Study on Reinforcement for Fatigue Cracking of Rib-to-Diaphragm Welded Joints of Steel Bridge Deck
-
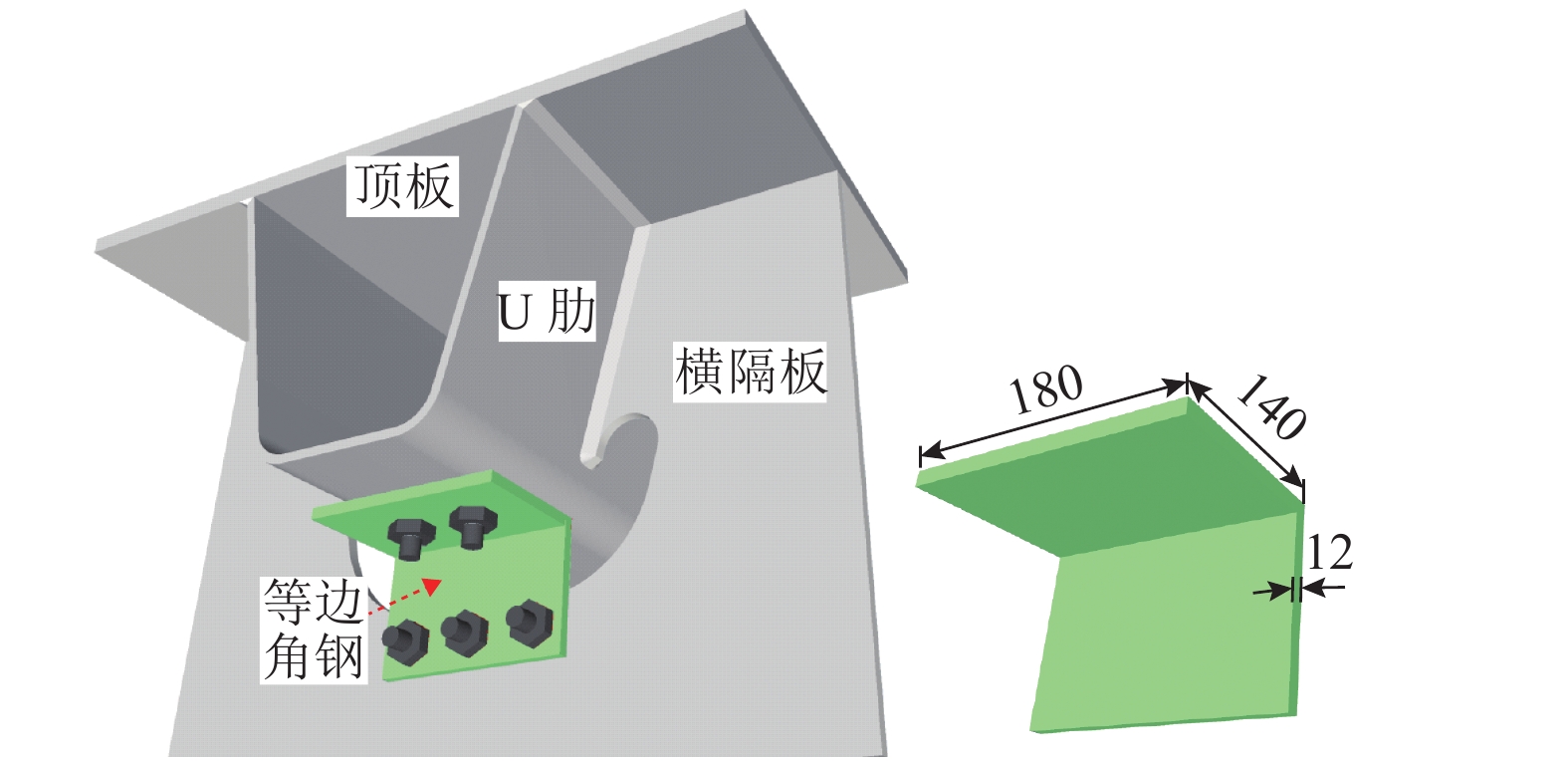
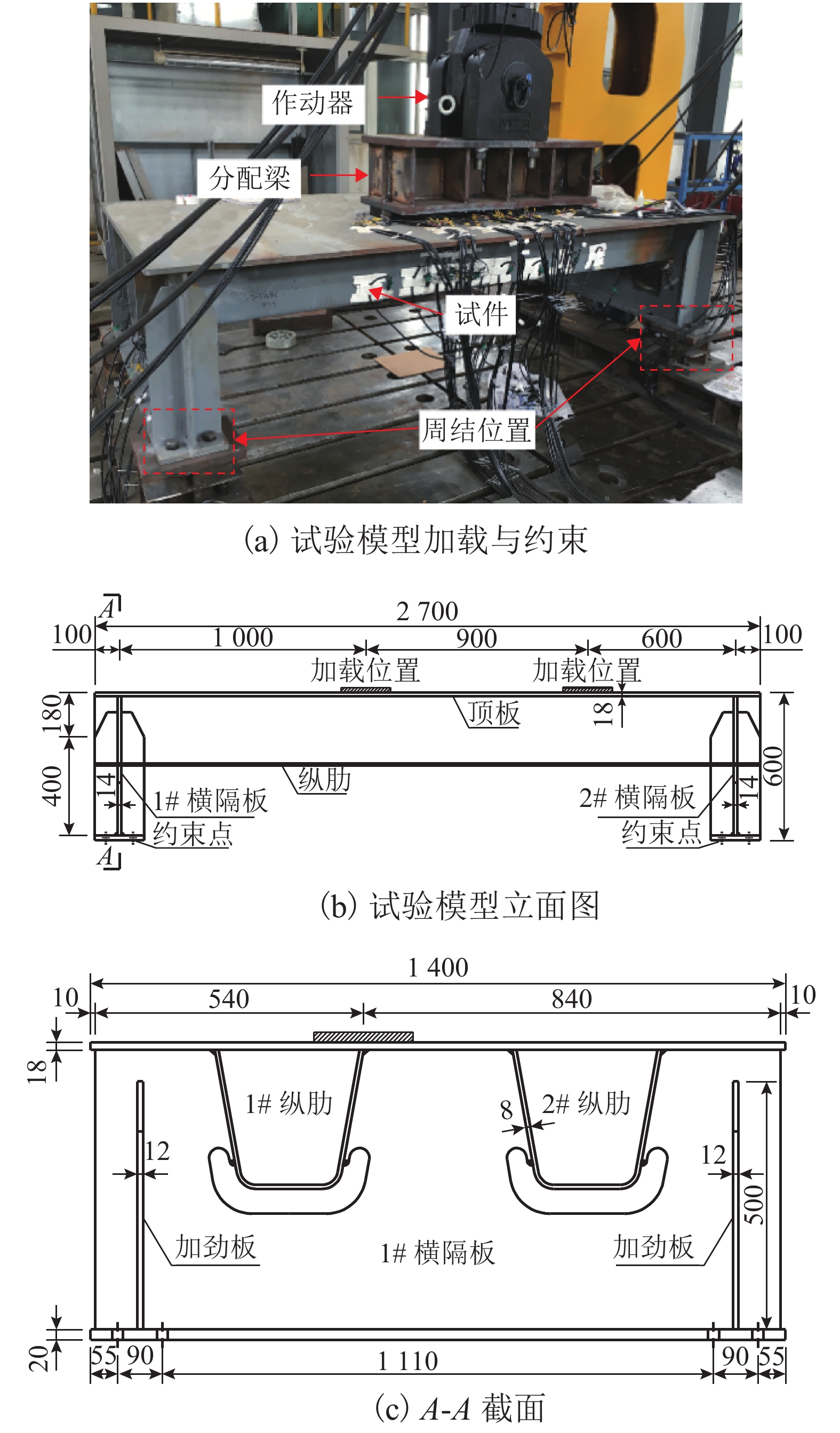
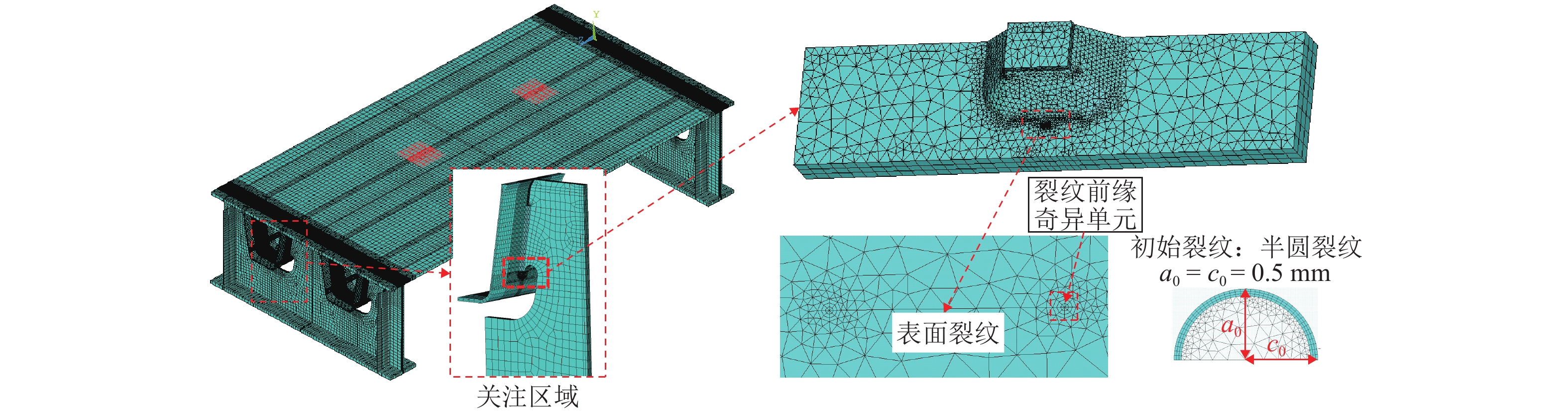
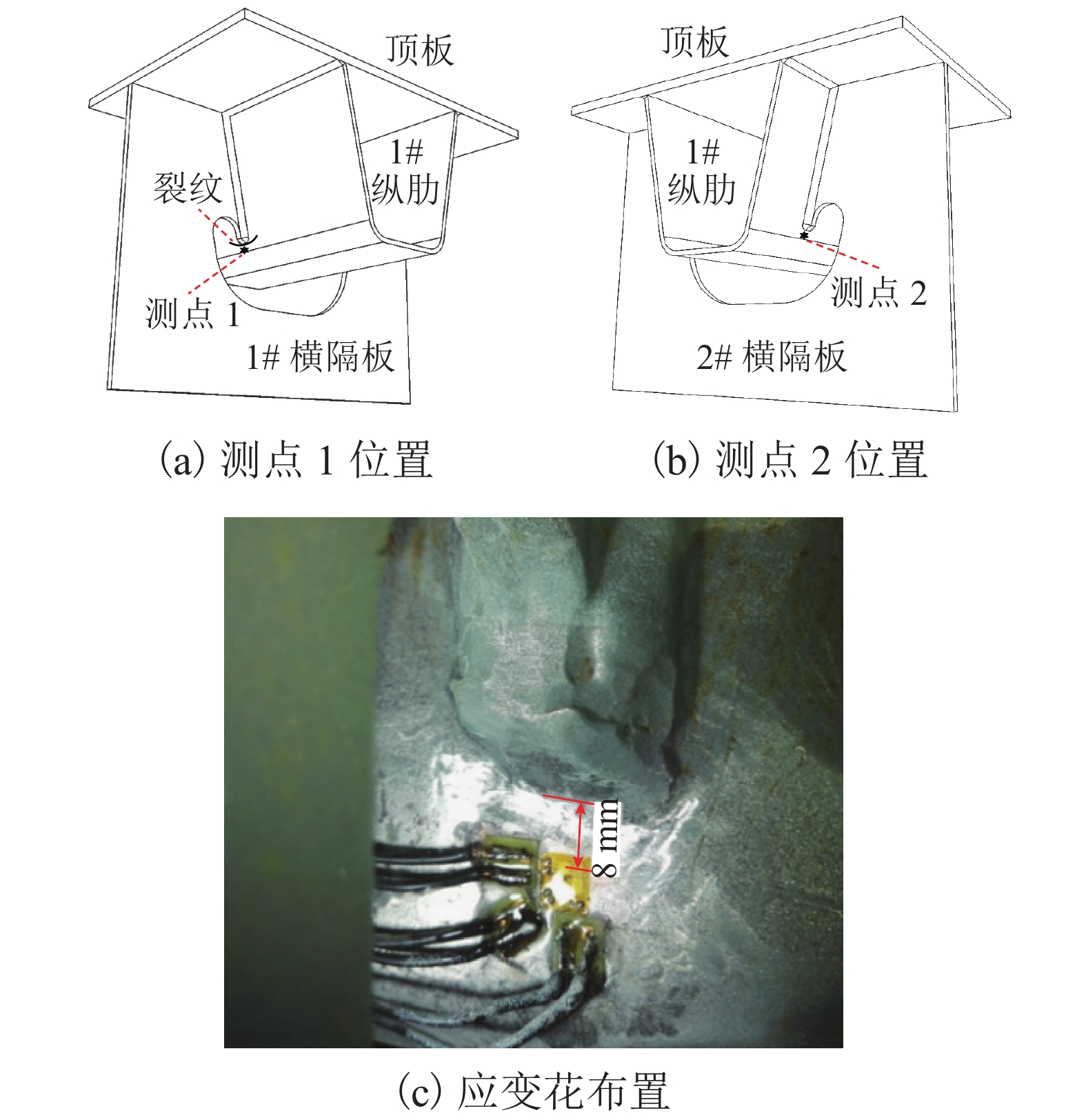
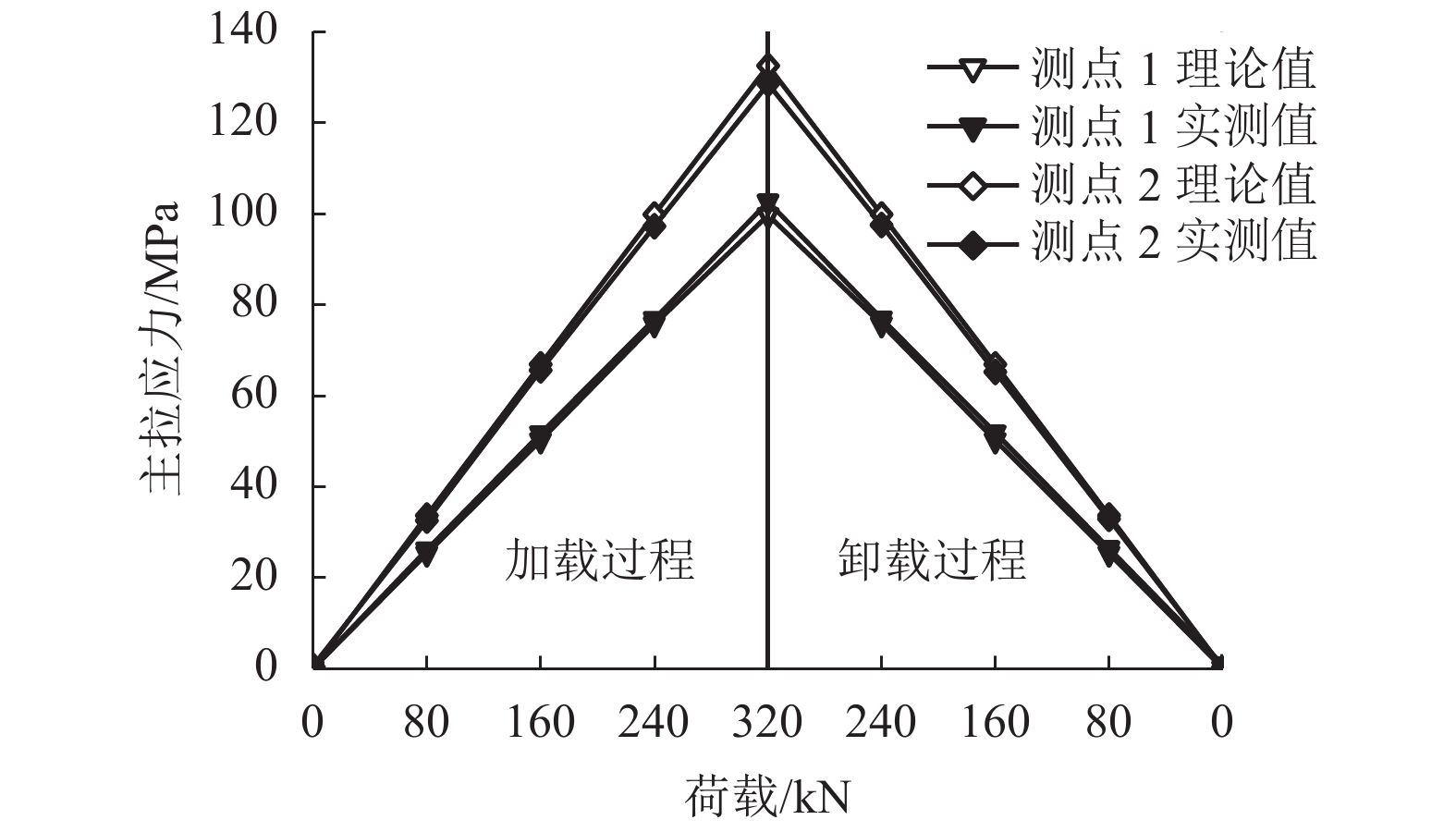
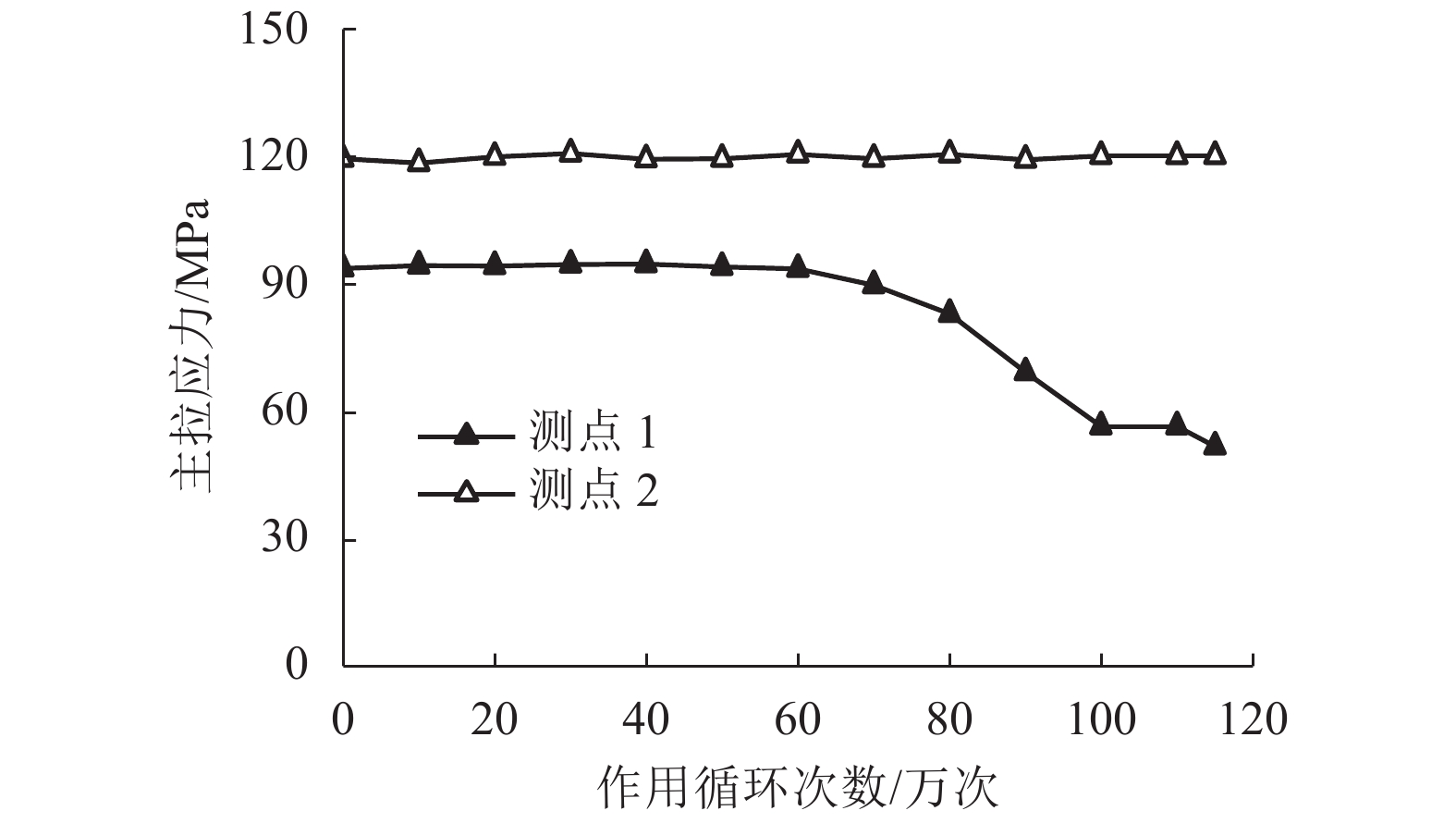
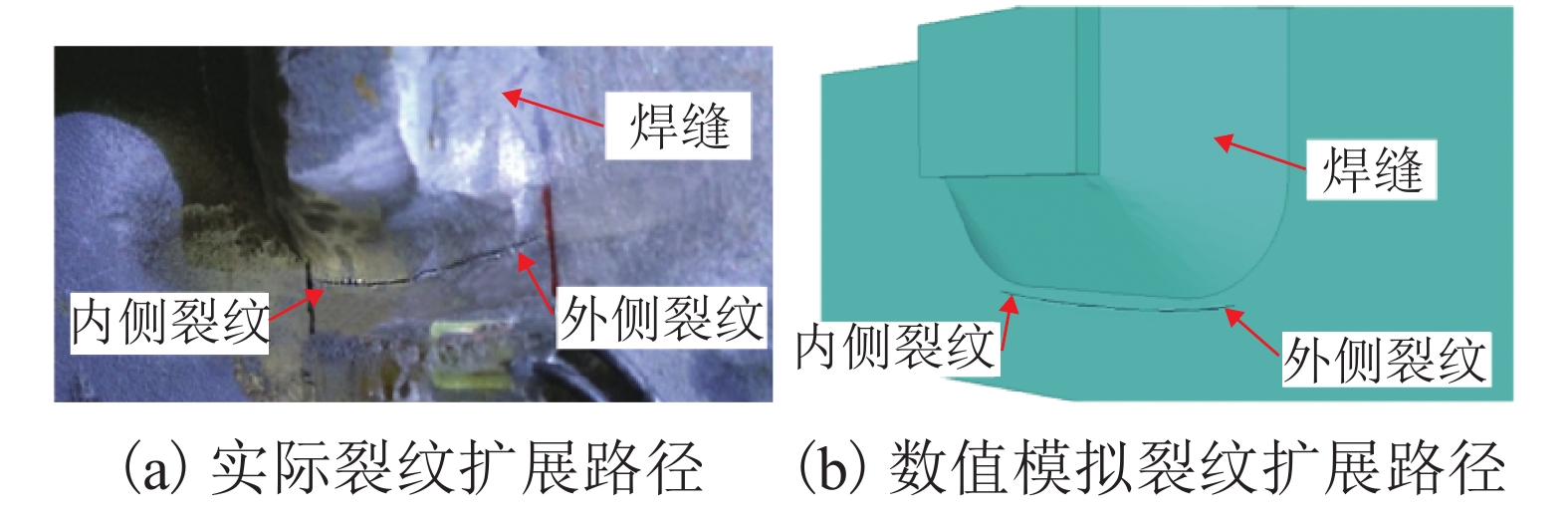
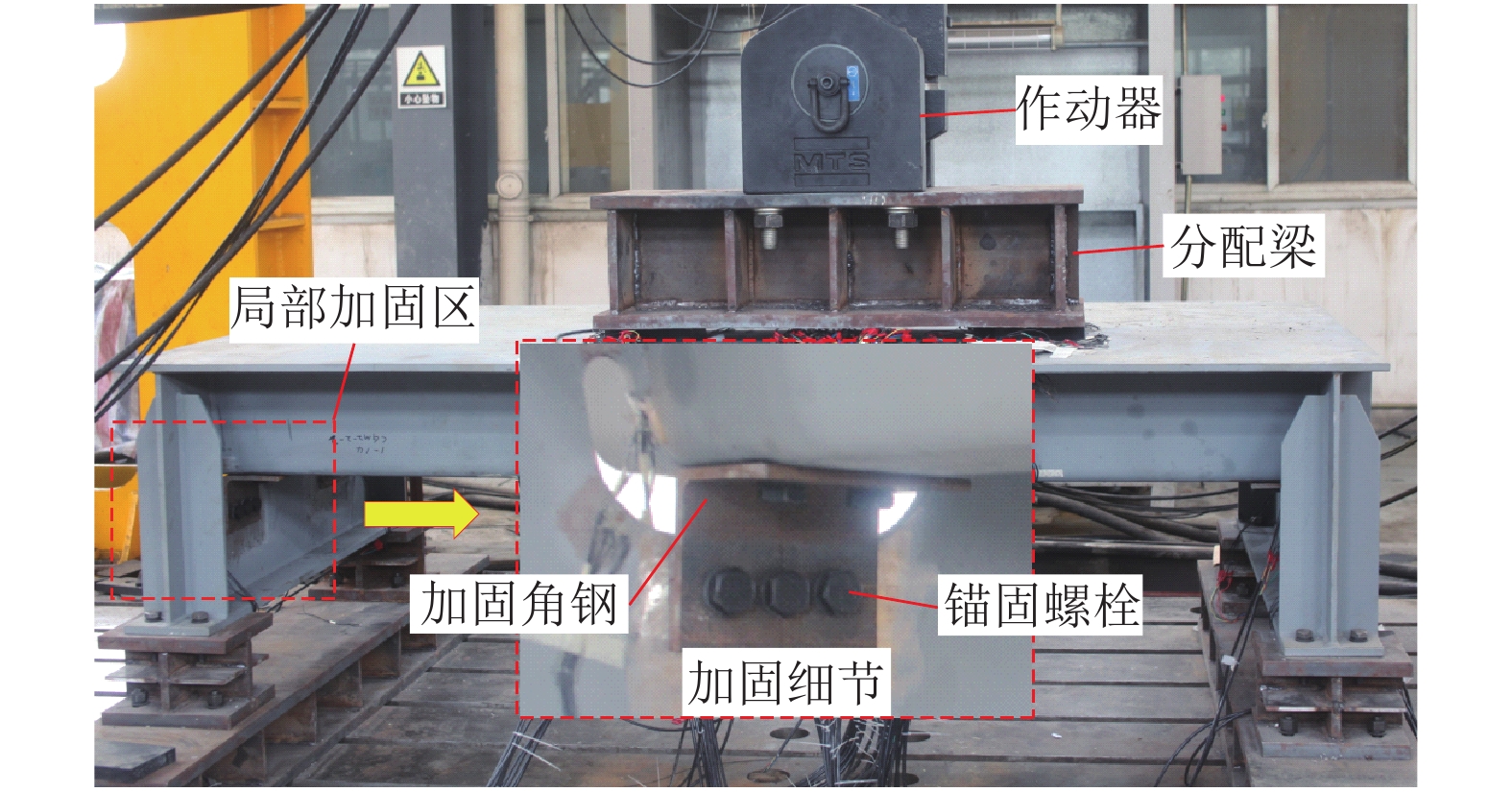
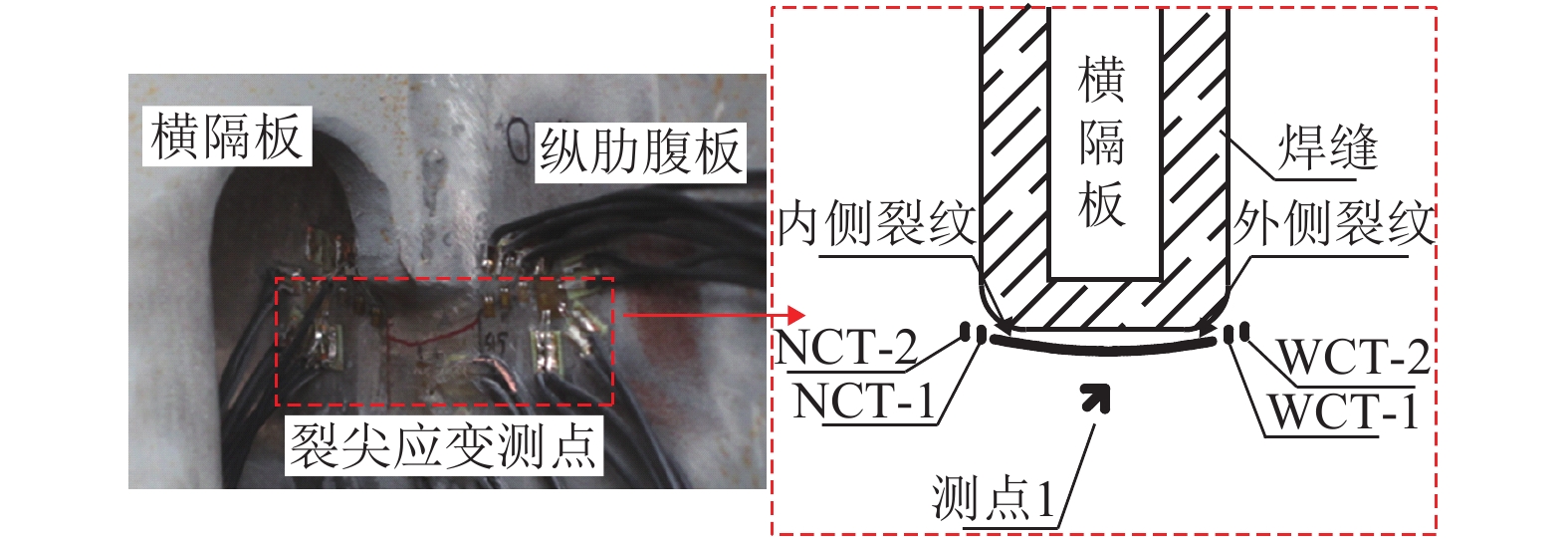
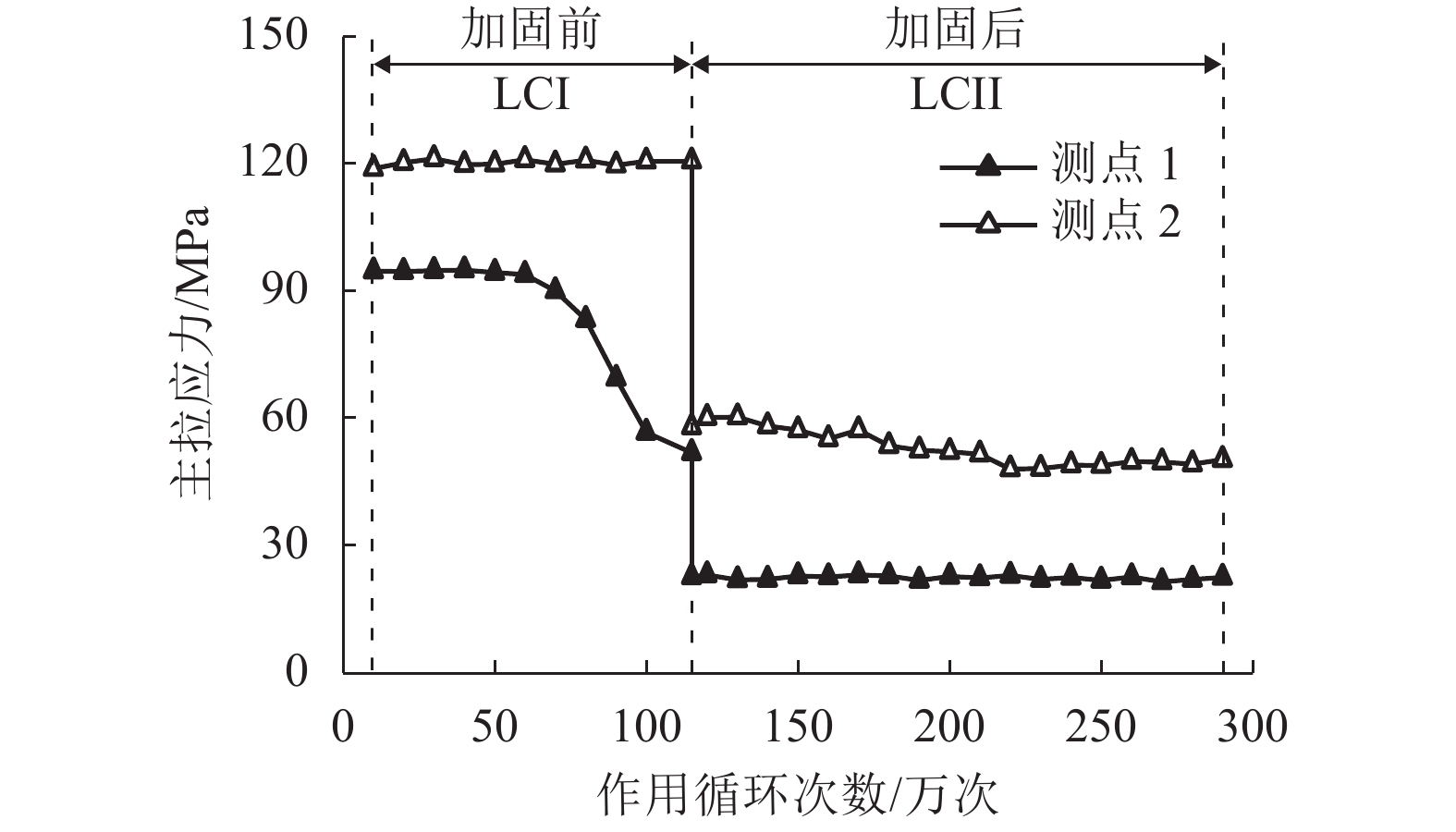
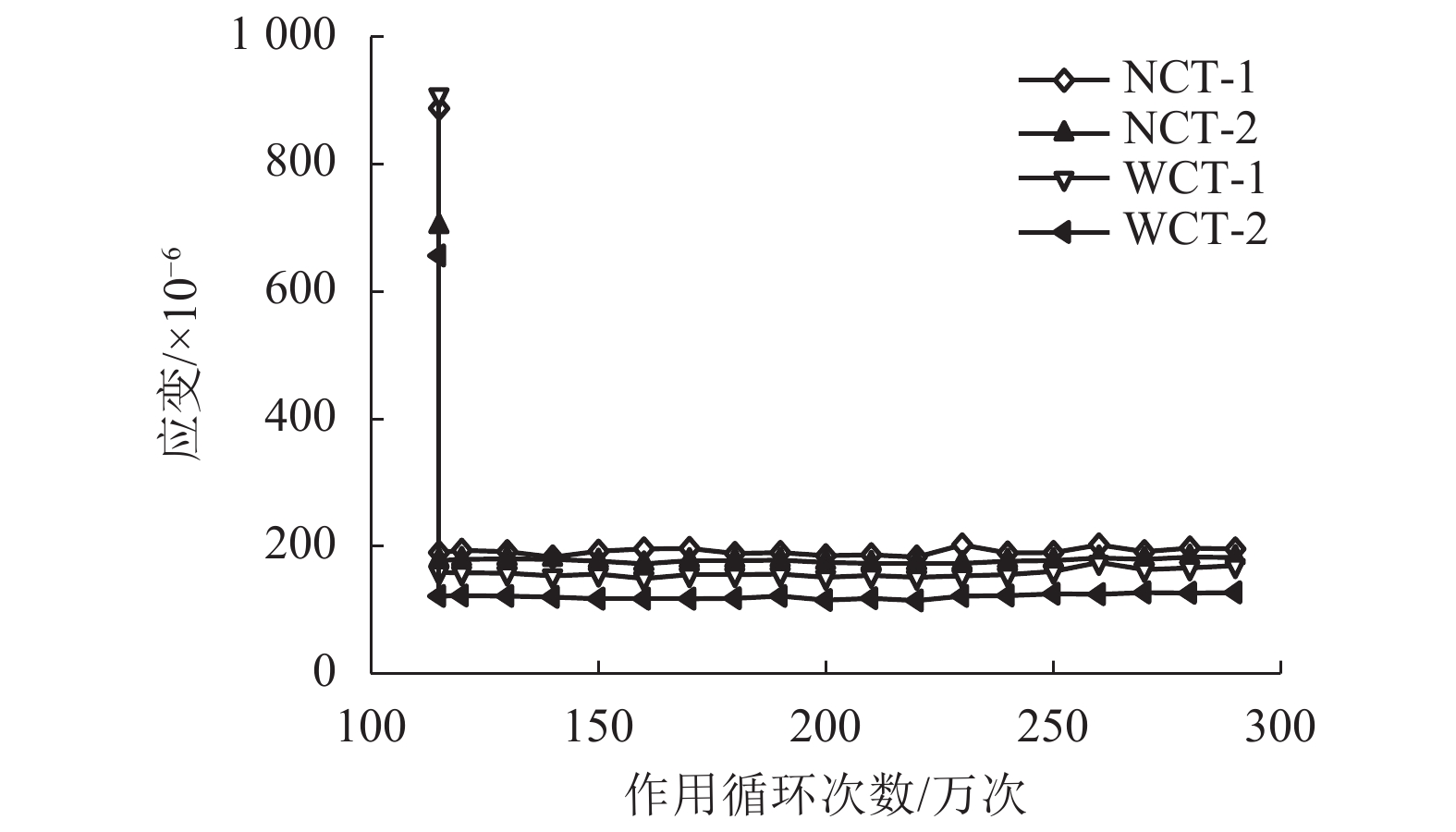
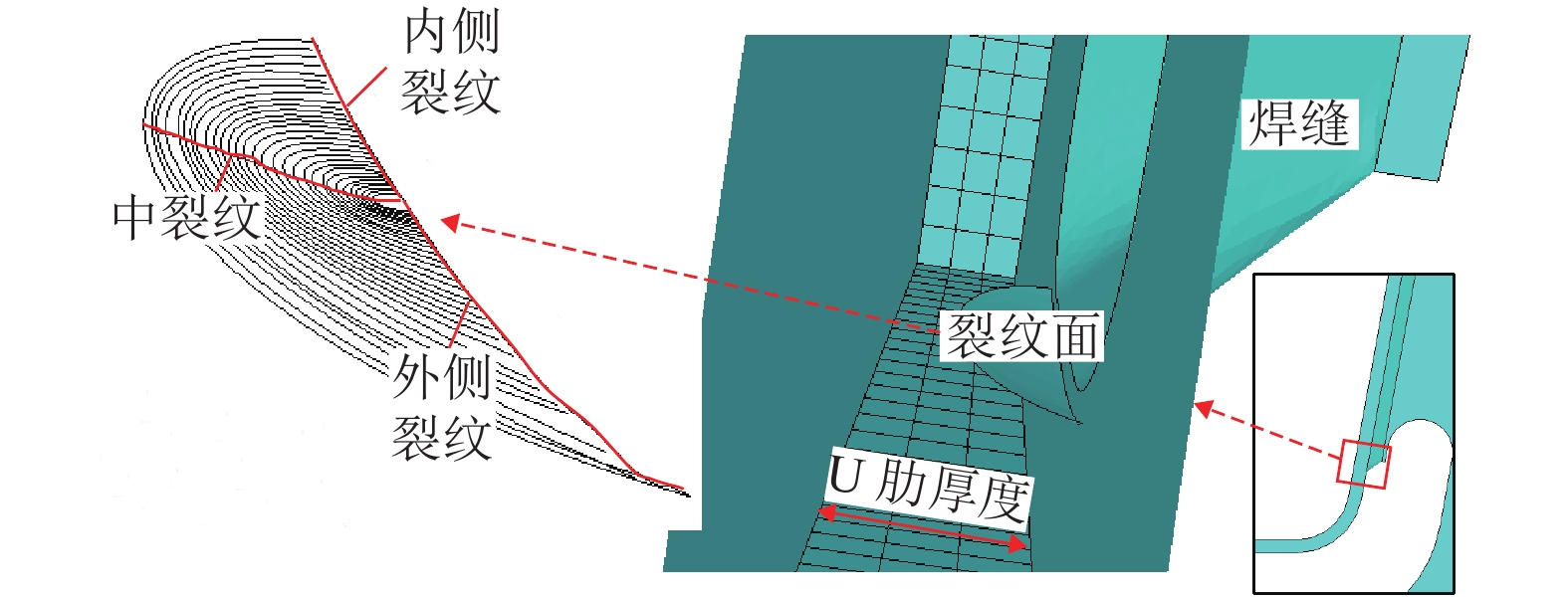
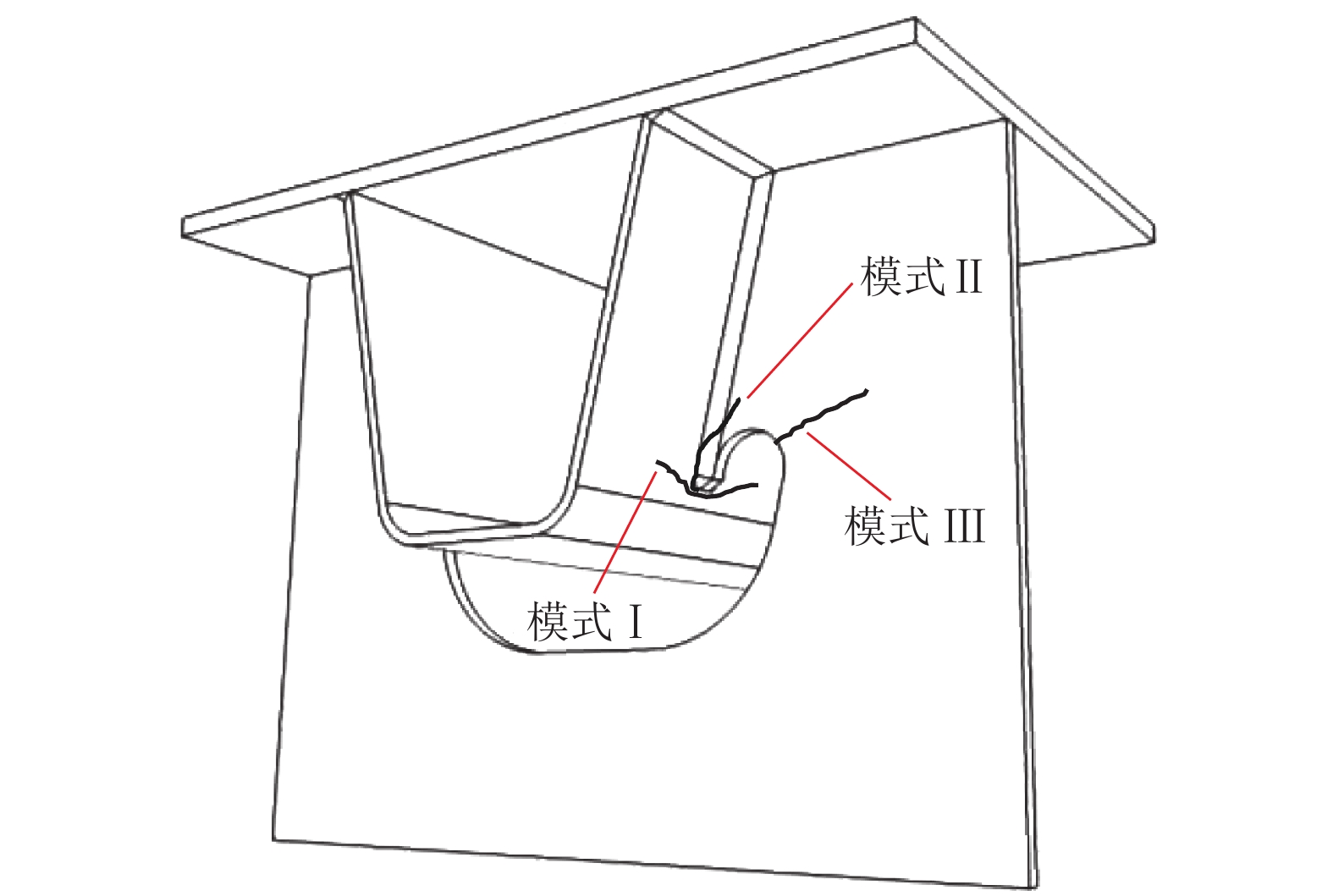
摘要: 为研究钢桥面板疲劳开裂部位栓接角钢的加固方法,采用足尺模型试验对纵肋与横隔板焊接细节疲劳裂纹的加固效果进行研究,采用ANSYS建立了含有疲劳裂纹的有限元模型,并基于断裂力学理论对比研究疲劳裂纹不同长度条件下的加固效果. 研究结果表明:纵肋与横隔板焊接细节的疲劳裂纹起裂于焊趾并沿纵肋腹板扩展,采用栓接角钢加固后可以使开裂部位关键测点的主拉应力和裂尖各测点的应变分别降低56%和80%,能够有效抑制疲劳裂纹的扩展;栓接角钢加固后裂尖的应力强度因子幅值最少降低80%,裂纹扩展速率显著降低;对贯穿纵肋腹板前不同长度的疲劳裂纹进行加固,裂尖应力强度因子幅值均降低60%~90%,但随着疲劳裂纹长度的增加,栓接角钢的加固方法对裂纹扩展的抑制效果不断降低,加固时机的合理选取是影响加固效果的关键因素之一.Abstract: In order to study the reinforcement effects of bolted angle steel on fatigue cracking of the orthotropic steel bridge deck, the full-scale test model was used to study the reinforcement effect of fatigue cracks on the rib-to-diaphragm welded joints. A finite element model with fatigue cracks was established using ANSYS, and to study the reinforcement effects under different length of fatigue cracks conditions based on the fracture mechanics theory. The results indicate that the fatigue cracks initiate from the toe of longitudinal rib-to-diaphragm welded joints and expand along the longitudinal web, the reinforcement method with bolted angle steel can reduce the main tensile stress of the key measure points at the cracking details and the strain of measure points at crack tips by 56% and 80%, respectively. The stress intensity factor of the crack tip is reduced by more than 80% after bolting angle steel reinforcement, and crack propagation rate is reduced significantly. For the different lengths of fatigue cracks before the longitudinal rib webs, the amplitude of the crack tip stress intensity factor is reduced by 60%−90% using the reinforcement method, but with the increase of the fatigue cracks length, the reinforcement effects are reduced continuously, the reasonable selection of the reinforcement time is one of the key factors in the reinforcement effects.
-
表 1 加固前后有效应力强度因子的变化
Table 1. Stress intensity factors before and after strengthening
裂纹位置 ΔKeff/(MPa•mm1/2) 降幅/% ΔKth/(MPa•mm1/2) 加固前 加固后 内侧裂纹 495 75 85 63 外侧裂纹 522 78 85 63 中裂纹 324 43 87 63 -
张清华,卜一之,李乔. 正交异性钢桥面板疲劳问题的研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报,2017,30(3): 14-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.002ZHANG Qinghua, BU Yizhi, LI Qiao. Review on fatigue research of orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(3): 14-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.002 孟凡超, 张清华, 谢红兵, 等. 抗疲劳钢桥面板关键技术[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2015: 5-10. 王春生,翟慕赛,HOUANKPO T N O,等. 正交异性钢桥面板冷维护技术及评价方法[J]. 中国公路学报,2016,29(8): 50-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.08.007WANG Chunsheng, ZHAI Musai, HOUANKPO T N O, et al. Cold maintenance technique and assessment method for orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(8): 50-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.08.007 WOLCUM R. Lessons from weld cracks in orthotropic decks on three european bridge[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1990, 116(1): 75-84. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1990)116:1(75) 钱冬生. 关于正交异性钢桥面板的疲劳——对英国在加固其塞文桥渡时所作研究的评价[J]. 桥梁建设,1996(2): 8-13.QIAN Dongsheng. On fatigue of steel orthotropic deck structure:comments on researches for strengthening the severn crossing in UK[J]. Bridge Construction, 1996(2): 8-13. RODRIGUEZ-SANCHEZ J E, DOVER W D, BRENNAN F P. Application of short repairs for fatigue life extension[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2004, 26(4): 413-420. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2003.07.002 李传习,李游,陈卓异,等. 钢箱梁横隔板疲劳开裂原因及补强细节研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2017,30(3): 121-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.013LI Chuanxi, LI You, CHEN Zhuoyi, et al. Fatigue cracking reason and detail dimension of reinforcement about transverse diaphragm of steel box girder[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(3): 121-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.013 朱爱珠,李牧,田杨,等. 设内隔板正交异性钢桥面板足尺疲劳试验[J]. 钢结构,2017,32(1): 45-50.ZHU Aizhu, LI Mu, TIAN Yang, et al. Fatigue test on full-scale orthotropic steel bridge deck with inner diaphragm[J]. Steel Construction, 2017, 32(1): 45-50. CHOI J H, KIM D H. Stress characteristics and fatigue crack behavior of the longitudinal rib-to-cross beam joints in an orthotropic steel deck[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2008, 11(2): 189-198. doi: 10.1260/136943308784466224 坂野昌弘, 鈴木博之, 舘石和雄. 厚板溶接継手に関する調査研究小委員会報告書[R]. 東京: 土木学会鋼構造委員会, 2007. 张清华,崔闯,卜一之,等. 正交异性钢桥面板足尺疲劳模型试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2015,48(4): 72-83.ZHANG Qinghua, CUI Chuang, BU Yizhi, et al. Experimental study on fatigue features of orthotropic bridge deck through full-scale segment models[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2015, 48(4): 72-83. 李小珍,任伟平,卫星,等. 现代钢桥新型结构型式及其疲劳问题分析[J]. 钢结构,2006,21(5): 50-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2006.05.013LI Xiaozhen, REN Weiping, WEI Xing, et al. New structural types and fatigue problems of modern steel bridge structures[J]. Steel Construction, 2006, 21(5): 50-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2006.05.013 刘益铭,张清华,崔闯,等. 正交异性钢桥面板三维疲劳裂纹扩展数值模拟方法[J]. 中国公路学报,2016,29(7): 89-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.07.011LIU Yiming, ZHANG Qinghua, CUI Chuang, et al. Numerical simulation methods for 3D fatigue crack growth of steel orthotropic bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(7): 89-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.07.011 马野,许希武,宁晋建. 整体加筋壁板裂纹扩展轨迹模拟及控制分析[J]. 固体力学学报,2009,30(3): 251-258.MA Ye, XU Xiwu, NING Jinjian. An analysis of crack growth simulation and crack arrest in integrally stiffened panel[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2009, 30(3): 251-258. 童乐为,顾敏,朱俊,等. 基于断裂力学的圆钢管混凝土T型焊接节点疲劳寿命预测[J]. 工程力学,2013,30(4): 331-336.TONG Lewei, GU Min, ZHU Jun, et al. Prediction of fatigue life for welded T-joints of concrete-filled circular hollow sections based on fracture mechanics[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2013, 30(4): 331-336. British Standards Institution. Guide to methods for assessing the acceptability of flaws in metallic structures: BS 7910—2005[S]. London: BSI Standards Limited, 2005. 张行, 崔德渝, 孟庆春, 等. 断裂与损伤力学[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2006: 25-49. -




 下载:
下载: