Analysis of Vibration Reduction and Vibration Measurement for Long-Span Railway Station Floor Slab
-
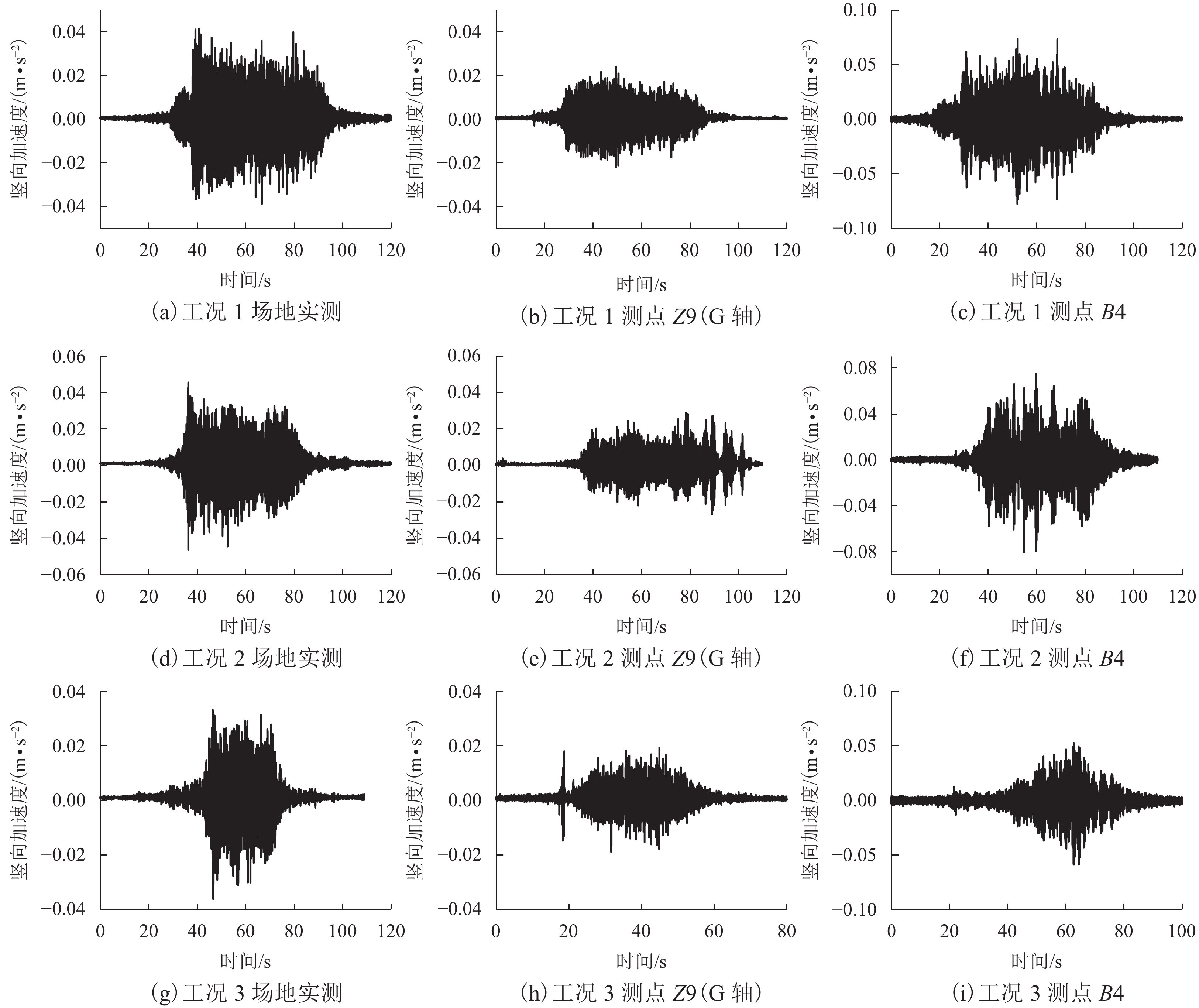
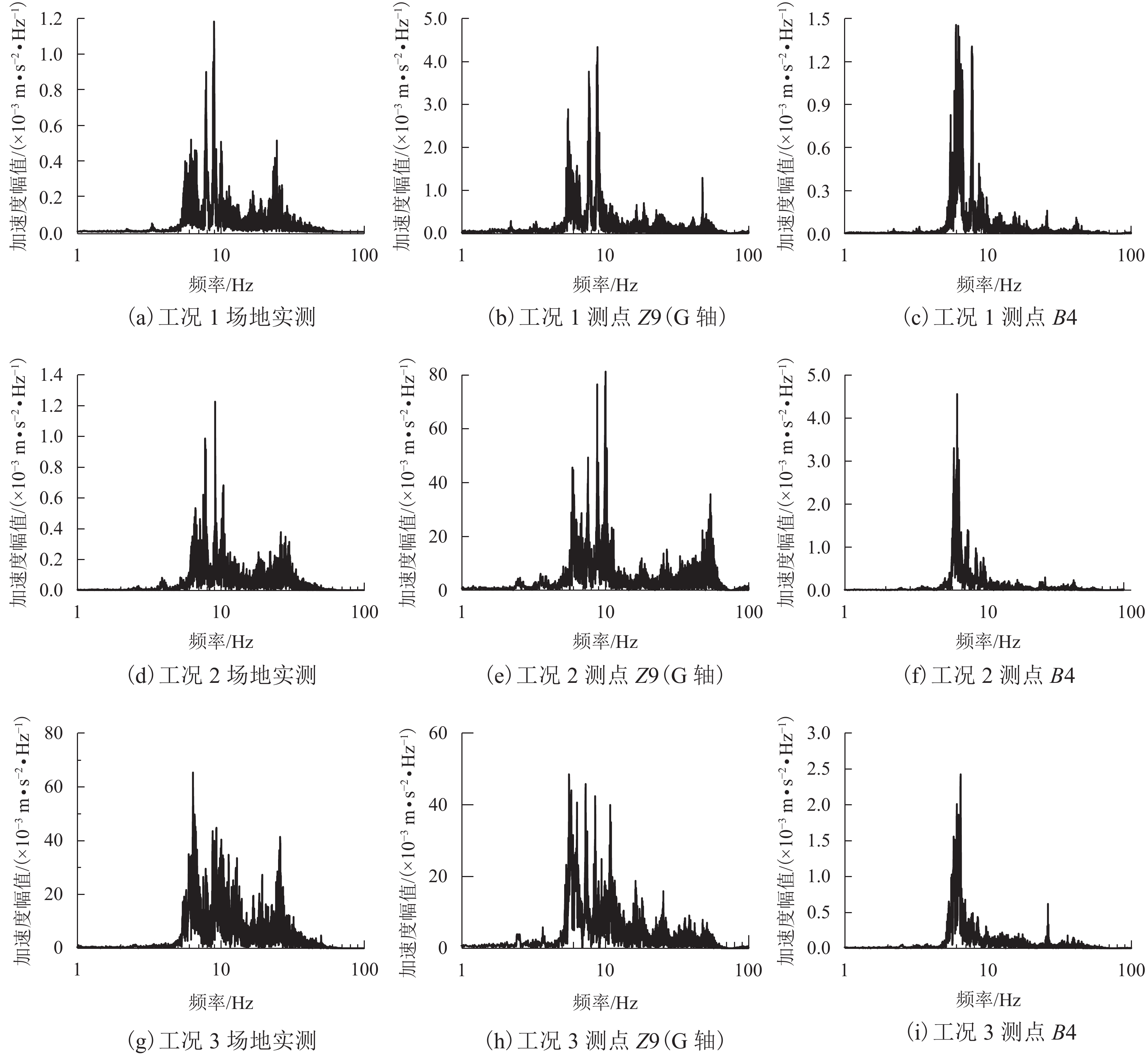
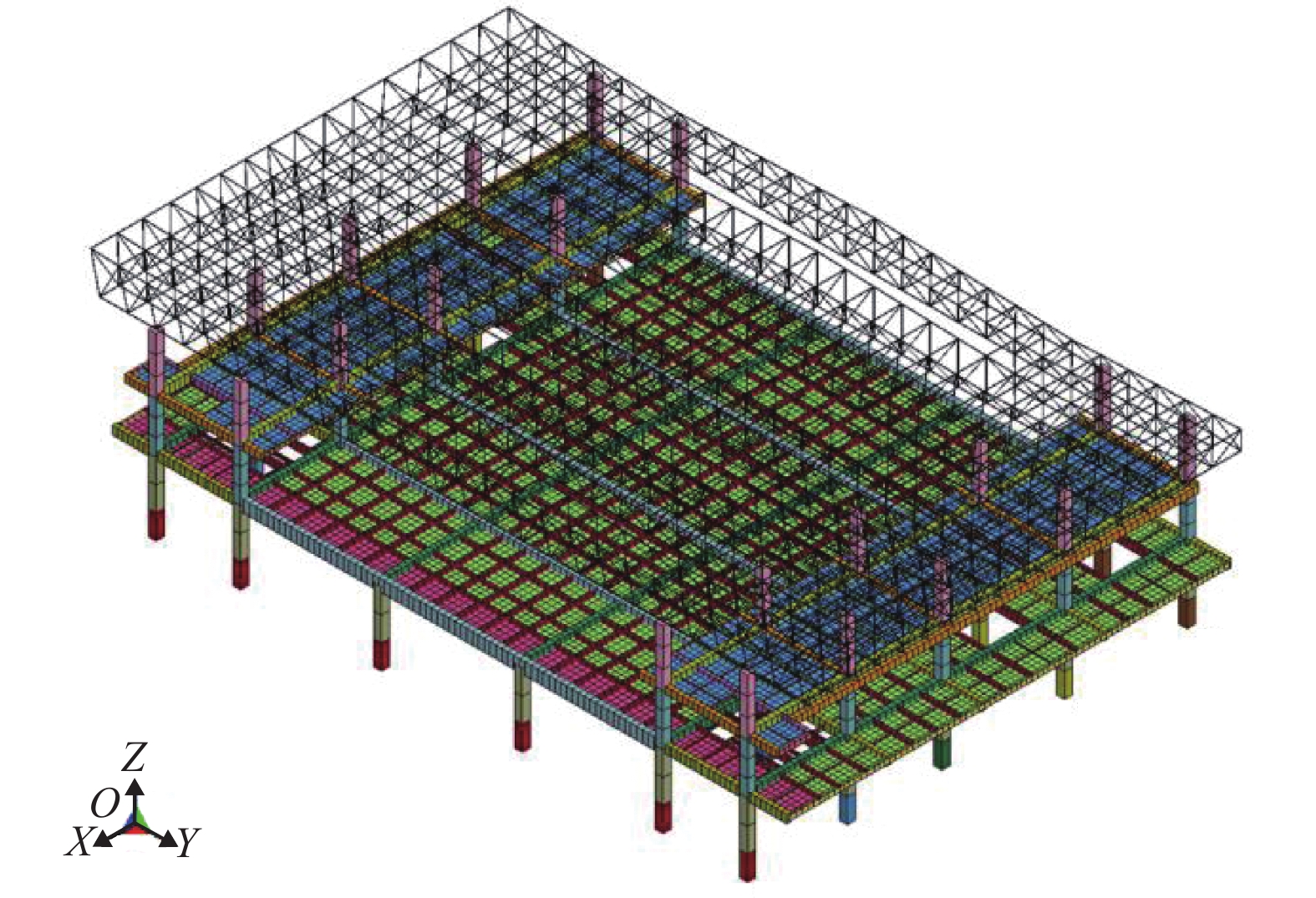
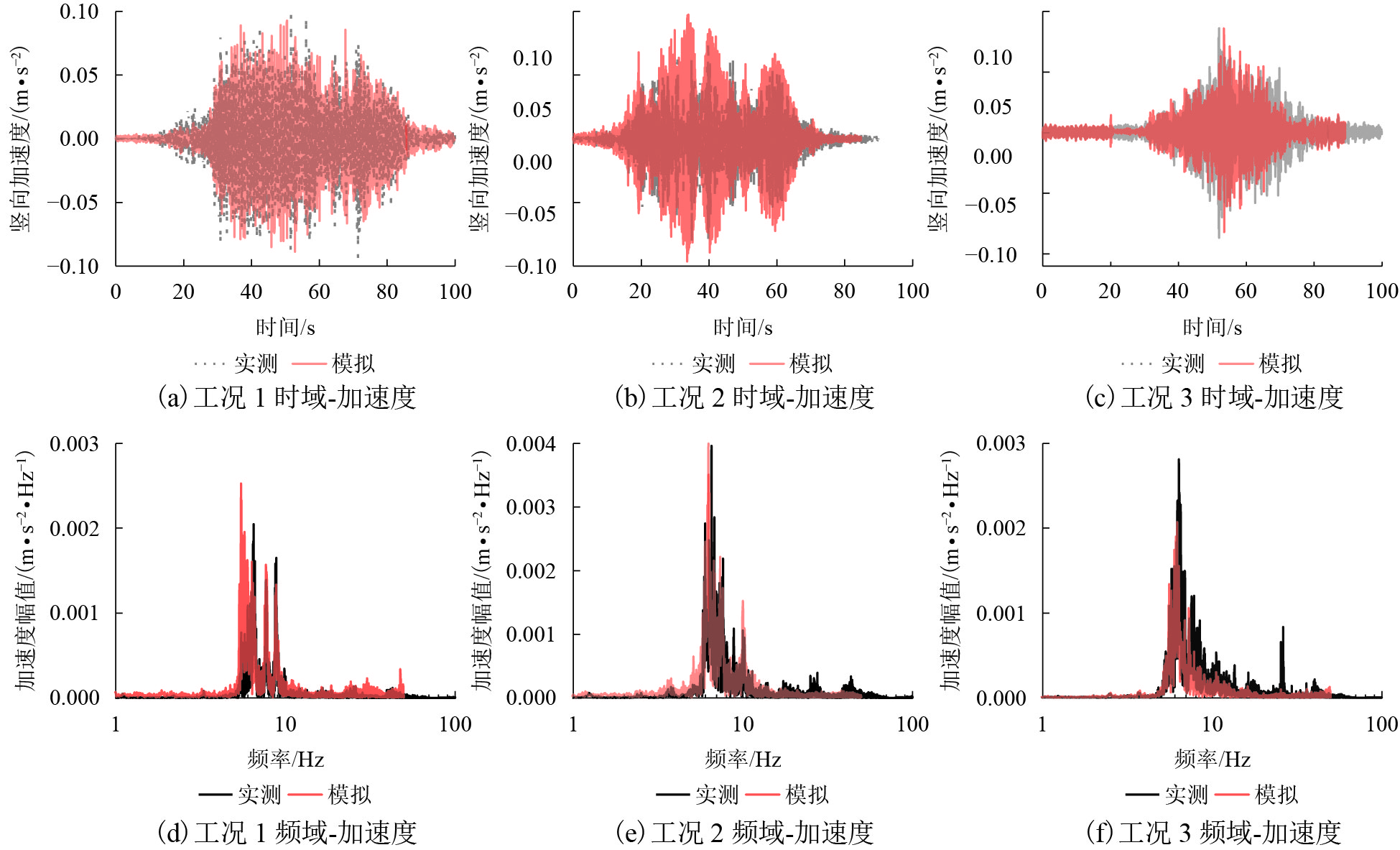
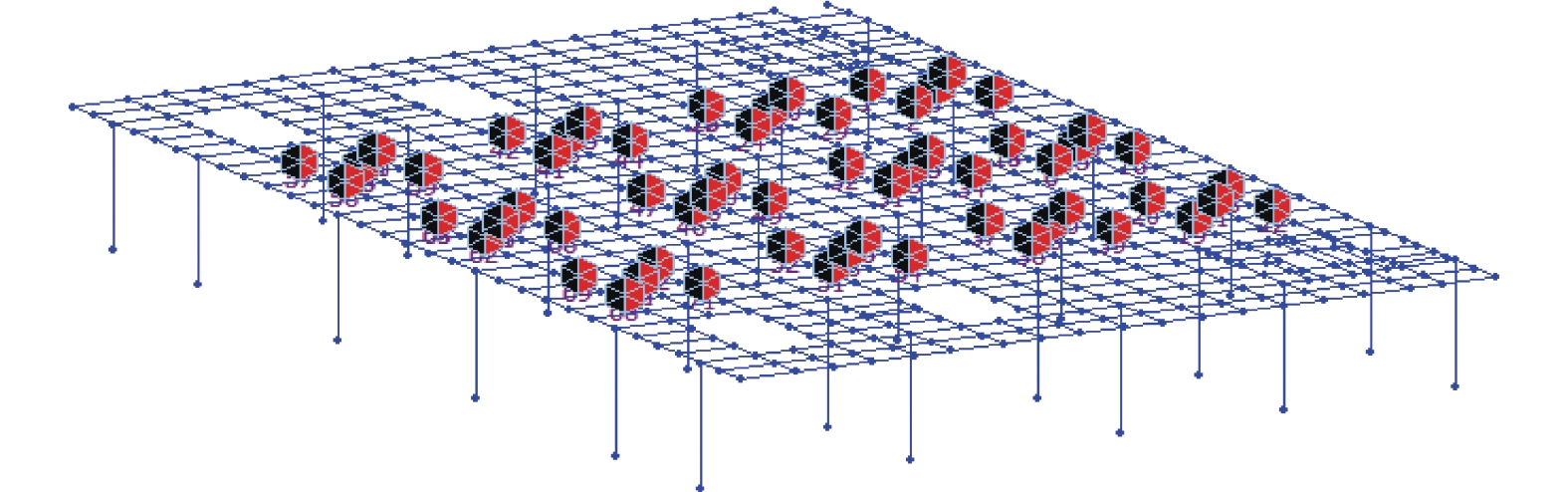
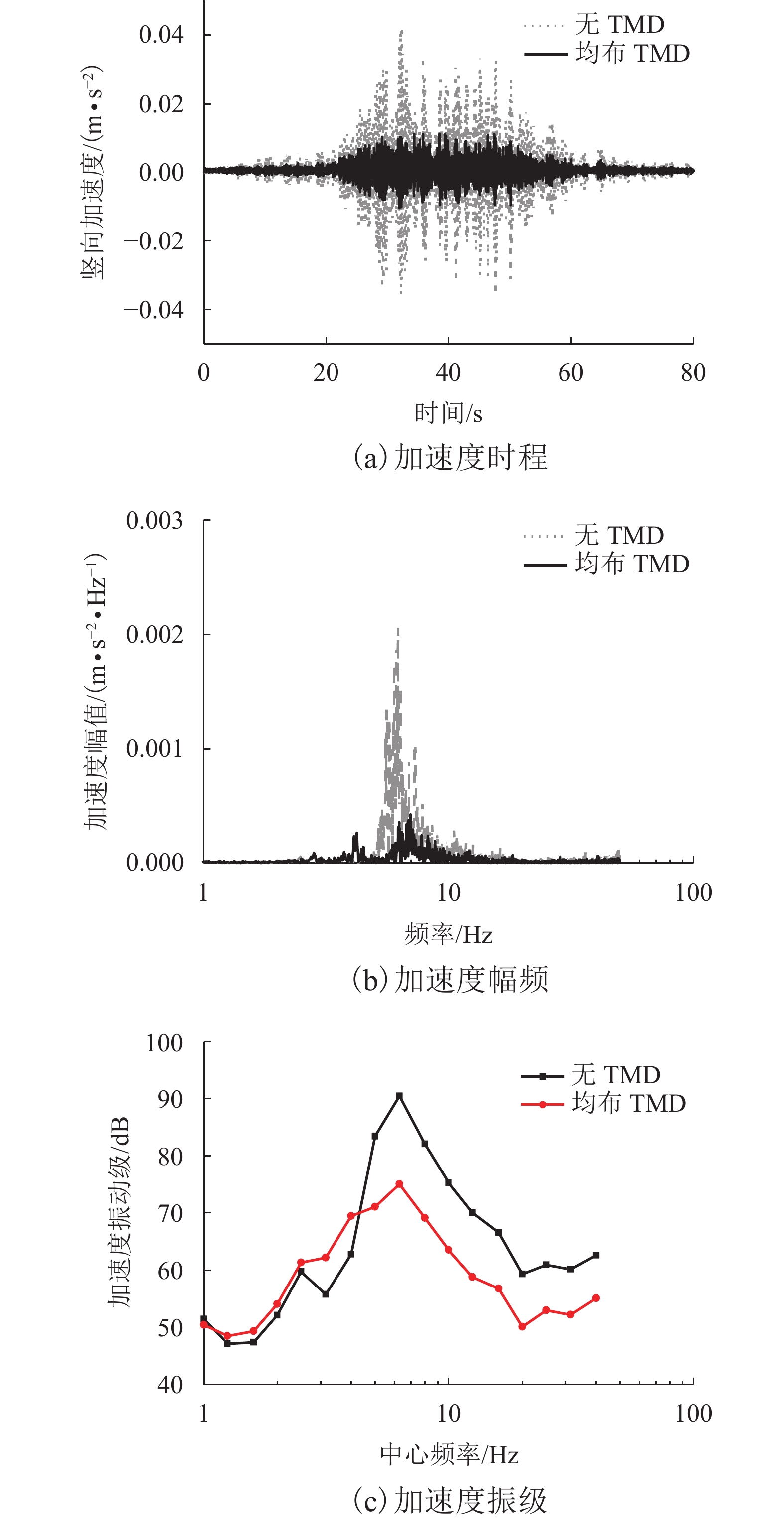
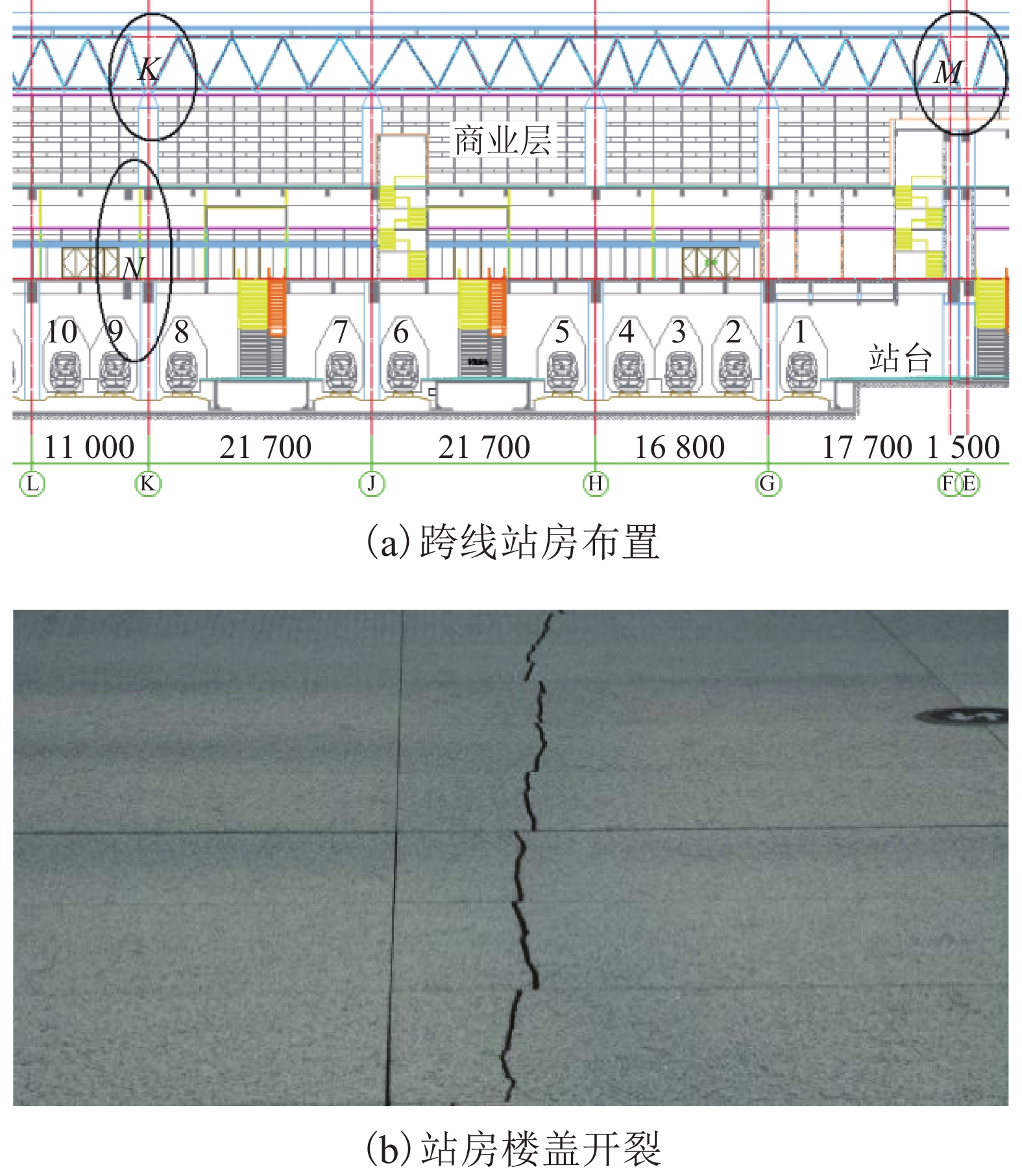
摘要: 针对高速列车过站引起的跨线站房车致振动问题,结合某运营客站跨线站房楼板在普速场重载货车正线通过时的车致振动,开展了振动实测,采用有限元方法构建了一致激励条件下的站房结构动力分析模型,开展了重载列车作用下的振动分析,采用1/3倍频程方法进行了振级评价,提出采用TMD (tuned mass damper)消能减振的方式抑制楼板的车致振动响应. 研究结果表明:当正线重载列车通过跨线站房时,楼盖在卓越振动频率(6.3 Hz)附近容易激发共振,且平均加速度振级超出规范容许值11.0~12.6 dB;设计了总质量比为0.1的调谐质量阻尼器后,加速度振级降幅达到13.0~17.0 dB,减振后的振动级水平基本达到标准限值.Abstract: To reduce the vibration of a cross-line station induced by long heavy trains and improve its comfort and safety, the vibration responses of a long-span elevated railway station waiting room floor slab were studied with measured data and finite element methods. The vibration level was evaluated by 1/3 octave method, and a method of suppressing the vibration of the floor slab via tuned mass damper (TMD) energy dissipation was proposed. The results show that the predominant frequency of floor vibration is in the vicinity of 6.3 Hz, and the average vibration response level due to vehicle acceleration exceeds the permissible value of 11.0–12.6 dB when a heavy long train passes through the cross-line beneath the waiting hall floor. After adding a mass damper with a mass ratio of 0.1 to each floor slab, the insertion loss of the vibration response level reached 13.0–17.0 dB, and the vibration level of the dampers were within the standard limit.
-
Key words:
- long-span floor slab /
- heavy long train /
- vibration comfort /
- TMD /
- vibration attenuation
-
表 1 加速度振级
Table 1. Vibration acceleration level
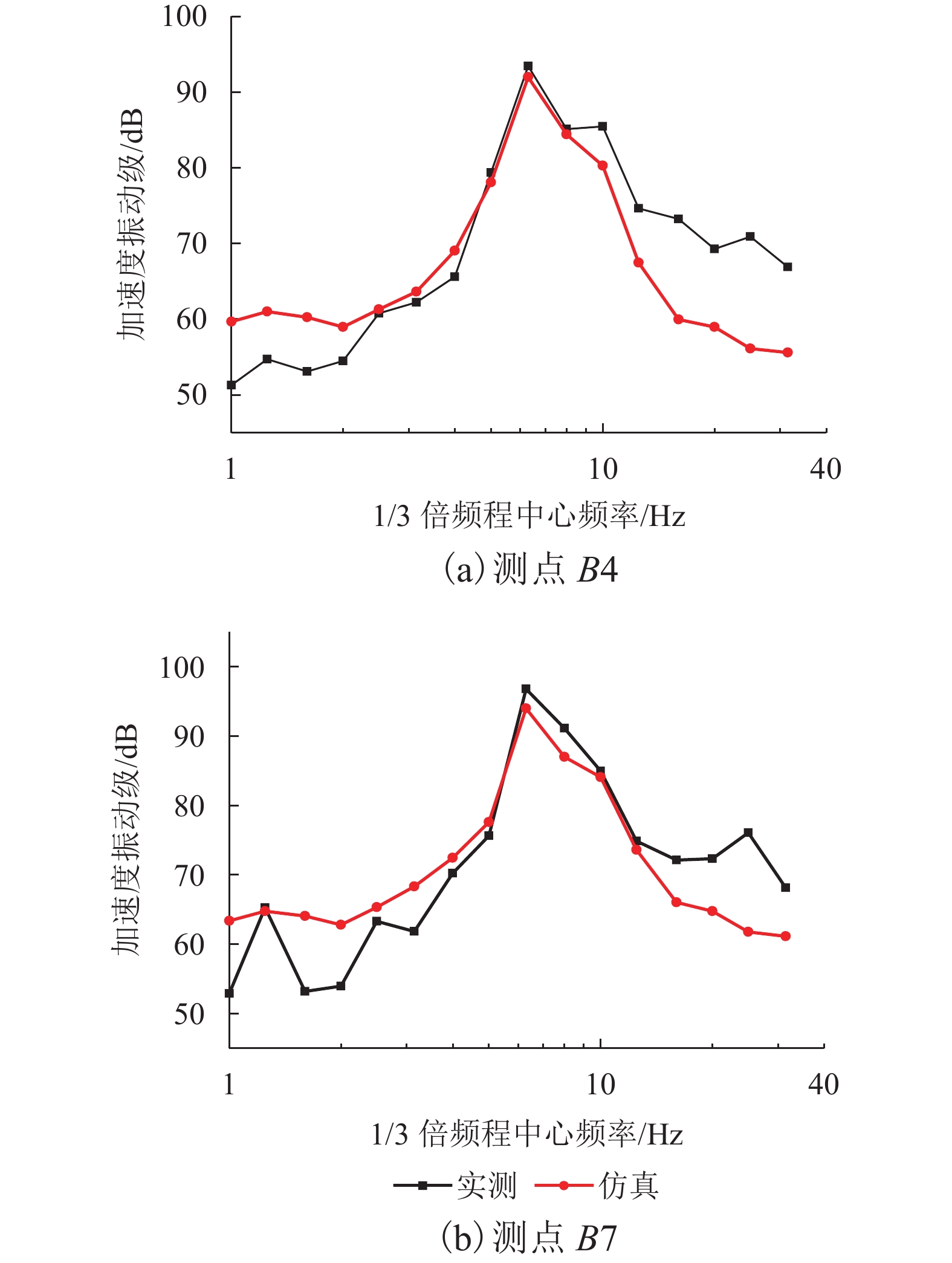
测点 工况1 工况2 工况3 B2 89.2 96.2 94.5 B3 91.2 93.4 94.3 B4 89.1 97.0 93.7 B7 92.4 96.7 95.5 B8 94.7 95.9 93.3 B9 89.6 95.3 95.6 均值 91.0 95.7 94.4 表 2 楼盖加速度振级均值对比
Table 2. Contrast of meanvibration acceleration level of floor
工况 减振前/dB 减振后/dB 降幅/dB 减振率/% 1 89.7 76.0 13.6 15.1 2 90.5 77.1 13.4 14.8 3 90.4 73.1 17.3 19.1 -
夏禾,曹艳梅. 轨道交通引起的环境振动问题[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2004,1(11): 44-51.XIA He, CAO Yanmei. Problem of railway traffic induced vibrations of environments[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2004, 1(11): 44-51. REIHER H, MEISTER F J. Die empfindlichkeit des menschen gegen erschütterungen[J]. Forschung Auf Dem Gebiet Des Ingenieurwesens, 1931, 2(11): 381-386. YANG Y B. Wave propagation for train induced vibrations; a finite/infinite element approach[A]. Singpa: Word Scientific Publishing Company, 2009 BATA M. Effects on buildings of vibrations caused by traffic[J]. Building Science, 1971, 6(4): 221-246. doi: 10.1016/0007-3628(71)90014-4 DAWN T M, STANWORTH C G. Ground vibrations from passing trains[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 1979, 66(3): 355-362. YOSHIKA O. Basic characteristics of Shinkansen-induced ground vibration and its reduction measures[C]//Proc. of International workshop WAVE 2000. Rotterdam: Balkema, 2000: 219-240 TAKEMIYA H, KOJIMA M. 2.5-D FEM simulation for vibration prediction and mitigation of track and ground interation under high-speed trains[C]//Proc. ISEV2003. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2003: 130-138 李小珍,刘全民,张迅,等. 铁路高架车站车致振动实测与理论分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(4): 612-618. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.008LI Xiaozhen, LIU Quanmin, ZHANG Xun, et al. Measurement and theoretical analysis of vehicle-induced vibration on elevated railway sation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4): 612-618. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.008 李小珍,张志俊,冉汶民,等. 桥上列车高速运行引起的地面振动试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5): 815-823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.001LI Xiaozhen, ZHANG Zhijun, Ran Wenmin, et al. Field test of ground vibration induced by high-speed train on elevated bridge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 815-823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.001 楼梦麟,李守继. 地铁引起建筑物振动评价研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2007,26(8): 68-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2007.08.017LOU Menglin, LI Shouji. Evaluation of buildings’ vibration induced by underground trains[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2007, 26(8): 68-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2007.08.017 周云,王柏生. 行驶列车引起的周边建筑物振动分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2006,25(1): 61-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2006.01.015ZHOU Yun, WANG Baisheng. Dynamic analysis of building vibration induced by train along railways[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2006, 25(1): 61-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2006.01.015 CHEN Y M, WANG C J, JI M X, et al. Train-induced ground vibration and deformation[C]//Proc. ISEV2003. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2003: 158-174 宋志刚,金伟良. 工程结构振动舒适度的抗力模型[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2004,38(8): 966-970. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2004.08.007SONG Zhigang, JIN Weiliang. Resistance model for vibration serviceability design of engineering structures[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2004, 38(8): 966-970. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2004.08.007 何浩祥,闫维明,张爱林,等. 竖向环境振动下人与结构相互作用及舒适度研究[J]. 振动工程学报,2008,21(5): 446-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2008.05.004HE Haoxiang, YAN Weiming, ZHANG Ailin, et al. Human-structure dynamic interaction and comfort evaluation in vertical ambient vibration[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2008, 21(5): 446-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2008.05.004 徐灏. 疲劳强度[M]. 北京: 北京高等教育出版社, 1988: 1-2 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 机械振动与冲击-人体暴露于全身振动的评价, 第1部分: 一般要求: GB/T 1344.1—2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007 Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC). LS-DYNA Keyword user’s Manual Volume Ⅰ[M/CD]. California: LSTC, 2016: 1-121 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 城市轨道交通引起的建筑物振动与二次辐射噪声限制及其测量方法标准: JGJ/T170—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009 孙家麒, 郭建国, 金志春. 城市轨道交通振动和噪声控制[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2002: 16-19 背户一登. 动力吸振器及其应用[M]. 机械工业出版社, 2013: 25-44 -




 下载:
下载: