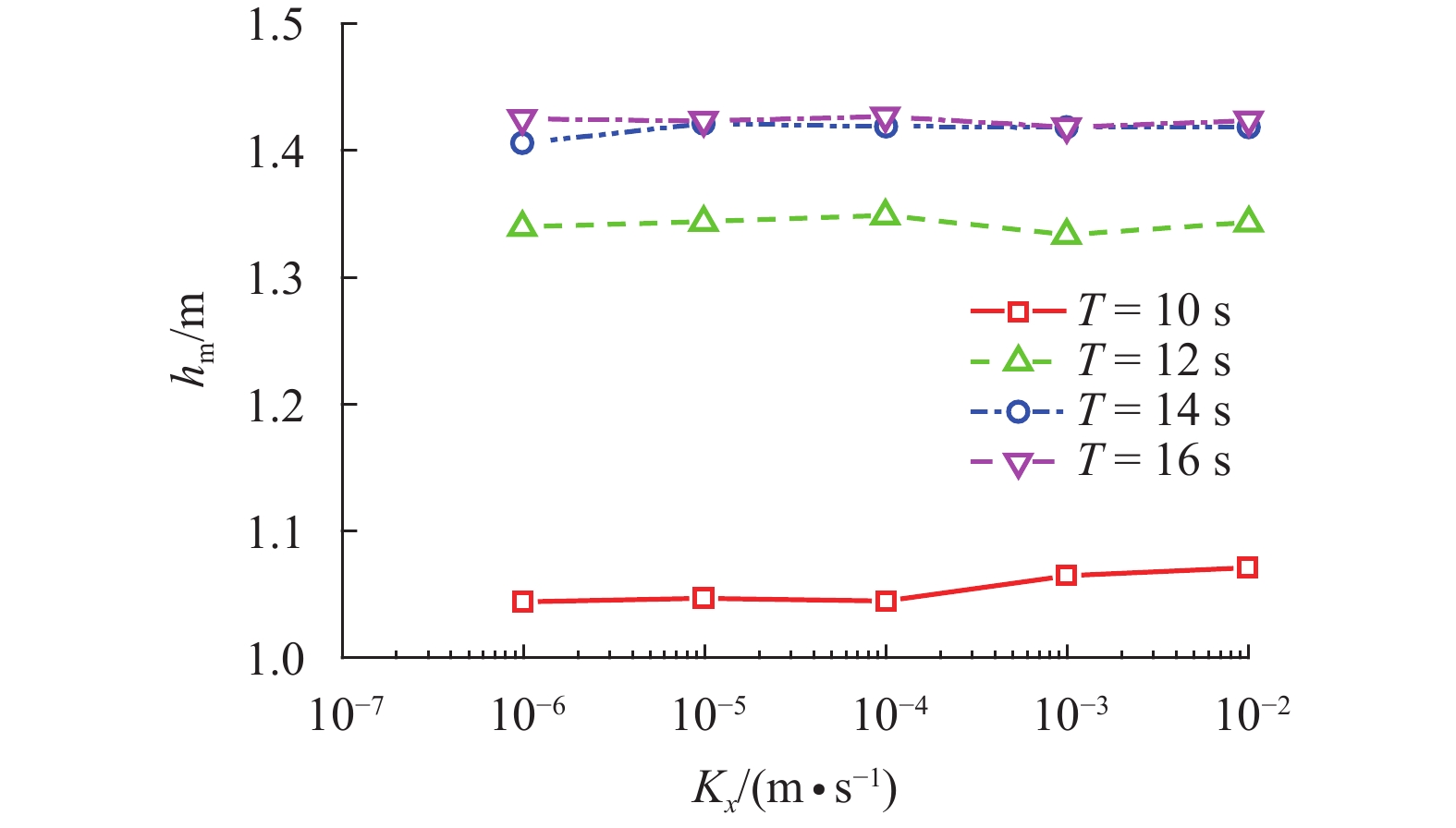
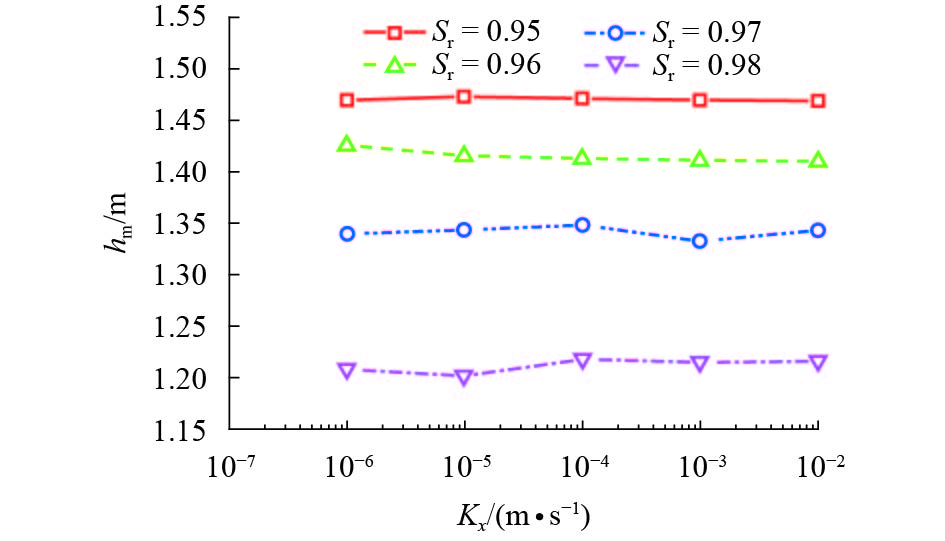
摘要: 为探究各向异性海床在波浪作用下的瞬态液化问题,采用有限元法求解RANS (reynolds averaged navier-stokes)方程及k-ε湍流模型进行数值造波,通过求解Biot多孔弹性方程获得海床瞬态响应,进而建立了波浪-各向异性海床耦合作用的二维数值仿真模型. 在完成对新建模型的验证后,基于此模型系统地研究了波浪及海床特性对各向异性海床瞬态液化的影响. 研究结果表明:海床瞬态液化深度随波高、周期增大而增大,随海床饱和度增大而减小;当海床垂向渗透系数在一定范围内时,海床最大液化深度随垂向渗透系数增大而减小,超出该范围时,海床垂向渗透系数对海床最大液化深度的影响不明显;海床瞬态液化深度对水平方向渗透系数的改变不敏感.Abstract: In order to investigate the wave-induced oscillatory liquefaction in an anisotropic seabed, a two-dimensional numerical model for wave-seabed interactions is proposed. The reynolds-averaged navier-stokes (RANS) equation with the standard k-ε turbulence model was used to describe wave motions, and Biot’s poro-elastic equation was taken as the governing equation for the seabed model. After validation with previous experimental data and analytical solution, the proposed model was further applied to investigate the effects of wave and soil characteristics on anisotropic soil liquefaction. Numerical results show that the maximum liquefaction depth increased with an increase in wave height and wave period, and decreased with the degree of soil saturation. When the value of the soil permeability coefficient along the vertical direction is within a certain range, the effects of soil permeability along the vertical direction on the wave-induced soil response are obvious. Beyond the range, however, the effects of soil permeability along the vertical direction are almost negligible. Besides, the wave-induced oscillatory liquefaction depth in an anisotropic seabed is not sensitive to the variations in soil permeability along the horizontal direction.
-
Key words:
- liquefaction /
- RANS equation /
- Biot’s equation /
- seabed /
- anisotropy
-
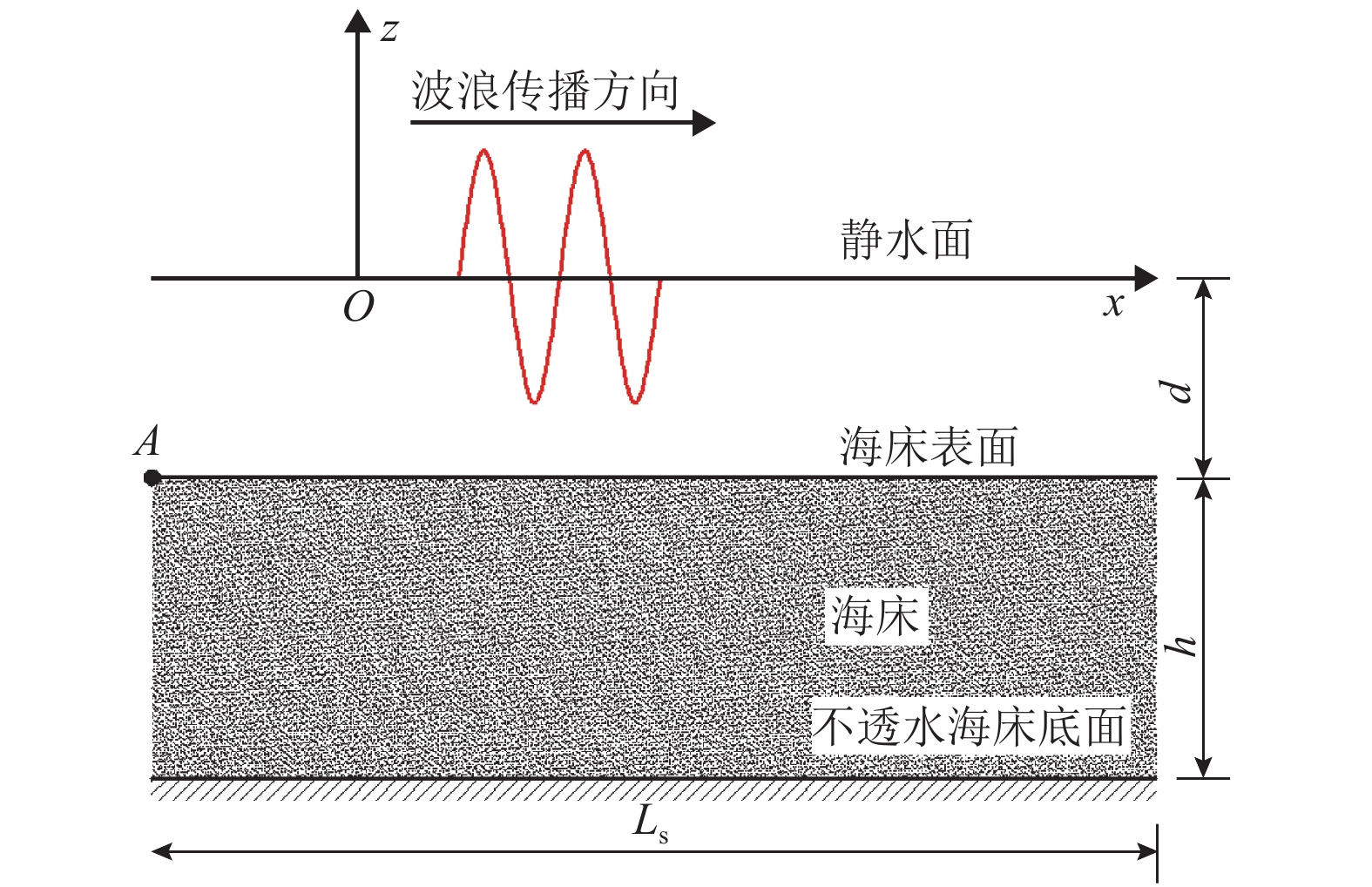
表 1 数值案例所取参数
Table 1. Parameters used in numerical examples
类型 参数 数值 波浪 H/m 2 d/m 10 T/s 12 h/m 20 海床土体 n 0.4 Kx/(m•s–2) 1 × 10–7 Kz/(m•s–1) 1 × 10–6 Sr 0.97 μs/(N•m–2) 1 × 107 -
ZHANG J S, JENG D S, LIU P L F, et al. Response of a porous seabed to water waves over permeable submerged breakwaters with bragg rection[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2012, 43: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2012.01.024 ZHANG J S, ZHANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. Numerical modeling of seabed response to the combined wave-current loading[J]. Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, 2013, 135(3): 031102. YE J H, JENG D S. Response of seabed to natural loadings-waves and currents[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 138(6): 601-613. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0000356 YE J H, JENG D S, WANG R, et al. Validation of a 2D semi-coupled numerical model for fluid-structure-seabed interaction[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2013, 42: 333-357. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2013.04.008 SUMER B M, TRUELSEN C, FREDSØE J. Liquefaction around pipelines under waves[J]. Journal of Waterway,Port,Coastal,and Ocean Engineering, 2006, 132: 266-275. 段伦良,郑东生,张启博,等. 半埋式海底管道周围海床瞬态液化稳定性研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(4): 671-677.DUAN Lunliang, ZHENG Dongsheng, ZHANG Qibo, et al. Numerical tudy on wave-induced oscillatory soil liquefaction around a partially buried pipeline[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(4): 671-677. 段伦良,王少华,张启博,等. 三维水流作用下哑铃型围堰周围海床局部冲刷[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(4): 704-711.DUAN Lunliang, WANG Shaohua, ZHANG Qibo, et al. 3D current-induced local scour around dumbbell-shaped steel suspending cofferdams[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(4): 704-711. BIOT M A. General theory of three-dimensional consolidation[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1941, 12: 155-164. doi: 10.1063/1.1712886 MADSEN O S. Wave-induced pore pressures and effective stress in a porous bed[J]. Geotechnique, 1978, 28(4): 377-393. doi: 10.1680/geot.1978.28.4.377 YAMAMOTO T, SELLMEIHER H L, HIJUM E V. On the response of a porous-elastic bed to water waves[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1978, 87(1): 193-206. doi: 10.1017/S0022112078003006 HSU J R C, JENG D S. Wave-induced soil response in an unsaturated anisotropic seabed of finite thickness[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 1994, 18(11): 785-807. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9853 ZEN K, YAMAZAKI H. Mechanism of wave-induced liquefaction and densification in seabed[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1990, 30(4): 90-104. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.30.4_90 SAKAI T, HANTANAKA K, MASE H. Wave-induced effective stress in seabed and its momentary liquefaction[J]. Journal of Waterway,Port,Coastal,and Ocean Engineering, 1992, 118(2): 202-206. JENG D S, ZHAO H Y. Two-dimensional model for accumulation of pore pressure in marine sediments[J]. Journal of Waterway,Port,Coastal,and Ocean Engineering, 2015, 14(3): 1-12. 黄光爵,郑永来,武伯弢. 波浪作用下可液化海床最大液化深度[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2012,32(5): 146-151.HUANG Guangjue, ZHENG Yonglai, WU Botao. The maximum liquefaction depth of liquefiable seabed under wave loading[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2012, 32(5): 146-151. SUZUKI K, TAKAHASHI S. Liquefaction of loosely deposited sandbed behind a breakwater due to wave overtopping[C]//Coastal Structures 2003. Portland: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2003: 656-662 LIU B, JENG D S, YE G L et al. Laboratory study for pore pressures in sandy deposit under wave loading[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 106: 207-219. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.06.029 张金凤,张庆河,秦崇仁. 波浪作用下非均质各向异性海床响应的数值模拟[J]. 天津大学学报,2006,39(2): 159-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0493-2137.2006.02.007ZHANG Jinfeng, ZHANG Qinghe, QIN Chongren. Numerical simulation of wave-induced response of inhomogeneous and anisotropic seabed[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 2006, 39(2): 159-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0493-2137.2006.02.007 YU H, ZENG X, LI B, et al. Effect of fabric anisotropy on liquefaction of sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2013, 139(5): 765-774. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000807 ZHOU X L, WANG J H, ZHANG J, et al. Wave and current induced seabed response around a submarine pipeline in an anisotropic seabed[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2014, 75: 112-127. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2013.11.016 ZHAO H Y, JENG D S, LIAO C C. Effects of cross-anisotropic soil behaviour on the wave-induced residual liquefaction in the vicinity of pipeline buried in elasto-plastic seabed foundations[J]. Soil Dynamic and Earthquake Engineering, 2016, 80: 40-55. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.10.004 LIN P Z, LIU P L F. Internal wave-maker for Navier-Stokes equations models[J]. Journal of Waterway,Port,Coastal,and Ocean Engineering, 1999, 125(4): 207-214. -




 下载:
下载: