Simplified Analysis of Wind-Induced Response of Transmission Tower-Line System Considering SSI Effect
-
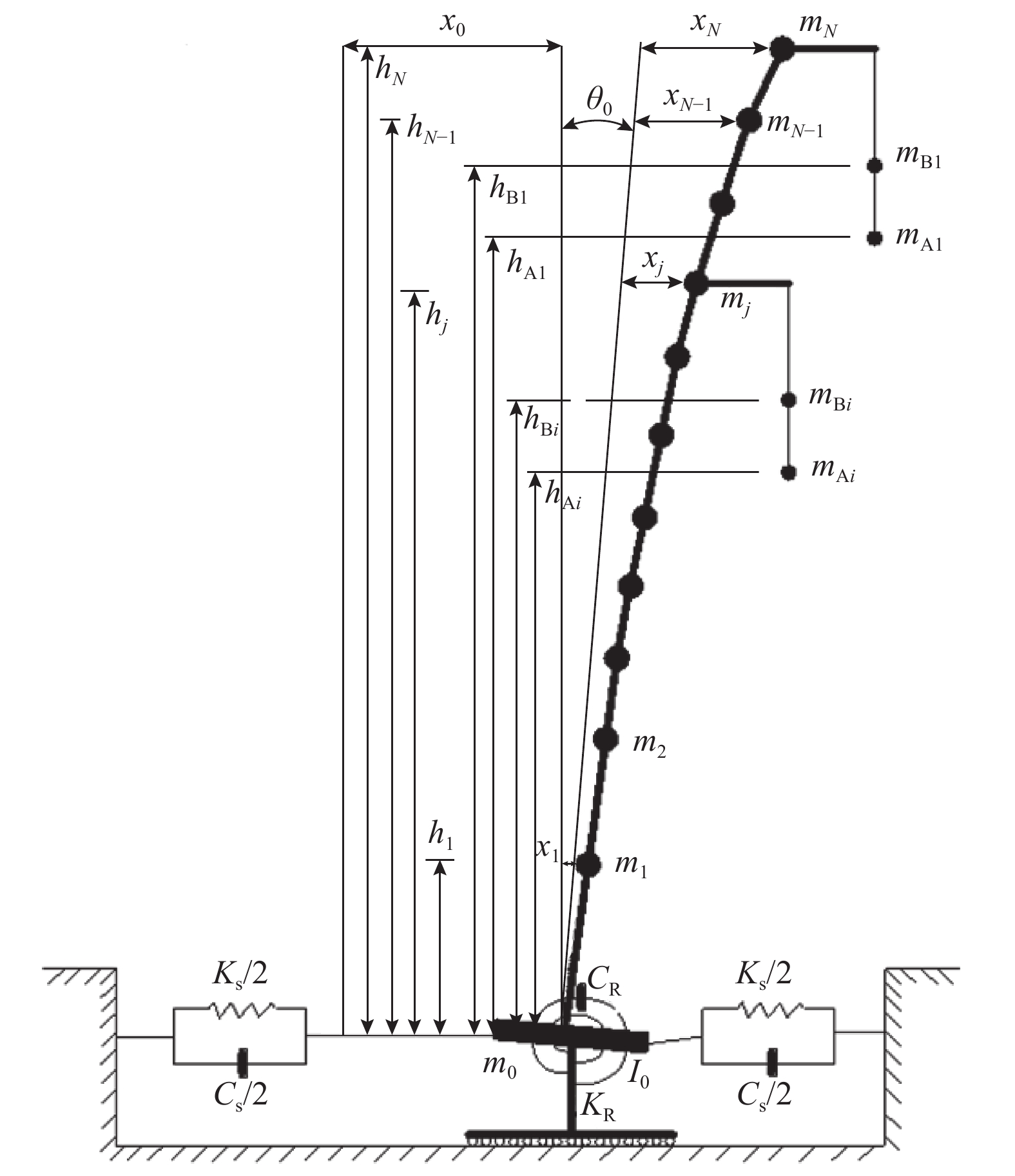
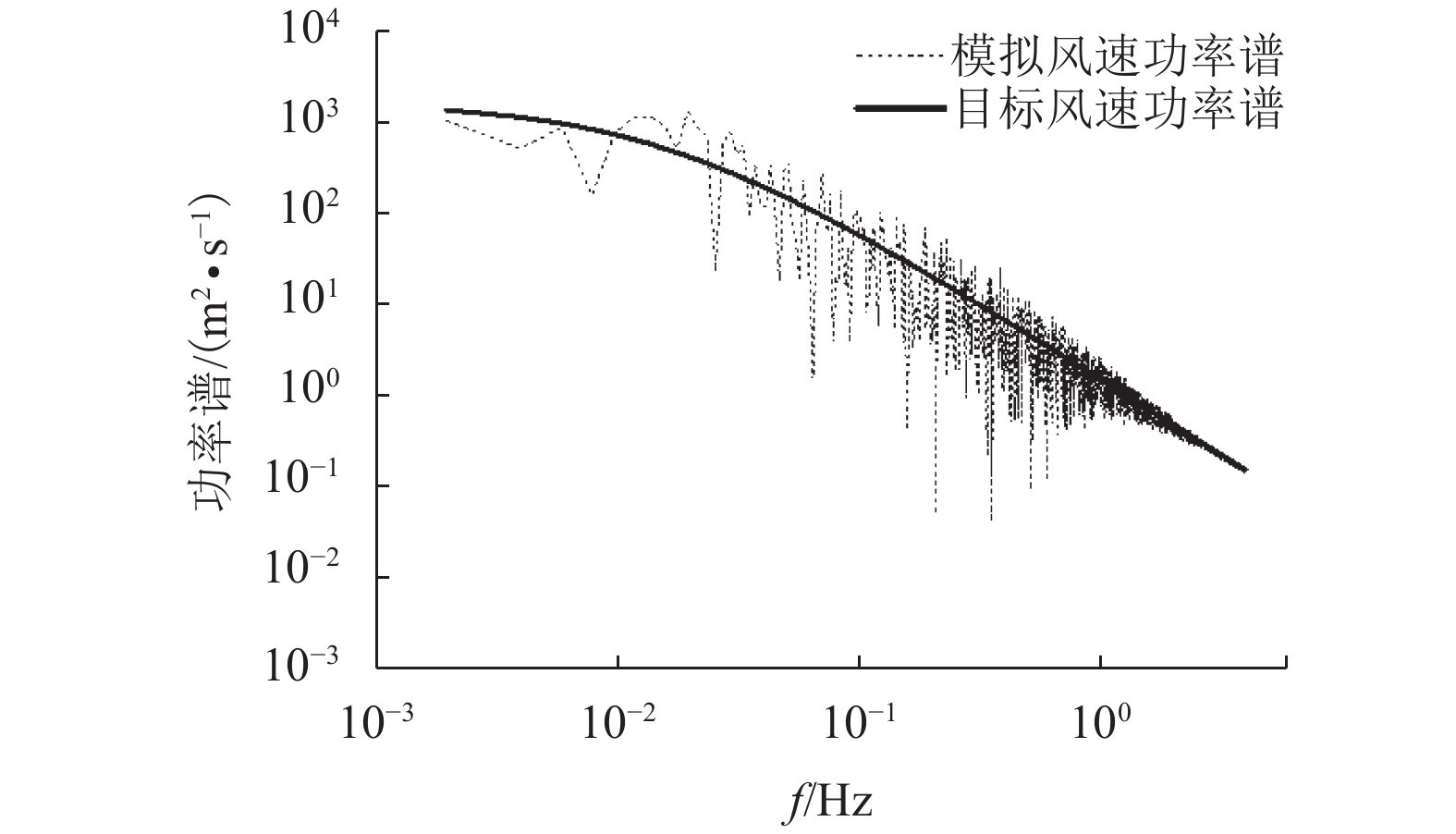
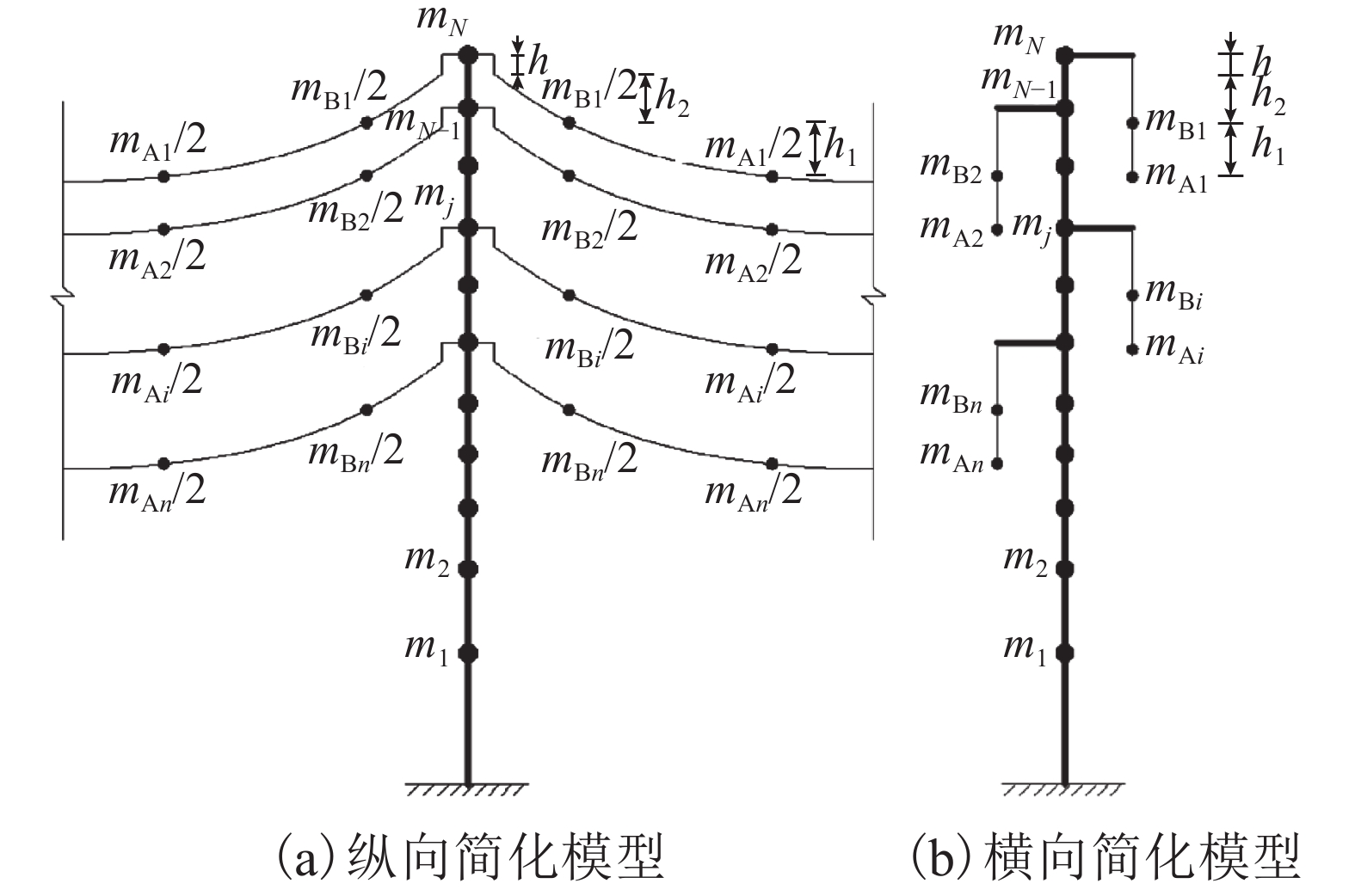
摘要: 输电塔的分析设计通常按基础固支来处理,然而多数情况下地基并不是刚性的. 为了考虑弹性地基对输电塔风振响应的影响,建立了考虑土与结构相互作用(soil-structure interaction,SSI)的输电塔-线体系简化计算模型,并推导了风振响应动力方程. 基于提出的简化计算模型,选取工程中某特高压输电塔-线体系,编写MATLAB程序进行了结构系统的动力特性分析和风振响应时程分析,并选取了3种不同参数的地基土对输电塔的风振响应进行了对比分析. 研究结果表明:考虑SSI效应后,单塔的位移均方根值增大约20%,加速度均方根值减小约14%,基底剪力及基底弯矩最大值分别减小约7%、12%;考虑塔线耦联和SSI效应后,与仅考虑SSI效应的单塔相比,输电塔的位移响应有所增大,但加速度响应变化很小;随着地基土刚度减小,SSI效应的影响越明显,表明软土地基下输电塔的风振响应分析不能忽略SSI效应.Abstract: Analysis and design of transmission tower is normally performed considering fixed base, however, in most cases, the foundations are not rigid. In this study, a simplified calculation model of transmission tower-line system was developed with consideration of the soil-structure interaction (SSI), and the dynamic equation of wind vibration response was derived. Based on the proposed simplified calculation model and MATLAB program, a transmission tower-line system from an actual project was selected to conduct the analysis of the dynamic characteristics and the time domain analysis of wind vibration of transmission tower. The model was tested and analysed with three different types of soil. The results show that the RMS displacement of transmission tower increases by about 20%, the RMS acceleration is reduced by about 14% and the maximum base shear and the base bending moment decrease by about 7% and 12%, respectively, when considering the SSI effect. The displacement response of transmission tower increases, but the acceleration changes are small if the tower line coupling effect and SSI effect are considered. As the soil hardness decreases, the SSI effect is more obvious; hence, the SSI effect should not be ignored when the transmission tower is built on soft soil.
-
Key words:
- transmission tower /
- SSI effect /
- tower line coupling effect /
- simplified model /
- wind-induced response
-
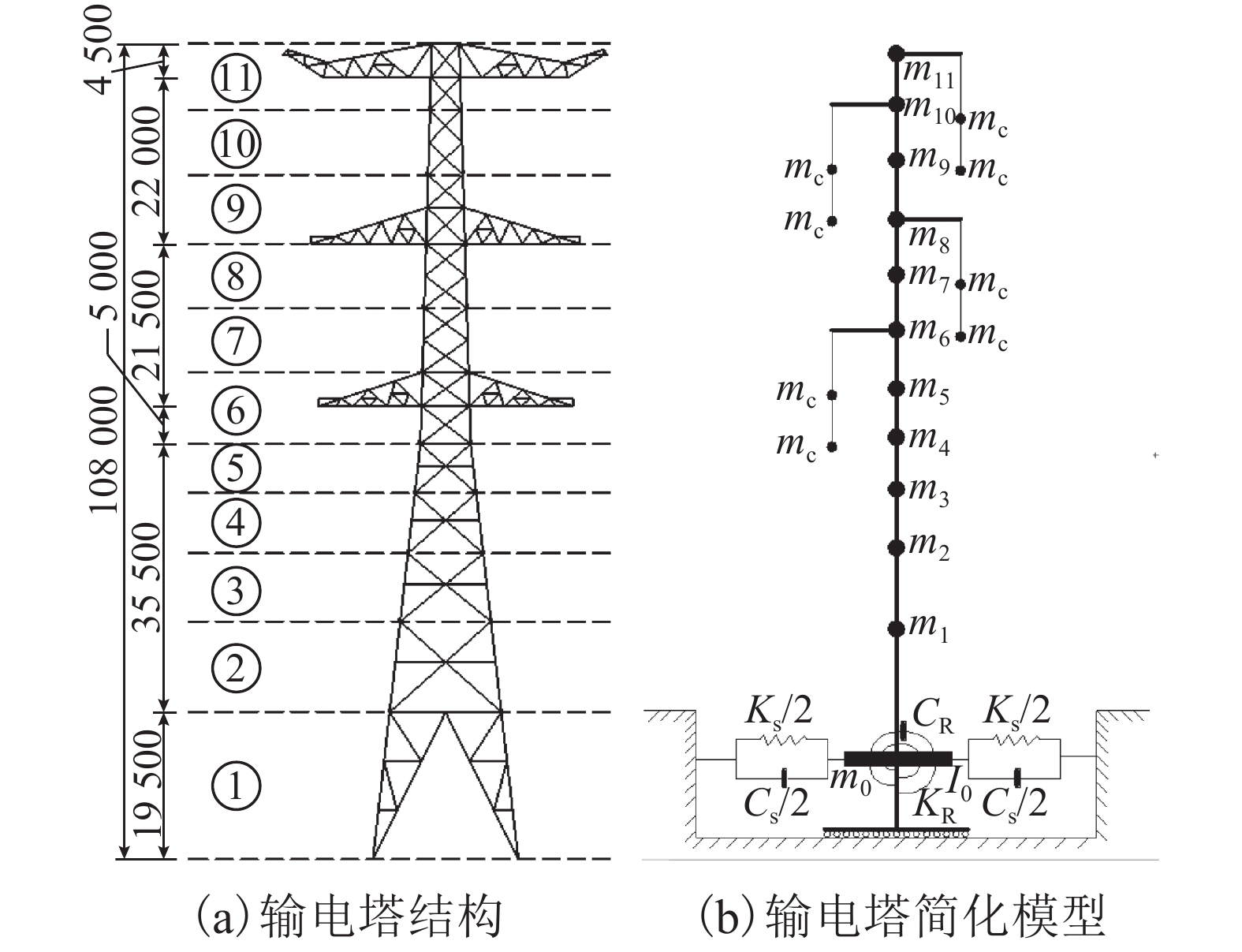
表 1 直线塔计算参数
Table 1. Calculate parameter of the tangent tower
点号 高度/m 挡风面积/m2 质量/kg ① 19.5 37.87 29 198 ② 31.5 25.01 20 253 ③ 40.5 16.80 10 628 ④ 48.5 14.15 8 948 ⑤ 55.0 11.79 7 753 ⑥ 64.5 17.06 17 897 ⑦ 73.0 13.07 7 219 ⑧ 81.5 12.22 9 512 ⑨ 90.6 13.43 13 453 ⑩ 99.2 9.82 4 530 ⑪ 108.0 12.59 16 842 表 2 前3阶自振频率
Table 2. First three natural frequencies
阶次 单塔 单塔+地基 塔线 塔线+地基 第1阶 0.842 1 0.781 4 0.842 8 0.782 1 第2阶 2.570 5 2.297 0 2.570 6 2.297 2 第3阶 4.087 0 4.067 0 4.087 0 4.067 3 表 3 塔顶位移值比较
Table 3. Comparison of the vertex displacement value
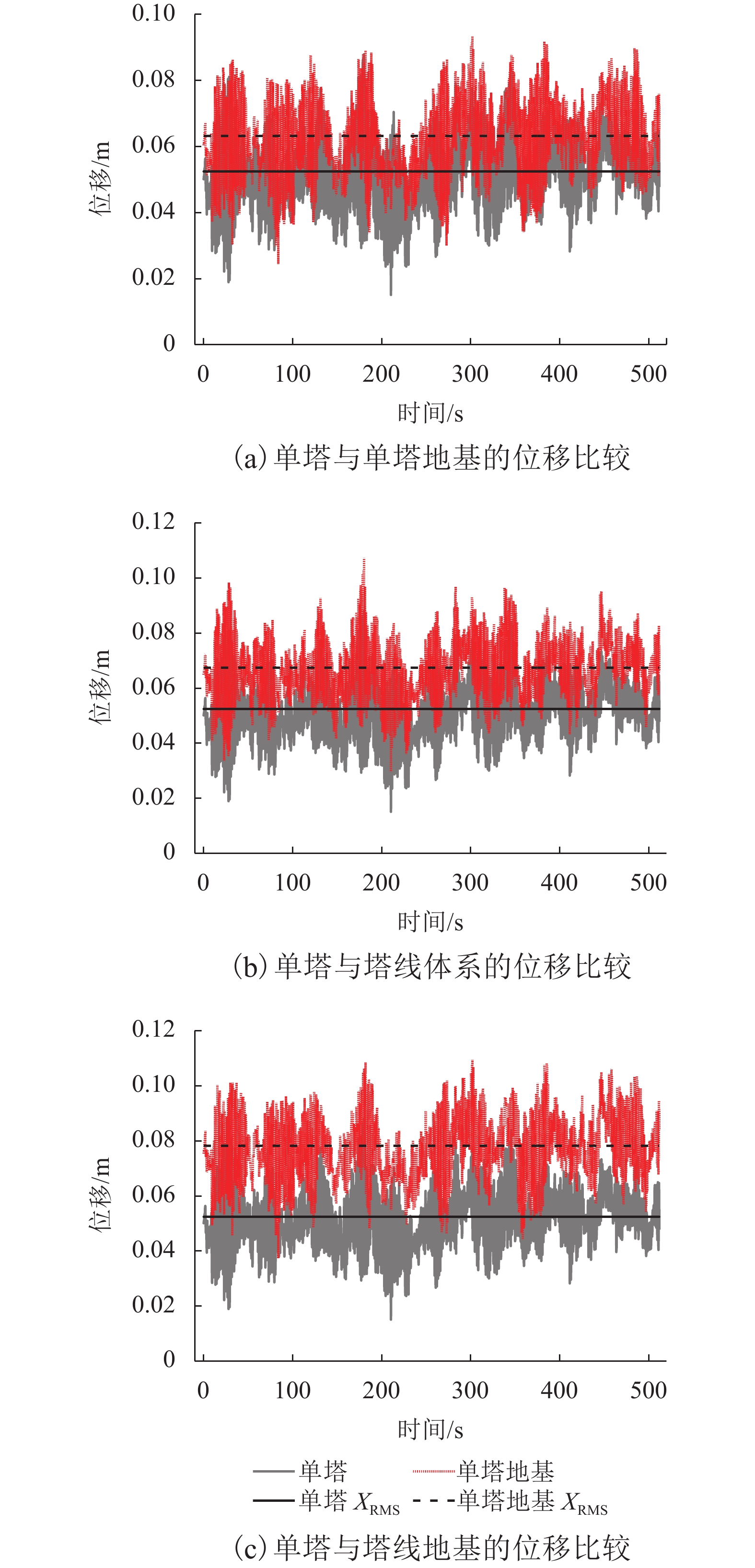
体系类型 Xmax/m 差值/% XRMS/m 差值/% 单塔 0.087 9 0.052 4 单塔地基 0.093 4 6.26 0.063 1 20.42 塔线 0.107 4 22.18 0.067 3 28.44 塔线地基 0.109 5 24.57 0.078 1 49.05 表 4 塔顶加速度值比较
Table 4. Comparison of the vertex acceleration value
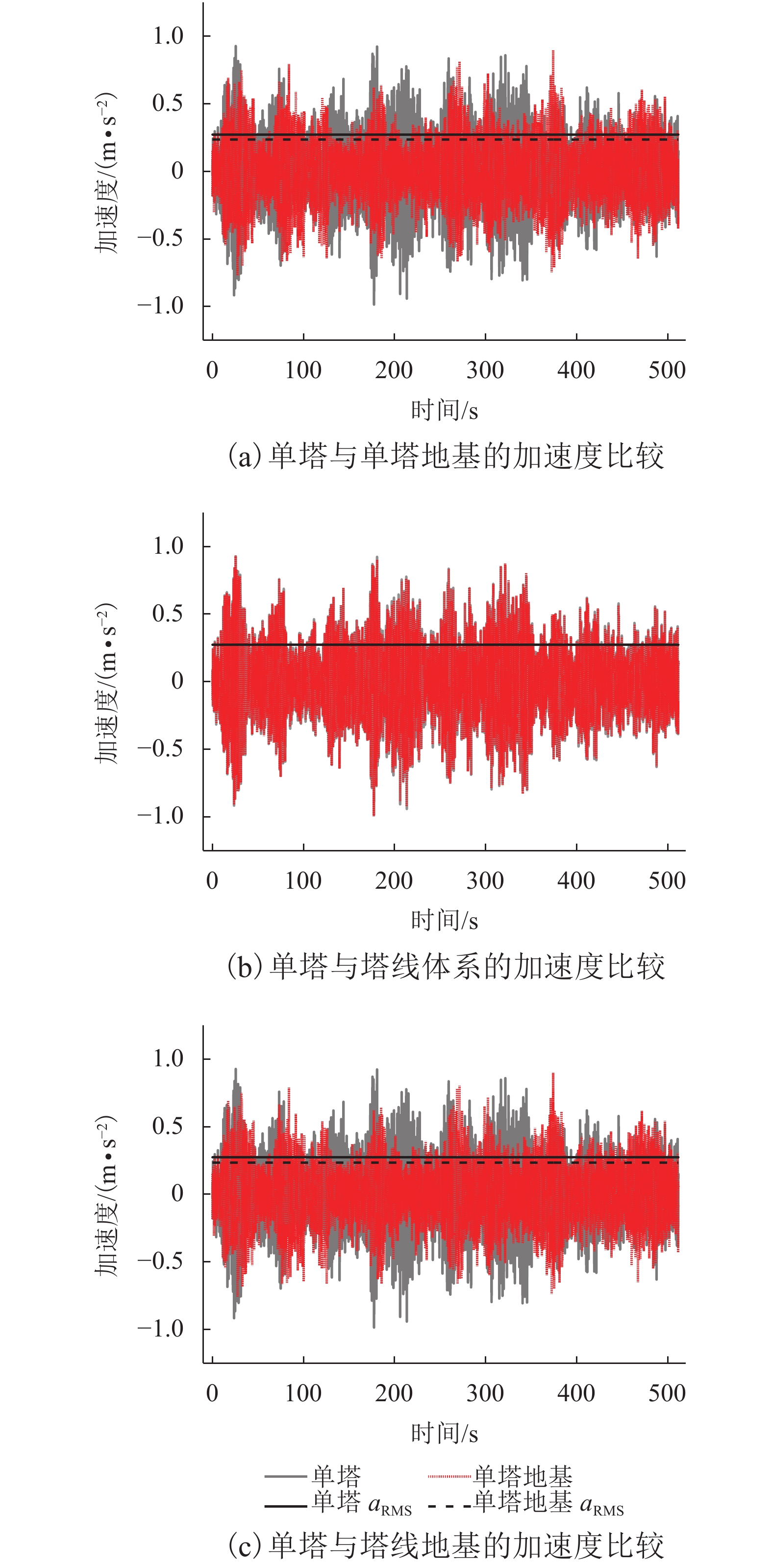
体系类型 amax/(m•s–2) 差值/% aRMS/(m•s–2) 差值/% 单塔 0.925 9 0.271 9 单塔地基 0.897 0 –3.12 0.233 9 –13.98 塔线 0.932 5 0.71 0.272 4 0.18 塔线地基 0.897 5 –3.07 0.233 3 –14.20 表 5 考虑SSI效应后基底剪力与基底弯矩值
Table 5. Variation of base shear and base bending moment after considering the SSI effect
类型 剪力/N 弯矩/(N•m) 最大值 均方根值 最大值 均方根值 基础固支 234 860 151 000 14 318 000 8 902 200 考虑SSI效应 217 970 150 690 12 475 000 8 871 200 差值/% –7.19 –0.21 –12.87 –0.35 表 6 不同地基土的参数
Table 6. Parameters of different foundation soil
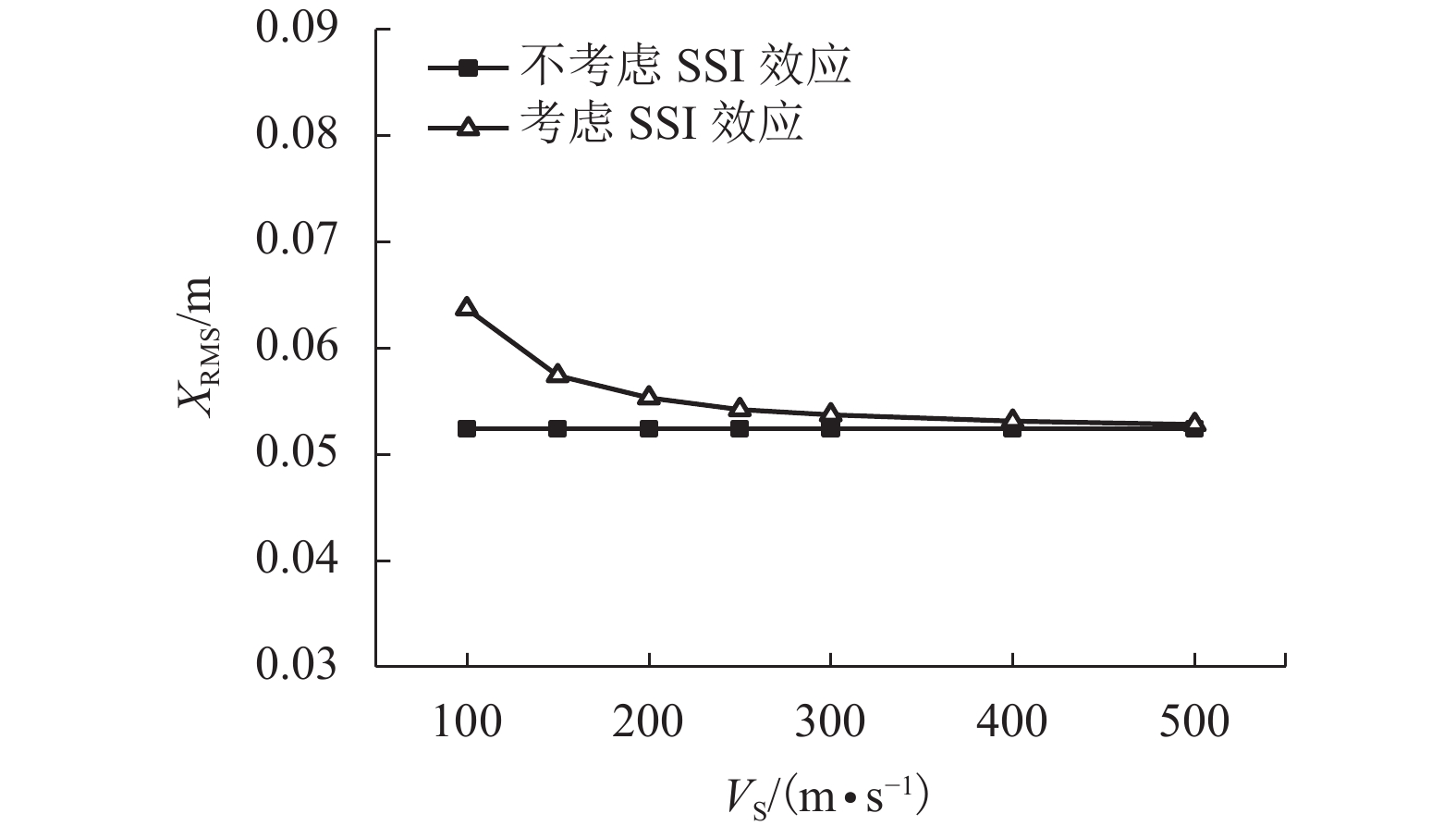
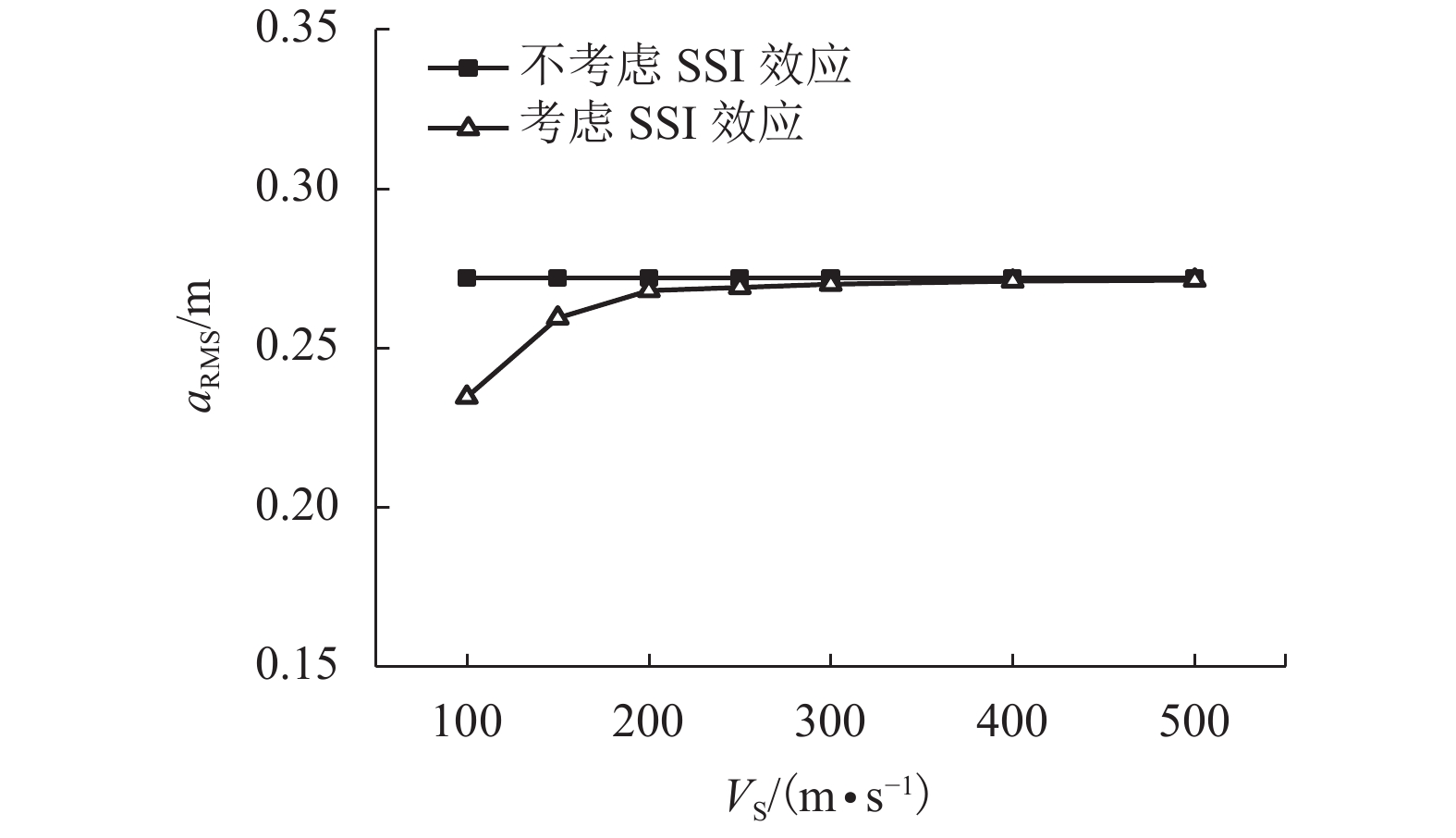
土的类别 泊松比 密度/(kg•m–3) 剪切波速/(m•s–1) CS/(N•s•m–1) CR/( × 109 N•s•m–1) KS/(N•m–1) KR/(N•m–1) 软土 0.49 1 800 100 5.48 × 107 1.41 9.54 × 108 9.41 × 1010 中硬土 0.48 1 900 300 1.73 × 108 4.38 9.00 × 109 8.77 × 1011 硬土 0.33 2 400 500 3.31 × 108 7.16 2.87 × 1010 2.39 × 1012 表 7 单塔塔顶位移及加速度比较
Table 7. Comparison of displacement and acceleration at the vertex of the tower
地基类型 Xmax/m 差值/% XRMS/m 差值/% amax/(m•s–2) 差值/% aRMS/m 差值/% 刚性地基 0.087 9 0.052 4 0.925 9 0.271 9 软土地基 0.093 4 6.26 0.063 1 20.42 0.897 0 –3.12 0.233 9 –13.98 中硬土地基 0.088 8 1.02 0.053 5 2.10 0.916 6 –1.00 0.269 8 –0.77 硬土地基 0.088 0 0.11 0.052 8 0.76 0.954 6 3.10 0.271 3 –0.22 表 8 塔线体系塔顶位移及加速度比较
Table 8. Comparison of displacement and acceleration at the vertex of the tower line system
地基类型 Xmax/m 差值/% XRMS/m 差值/% amax/(m•s–2) 差值/% aRMS/m 差值/% 刚性地基 0.107 4 0.067 3 0.932 5 0.272 4 软土地基 0.109 5 1.96 0.078 1 16.05 0.897 5 –3.75 0.233 3 –14.35 中硬土地基 0.108 6 1.12 0.068 5 1.78 0.915 9 –1.78 0.269 4 –1.10 硬土地基 0.107 5 0.09 0.067 7 0.59 0.943 6 1.19 0.271 6 –0.29 -
李宏男,徐静. 考虑桩-土-结构动力相互作用的输电塔线体系简化抗震计算模型[J]. 岩土工程学报,2009,31(11): 1763-1767. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.11.019LI Hongnan, XU Jing. Simplified aseismic calculation model for transmission tower-line system considering pile-soil dynamic interaction[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(11): 1763-1767. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.11.019 刘海卿, 杜岩, 于春艳. 考虑土-结构相互作用锥形管风电塔架地震响应分析[J]. 建筑结构, 2010, 40(增刊): 116-118LIU Haiqing, DU yan, YU Chunyan. Considering soil-structure interaction tapered pipe wind power tower earthquake response analysis[J]. Building Structures, 2010, 40 (S): 116-118 EBRAHIM N, SEYED M Z. Seismic control of irregular multistory buildings using active tendons[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2016, 89: 100-115. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2016.07.005 ANOOSHIRAVAN F, SAEED S. Ant colony optimization of tuned mass dampers for earthquake oscillations of high-rise structures including soil-structure interaction[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2013, 51: 14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2013.04.002 陈镕,薛松涛,王远功,等. 土-结构相互作用对结构风振响应的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2003,22(2): 309-315. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.02.028CHEN Rong, XUE Songtao, WANG Yuangong, et al. Effect of soil-structure interaction on the response of structure to wind-induced vibration[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(2): 309-315. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.02.028 LIU M Y, CHIANG W L, HWANG J H, et al. Wind-induced vibration of high-rise building with tuned mass damper including soil-structure interaction[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96: 1092-1102. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2007.06.034 ILARIA V, DIANA S, CLAUDIO T. The effect of soil-foundation-structure interaction on the wind-induced response of tall building[J]. Engineering Structures, 2014, 79: 117-130. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.08.002 刘春城,龙祖梁,景欢,等. 考虑桩-土-结构相互作用的输电塔风振响应分析[J]. 东北电力大学学报,2016,36(6): 84-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2992.2016.06.016LIU Chuncheng, LONG Zuliang, JING Huan, et al. Wind vibration response analysis of transmission tower in consideration of the pile-soil-structure interaction[J]. Journal of Northeast Dianli University, 2016, 36(6): 84-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2992.2016.06.016 JENDOUBI A, LEGERON F. Effect of the dynamic soil-structure interaction on rigid transmission line towers subjected to wind and impulse loads[J]. Electrical Transmission and Substation Structures, 2012, 27(6): 250-261. 张琳琳,谢强,李杰. 输电线路多塔耦联体系的风致动力响应分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2006,26(3): 261-267.ZHANG Linlin, XIE Qiang, LI Jie. Dynamic wind-induced response analysis of multi-tower-line coupled system of transmission line[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2006, 26(3): 261-267. 李宏男,王前言. 大跨越输电塔体系的动力特性[J]. 土木工程学报,1997,30(5): 28-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.1997.05.004LI Hongnan, WANG Qianyan. Dynamic characteristics of long-span transmission lines and their supporting towers[J]. Civil Engineering Journal, 1997, 30(5): 28-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.1997.05.004 梁枢果,朱继华,王力争. 大跨越输电塔-线体系动力特性分析[J]. 地震工程学报,2003,23(6): 63-69.LIANG Suguo, ZHU Jihua, WANG Lizheng. Analysis of dynamic characters of electrical transmission tower-line system with a big span[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2003, 23(6): 63-69. 瞿伟廉,殷惠君,陈波. 输电线路动力分析的多质点模型研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报(城市科学版),2003,20(2): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0985.2003.02.001QU Weilian, YIN Huijun, CHEN Bo. Study on multi-degree-of-freedom model of transmission tower-line system[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Urban Science Edition), 2003, 20(2): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0985.2003.02.001 梁峰,李黎,尹鹏. 大跨越输电塔-线体系数值分析模型的研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2007,26(2): 61-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2007.02.016LIANG Feng, LI Li, YIN Peng. Investigation on numerical model of electrical transmisson tower-line systerm with a big span[J]. Vibration and Shock, 2007, 26(2): 61-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2007.02.016 WOLF J P. 土-结构动力相互作用[M]. 昊世明, 唐有职, 译. 北京: 地震工程出版社, 1989: 112-118 NOVAK M, EL HIFANAWY L. Structure response to wind with soil-structure interaction[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1988, 28: 329-338. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(88)90129-8 -




 下载:
下载: