Research on Equivalent Static Load of High-Rise Buildings Based on Wind-Induced Responses
-
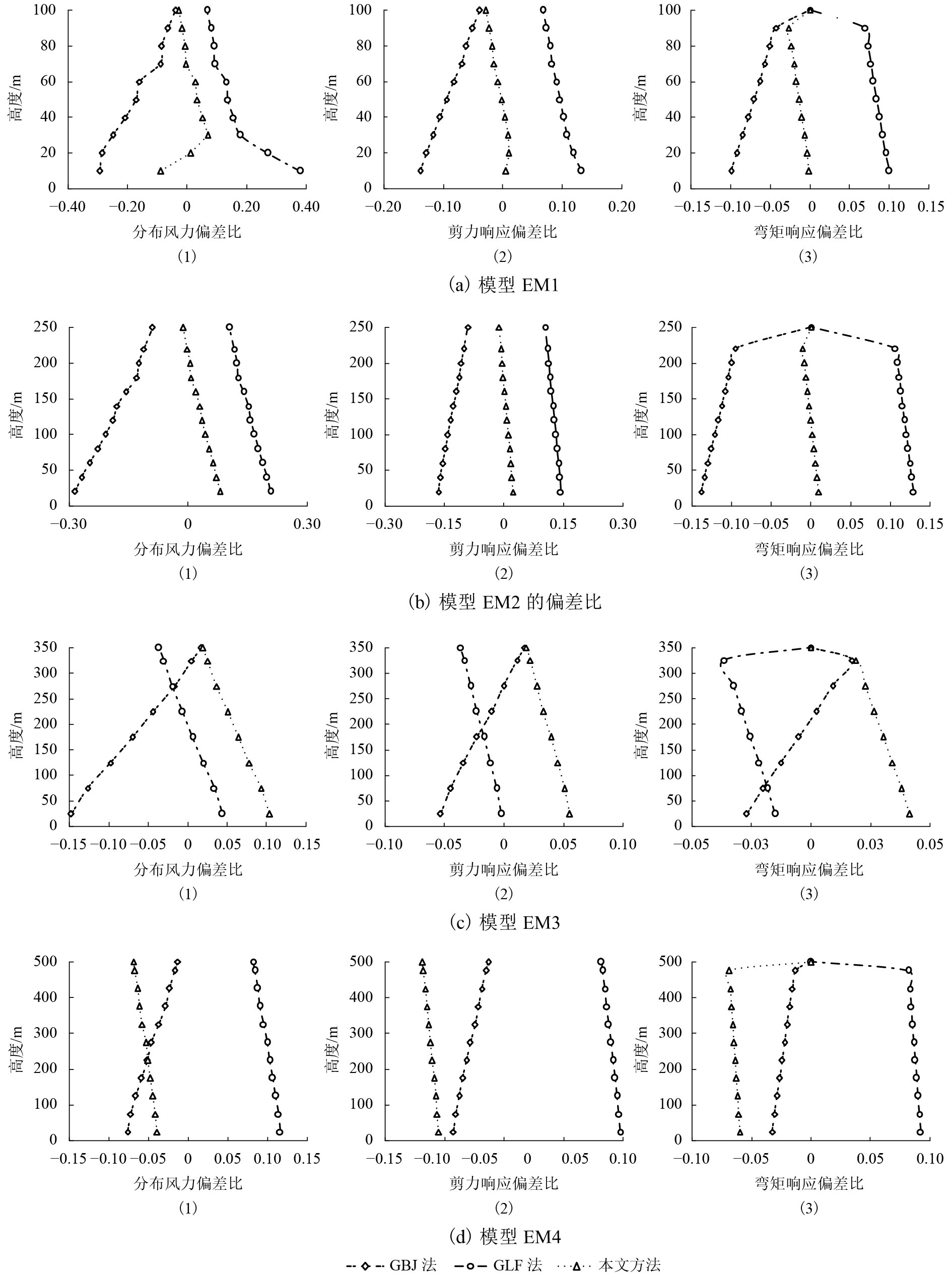
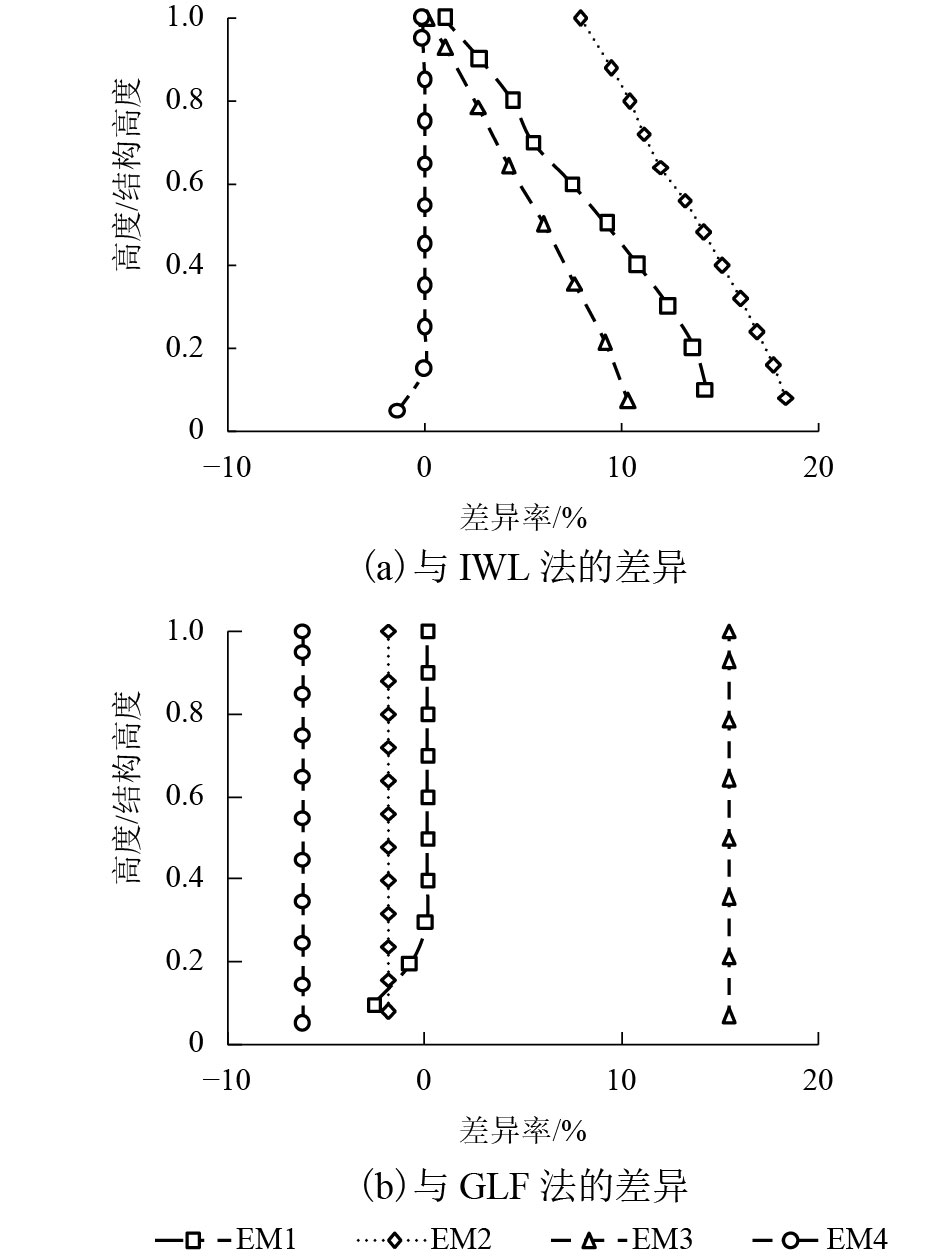
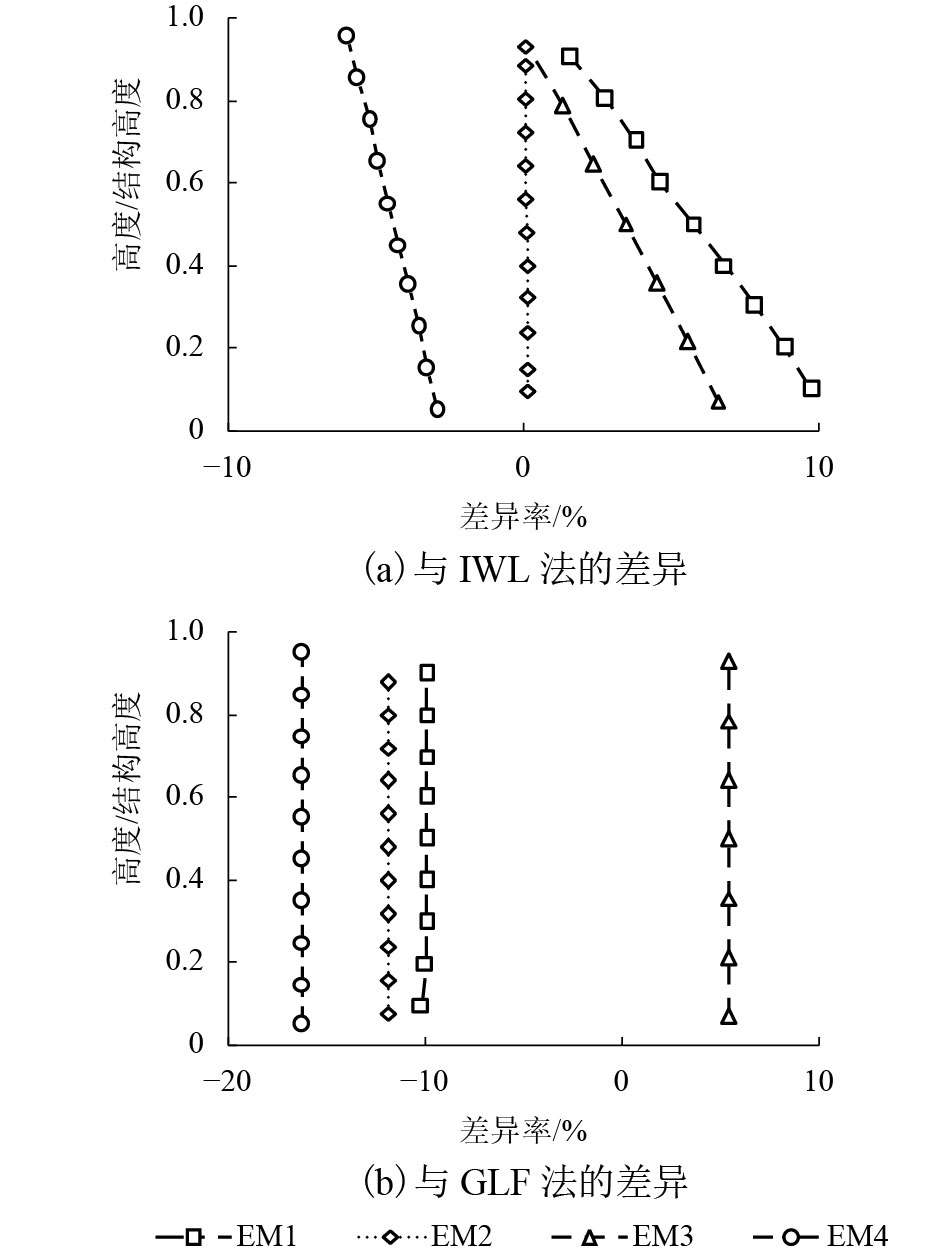
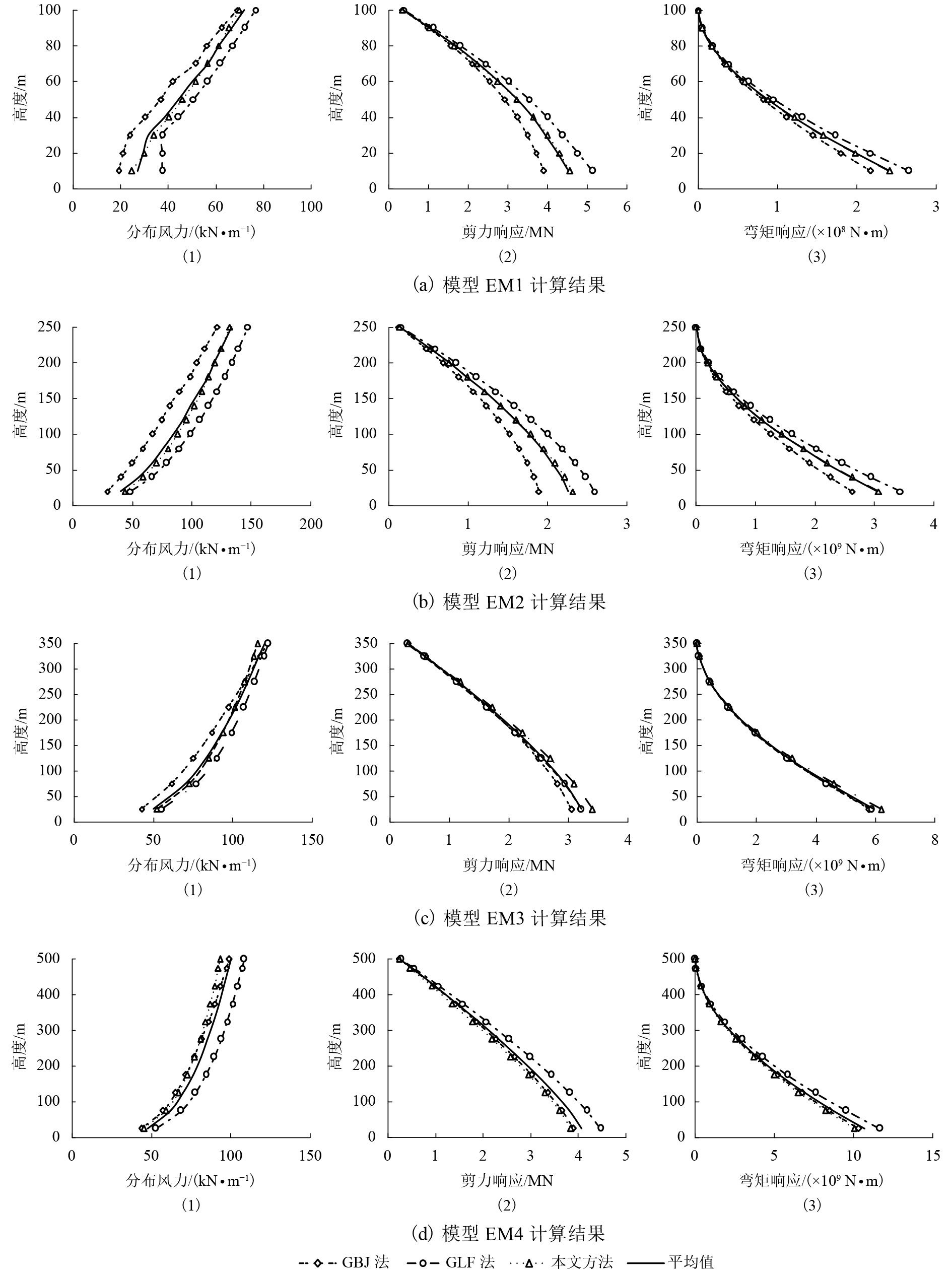
摘要: 为研究风荷载作用下高层建筑动力响应对其顺风向等效静力风荷载的影响,基于结构风致响应动力学理论、脉动风速功率谱密度函数与相干函数的维纳辛钦关系及脉动风速准定常关系,采用随机振动振型分解方法对高层建筑的风致响应进行了研究. 首先,对高层建筑的平均风响应、背景风响应和共振风响应进行了理论分析,并推导出了沿结构高度分布的高层建筑顺风向等效静力风荷载理论计算公式;其次,通过对理论公式中各参数对计算结果的影响进行分析,提出了便于实际应用的高层建筑顺风向等效静力风荷载简化计算方法;最后,设计了4个典型高层建筑算例模型,并与阵风荷载因子法(gust load factor method,GLF)和惯性风荷载法(inertial wind load method,IWL )进行对比,研究了本文方法的可靠性和有效性. 研究结果表明:当结构高度小于250 m时,3种方法所计算出的分布风力、剪力响应和弯矩响应偏差要大一些,GLF法计算结果最大,IWL法的计算结果最小,本文方法介于二者之间;当结构高度大于350 m时,分布风力的偏差在15%以内,对于剪力响应和弯矩响应的偏差在10%以内;本文方法与IWL法在剪力响应方面的差异率在–1%~18%之间,与GLF法的差异率在–12%~5%之间;本文方法与IWL法在弯矩响应方面的差异率在–6%~10%之间,与GLF法的差异率在–16%~5%之间.Abstract: To study the influence of dynamic response of a high-rise building under wind loads on the along-wind equivalent static wind load, the wind-induced response of high-rise buildings was studied using the random vibration mode decomposition method. This method is based on the wind-induced response dynamics theory, the relationship between the pulsating wind power spectral density function and the coherent function, and the quasi-stationary relationship of the pulsating wind speed. First, theoretical analyses of the average wind response, background wind response, and resonance wind response of high-rise buildings were performed, and the theoretical calculation formula of the along-wind equivalent static wind load of high-rise buildings along its height was deduced. Second, the influence of each parameter on the calculation result in the theoretical formula is analysed, and a simplified calculation method for the along-wind equivalent static wind load of the high-rise building is presented, which is convenient for practical applications. Finally, four typical example models of high-rise buildings are designed and compared with the gust load factor(GLF)and inertial wind load(IWL)methods, and the feasibility and effectiveness of our method are investigated. The results demonstrate that when the height of the structure is less than 250 m, the deviations of the distributed wind force, shear force response, and bending moment response calculated by the three methods are large, the calculation result by the GLF method is the largest, and the calculation result by the IWL method is the smallest; the method proposed in this paper is between the two; when the structural height is greater than 350 m, the deviation of the distributed wind force is within 15%, and the deviation between the shear response and the bending moment response is within 10%; the difference between our proposed method and the IWL method in that the shear response is between –1% and 18% and that the difference between our method and the GLF method is between –12% and 5%; when our proposed method and the IWL method are applied to the moment response, the difference rate is between –6% and 10%, and the difference with the GLF method is between –16% and 5%.
-
表 1 算例模型参数
Table 1. Example model parameters
算例
模型高度/m 迎风面
宽度/m基频
/Hz阻尼比 基本风
压/kPa地貌 EM1 100 35 1.31 0.05 0.8 D EM2 250 45 1.12 0.04 0.65 C EM3 350 55 1.01 0.03 0.45 B EM4 500 70 0.96 0.02 0.30 A -
黄东梅,朱乐东,丁泉顺,等. 超高层建筑等效静力风荷载的反演法[J]. 工程力学,2012,29(1): 99-104HUANG Dongmei, ZHU Ledong, DING Quanshun, et al. Equivalent static wind loads on high-rise buildings based on inversion method[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29(1): 99-104 张建国,顾明,张永山. 高层建筑静力等效风荷载研究[J]. 广州大学学报(自然科学版),2005,4(6): 532-535 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4229.2005.06.013ZHANG Jianguo, GU Ming, ZHANG Yongshan. The research of the equivalent static wind load on tall buildings[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 4(6): 532-535 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4229.2005.06.013 DAVENPORT A G. Gust loading factors[J]. Journal of the Structural Division,ASCE, 1967, 93(3): 11-34 冯鹤,黄铭枫,李强,等. 大跨干煤棚网壳风振时程分析和等效静风荷载研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2016,35(1): 164-173FENG He, HUANG Mingfeng, LI Qiang, et al. Wind-induced vibration time history analysis and equivalent static wind loads for long-span lattice shells[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(1): 164-173 ZHOU Y, GU M, XIANG H F. Along-wind static equivalent wind loads,I:unfavorable distributions of wind loads on tall buildings[J]. Journal Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics, 1999, 79: 135-150 沈国辉,王宁博,孙炳楠,等. 基于风洞试验的高层建筑风响应和等效风荷载计算[J]. 浙江大学学报 (工学版),2012,46(3): 448-553SHEN Guohui, WANG Ningbo, SUN Bingnan, et al. Calculation of wind-induced responses and equivalent static wind loads of high-rise building based on wind tunnel tests[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2012, 46(3): 448-553 周印. 高层建筑静力等效风荷载和响应的理论与试验研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2001 黄友钦,林俊宏,岳启哲,等. 基于稳定等效的覆雪屋盖静力风荷载计算方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2013,48(4): 639-644 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.04.008HUANG Youqin, LIN Junhong, YUE Qizhe, et al. Stability-based equivalent static wind loads on large-span snowy roofs[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(4): 639-644 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.04.008 KASPERSKI M, NIEMANN H J. The L.R.C. Method-a general method of estimating unfavorable wind load distributions for linear and nonlinear structures behaviour[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1992, 43(1/2/3): 1753-1763 doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(92)90588-2 张相庭. 工程结构风荷载理论和抗风计算手册[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 1990: 176-194 中华人民共和国国家标准. 建筑结构荷载规范: GB50009—2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012 ZHOU Y, KAREEM A. Gust loading factor:new model[J]. Journal of Structure Engineering, 2001, 127(2): 168-175 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2001)127:2(168) HOMES J D. Effective static load distributions in wind engineering[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2002, 90(2): 91-109 doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(01)00164-7 叶丰,顾明. 高层建筑顺风向背景响应及其等效风荷载的计算方法[J]. 建筑结构学报,2002,23(1): 58-60 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2002.01.011YE Feng, GU Ming. Along-wind background response and background equivalent wind loads of tall buildings[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2002, 23(1): 58-60 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2002.01.011 汪大海,梁枢果. 基于内力的高层建筑顺风向等效静力荷载研究[J]. 工程力学,2016,27(1): 134-140WANG Dahai, LIANG Shuguo. Along-wind equivalent static load of high-rise buildings[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2016, 27(1): 134-140 钟振宇,楼文娟. 基于风重耦合效应超高层建筑顺风向等效静力风荷载[J]. 工程力学,2016,33(5): 74-81ZHONG Zhenyu, LOU Wenjuan. Equivalent static wind load on extra-high buildings along wind based on wind-gravity coupling effect[J]. Engineering mechanics, 2016, 33(5): 74-81 楼文娟,钟振宇. 计入风重耦合效应超高层建筑风振响应计算方法[J]. 振动与冲击,2015,34(11): 178-182LOU Wenjuan, ZHONG Zhenyu. Computing method for wind-induced ibration response of extra-high buildings based on wind-gravity coupled effect[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(11): 178-182 黄本才, 汪丛军. 结构抗风分析原理及应用[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 2008: 59-68 顾明,叶丰. 高层建筑风响应和等效静力风荷载的特征[J]. 工程力学,2006,23(7): 93-98 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.07.017GU Ming, YE Feng. Characteristics of wind induced responses and equivalent static wind loads of tall buildings[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2006, 23(7): 93-98 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.07.017 DAVENPORT A G. The relationship of wind structure to wind loading[C]//Proc. of the Symposium on Wind Effect on Building and Structures. London: [s.n.], 1965: 54-102 GU M, YE F. Along-wind equivalent wind loads and responses on tall buildings[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering, 2001, 89: 609-612 -




 下载:
下载: